What is lateral trochlea?
Lateral trochlear inclination (LTI) is the inclination angle between the femoral trochlea and a posterior condylar tangential line 1.
Where is the trochlea in the knee?
The trochlea is a groove in the femur bone underneath the kneecap (patella). The walls of the trochlea stabilize the patella and allow it to glide down the center of the trochlea as the knee bends.
Where is the central trochlea?
In most knees, there is a groove on the end of the femur, called the trochlea, in which the kneecap sits.
What is lateral trochlear inclination?
Lateral trochlear inclination (LTI) angle is measured on two separate axial MRI images. The first is a measure of the proximal trochlea relative to a horizontal line. C) the second measure is the angle of the fully formed posterior femoral condyles relative to the horizontal taken on a separate axial MRI image.
What is the trochlea?
Definition of trochlea : an anatomical structure that is held to resemble a pulley especially : the articular surface on the medial condyle of the humerus that articulates with the ulna.
What is the function of the trochlear?
The trochlear nerve is one of 12 sets of cranial nerves. It enables movement in the eye's superior oblique muscle. This makes it possible to look down. The nerve also enables you to move your eyes toward your nose or away from it.
What can be done for arthritis under the kneecap?
Knee Arthritis TreatmentActivity modifications that may keep joint pain and inflammation from flaring. ... Physical therapy to improve strength and range of motion.Weight loss (if applicable) to reduce stress placed on the joint.Bracing to provide more stability to the joint.More items...
What is a Chondroplasty of the knee?
Chondroplasty is a surgical procedure to repair and reshape damaged cartilage in a joint. The procedure involves smoothing degenerative cartilage and trimming any unstable flaps of cartilage.
Does trochlear dysplasia require surgery?
In the early 1990's, researchers reported that up to 90% of patellofemoral instability is caused by trochlear dysplasia. Initially treatment consists of rest, use of crutches or braces, followed by physiotherapy. In cases where the patella instability is affecting patient's lifestyle, surgery is warranted.
What is lateral patellar subluxation?
A patellar subluxation means that the kneecap has briefly slid out of its normal place in that groove. In most cases the kneecap moves towards the outside of the body when it slides out of place. This can be a one-time event, or it can happen multiple times.
Does patellofemoral show on MRI?
Patellofemoral disorders and MRI technique Both conditions commonly occur in association rather than in isolation. Kinematic MRI and CT studies exploit these dynamic patellofemoral relationships by imaging patients in varying degrees of knee flexion and extension [5–7].
What is the Trochlear angle?
The trochlear angle refers to the opening angle of the trochlea as visualized on a 30° flexion axial radiograph. In the study of Henri Dejour et al., a threshold of 145° successfully excluded all normal patients.
Does trochlear dysplasia require surgery?
In the early 1990's, researchers reported that up to 90% of patellofemoral instability is caused by trochlear dysplasia. Initially treatment consists of rest, use of crutches or braces, followed by physiotherapy. In cases where the patella instability is affecting patient's lifestyle, surgery is warranted.
Is walking good for arthritis in knees?
Walking is recommended for people with arthritis as it's low impact, helps to keep the joints flexible, helps bone health and reduces the risk of osteoporosis.
Is trochlear dysplasia painful?
Trochlear dysplasia also causes knee pain during activities that involve bending the knee such as walking up or down the stairs or running. In the long term, the abnormal movement of the patella on the femur can lead to the development of wear and tear of your joint surface known as osteoarthritis.
How do you fix a shallow trochlear groove?
Trochleoplasty involves either lengthening the walls of the trochlear groove or deepening the groove by removing bone or any abnormal bony growths. You may sometimes need additional surgical procedures such as ligament reconstruction to improve the outcome.
What is lateral trochlear inclination?
The lateral trochlear inclination angle is used in the assessment of trochlear dysplasia, a dysplastic deformity of the distal femur, which is a known risk factor for patellofemoral instability 1-5. It has been primarily introduced for magnetic resonance imaging 1. A review of the quality assessment of measurements for trochlear dysplasia identified the lateral trochlear inclination as the most useful measurement 3.
Where is the inclination angle measured?
Traditionally the inclination angle is measured between the bony contours of the lateral trochlear facet on the most superior/proximal axial slice containing trochlear cartilage and a posterior condylar tangential line at the same level 1.
How to treat trochlear dislocation?
Because the severity of trochlea dysplasia can run from minor to severe, treatment options are also varied. They can include a reconstruction of the medial patellofemoral ligament, a tibial tubercle osteotomy, a trochleoplasty, where the distal aspect of the femur is cut and reshaped to create more of a normal groove, a distal femoral osteotomy, and other associated treatments. Thus, no one patient has the same treatment as another, and a thorough workup is necessary to determine the best course of action, if any, for a particular patient with trochlear dysplasia.
What is the X-ray of a trochlear groove?
X-ray demonstrating the flatter curvature of the trochlear groove which is present with trochlear dysplasia. Patients with significant trochlear dysplasia are at a much higher risk of having their kneecap re-dislocate after an initial dislocation.
Why is the patella not sitting in the groove?
This is because a patella can sit up high above the trochlear groove and it is possible that developmentally a trochlear groove may not form as deep of a groove if the patella is not sitting within it as well as in some patients compared to those whose patellar tendon height is normal.
What is it called when the kneecap is flat?
When the trochlea is flat, or even possibly has a convex or dome shape, it is known as trochlear dysplasia which usually is referred to as an unstable kneecap. In these circumstances, the trochlea is not shaped normally, and the patella does not have the normal bony constraints to provide stability. Thus, one needs to rely on the medial patellofemoral ligament and their quadriceps mechanism to hold the patella in place.
How to diagnose trochlea dysplasia?
A diagnosis of trochlea dysplasia is usually made by a thorough physical exam and radiographic work-up. Patients with trochlear dysplasia often have increased medial and lateral patellar translation near full extension and at 45 degrees of knee flexion. They may also have an apprehension test where they feel their patella is going ...
What is the patella of the knee?
This area of the knee is easy to identify. When the knee is bent, the undersurface of the kneecap (the patella) lies in an area known as the trochlear groove. The sides of the patella and the walls of the groove should be almost parallel. The normal shape of the trochlea groove is concave. In fact, the outside, or lateral aspect of the trochlea groove has a higher bump than the inside part. This allows the patella, or kneecap, to glide down the central aspect of the distal femur rather effortlessly due to its bony constraints. This is important because the patella serves as a fulcrum to increase the overall strength and efficiency of the quadriceps muscles of the thigh.
Why is it important to have a plain X-ray of the patella alta?
This is important because surgical treatments may not always be indicated if there is significant arthritis present. In addition, a plain X-ray to look at the amount of patella alta, or a high-riding patella, is indicated. The treatment of trochlear dysplasia can be very difficult.
Which side of the trochlea is vertical?
Most frequently, the groove is vertical on the anterior side but runs down laterally on the posterior side. During elbow flexion, the vertical anterior part of the trochlea keeps the upper arm and forearm aligned (when viewed in front).
What is the shape of the trochlea?
When viewed from in front or behind, the trochlea looks roughly cylindrical, but when viewed from below its true oblique shape and the spiralling nature of its groove become apparent. The spiralling nature of the trochlear groove results in the varying transverse axes of the elbow joint.
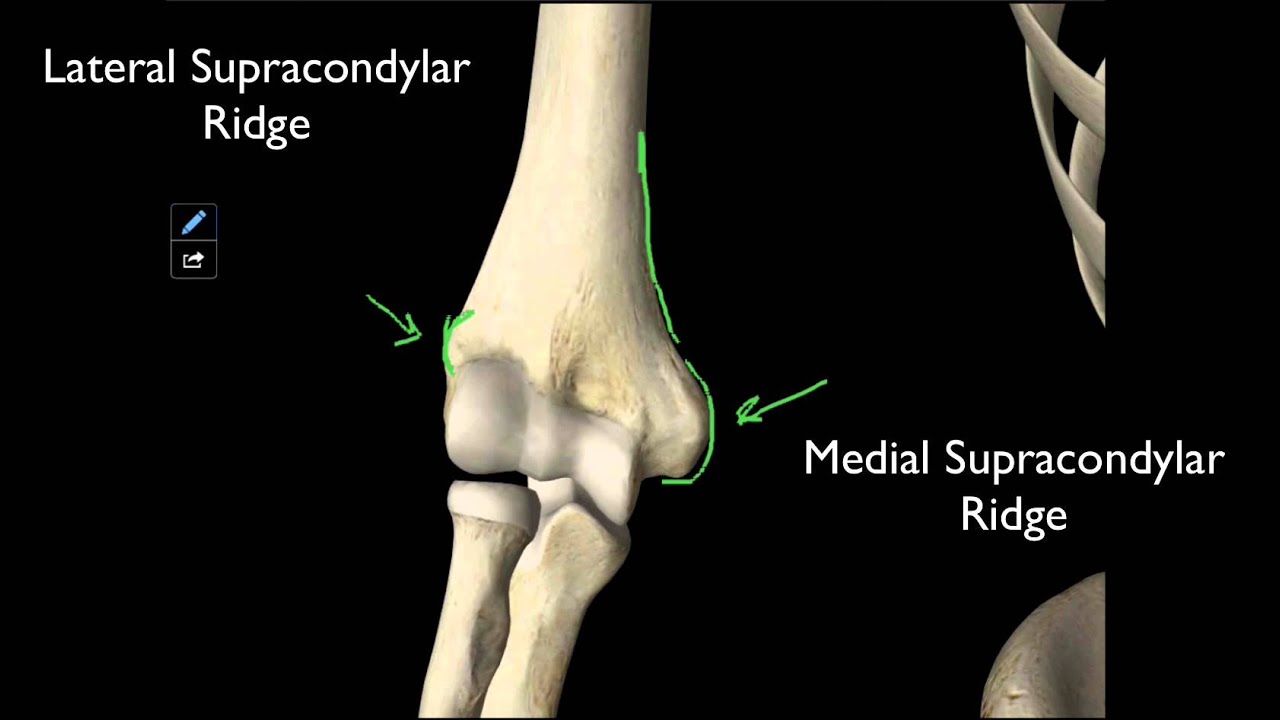
What is the trochlea of the humerus?
In the human arm, the humeral trochlea is the medial portion of the articular surface of the elbow joint which articulates with the trochlear notch on the ulna in the forearm.
What is the carrying angle of the elbow?
During elbow extension, however, the oblique posterior part makes contact with the trochlear notch on the ulna so that this obliquity forces the main axis of the forearm to form a small angle with that of the upper arm. This angle is known as the carrying angle and is more prominent in women than in men.
Which joint articulates with the trochlear notch?
The trochlea articulated with the trochlear notch. The elbow is a hinge joint with a rotatory component where the trochlea forms the convex, proximal surface which articulates with the concave, distal surface on the ulna, the trochlear notch.
Where is the humeral trochlea?
In the human arm, the humeral trochlea is the medial portion of the articular surface of the elbow joint which articulates with the trochlear notch on the ulna in the forearm.
How old is the trochlea?
While the ossification of the capitulum has started a year after birth, the ossification of the trochlea begins at 8–9 years of age; that of the head of radius and the medial epicondyle at 4–5 years and that of the lateral condyle at 10 years.
How to treat trochlear dislocation?from drrobertlaprademd.com
Because the severity of trochlea dysplasia can run from minor to severe, treatment options are also varied. They can include a reconstruction of the medial patellofemoral ligament, a tibial tubercle osteotomy, a trochleoplasty, where the distal aspect of the femur is cut and reshaped to create more of a normal groove, a distal femoral osteotomy, and other associated treatments. Thus, no one patient has the same treatment as another, and a thorough workup is necessary to determine the best course of action, if any, for a particular patient with trochlear dysplasia.
What is the X-ray of a trochlear groove?from drrobertlaprademd.com
X-ray demonstrating the flatter curvature of the trochlear groove which is present with trochlear dysplasia. Patients with significant trochlear dysplasia are at a much higher risk of having their kneecap re-dislocate after an initial dislocation.
What is a recurrent patellar dislocation?from pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Recurrent patellar dislocation is a disabling condition, which can lead to articular cartilage injuries, osteochondral fractures, recurrent instability, pain, decreased activity and patellofemoral osteoarthritis. Trochlear dysplasia represents an important component of patellar dislocation.Imaging provides an objective basis for the morphological abnormalities and thus allows determination of the surgical strategy according to the concept of 'à la carte' surgery.The main surgical techniques of trochleoplasty are the sulcus deepening trochleoplasty, the 'Bereiter' trochleoplasty and the recession trochleoplasty.At mid-term, all techniques have shown a postoperative improvement in clinical scores, with a low rate of recurrence of dislocation and a possible return to sport. But these techniques do not halt the progression of patellofemoral arthritis. Cite this article: EFORT Open Rev2018;3 DOI: 10.1302/2058-5241.3.170058.
What is it called when the kneecap is flat?from drrobertlaprademd.com
When the trochlea is flat, or even possibly has a convex or dome shape, it is known as trochlear dysplasia which usually is referred to as an unstable kneecap. In these circumstances, the trochlea is not shaped normally, and the patella does not have the normal bony constraints to provide stability. Thus, one needs to rely on the medial patellofemoral ligament and their quadriceps mechanism to hold the patella in place.
Why is the patella not sitting in the groove?from drrobertlaprademd.com
This is because a patella can sit up high above the trochlear groove and it is possible that developmentally a trochlear groove may not form as deep of a groove if the patella is not sitting within it as well as in some patients compared to those whose patellar tendon height is normal.
What is the shape of the patella?from drrobertlaprademd.com
The sides of the patella and the walls of the groove should be almost parallel. The normal shape of the trochlea groove is concave. In fact, the outside, or lateral aspect of the trochlea groove has a higher bump than the inside part.
How to diagnose trochlea dysplasia?from drrobertlaprademd.com
A diagnosis of trochlea dysplasia is usually made by a thorough physical exam and radiographic work-up. Patients with trochlear dysplasia often have increased medial and lateral patellar translation near full extension and at 45 degrees of knee flexion. They may also have an apprehension test where they feel their patella is going ...
What is the term for a deformity of the femoral trochlea?
Trochlear dysplasia. Trochlear dysplasia refers to a dysplastic deformity of the femoral trochlea and is a known risk factor for patellofemoral instability.
What is the prevalence of trochlear dysplasia?
The reported prevalence of trochlear dysplasia in recurrent patellar dislocations is ~80% (range 74-85%) 1,15. The latter is most common in the adolescent age group 4,5.
What is a known association with patellofemoral instability?
Trochlear dysplasia is a known association with patellofemoral instability.
What imaging method is used to diagnose trochlear dysplasia?
Different radiographic methods exist to assess for trochlear dysplasia in true lateral radiographic images of the knee and cross-sectional imaging CT and MRI respectively.
What is the bump in the distal femur?
trochlear bump: the increased distance between the anterior trochlear groove and extension of the anterior cortex of the distal femur
Is trochlear dysplasia a predisposing factor?
Trochlear dysplasia is a predisposing factor of patellofemoral instability and should be only treated in that context.
Is it worth getting both trochlear and radiographs?
Since cross-sectional images and radiographs show different aspects of trochlear dysplasia it might be worthwhile acquiring both if there are doubts with respect to the diagnosis ref.