What is the hippocampus in the brain?
The hippocampus is part of the limbic system, which is associated with the functions of feeling and reacting. The limbic system is situated on the edge of the cortex, and it includes the hypothalamus and the amygdala.
What is the function of the hippocampal?
Hippocampal function plays a critical role in learning, emotional responses, and memory formation and storage. The human brain contains two hippocampi, one on each side of the brain, located a few inches above each ear.
Where does the hippocampus receive input and output from?
The hippocampus receives input from and sends output to the rest of the brain via a structure known as the entorhinal cortex, which is located beneath the anterior (frontal) region of the hippocampus.
What is the function of the anterior hippocampus?
The anterior hippocampus is preferentially connected to the amygdala and orbitofrontal cortex and is thought to be involved principally in the regulation of emotion and stress.
See more

Where is the hippocampus located?
The hippocampus is a part of the brain. It is found in the inner folds of the bottom middle section of the brain, known as the temporal lobe. Humans have known about the hippocampus for more than 4 centuries. It is one of the most studied parts of the brain. The name comes from the Greek words hippo, meaning horse, and kampo, meaning monster, ...
What is the meaning of the word "hippo"?
The name comes from the Greek words hippo, meaning horse, and kampo, meaning monster, as its shape resembles that of a sseahorse. Its main functions involve human learning and memory. Knowing about the hippocampus has helped researchers understand how memory works. Share on Pinterest.
What are some examples of hippocampus memory?
Declarative memories are those related to facts and events. Examples include learning how to memorize speeches or lines in a play. Spatial relationship memories involve pathways or routes.
Where are short term memories stored?
The hippocampus is also where short-term memories are turned into long-term memories. These are then stored elsewhere in the brain. throughout adulthood. The hippocampus is one of the few places in the brain new nerve cells are generated.
How much does the hippocampus shrink in Alzheimer's?
In people with depression, the hippocampus can shrink by up to 20 percent. Trusted Source. , according to some researchers.
What happens if you lose your hippocampus?
If one or both parts of the hippocampus are damaged by illnesses such as Alzheimer’s disease, or if they are hurt in an accident, the person can experience a loss of memory and a loss of the ability to make new, long-term memories.
Which part of the brain is responsible for feeling and reacting?
The hippocampus is part of the limbic system, which is associated with the functions of feeling and reacting. The limbic system is situated on the edge of the cortex, and it includes the hypothalamus and the amygdala. These structures help control different bodily functions, such as the endocrine system and what is commonly known as ...
Why is the hippocampus important?
It is particularly important for the process of learning, and seeing relationships between what has been learned.
How many fields does the hippocampus have?
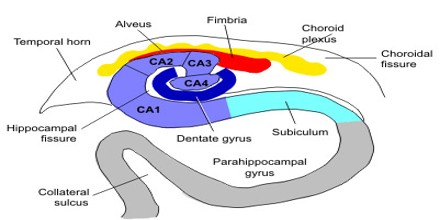
To make matters even more complicated, the hippocampus is divided into different regions called fields. One classification divides the hippocampus into four fields (although thankfully with names much easier to remember than the names of the layers):
What are the parts of the hippocampal?
The hippocampal formation is an important component of the limbic system, along with the amygdala and septal area (although some also include the cingulate gyrus and prefrontal cortex as part of this system). The world “hippocampus” is derived from the Greek words “hippos” meaning horse and “kampos” meaning sea monster, and refers to the structure’s shape resembling a seahorse. The elongated hippocampal structures lie along the longitudinal axis of the brain, one in each of the medial parts of the temporal lobes, and form the medial walls of the inferior horns of the lateral ventricles. It is made up of three components: 1 the hippocampus 2 dentate gyrus 3 subicular cortex
What is the hippocampal structure?
The elongated hippocampal structures lie along the longitudinal axis of the brain, one in each of the medial parts of the temporal lobes, and form the medial walls of the inferior horns of the lateral ventricles. It is made up of three components:
What are the three parts of the hippocampal system?
It is made up of three components: the hippocampus. dentate gyrus. subicular cortex.
What is the fimbria of the hippocampus?
Fimbria of the hippocampus (cranial view) The tissue comprising the hippocampus has many layers. From the ventricular surface to the dentate gyrus, the hippocampus is made up of: an external plexiform layer, a stratum oriens layer, a pyramidal cell layer, a stratum radiatum layer, a stratum lacunosum-moleculare layer.
Where do axons travel?
The axons of pyramidal cells take information received by the hippocampus and send it to other structures in the brain: these efferent processes extend from the pyramidal cell body, travel through a structure called the alveus ‒a fiber layer next to the inferior horn of the lateral ventricle‒and then enter into either the entorhinal cortex or the fimbria - fornix.
What is the hippocampus?
The hippocampus is a part of the limbic system that is closely related to memory. The integral functions of the hippocampus include: Influences memory formation: The hippocampal formation influences new memory formation and memory consolidation. This section of the brain also influences our ability to encode and retrieve information—where ...
Where is the hippocampus located?
The hippocampus is a small part of the brain located in the medial temporal lobes (MTL), under the cerebral cortex. The hippocampus is an essential part of the brain’s limbic system, a group of brain structures in the cerebral cortex responsible for behavioral and emotional responses.
What are the disorders of the hippocampus?
Damage, impairment, or underdevelopment of the human hippocampus can lead to many brain disorders, such as: Alzheimer’s disease: In people with Alzheimer’s, neurogenesis (creation of new neurons) is inhibited, and important cells and connections die off, leading to memory loss and impairment, ...
What is the meaning of the word "hippocampus"?
The term “hippocampus”—derived from the Greek words hippo (meaning horse) and kampos (meaning monster)—translates to “seahorse,” a reference to its shape.
Which part of the brain is responsible for learning and memorizing facts and concepts?
These neurons are divided into two pathways: the polysynaptic pathway, the part of the hippocampus responsible for learning and memorizing facts and concepts, and the direct pathway, which is important for event recollection and spatial recognition.
What is the human brain?
Articles. Videos. Instructors. The human brain is a complex network of neural and synaptic connectivity. The hippocampus and other brain structure areas, like the prefrontal cortex, amygdala, hypothalamus, and thalamus, work together to produce our feelings, thoughts, personality, and behavior, along with our other natural bodily functions.
What is the function of the hippocampus?
Spatial Memory and Navigation. Another key function of the hippocampus is its role in spatial navigation. The rear part of the hippocampus is believed to be involved in processing spatial memories, this is so we can encode the environment around us and remember where everything is.
What is the hippocampus?
Hippocampus Function and Location. The hippocampus is a curved-shaped structure in the temporal lobe associated with learning and memory. The name being derived from the Greek words for ‘sea monster’ but is more commonly recognizable for being shaped like a seahorse. The hippocampus is considered to be a part of the limbic system, ...
How does exercise strengthen the hippocampus?
For instance, it has been found that physical exercise is a way that can strengthen the hippocampus as it stimulates neurogenesis (Van Praag, Shubert, Zhao, & Gage, 2005). Being able to manage stress can reduce the number of stress-related neurotransmitters being taken in by the hippocampus.
How to keep the hippocampus active?
As the hippocampus is more concerned with memory, completing memory-based activities can help to keep the hippocampus active. Exercises such as trying to memorize lists of words or reading and writing could all help to keep the hippocampus working properly.
What is the role of sleep in memory?
Sleep is thought to play a critical role in the process of this. Information in the hippocampus circulates in this area whilst neurons start to encode this information through a process called long-term potentiation. Long-term potentiation is a form of neural plasticity and is a vital mechanism in the storage of memory.
Why is the hippocampus important?
The hippocampus is important in the organization and storage of new memories , especially those which are declarative memories (e.g., memories relating to facts and events). This area is also responsible for making memories stronger by connecting sensations and emotions to these memories.
Which part of the brain is most studied?
The hippocampus is one of the most studied areas of the brain and is also one of the few places where neurogenesis occurs, the process by which new neurons are produced.
What is the hippocampus?
This system is located in the brain’s medial temporal lobe, near the center of the brain. The hippocampus is involved in the storage of long-term memory, which includes all past knowledge and experiences.
Which part of the brain is involved in declarative memory?
Scientists are unsure exactly how this occurs. In particular, the hippocampus seems to play a major role in declarative memory, the type of memory involving things that can be purposely recalled, such as facts or events. The hippocampus is not involved with short-term memory and procedural memory types (memory of how to do motor actions, ...
Can hippocampus memory be recorded?
Those that have lost function or had removed major portions of the limbic system but still have the hippocampus, have only long-term memory and cannot record any new memories or functions. Last medically reviewed on January 21, 2018.
What is the hippocampus?
The hippocampus is part of the limbic system, which is responsible for regulating physiological responses to certain stimuli.
Where is the hippocampus located?
It’s located in the medial temporal lobe, and is part of the limbic system (which is related to emotions, information storage, and motivation). The hippocampus is a very old structure from an evolutionary point of view, and forms part of the archicortex.
What is the role of the hippocampus in memory?
In reality, the hippocampus acts as a mediator (or directory) for memories. The activation of memories is associated with the proper functioning of the neural networks distributed throughout the brain.
What is the role of the hippocampus in spatial navigation?
This refers to the way we interact with and understand the three-dimensional space that we move through. This also includes taking into account the spatial references and volumes.
Which part of the brain is the heart of the brain?
But what do the findings of this study indicate? That the hippocampus could be considered the “heart” of the brain, as it integrates very diverse functions and is located in the “epicenter” of the brain.
Which part of the brain has a complex structure?
The hippocampus has a complex structure, and it has quite a few neural connections with the rest of the brain.
Which lobe of the brain is responsible for coordinating the somatic expression of emotion and conscious feeling?
Both are located in the medial temporal lobe. The amygdala is responsible for assessing the emotional meaning of experiences, as well as coordinating the somatic expression of emotion and conscious feeling.