Where is the ITCZ located in Africa?
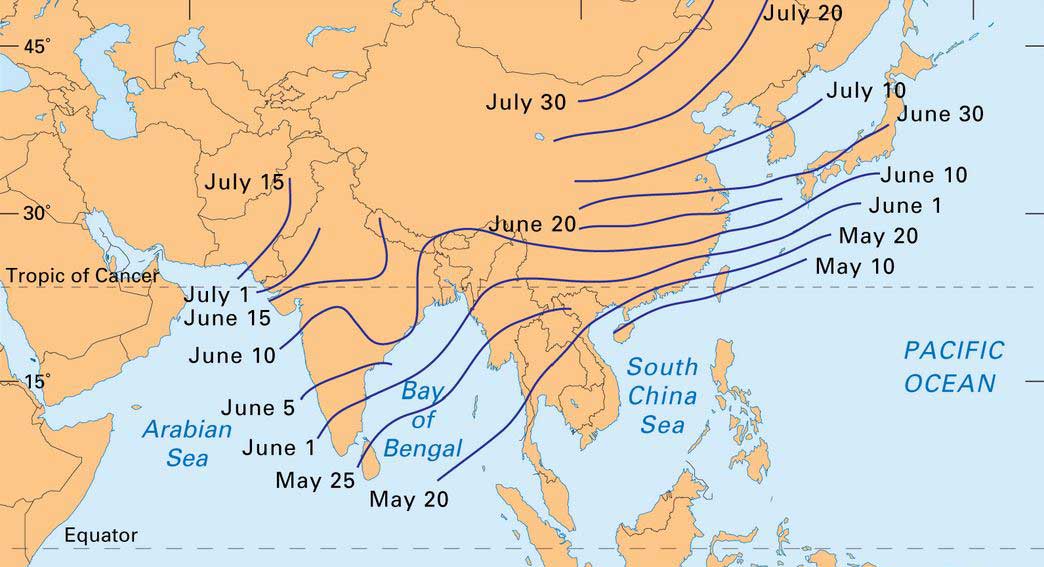
In Africa in July and August, for instance, the ITCZ is located just south of the Sahel desert at about 20 degrees north of the Equator, but the ITCZ over the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans is usually only 5 to 15 degrees North; meanwhile, over Asia, the ITCZ can go as far as 30 degrees North.
How does the location of the ITCZ affect rainfall?
As the air rises it expands and cools, releasing the accumulated moisture in an almost perpetual series of thunderstorms. Seasonal shifts in the location of the ITCZ drastically affects rainfall in many equatorial nations, resulting in the wet and dry seasons of the tropics rather than the cold and warm seasons of higher latitudes.
Why is the ITCZ called the doldrums?
In the seamen's speech, the zone is referred to as the doldrums because of its erratic (monotonous) weather patterns with stagnant calms and violent thunderstorms. The ITCZ appears as a band of clouds, usually thunderstorms, that encircle the globe near the Equator.

Where is the ITCZ located now?
The Intertropical Convergence Zone, or ITCZ, is a band of low pressure around the Earth which generally lies near to the equator.
Is ITCZ always at equator?
The ITCZ tends to be located under and near where the sun's rays are most direct. Thus, the ITCZ will be located north of the equator in the Northern Hemisphere summer and south of the equator in the Northern Hemisphere winter. However, the mean or average position of the ITCZ is located north of the equator.
Why is the ITCZ at the equator?
The contrast between weak winds north and strong winds south of the equator is a direct consequence of southerly winds blowing onto the ITCZ. The Coriolis force cause these southerlies to veer, enhancing (weakening) the prevailing easterly trades before (after) they cross the equator.
Is the ITCZ always on the same place on Earth?
The location of the ITCZ gradually varies with the seasons, roughly corresponding with the location of the thermal equator. As the heat capacity of the oceans is greater than air over land, migration is more prominent over land.
Why does the ITCZ move north and south?
The position of the ITCZ varies predictably throughout the year. Although it remains near the equator, the ITCZ moves farther north or south over land than over the oceans because it is drawn toward areas of the warmest surface temperatures.
Where does the ITCZ shift during summer and why?
Answer: In the northern hemisphere the northeast trade winds converge with southeast winds from the Southern Hemisphere. The point at which the trade winds converge forces the air up into the atmosphere, forming the ITCZ. ... It moves north in the Northern Hemisphere summer and south in the Northern Hemisphere winter.
Why is the ITCZ in the Northern Hemisphere?
It exists because of the convergence of the trade winds. In the northern hemisphere the northeast trade winds converge with southeast winds from the Southern Hemisphere. The point at which the trade winds converge forces the air up into the atmosphere, forming the ITCZ.
What is the difference between monsoon and ITCZ?
ITCZ - a zonally elongated axis of surface wind confluence of northeasterly (NE) and southeasterly (SE) trade winds in the tropics. Monsoon Trough - the portion of the ITCZ which extends into or through a monsoon circulation, as depicted by a line on a weather map showing the location of minimum sea level pressure.
Which climate is influenced by the ITCZ most of the year?
-The ITCZ migrates with the high Sun and influences the Tropical Monsoon climates.
Where is the ITCZ located at the month of January?
In January, over the Atlantic, the ITCZ generally sits no further south than the Equator, but extends much further south over South America, Southern Africa, and Australia. Over land, the ITCZ tends to follow the sun's zenith point.
Where does the ITCZ shift during the summer season?
( The shift of the position of Inter Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) in summer, over the Ganga plain (this is the equatorial trough normally positioned about 5°N of the equator. It is also known as the monsoon- trough during the monsoon season).
What countries are affected by ITCZ?
The ITCZ is a very large feature which circles the globe. It affects many tropical areas around the world including territories in the southern Caribbean. The ITCZ is not stationary. It moves north of the equator during the northern hemisphere summer, bringing heavy rain to Trinidad and Tobago and Grenada.
What is the ITCZ?
The position of the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) varies with different seasons. The Intertropical Convergence Zone is commonly known as the ITCZ. It is also called Equatorial Convergence Zone (ECZ) or Intertropical Front.
What is the ITCZ belt?
The belt is mostly characterized by vigorous thunderstorms over broad areas due to convective activity. The position of the ITCZ varies with different seasons. Thermal energy characterizes the weather in this region from within the earth’s core and from the sun. This zone receives the highest amount of heat from the sun.
What are the characteristics of the intertropical convergence zone?
Characteristics of The Intertropical Convergence Zone. Low air pressure mostly characterizes the ITCZ. The northern and the southern trade winds converge at the ITCZ and to due to Earth’s rotation, the winds lose energy as they cross the equator. The heat from the ocean currents makes the air warm at the Earth’s surface creating a region ...
Why is the Intertropical Convergence Zone called the Doldrums?
Sailors refer to the Intertropical Convergence Zone as doldrums because the belt lacks horizontal air movement since the warm air simply rises. The ITCZ is not static, in that inconsistent location around the equator characterizes it. Different places receive varying heat energy amounts as the earth rotates with the seasons.
Why do ITCZ have doldrums?
The belt receives afternoon showers due to high humidity. Sailors refer to the Intertropical Convergence Zone as doldrums because the belt lacks horizontal air movement since the warm air simply rises.
What is the wettest zone in the world?
According to scientists, the ITCZ is the wettest zone on earth since it receives precipitation up to 200 days in a single year. Due to the storms collected in this area, it makes it hard for aircraft to fly over the zone and also for a ship to sail through.
Why does the ITCZ exist?
It exists because of the convergence of the trade winds. In the northern hemisphere the northeast trade winds converge with southeast winds from the Southern Hemisphere. The point at which the trade winds converge forces the air up into the atmosphere, forming the ITCZ. The location of the Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone is usually readily seen as ...
When is the dry season in the ITCZ?
The short dry season is in August and lasts for 3-4 weeks. This is due to the ITCZ moving to the north of the region. The short rainy season follows the brief dry period in August and lasts from early September to mid-October as the ITCZ moves south again, with a peak period at the end of September.
Where is the ITCZ located?
In Africa in July and August, for instance, the ITCZ is located just south of the Sahel desert at about 20 degrees north of the Equator, but the ITCZ over the Pacific and Atlantic Oceans is usually only 5 to 15 degrees North; meanwhile, over Asia, the ITCZ can go as far as 30 degrees North. Rosenberg, Matt.
What is the ITCZ?
Solar heating in the region forces air to rise through convection which results in the accumulation of large thunderstorms and plethora of precipitation, spreading rain around the Equator year-round; as a result of this, combined with its central location on the globe, the ITCZ is a key component of the global air and water circulation system.
Why is the intertropical convergence zone called the doldrums?
The Intertropical Convergence Zone has been called the doldrums by sailors due to the lack of horizontal air movement (the air rises with convection), and it's also known as the Equatorial Convergence Zone or Intertropical Front.
Why is the ITCZ zone farther north than the ITCZ zone?
The ITCZ over land ventures farther north or south than the ITCZ over the oceans, this is due to the variations in land and water temperatures. The zone mostly stays close to the Equator over water. It varies throughout the year over land.
Why do airlines avoid ITCZ?
Most commercial airlines avoid the ITCZ while traveling across continents for this reason, and while the ITCZ over the ocean is usually calmer during the day and night and only active in the morning, many boats have been lost at sea from a sudden storm there.
What is the trade wind zone?
Near the equator, from about 5 degrees north and 5 degrees south, the northeast trade winds and southeast trade winds converge in a low-pressure zone known as the Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ).
When does the ITCZ move south?
In July and August, the ITCZ lies well to the north of the equator over Africa, Asia and Central America before moving south into South America, central Africa and Australia by January and February.
How long does it take for the ITCZ to move?
The ITCZ moves throughout the year and follows the migration of the Sun’s overhead position typically with a delay of around 1-2 months. As the ocean heats up more slowly than land, the ITCZ tends to move further north and south over land areas than that over water.
What is the intertropical convergence zone?
The Intertropical Convergence Zone is a band of low pressure around the Earth which generally lies near to the equator. The Intertropical Convergence Zone, or ITCZ, is a band of low pressure around the Earth which generally lies near to the equator. The trade winds of the northern and southern hemispheres come together here, ...
What is the ITCZ?
The ITCZ is a zone of convergence at the thermal equator where the trade winds meet. It is a low pressure belt and migrates with the changing position of the thermal equator. The thermal equator receives the most intense heat from the Sun. Around 20th June each year the Sun is overhead at 23½º North, the Tropic of Cancer.
Where is the Sun on December 20th?
Around 20th December the Sun is overhead at 23½º South, the Tropic of Capricorn. The movement of the thermal equator shifts the belts of planetary winds and pressure systems to the north and to the south annually, as the diagram below shows.

Overview
ITCZ over oceans vs. land
The ITCZ is commonly defined as an equatorial zone where the trade winds converge. Rainfall seasonality is traditionally attributed to the north–south migration of the ITCZ, which follows the sun. Although this is largely valid over the equatorial oceans, the ITCZ and the region of maximum rainfall can be decoupled over the continents. The equatorial precipitation over land is not si…
Meteorology
The ITCZ was originally identified from the 1920s to the 1940s as the Intertropical Front (ITF), but after the recognition in the 1940s and the 1950s of the significance of wind field convergence in tropical weather production, the term Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) was then applied.
The ITCZ appears as a band of clouds, usually thunderstorms, that encircle the globe near the Equator. In the Northern Hemisphere, the trade winds move in a southwestward direction from th…
South Pacific convergence zone
The South Pacific convergence zone (SPCZ) is a reverse-oriented, or west-northwest to east-southeast aligned, trough extending from the west Pacific warm pool southeastwards towards French Polynesia. It lies just south of the equator during the Southern Hemisphere warm season, but can be more extratropical in nature, especially east of the International Date Line. It is consi…
Effects on weather
Variation in the location of the intertropical convergence zone drastically affects rainfall in many equatorial nations, resulting in the wet and dry seasons of the tropics rather than the cold and warm seasons of higher latitudes. Longer term changes in the intertropical convergence zone can result in severe droughts or flooding in nearby areas.
Role in tropical cyclone formation
Tropical cyclogenesis depends upon low-level vorticity as one of its six requirements, and the ITCZ fills this role as it is a zone of wind change and speed, otherwise known as horizontal wind shear. As the ITCZ migrates to tropical and subtropical latitudes and even beyond during the respective hemisphere's summer season, increasing Coriolis force makes the formation of tropical …
Hazards
Thunderstorms along the Intertropical Convergence Zone played a role in the loss of Air France Flight 447, which left Rio de Janeiro–Galeão International Airport on Sunday, 31 May 2009, at about 7:00 p.m. local time (6:00 p.m. EDT or 10:00 p.m. UTC) and had been expected to land at Charles de Gaulle Airport near Paris on Monday, 1 June 2009, at 11:15 a.m. (5:15 a.m. EDT or 9:15 a.m. UTC). The aircraft crashed with no survivors while flying through a series of large ITCZ thun…
In literature
The doldrums are notably described in Samuel Taylor Coleridge's poem The Rime of the Ancient Mariner (1798) and also provide a metaphor for the initial state of boredom and indifference of Milo, the child hero of Norton Juster's classic children's novel The Phantom Tollbooth. It is also cited in the book Wind, Sand and Stars.