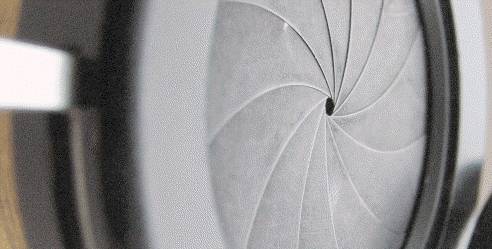
What does the iris diaphragm lever do on a microscope?
The main function of the iris diaphragm is to maximize resolution and image contrast by properly channeling the light rays passing through the specimen. In this way, how does a microscope iris diaphragm lever work like the iris of an eye? Iris diaphragm: located beneath the condenser, the iris diaphragm works similarly to the iris of the eye.
How do you open iris on microscope?
When using the 4x microscope objective lens, the iris diaphragm lever should be pushed all the way to the right. When this lever is moved to the right, less light is sent through the condenser, resulting in an image that is not too bright. When using the 100x objective, move the lever all the way to the left to open the iris diaphragm and allow more light to pass through the condenser, resulting in a better image. Adjusting the Field Iris for Koehler Illumination
What does the iris do on the microscope?
The main function of an iris diaphragm of a microscope is to control the amount of light that reaches the specimen. This light comes from the microscope’s light source, and is gathered by the condenser, before being regulated by the diaphragm, then passing through the specimen. Increasing the amount of light passing through by widening the ...
What effect has the iris diaphragm on the image?
The main function of the iris diaphragm is to maximize resolution and image contrast by properly channeling the light rays passing through the specimen. What does Parfocal mean? A. Parfocal means that the microscope is binocular.

Where is the iris diaphragm found?
The diaphragm is located between a light source and a lens, along the optical axis of the lens system, in order for it to regulate the amount of light coming from the light source and passing through the lens.
What is an iris diaphragm function on a microscope?
The condenser has an iris diaphragm that controls the angle of the beam of light focused onto the specimen. The iris diaphram is an adjustable shutter which allows you to adjust the amount of light passing through the condenser.
What is diaphragm or iris?
The iris is the diaphragm, the pupil is the aperture. In the human eye, the iris can both constrict and dilate, which varies the size of the pupil.
Which comes first iris diaphragm or condenser?
The pathway of light through a compound microscope is: light source → condenser → iris diaphragm → stage → object/specimen → objective lens → ocular lens → eye or camera.
What is the function of the iris diaphragm to what part of the human eye would you compare it?
The iris of the eye functions like the diaphragm of a camera, controlling the amount of light reaching the back of the eye by automatically adjusting the size of the pupil (aperture).
What happens to the image when the iris diaphragm is closed or fully opened?
Looking at the image Adjust the iris diaphragm to achieve the optimum balance between definition and glare. If the diaphragm is open, the image is brighter but the contrast is low. If the diaphragm is closed, the image is darker but the contrast greater.
When should the iris diaphragm be used?
The iris diaphragm should be used to adjust amount of light needed to improve contrast. Correct the statement. The condenser should be in the lowest position to the focus the most light on the specimen. The condenser is raised completely up to the stage to focus the most light on the specimen.
What is diaphragm of eye?
Iris :A diaphragm called the Iris controls the amount of light entering the eye. Pupil :The iris has a small opening or aperture in the center called the Pupil, which dilates and constricts according to the external light.
What part of the eye is like the diaphragm of a camera?
IrisIris. Inside the anterior chamber is the iris. This is the part of the eye that is responsible for one's eye color. It acts like the diaphragm of a camera, dilating and constricting the pupil to allow more or less light into the eye.
What is the correct order of microscope parts from the base to the ocular?
The path of light begins with the illuminator, then passes through the condenser, the specimen, the objective lens, then then the ocular lens.
Where is the condenser diaphragm on a microscope?
On upright microscopes, the condenser is located beneath the stage and serves to gather wavefronts from the microscope light source and concentrate them into a cone of light that illuminates the specimen with uniform intensity over the entire viewfield.
Is the aperture and iris diaphragm same?
Inside a lens is a ring of overlapping blades collectively known as an iris diaphragm, or iris. The expansion or contraction of the iris blades adjusts the size of the opening at its centre, which is called an aperture.
What is the function of the diaphragm?
Upon inhalation, the diaphragm contracts and flattens and the chest cavity enlarges. This contraction creates a vacuum, which pulls air into the lungs. Upon exhalation, the diaphragm relaxes and returns to its domelike shape, and air is forced out of the lungs.
When should the iris diaphragm be used?
The iris diaphragm should be used to adjust amount of light needed to improve contrast. Correct the statement. The condenser should be in the lowest position to the focus the most light on the specimen. The condenser is raised completely up to the stage to focus the most light on the specimen.
When would you use the diaphragm in microscope?
Condenser Diaphragm- This diaphragm controls the amount of light entering the lens system. This feature is useful for viewing unstained biological specimens that are translucent. Reducing the amount of light improves contrast, making the specimen "stand out" against the background.
What is the function of the iris diaphragm The substage condenser?
The iris diaphragm controls the amount of light passing through the slide or specimen, while the substage condenser focuses a cone of light on the slice or specimen.
What is the best way to adjust my iris diaphragm?
Adjust the diaphragm to the largest hole diameter in your microscope, allowing the most light to pass through. Slide the lever until the most light comes through if you have an iris diaphragm.
What happens when the iris diaphragm is opened?
In light microscopy, the iris diaphragm determines the size of the opening between the specimen and the condenser through which light passes. The specimen’s illumination will be reduced by closing the iris diaphragm, but the contrast will increase.
What are the 12 components of a microscope?
Learn more about microscope parts and how to use them in this article. The lens on the eyepiece.
What are the functions and parts of a microscope?
The microscope’s basic components include the eyepiece lens, which is the lens at the top through which you look. The eyepiece is connected to the objective lenses via a tube. The tube is supported by the arm, which connects it to the base.
What are the different types of microscopes?
Compound, Stereo, Digital, and Pocket or handheld microscopes are the most popular types of microscopes used in light microscopy.
On a microscope, what does the mirror do?
Mirror: Allows you to direct ambient light into the stage’s hole and illuminate the specimen without using electricity. Mirrors are no longer widely available on microscopes. A monocular head is a microscope with a single eyepiece lens.
On a microscope, what are the objective lenses?
The Revolving Nosepiece or Turret is a part that can be rotated to change power and holds two or more objective lenses. Objective Lenses: On a microscope, you’ll usually find three or four objective lenses. They almost always have 4X, 10X, 40X, and 100X power.
What is the diaphragm of a microscope?
The microscope diaphragm, also known as the iris diaphragm, controls the amount and shape of the light that travels through the condenser lens and eventually passes through the specimen by expanding and contracting the diaphragm blades that resemble the iris of an eye. Depending on the type of diaphragm and the settings applied to ...
What happens if you open the diaphragms of a microscope?
If you just have all the diaphragms fully open – the image is going to be flooded with light. It will appear bland and no contrast and almost “blurry”. On the other hand, if you have it almost completely closed, you are preventing a lot of light from getting to the sample. This image will look “incomplete” and grainy and not resolved.
Why is the size of the cone of light important?
The size of this cone of light is important because if there is a mismatch between the size of the cone of light and the optimal numerical aperture on the objective lens in place you will not get the optimal image quality. For example we can use the diaphragm to change how much light will get focused onto the sample.
What are the two things that must happen for a microscope to work?
There are two things that must happen for a microscope to work successfully. One, the light must hit the specimen we want to see , and two, after hitting the specimen, the light needs to get collected and magnified. The diaphragm and condenser are important components of this first mechanism, in focusing the incoming light.
How long does it take for the iris to expand?
It’s like when you are outside in the dark for 1 minute vs. 15 minutes – your iris is slowly expanding so it gathers more light. This diaphragm is located closer to the condenser system of a microscope. In fact, the condenser sits right on top of the iris diaphragm. The image below is an example of the iris diaphragm and it opens ...
Why is the iris called the iris?
The iris diaphragm is named “iris” mainly because it does the same exact thing as the iris does for our eyes. Your iris controls the amount of light that enters your cones and rods of your eye by adjusting itself to be larger or smaller.
What are the trade-offs of a microscope?
As with many of the settings in the microscope, there are always trade-offs. When you are fine-tuning your image, you must balance the contrast with the total image you are seeing. You cannot fully open your field diaphragm while having high contrast.
What Is The Purpose Of The Iris Diaphragm?
The primary responsibility of the iris diaphragm is controlling how much light hits the specimen. The light in question is the microscope’s primary light source, and this is collected by the microscope’s condenser, subsequently regulated by the diaphragm before shining through the specimen.
What does it mean when the iris diaphragm is more circular?
Increasing the number of blades in the iris diaphragm means the opening is much more circular resulting in higher contrast and more focused light. Perhaps unsurprisingly, these iris diaphragms are more expensive to make and therefore are typically found on more elaborate and advanced equipment.
What Is A Diaphragm?
A diaphragm on a microscope is responsible for how much light leaves the microscope condenser. This light controls the illumination of the object in view. In addition to that, it simultaneously controls the contrast between the background and the specimen.
What controls the contrast of an object?
As we previously discussed, the iris diaphragm controls illumination and contrast levels on the magnified image of an object being viewed. Open the diaphragm’s aperture wider if you want more illumination and lower contrast, and so forth.
How to manage contrast?
Managing the contrast by controlling how much the diaphragm illuminates the specimen is crucial in specimens’ high and intermediate magnification. Basically, when using higher magnification levels, less light can pass through; therefore, iris diaphragms must have wider openings to allow more light through.
How many blades does a microscope have?
Most microscope iris diaphragms contain between five and ten blades; however, diaphragms can be as few as two and upwards to twenty blades. Because the diaphragm is a circle curving the blades make a more circular opening, whereas straight blades generate a multifaceted shape.
Why is opening the aperture in the iris diaphragm wider?
Opening the aperture in the iris diaphragm wider will intensify the amount of illumination reaching the specimen; Simultaneously, this makes the image brighter. The light is not so focused, and that reduces the contrast.
Where is the diaphragm of the microscope?
The diaphragm can be found near the bottom of the microscope, above the light source and the condenser, and below the specimen stage. This can be controlled through a mechanical lever, or with a dial fitted on the diaphragm.
What is the difference between iris diaphragm and condenser?
Iris Diaphragm controls the amount of light reaching the specimen. It is located above the condenser and below the stage. Most high quality microscopes include an Abbe condenser with an iris diaphragm. Combined, they control both the focus and quantity of light applied to the specimen.
What is the difference between the condenser and the diaphragm on a microscope?
Field diaphragms are useful to adjust for correct microscope alignment, but are not always included in less expensive microscope models. The aperture diaphragm (also called an iris diaphragm) controls contrast, and is found in the condenser, which sits right below the stage in line with the microscope objectives.
Can I Use My Phone or Camera to Focus a Microscope?
You can use your phone or camera to focus a microscope, but there are a few caveats. When you use your phone to focus, your phone will get all the light from your scope instead of your lens. So, you’ll have to experiment with different angles to see if you can get the best image.
How Does The Iris Diaphragm Work?
The iris diaphragm is what controls the amount of light that passes through a microscope. This is because light is reflected through the lens to the object. The diaphragm is a circular ring that is placed just in front of the lens. When it’s open, light is allowed to enter the lens, allowing the user to see the object.
How Does It Work?
The iris diaphragm is a device that is typically placed in front of the objective lens of a microscope. It is used to make sure that the light that enters the microscope goes through only one part of the objective lens. This prevents light from other parts of the objective lens from entering the microscope, which can cause inaccurate results.
How Can I Use the Iris Diaphragm?
This diaphragm allows you to adjust the amount of light that gets through the diaphragm to the camera sensor, or focal plane, on your microscope. You can use it to maximize the image you see and for your best possible picture. The larger the diaphragm opening, the less light you get through.
Why Do I Need It?
The iris diaphragm is one of the most important components of a microscope. It helps to ensure that everything in the image is in focus. The aperture is the opening in the diaphragm and the iris allows light into the objective lens.
Where is the field diaphragm on a microscope?
The field diaphragm control is located around the lens located in the base. Fine Adjustment Knob – This knob is inside the coarse adjustment knob and is used to bring the specimen into sharp focus under low power and is used for all focusing when using high power lenses.
What is the difference between iris diaphragm and condenser?
Iris Diaphragm controls the amount of light reaching the specimen. It is located above the condenser and below the stage. Most high quality microscopes include an Abbe condenser with an iris diaphragm. Combined, they control both the focus and quantity of light applied to the specimen.
What happens when you adjust the diaphragm on a microscope?
In light microscopy the iris diaphragm controls the size of the opening between the specimen and condenser, through which light passes. Closing the iris diaphragm will reduce the amount of illumination of the specimen but increases the amount of contrast.
Why does the diaphragm need to be opened?
If the sample is thick, strongly stained or pigmented then the diaphragm has to be opened to allow more light to pass through the specimen. As a consequence, the depth of field becomes smaller. It is then necessary to use the fine focus adjustment knob to focus through the different layers of the specimen. The condenser aperture diaphragm can be ...
What is the purpose of the condenser aperture diaphragm?
The condenser aperture diaphragm (or iris diaphragm) is used to control the contrast and resolution of an image. This article explains the usage of the diaphragm. An improper setting of the condenser aperture diaphragm (especially at higher magnifications) can be the cause of much frustration both for teachers and students.
Why can't students see anything at all when working with high magnifications?
Students may not see anything at all when working with high magnifications because the image is too dark. In this case the diaphragm is closed too much. The diaphragm should not be used to control the amount of light, but for some specimens or magnifications there may simply be no way around this especially if the lamp is not very powerful.
When switching to a higher magnification, should the students start to gradually open the condenser aperture di?
When switching to a higher magnification, the students should start to gradually open the condenser aperture diaphragm, to observe the differences in image quality. At the same time they have to adjust the light intensity with the dimmer to prevent glare.
Can you see more at higher magnification?
Many think that they are able to see more at a higher magnification. But especially at higher magnifications the role of the condenser diaphragm becomes more important. I recommend the following steps: Instruct the students to completely close the condenser aperture diaphragm when starting to use the microscope.

Function and Purpose
- The primary function of the diaphragm is to change the angular aperture of the cone of light that is produced after the light travels through the condenser. The size of this cone of light is important because if there is a mismatch between the size of the cone of light and the optimal numerical aperture on the objective lens in place you will not g...
Types of Diaphragms
- Disc Diaphragm
A less common diaphragm is a disc diaphragm looks a little something like this. It is basically a spinning wheel with different diameter openings. Want more light? Switch it over to the large hole. Want less light? Go to the smaller sized hole. - Aperture Iris Diaphragm
The more common type of diaphragm is the iris diaphragm. These are a little more sophisticated and are more common among more expensive and more advanced microscopes. The iris diaphragm is named “iris” mainly because it does the same exact thing as the iris does for our e…
Trade-Offs
- As with many of the settings in the microscope, there are always trade-offs. When you are fine-tuning your image, you must balance the contrast with the total image you are seeing. You cannot fully open your field diaphragm while having high contrast. The more light you are inputting, the less contrast you will get and vice-versa. The less light you put in, the more contrast you get. Thi…
Takeaways
- There are no formulas for how to go about using the diaphragms in a complementary manner. It depends on many factors that could be specific to the specimen, or your microscope. There is balance between contrast, brightness and area that you just need to play with and get a feel for. You can never get an image that is high contrast, bright and large. Adjusting the different kind o…
References