Where is the pyramid located in the kidney?
medullaThe renal pyramids are located in the medulla (innermost portion) of the kidney. The points of renal pyramids are called papilla, and they point towards the renal calyx.
Where is the medulla located in the kidney?
The medulla is the inner part of the kidney. It consists of cone-shaped renal pyramids that contain the blood vessels and tubular structures of nephrons. The NIDDKD notes that nephrons are the filtering units of the kidney and include a glomerulus — a specially modified blood vessel that filters blood — and tubule.
How many medullary pyramids are in each kidney?
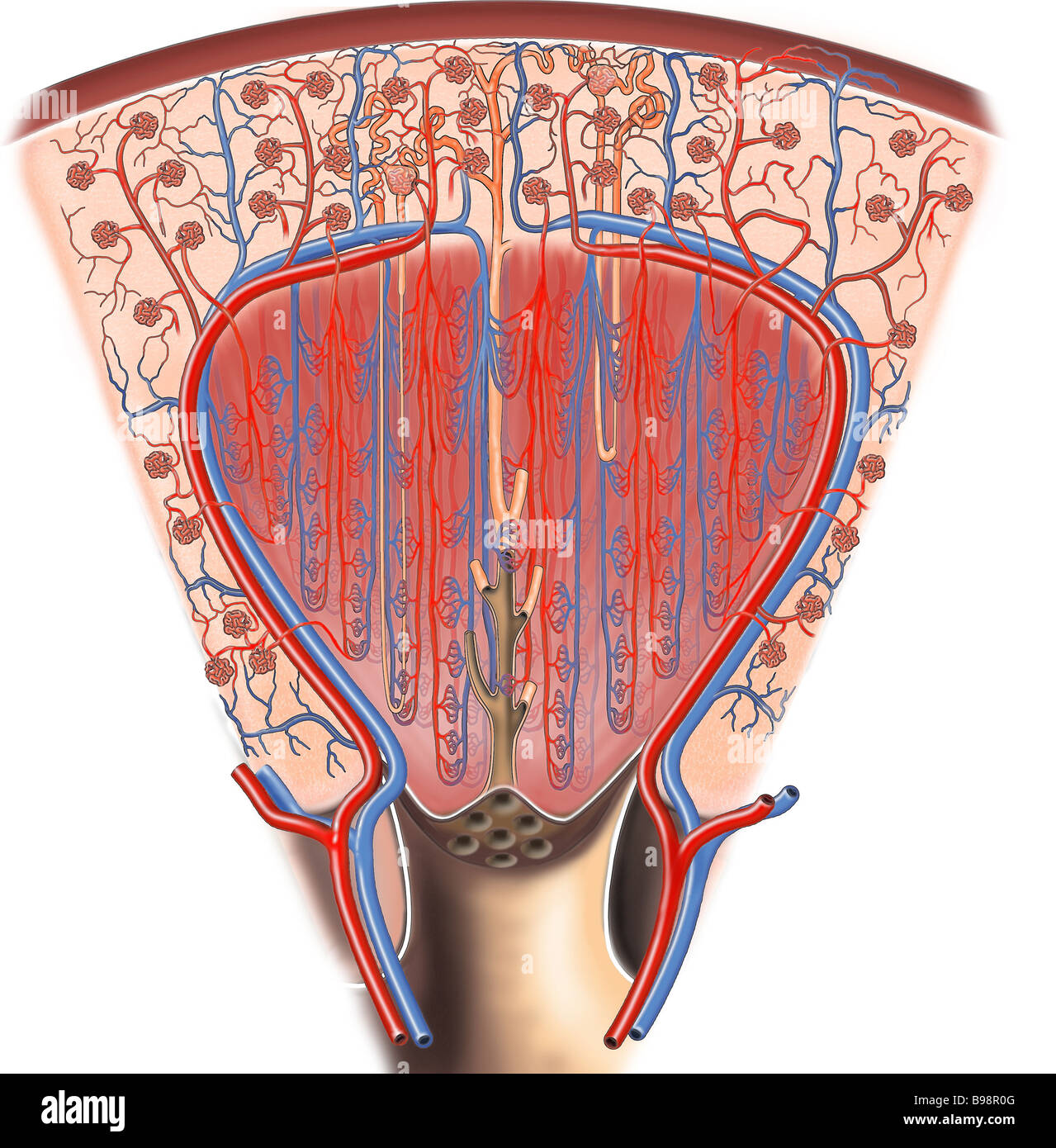
The medulla is divided into 8-18 conical regions, called the renal pyramids; the base of each pyramid starts at the corticomedullary border, and the apex ends in the renal papilla which merges to form the renal pelvis and then on to form the ureter.
What are the pyramids of the kidney?
The pyramids consist mainly of tubules that transport urine from the cortical, or outer, part of the kidney, where urine is produced, to the calyces, or cup-shaped cavities in which urine collects before it passes through the ureter to the bladder. The point of each pyramid, called the papilla, projects into a calyx.
What is the function of the medullary pyramid in the kidney?
The main renal pyramid function is to collect and transport urine through almost 1.25 million nephrons in the kidneys. The glomerulus is a small network of blood vessels that filter substances from the blood into the nephron.
What is the medullary pyramid?
In neuroanatomy, the medullary pyramids are paired white matter structures of the brainstem's medulla oblongata that contain motor fibers of the corticospinal and corticobulbar tracts – known together as the pyramidal tracts. The lower limit of the pyramids is marked when the fibers cross (decussate).
Is renal and medullary pyramid the same?
The renal medulla is the innermost part of the kidney. The renal medulla is split up into a number of sections, known as the renal pyramids. Blood enters into the kidney via the renal artery, which then splits up to form the segmental arteries which then branch to form interlobar arteries.
Which of the following is a part of medullary pyramid?
Complete Step by Step Answer: The medulla is divided into a few conical masses projecting into the calyces known as medullary pyramids or renal pyramids. These medullary pyramids contain all the contents of the medulla i.e., transporting tubules like PCT, DCT, and the collecting ducts.
What is the difference between the medulla and the renal pyramid?
The medulla is the inner region of the parenchyma of the kidney. The medulla consists of multiple pyramidal tissue masses, called the renal pyramids, which are triangle structures that contain a dense network of nephrons.
What are the renal pyramids located within the kidney quizlet?
Where are the renal pyramids located? Within the renal medulla, deep to the cortex, projecting to the center.
What are the 3 layers of the kidney What are their functions?
The cortex is the outer layer and contains the kidney's filtering structures. The medulla is the middle layer. It drains the urine into tubes and empties into the renal pelvis. The renal pelvis is the inner layer that leads to the ureter.
Where is the medulla located and what is its function?
Key takeaways. Your medulla oblongata is located at the base of your brain, where the brain stem connects the brain to your spinal cord. It plays an essential role in passing messages between your spinal cord and brain. It's also essential for regulating your cardiovascular and respiratory systems.
Where is the cortex and medulla located?
The kidneyThe kidney is made up of solid tissue called parenchyma which consists of cortex and the medulla. The renal cortex is the outside section of the kidney, while the medulla is the inside section. The renal cortex has a more grainy texture, while the medulla is smoother.
What does the renal medulla contain?
The renal medulla contains about a dozen cone-shaped structures called renal pyramids. Each renal pyramid contains more than a million tubules are...
What is the renal medulla in the kidney?
The renal medulla is the tissue that occupies the central and inner parts of the parenchyma in both kidneys. The renal medulla contains renal pyram...
What is the difference between the renal cortex and medulla?
The renal medulla is the kidney's heart and where the urine is ultimately channeled to the bladder. The renal cortex is where the urine is collecte...
What is the renal medulla divided into?
The renal medulla is the inner part of the kidney's parenchyma where it contains about a dozen triangle-shaped structures called renal pyramids. Ea...
What collects urine from a renal pyramid?
Urine is guided through millions of tubules are called nephrons located in the renal pyramids where they empty into an extension of the renal pelvi...
Is the renal medulla a tissue?
The parenchyma of the kidneys is the solid part of the kidney, and the renal medulla is the tissue that occupies the central and inner parts of the...
What are the pyramids of the medulla?
Anterior in the medulla are the paired medullary pyramids, which carry corticospinal tracts to their decussation at the medullary-spinal jun ction, then continue as the lateral corticospinal tracts in the spinal cord. Posterior to the pyramids in the midline is the medial lemniscus, a white matter tract projecting from the contralateral nucleus cuneatus and gracilis. More lateral in the rostral medulla are the dominant olivary nuclei, seen as bulges (olives) on the anterolateral medullary surface (see Fig. 2.15C ). This ovoid structure consists of a ribbon of convoluted gray matter with large pyramidal-type neurons surrounding a hilus of outwardly projecting white matter tracts that extend to the contralateral cerebellar peduncle. The olivary nucleus is developmentally and functionally related to the cerebellar dentate nucleus and bears resemblance to it histologically. Posteriorly, the fasciculus gracilis and cuneatus are continuations of the posterior columns and terminate in the nucleus gracilis and nucleus cuneatus, respectively. The medial longitudinal fasciculus is a white matter tract that rides the midline dorsally, while the spinothalamic tract maintains its anterolateral position in the brainstem, immediately dorsal to the olive in the medulla.
Which pyramid extends from the cortex to the kidney?
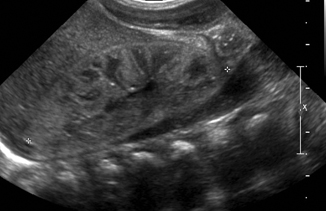
Medullary Pyramid. Medullary pyramids extend from cortex into central kidney, usually less echogenic than cortex. From: Diagnostic Ultrasound: Abdomen and Pelvis, 2016. Download as PDF.
Why is the corticospinal tract called the pyramidal tract?
Because the corticospinal fibers form the medullary pyramids in mammals, it has traditionally been called the ‘pyramidal tract’. The use of this term has the potential to cause some confusion because, by coincidence, the cells of origin are pyramidal neurons in the cerebral cortex. Moreover, it seems that the corticospinal fibers in monotreme mammals do not assemble in a paramedian pyramid as they do in other mammals (Goldby, 1939 ). A further reason to avoid the term ‘pyramidal tract’ is the unfortunate and now discredited ‘pyramidal/extrapyramidal’ dichotomy that was created in an attempt to explain the organization, and presumed voluntary versus involuntary components, of the different parts of the motor systems (see discussion in Brodal, 1981 ). For all of these reasons, we prefer to use the term ‘corticospinal tract’.
What is the term for calcification of the medullary pyramids?
NEPHROCALCINOSIS. Medullary nephrocalcinosis refers to calcification in the medullary pyramids rather than the renal collecting system. It is caused by a number of processes, but the three most common are medullary sponge kidney (tubular ectasia), renal tubular acidosis, and hyperparathyroidism.
Why are medullary pyramids more prominent?
The medullary pyramids may be more prominent in many cases of parenchymal disease as the increased cortical reflectivity increases contrast with the echo-poor medullary tissue.
How long does it take for contrast to enhance the kidneys?
The cortices of the kidneys enhance before the medullary pyramids do, and within about 30 to 45 seconds of intravenous contrast agent administration, the corticomedullary phase of enhancement is seen, in which only the renal cortices enhance. A short time later, homogeneous enhancement of the kidneys can be seen during the nephrographic phase of enhancement, when the cortices and medullary pyramids enhance. Finally, after a few minutes, contrast material that is excreted by the kidneys can be seen within the collecting systems, ureters, and bladder during the delayed or excretory phase of enhancement.
Where are olives located in the medulla?
Axial graphic of the upper medulla shows the medullary pyramids on each side of the ventral median fissure. The olives lie just posterior to the preolivary sulci .
What are renal pyramids?
Renal pyramids are kidney tissues that are shaped like cones. Another term for renal pyramids is malpighian pyramids. Between seven and eighteen pyramids exist in the innermost part of the kidney, which is called the renal medulla; in humans, there are usually only seven of the pyramids. The base of each pyramid faces the outer portion ...
Why do renal pyramids appear as though they are striped?
Renal pyramids appear as though they are striped because they are situated in segments of parallel nephrons. The nephron is the basic functional and structural unit of the kidney that filters the blood that regulates water concentration and soluble substances such as sodium salts.
Where is the renal cortex located?
The renal cortex is located between the renal medulla and the renal capsule. The renal capsule is defined as the layer that surrounds the kidneys with tough fibrous tissue. The capsule is covered in a connective fatty tissue. Renal pyramids appear as though they are striped because they are situated in segments of parallel nephrons.
What Is the Renal Medulla?
Did you ever wonder what the interior portion of a kidney is called? Well, maybe not, but you're about to find out. It's called the renal medulla. The word 'renal' comes from the Latin name for 'kidney' and can be used in both an anatomical or diagnostic sense. For instance, 'renal disease' means a disease of the kidneys. The word 'medulla' means 'middle' and comes from the Latin word for 'marrow,' the interior portion of bone. So, the renal medulla is found in the inside region of the kidney.
What is the filtering process in the renal medulla pyramid?
The filtering that occurs in the renal medulla pyramids is fairly simple and occurs in relation to size. Small particles, like sodium, calcium, potassium and chlorine ions, pass through the filter to be excreted. Glucose, the basic molecule of sugar, is also small enough to be filtered out this way.
What is the function of the renal medulla?
The renal medulla is the interior portion of the kidney where the primary functions of the organ occur: the filtering of waste materials and elimination of fluid from the body. The kidney filters blood and sends waste materials to the bladder to become excreted urine. Inside the renal medulla are pyramids, each of which contains thousands ...
What is the outermost layer of the kidney?
The outermost layer of the kidney is a tough, protective skin called the renal capsule. Under that is a layer filled with blood vessels and tubules called the renal cortex. Underneath the cortex, we find the center of the kidney, the renal medulla. The main structures inside the medulla are pyramid-shaped; they're called the renal pyramids.
What is the interior of the kidney?
The interior of your kidney is where all the action happens. In the renal medulla, your kidney gets to work filtering blood and balancing your body's fluids, a process that eventually leads to the release of urine. In this lesson, you'll learn about the different parts of the renal medulla and how they work. Create an account.
How many pyramids are there in the kidney?
The apex of each pyramid faces the center of the kidney and is connected to urine-collecting tubules. Each kidney's renal medulla has between 27 and 30 pyramid s, and each of these is made up of tens of thousands of nephrons.
How many kidneys are there in the human body?
If you're lucky, you have two kidneys in your body. Each performs the same major functions, which include filtering out waste, eliminating and balancing fluids and controlling blood pressure. The main function of the kidneys, and the one that we experience several times a day as we go to the bathroom, is to filter out waste and produce urine to be eliminated from the body.
What are renal pyramids?
Renal pyramids are kidney tissues that are shaped like cones. Another term for renal pyramids is malpighian pyramids. Between seven and eighteen pyramids exist in the innermost part of the kidney, which is called the renal medulla in humans, there are usually only seven of the pyramids.
Why are medullary pyramids more prominent?
The medullary pyramids may be more prominent in many cases of parenchymal disease as the increased cortical reflectivity increases contrast with the echo-poor medullary tissue. In other cases there may be a decrease in the degree of corticomedullary differentiation so that the pyramids are poorly defined or even indistinguishable as separate structures . However, as with cortical reflectivity, there is no correlation with the aetiology of the renal disease.3 In acute conditions involving primarily the medulla, such as acute tubular necrosis, the pyramids can be enlarged due to oedema. Increased medullary reflectivity can be detected in nephrocalcinosis of any aetiology and also in some other conditions such as gout.
What is the role of the vasa recta in the kidney?
These vessels play an important role in the maintenance of mass balance and osmotic gradient in the medulla by returning the NaCl and water reabsorbed in the LOH and medullary collecting tubule to the systemic circulation. The vasa recta function as countercurrent exchangers to delay the washout of NaCl and urea and prevent the excess accumulation of water in the inner medulla. In the developing rat kidney, vasa recta bundles grow centrally into the medulla around the previously developed collecting ducts.
How to homogenize renal cortex?
Frozen renal cortex or medulla were firstly placed into pre-cooled 2mL homogenization tubes containing ceramic beads. Then, pre-cooled methanol was added . The samples were homogenized for three times , with 60s intervals between homogenization steps. After two centrifugations , the supernatant was removed and named as kidney homogenate. For LC-MS analysis, 125L acetonitrile was added to a 25L aliquot of the kidney homogenate. The solution was mixed thoroughly and centrifuged twice , and the supernatant was removed for LC-MS analysis. For GC-MS analysis, 100L methanol was added to a 10L kidney homogenate. The next derivation steps referred to our previous studies,.
What is the function of the renal medulla?
The renal medulla is the interior portion of the kidney where the primary functions of the organ occur: the filtering of waste materials and elimination of fluid from the body. The kidney filters blood and sends waste materials to the bladder to become excreted urine.
What is the function of the kidneys?
Nephrons perform the primary function of the kidneys: regulating the concentration of water and other substances in the body. They filter the blood, reabsorb what the body needs, and excrete the rest as urine.
Where is the renal papilla located?
The renal papilla is the location where the renal pyramids in the medulla empty urine into the minor calyx in the kidney. Histologically it is marked by medullary collecting ducts converging to form a papillary duct to channel the fluid.