Where is a cartilage found?
Cartilage is the main type of connective tissue seen throughout the body. It serves a variety of structural and functional purposes and exists in different types throughout our joints, bones, spine, lungs, ears and nose.
Where is the cartilage located and what is its function?
What is cartilage? Cartilage is a strong, flexible connective tissue that protects your joints and bones. It acts as a shock absorber throughout your body. Cartilage at the end of your bones reduces friction and prevents them from rubbing together when you use your joints.
Where are 4 places cartilage is found in your body?
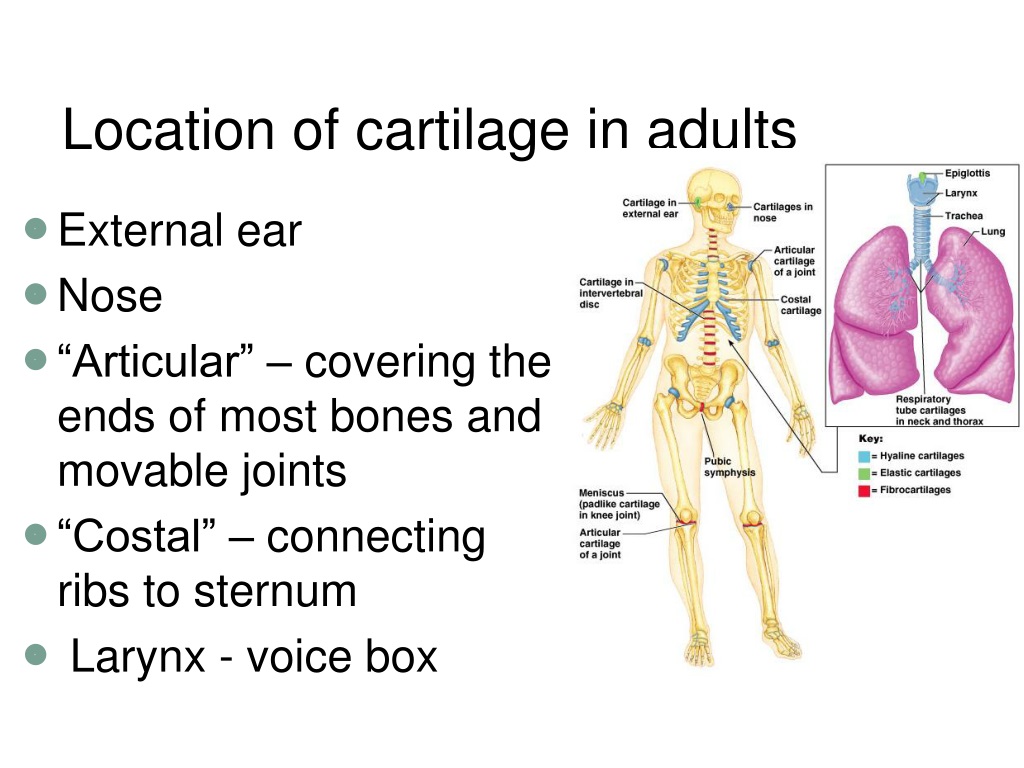
Hyaline cartilage is found in the nose, ears, trachea, parts of the larynx, and smaller respiratory tubes. Fibrous cartilage has the fewest cells so it has the most intercellular space. Fibrous cartilage is found in the spine and the menisci.
Where are the 3 types of cartilage located?
Cartilage: The three types of cartilageHyaline - most common, found in the ribs, nose, larynx, trachea. Is a precursor of bone.Fibro- is found in invertebral discs, joint capsules, ligaments.Elastic - is found in the external ear, epiglottis and larynx.
What is the role of cartilage?
Cartilage has many functions, including the ability to resist compressive forces, enhance bone resilience, and provide support on bony areas where there is a need for flexibility. The primary cell that makes cartilage is the chondrocyte, which resides within the lacunae.
What are 3 types of cartilage?
Cartilage is a specialized form of connective tissue. Composed of cells (chondrocytes) and an extracellular matrix composed of fibers and ground substance. The three types of cartilage include hyaline, elastic, and fibrocartilage. Hyaline cartilage is the most common type of cartilage.
Where is cartilage found in adults?
It persists in human adults at the ends of bones in free-moving joints as articular cartilage, at the ends of the ribs, and in the nose, larynx, trachea, and bronchi. It is a glossy blue-white in appearance and very resilient.
What cartilage is in the ear?
Elastic cartilage is found in the ear and epiglottis (located in the throat) as well as parts of the nose and trachea. This cartilage serves to provide strength and elasticity to organs and body structures, such as the outer ear.
How many cartilage are there in the human body?
There are three types of cartilage: hyaline, fibrous, and elastic cartilage. Hyaline cartilage is the most widespread type and resembles glass. In the embryo, bone begins as hyaline cartilage and later ossifies. Fibrous cartilage has many collagen fibers and is found in the intervertebral discs and pubic symphysis.
Do all joints have cartilage?
Joints consist of the following: Cartilage. This is a type of tissue that covers the surface of a bone at a joint. Cartilage helps reduce the friction of movement within a joint.
What is cartilage in knee?
Within the knee joint, the cartilage – the joint surface covering the ends of the bones – acts as a shock absorber that cushions the bones, allowing them to move smoothly. It can become damaged through arthritis or by an accident where the meniscus is torn during sports such as tennis, hockey, football or skiing.
What are the examples of cartilage?
The discs between the vertebrae contain fibro cartilage. The larynx, nose, and ribs all contain hyaline cartilage. The ear contains elastic cartilage.
What are the functions of cartilage quizlet?
Supports soft tissues, Facilitates smooth movement of joints, Involved in the growth of long bones, What are the three types of cartilage cells?
What is function of cartilage and bone?
Both bone and cartilage play an important role in protecting the internal organs of our body, providing structural support and surfaces for muscle attachment....Difference between Bone and Cartilage.BonesCartilageBones are of two types: compact or spongy.Cartilage is of three types: Hyaline cartilage, fibrocartilage and elastic cartilage.11 more rows•Oct 14, 2020
What is the function of cartilage located in the epiphyseal plates?
Epiphyseal cartilage is hyaline cartilage tissue with a gelatinous texture, and it is responsible for the longitudinal growth of the long bones in birds and mammals. It is located between the epiphysis and the diaphysis.
What is the function of cartilage in trachea?
A normal trachea (windpipe) has many rings made of cartilage (a strong and flexible tissue). These rings are C-shaped and support the trachea but also allow it to move and flex when your child breathes.
Where is cartilage in the human body?
Cartilage is found in many locations within the human body. Common locations include joints, in between vertebrae, the nose and ears, within the tr...
What is the main difference between the different types of cartilage?
The cartilage types are classified based on their composition. Elastic cartilage has the highest concentration of chondrocytes and the lowest conce...
Is cartilage made of water?
Cartilage contains a large amount of water. However, this water is retained by the materials that cartilage is composed of including collagen, prot...
What is the most common type of cartilage?
The most common type of cartilage found in the human body is hyaline cartilage. It is found in the trachea, at the ends of bones, and within the ri...
What is cartilage and its function?
Cartilage is a specialized type of connective tissue. It functions to cushion joints, provide a smooth surface for bones to glide and rotate on, an...
What do all types of cartilage have in common?
All cartilage types are avascular, contain no nerves, and are composed of similar material. Each cartilage type contains chondroblasts which produc...
Where is cartilage found?
Cartilage is found throughout the human body in areas such as the joints, nose, airway, intervertebral discs of the spine, and the ear.
What is the most common form of cartilage?
The most common form of cartilage is hyaline cartilage. Hyalos is the Greek word for glass, which describes the appearance of this type of connective tissue – translucent, blueish-white, and shiny. Hyaline cartilage is usually only 2 – 4 mm thick (all cartilage must be thin, as there is no vascularization in this tissue type, ...
What are the main components of cartilage?
The Main Ingredients of Cartilage. Cartilage is made up of highly specialized cells called chondrocytes and chondroblasts (chondro refers to cartilage), and other extracellular material which forms the cartilage matrix. All connective tissue types within the human body are derived from the embryonal mesoderm.
Why does cartilage grow slowly in older people?
Because of this, there is little metabolic activity, and little to no new growth in cartilage tissue – one of the reasons the elderly commonly suffer from degenerative joint pain. Cartilage does continue to grow slowly, however. This can be seen in the larger ears and noses of older individuals.
What is the role of elastic cartilage?
Elastic cartilage’s role is purely structural, offering flexibility and resilience due to a mixture of elastic fibers and type II collagen fibers. It is yellow in color, and without the organized structure of fibrocartilage when viewed on a microscope slide. Types of Cartilage.
What is the role of cartilage in the body?
Cartilage is a supple tissue which allows for facial movement as well as providing a lightweight supportive structure in the external ear, and the tip and septum of the nose. In other regions it acts as a shock absorber, cushioning areas where bone meets bone and preventing abrasion and damage. A joint would also not be able to bend without ...
How many types of cartilage are there?
Types of Cartilage. There are three cartilage types in the human body. Although their components are very similar, the quantities of each component differ, providing different qualities to each type. Accordingly, each type has a particular location.
Where is cartilage found?
Cartilage is a robust and viscoelastic connective tissue that can be found in joints between bones, the rib cage, intervertebral discs, the ear, and the nose. While more rigid and less flexible than muscle, cartilage is not as stiff as bone. These properties allow cartilage to serve as a support structure for holding tubes open or ...
What is the most abundant type of cartilage?
Cartilage is a flexible connective tissue found in multiple areas of the body, including joints, the ear and nose, and intervertebral discs. Hyaline cartilage, the most abundant type of cartilage, plays a supportive role and assists in movement.
What is the articular cartilage of the elbow?
Articular cartilage of the elbow (sagittal view) The function of articular cartilage is dependent on the molecular composition of the extracellular matrix (ECM), which consists mainly of proteoglycans and collagen.
Why is cartilage so slow to repair?
Moreover, cartilage has a very slow turnover and is difficult to repair due to the fact that cartilage tissue is avascular (and also aneural ). Its growth is not usually quantified by an increase in size or mass of the cartilage itself, but instead by its biomechanical properties. Chondrocytes (histological slide)
What are the cells that make up the cartilage matrix?
The chondroblasts that are caught in the matrix are called chondrocytes, and are the main type of specialized cells found in cartilage. Chondrocytes are responsible for producing large quantities of collagenous extracellular matrix and ground substance that is rich in proteoglycans and elastin fibers.
Why does cartilage breakdown occur?
Damage or injury can also happen through pathologic states, where ossification or breakdown of cartilage occurs due to dysfunction of cartilage-specific cells or synovial cells, or imbalances in the microenvironment surrounding the cartilage . Cartilage has limited reparative capacities for a number of reasons:
How does ECM affect cartilage?
Therefore, when this ECM is affected, it can lead to damage or injury. This can happen through physical mechanical forces, where excessive friction and applied forces wear down the cartilage (e.g. due to overuse or traumatic injury during athletics). Damage or injury can also happen through pathologic states, where ossification or breakdown of cartilage occurs due to dysfunction of cartilage-specific cells or synovial cells, or imbalances in the microenvironment surrounding the cartilage.
What are the cells that make up cartilage?
Cartilage cells, called chondrocytes, occur at scattered sites through the cartilage and receive nutrition by diffusion through the gel; cartilage contains no blood vessels or nerves, unlike bone. Histological image of hyaline cartilage. The rather weak skull of adults is composed of various paired and unpaired bones.
Why is cartilage yellow?
Elastic cartilage, which is yellow in appearance, is more pliable than the other two forms because it contains elastic fibres in addition to collagen. In humans it makes up the external ear, the auditory tube of the middle ear, and the epiglottis. cartilage.
What is the Caudata?
Caudata: Bones and cartilage. The rather weak skull of adults is composed of various paired and unpaired bones. These bones may fuse or be lost in different groups, and... Three main types of cartilage can be distinguished. Hyaline cartilage is the most widespread and is the type that makes up the embryonic skeleton.
What is the only component of the skeletons of certain primitive vertebrates, including lampreys and?
See Article History. Cartilage, connective tissue forming the skeleton of mammalian embryos before bone formation begins and persisting in parts of the human skeleton into adulthood. Cartilage is the only component of the skeletons of certain primitive vertebrates, including lampreys and sharks. It is composed of a dense network ...
What is collagen made of?
It is composed of a dense network of collagen fibres embedded in a firm, gelatinous ground substance that has the consistency of plastic; this structure gives the tissue tensile strength, enabling it to bear weight while retaining greater flexibility than bone.
Where is fibrous tissue found?
Fibrocartilage is the tough, very strong tissue found predominantly in the intervertebral disks and at the insertions of ligaments and tendons; it is similar to other fibrous tissues but contains cartilage ground substance and chondrocytes.
Where does a syringe live?
It persists in human adults at the ends of bones in free-moving joints as articular cartilage, at the ends of the ribs, and in the nose, larynx, trachea, and bronchi. It is a glossy blue-white in appearance and very resilient.
Where is cartilage found in the human body?
Other areas (such as the cartilage that forms at the ends of bones) are more rigid and resistant to bending. Cartilage can be found in multiple locations in the human body, and its appearance will change based on the location and function. Some of these locations include: Ears. Nose.
What is cartilage made of?
Cartilage Meaning. Cartilage is a connective tissue that is composed of unique and specialized cells called chondrocytes. Chondrocytes are responsible for turning over the large collection of material that composes the extracellular matrix.
How do chondroblasts form?
As an embryo, chondroblasts form through a process called chondrification within a collection of unspecialized cells collectively known as the mesenchyme. Cartilage is avascular and receives its nutrients from a nearby connective tissue caller perichondrium. There are three types of cartilage: Hyaline cartilage.
Why is cartilage repair slower than other tissue types?
This also means that cartilage repairs much slower than other tissue types. Diffuse replenishes nutrients at a lower rate than what can be delivered by vessels and so cartilage receives the material needed to repair much slower than skin or bone. Repair of cartilage is also limited by the extracellular matrix. Because the chondrocytes are responsible for producing the material that composes cartilage, they must be within the area of damage to produce new needed material. However, chondrocytes are trapped within this matrix and cannot migrate to new areas.
Why is cartilage avascular?
Recall that cartilage is avascular. This means that it cannot receive nourishment to grow and repair from vessels like other tissue types. Instead, it must rely on diffusion. Nutrients diffuse across cartilage from capillaries observed in the perichondrium. The perichondrium is a type of connective tissue that surrounds cartilage and aids in repair and growth. Because cartilage depends on diffusion to maintain its nutrient requirements, it makes sense that it remains relatively thin throughout the body. A thick piece of tissue would be unable to diffuse nutrients throughout its entire volume.
Why is cartilage important?
Joints are incredibly important to provide movement. Cartilage allows joints to function by providing a smooth, lubricated surface for joints to rotate or bend at. Without cartilage, bones would grind against each other at joint sites and cause discomfort, potentially even limiting mobility.
How many types of cartilage are there in the human body?
There are three types of cartilage found within the human body:
Where is cartilage found?
Cartilage is a connective tissue found in various parts of the adult skeleton including all joints between bones and structures which is deformable as well as strong e.g. the elbows, knees, and ankles, ends of the ribs, Between the vertebrae in the spine, ears, and nose, Bronchial tubes or airways.
How does cartilage grow?
Cartilage grows by interstitial and appositional mechanisms. Interstitial growth is the result of continued mitosis of early chondroblasts throughout the tissue mass and is obvious only in young cartilage, where the plasticity of the matrix permits continued expansion.
What is the MICROSTRUCTURE OF CARTILAGE?
Cartilage is a pliant, load-bearing connective tissue, covered by a fibrous perichondrium except at its junctions with bones and over the articular surfaces of synovial joints. It has a capacity for rapid interstitial and appositional growth in young and growing tissues. Three types of cartilage (hyaline cartilage, ...
What is the most common cartilage type?
Hyaline Cartilage. It is the most widespread cartilage type and, in adults, it forms the articular surfaces of long bones, the rib tips, the rings of the trachea, and parts of the skull. It is predominately collagen (yet with few collagen fibers), and its name refers to its glassy appearance.
Where is collagen found in the body?
Most fibrous tissues contain collagen type I, which forms large fibers with a wavy ‘crimped’ structure; however, this type of collagen is only found in cartilage in the outer layers of the perichondrium and in white fibrocartilage.
Which cartilage is found in the pubic symphysis?
It is the only type of cartilage that contains type I collagen in addition to the normal type II. Fibrocartilage is found in the pubic symphysis, the annulus fibrosus of intervertebral discs, menisci, and the temporal-mandibular joint.
What type of tissue is white fibrocartilage?
White fibrocartilage consists of a mixture of white fibrous tissue and cartilaginous tissue in various proportions.
What is cartilage in the body?
What is Cartilage? Cartilage is a tough but flexible tissue that is the main type of connective tissue in the body. Around 65–80% of cartilage is water, although that decreases in older people, and the rest is a gel-like substance called the ‘matrix’ that gives it its form and function.
Where is elastic cartilage found?
Elastic cartilage, which has elastic fibres that make the cartilage more flexible, is found in the ear, part of the nose and the trachea. Fibrous cartilage occurs in special cartilage pads called menisci that help to disperse body weight and reduce friction, such as in the knee.
Where does the articular cartilage matrix come from?
These come from a mesh of connective tissue in the embryo called the ‘mesenchyme’.
Which type of cartilage is found in the joints, septum of the nose, and the trachea?
They have different properties that correspond to their specific functions in the body and make it the most appropriate type of cartilage at that particular site. Hyaline, or articular cartilage, is found in the joints, septum of the nose (which separates the nostrils), and the trachea (air tube).
How thick is hyaline cartilage?
In the joints, hyaline cartilage forms a very low friction, 2-4 mm thick layer that coats the bony surfaces. This allows the bones of the joint to glide over one another during movement and, ideally, last a lifetime.
What is cartilage?
Cartilage is the fibrous, elastic tissue that cushions joints and provides organ structures.
What is the function of cartilage?
Cartilage serves various purposes depending on its type and location in the body. Cartilage gives shape to organs like ears and nostrils, keeping them stiff but flexible. Cartilage attaches the ribs to the breast bone (sternum) and provides flexibility to the ribcage to allow expansion of the chest while breathing. Cartilage helps keep the trachea open and flexible.
How do you repair damaged cartilage?
Damaged cartilage has minimal capacity to heal itself or grow back because it does not have blood supply. There are several types of treatments to repair damaged cartilage depending on the extent of damage. Cartilage treatments include the following:
What is the role of cartilage in the body?
Cartilage in the weight-bearing joints such as the vertebrae, knees and hips absorb impact from movement, and help disperse the body weight. Cartilage cushions all the joints, allows gliding movement, and reduces friction between bones.
What supplements help with cartilage damage?
Dietary supplements of compounds such as glucosamine and chondroitin which naturally occur in the body. Supplements are thought to help with limiting cartilage damage and reducing pain, but it is essential to check with the doctor before taking any.
What are the different types of cartilage?
Cartilages have different properties depending on their location in the body, and their function. The three three main types of cartilage are: Hyaline cartilage: Also known as articular cartilage, hyaline cartilage forms a thick layer over bone ends in joints. Hyaline cartilage is also found in the ribs, the septum of the nose which separates ...
Which cartilage is most flexible?
Elastic cartilage: Elastic cartilage is principally made up of elastin protein fibers which make it more flexible and is found in the external ears, part of the nose and larynx. Fibrocartilage: Fibrocartilage is a tough, flexible and elastic cartilage that is found in the joints of the knee ( meniscus ), hip (labrum) and shoulder (labrum), ...
What is the function of articular cartilage?
The function of articular cartilage is to absorb shock and provide an extremely smooth surface to make movement easier. Two clicks for more privacy: The Facebook Like button will be enabled once you click here. Activating the button already sends data to Facebook – see i. Two clicks for more privacy: The Google+ button will be enabled once you ...
What is the white tissue that allows bones to glide smoothly against each other?
Articular cartilage is a white elastic tissue that allows bones to glide smoothly against each other. It covers the ends of the femur and tibia as well as the back of the patella.
Where is the most rigid cartilage found?
It is the most rigid type of cartilage and can be found in intervertebral discs (the cushioning structures present between the bones of the spine or vertebrae) in the spine. It is also the strongest type of cartilage. This quality makes it a good connector in high- stress areas of the body, such as between bones, ligaments, and tendons.
Which type of cartilage is most common in the human body?
Hyaline cartilage: It contains mostly collagen fibers. It lines the bones in all joints, helping the body to move freely. This type of cartilage is the most common throughout the human body.
What is cartilage made of?
Cartilage is a strong and smooth tissue made of “chondrocytes,” or specialized cartilage cells. These cells produce a matrix of collagen, proteoglycans (a special type of protein), and other non-collagenous proteins. These materials help cartilage attract water and give it its shape and specific properties.
What is the difference between cartilage and ligament?
The differences are: A ligament is a band of tissue that connects bones to each other and ensures the joint is stable whereas cartilage is the line of connective tissue that works as a padding between the bones. Cartilage allows the body to move freely by protecting the joints from rubbing against each other.
What is the main type of connective tissue?
Cartilage is the main type of connective tissue seen throughout the body. It serves a variety of structural and functional purposes and exists in different types of joints, bones, spine, lungs, ears, and nose. It consists of cells called chondrocytes that is mixed with collagen and sometimes elastin fibers meshed into a matrix.
How does cartilage help the body move?
Cartilage allows the body to move freely by protecting the joints from rubbing against each other. Cartilage is harder and not as flexible as tendons and ligaments but is not as rigid as bone.
What is the function of cartilage?
The most important functions of cartilage include: Cartilage gives shape, support, and structure to other body tissues. It also helps to cushion joints. Cartilage also smoothens the bone surfaces at the joints. It is essential for the development and growth ...