Where does the parasympathetic nervous system start?
Parasympathetic nervous system function. Your PSNS starts in your brain and extends out via long fibers that connect with special neurons near the organ they intend to act on. Once PSNS signals hit these neurons, they have a short distance to travel to their respective organs.
Where do parasympathetic nerves come from?
Trusted Source. of all parasympathetic nerve fibers in the body come from this nerve. This nerve has branches in many key organs, including the stomach, kidneys, liver, pancreas, gallbladder, bladder, anal sphincter, vagina, and penis.
What is the acronym for parasympathetic response?
Examples of parasympathetic responses. An easy acronym to remember how and where the PSNS works is SLUDD. This stands for: Salivation: As part of its rest-and-digest function, the PSNS stimulates production of saliva, which contains enzymes to help your food digest.
How does the PSNS work?
An easy acronym to remember how and where the PSNS works is SLUDD. This stands for: 1 Salivation: As part of its rest-and-digest function, the PSNS stimulates production of saliva, which contains enzymes to help your food digest. 2 Lacrimation: Lacrimation is a fancy word for making tears. Tears keep your eyes lubricated, preserving their delicate tissues. 3 Urination: The PSNS contracts the bladder, which squeezes it so urine can come out. 4 Digestion: The PSNS stimulates the release of saliva to promote digestion. It also enacts peristalsis, or the movement of the stomach and intestines, to digest food as well as release bile for the body to digest fats. 5 Defecation: The PSNS constricts the sphincters in the intestine and moves digested food material down the digestive tract so a person can have a bowel movement.
What happens if your parasympathetic nervous system doesn't work?
Your PSNS is a vital part of your body’s key functions. When it doesn’t work properly, you can face a number of bodily dysfunctions that affect your health. If you think you may be having trouble with one of your body’s parasympathetic nervous system functions, talk to your doctor to find out how you can get help.
What is the nervous system?
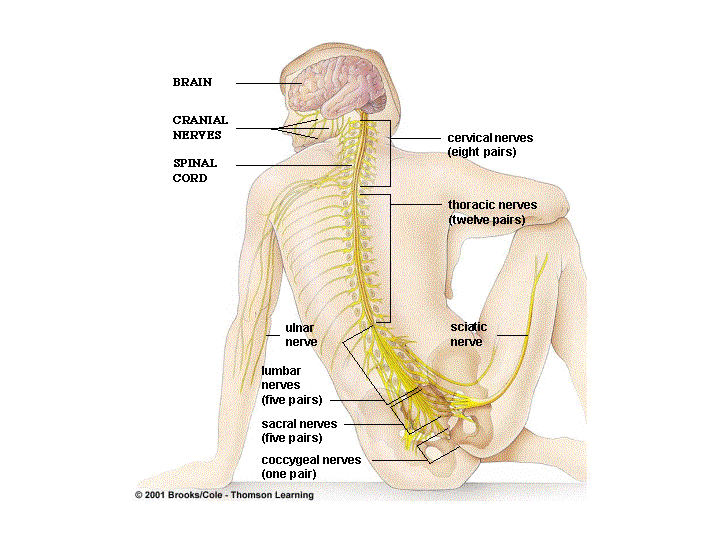
Your nervous system is a wild and wonderful network of nerves that act in different key functions to keep your body moving, responding, sensing, and more. This article is going to examine the parasympathetic nervous system, one of two majors divisions of the larger autonomic system. In the simplest terms, the parasympathetic ...
How does heart failure affect the nervous system?
For example, heart failure reduces the response of the parasympathetic nervous system. The results can be an increased heart rate, which is the body’s way of trying to improve the amount of blood it pumps through the body.
Which nerves are parasympathetic?
Specific nerves include several cranial nerves, specifically the oculomotor nerve, facial nerve, glossopharyngeal nerve, and vagus nerve. Three spinal nerves in the sacrum (S2-4), commonly referred to as the pelvic splanchnic nerves, also act as parasympathetic nerves. Owing to its location, the parasympathetic system is commonly referred ...
Who invented the parasympathetic nervous system?
The terminology ‘Parasympathetic nervous system’ was introduced by Langley in 1921. He was the first person who put forward the concept of PNS as the second division of the autonomic nervous system.
What is the vagus nerve?
The vagus nerve is an unusual cranial parasympathetic in that it doesn't join the trigeminal nerve in order to get to its target tissues. Another peculiarity is that the vagus has an autonomic ganglion associated with it at approximately the level of C1 vertebra. The vagus gives no parasympathetic to the cranium. The vagus nerve is hard to track definitively due to its ubiquitous nature in the thorax and abdomen so the major contributions will be discussed. Several parasympathetic nerves come off the vagus nerve as it enters the thorax. One nerve is the recurrent laryngeal nerve, which becomes the inferior laryngeal nerve. From the left vagus nerve the recurrent laryngeal nerve hooks around the aorta to travel back up to the larynx and proximal esophagus while, from the right vagus nerve, the recurrent laryngeal nerve hooks around the right subclavian artery to travel back up to the same location as its counterpart. These different paths are a direct result of embryological development of the circulatory system. Each recurrent laryngeal nerve supplies the trachea and the esophagus with parasympathetic secretomotor innervation for glands associated with them (and other fibers that are not PN).
How many neurons are involved in the efferent parasympathetic nerve?
As in the sympathetic nervous system, efferent parasympathetic nerve signals are carried from the central nervous system to their targets by a system of two neurons. The first neuron in this pathway is referred to as the preganglionic or presynaptic neuron.
What is the mechanism by which the parasympathetic nervous system acts on vascular and cardiac control?
The main mechanism by which the parasympathetic nervous system acts on vascular and cardiac control is the so-called respiratory sinus arrhythmia (RSA).
What nerves are responsible for the movement of the eye?
The oculomotor nerve is responsible for a number of parasympathetic functions related to the eye. The oculomotor PNS fibers originate in the Edinger-Westphal nucleus in the central nervous system and travel through the superior orbital fissure to synapse in the ciliary ganglion located just behind the orbit (eye). From the ciliary ganglion the postganglionic parasympathetic fibers leave via short ciliary nerve fibers, a continuation of the nasociliary nerve (a branch of ophthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve (CN V 1 )). The short ciliary nerves innervate the orbit to control the ciliary muscle (responsible for accommodation) and the iris sphincter muscle, which is responsible for miosis or constriction of the pupil (in response to light or accommodation). There are two motors that are part of the oculomotor nerve known as the somatic motor and visceral motor. The somatic motor is responsible for moving the eye in precise motions and for keeping the eye fixated on an object. The visceral motor helps constrict the pupil.
Where do postganglionic parasympathetic fibers leave?
The postganglionic parasympathetic fibers leave the pterygopalatine ganglion in several directions. One division leaves on the zygomatic division of CN V 2 and travels on a communicating branch to unite with the lacrimal nerve (branch of the ophthalmic nerve of CN V 1) before synapsing at the lacrimal gland.
What is the function of the parasympathetic nervous system?
The parasympathetic nervous system is also referred to as the ‘rest and digest’ system as it functions to conserves the body’s natural activity, and relaxes the individual once an emergency has passed. The parasympathetic nervous system leads to decreased arousal.
What is the parasympathetic system?
Parasympathetic Nervous System Dysfunction. Dysfunctions within the PSNS can be varied and may only affect one or more organs. If the nerves in the system are damaged, this can interfere with messages being sent between the brain and organs such as the heart, blood vessels and sweat glands.
What is the difference between parasympathetic and sympathetic?
Parasympathetic Nervous System and the Fight or Flight Response. Sympathetic activation prepares us for fight or flight, while parasympathetic activation is associated with normal functioning under relaxed conditions.
Why do PSNS come into action?
The PSNS can also come into action after a stressful situation has concluded, essentially undoing all the work that the SNS has done to stimulate the body. When stressed, the PSNS triggers the necessary responses in order to return to homeostasis (the maintaining of balancing internal physiology).
Where is acetylcholine found?
Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter found in both the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system and plays a role in brain and muscle function. The preganglionic neurons within the thoracic and lumbar regions in the spinal cord carry acetylcholine and release it at synapses within the ganglia.
What nerves are in the sacral region?
As well as cranial nerves , there are three spinal nerve types which project from the sacral region of the spinal cord (known as S2, S3, and S4). The sacrum nerves send signals to regions of the bladder, reproductive organs, and the colon.
Where does the PSNS begin?
The PSNS begins in the brain and branches out via long fibers, which lead to connecting neurons that are near the organs they intend to act upon, enabling quick responses. Another branch of the PSNS is the sympathetic nervous system (SNS).
What is the function of the parasympathetic system?
The parasympathetic activity increases the contraction of smooth muscles present in the wall of the gut. Thus, it promotes peristalsis and the process of digestion. The parasympathetic system also promotes the. secretions of different glands associated with the alimentary tract.
What are the two types of nerves in the parasympathetic nervous system?
The parasympathetic system also has two types of nerve. fibers: Pre-ganglionic nerve fibers: These nerve fibers originate from the central nervous system and terminate at the ganglia of the parasympathetic nervous system. Contrary to the sympathetic nervous system, the pre-ganglionic fibers in PSNS are long.
Why is the parasympathetic system important?
The parasympathetic system is important in regulating the blood pressure under resting conditions. It prevents any abnormal increase in blood pressure. If the blood pressure increases due to any reason, it is sensed by the baroreceptor system.
Which system has longer preganglionic fibers?
Ganglia. Ganglia are the collections of neuronal cell bodies located outside the CNS. As stated earlier, the parasympathetic system has longer preganglionic fibers because the ganglia are present away from the CNS. They are present near the effector organs.
Where are muscarinic receptors located?
The muscarinic receptors are present in the ciliary#N#muscles as well as the circular muscles of the eye. The activation of#N#muscarinic receptors by parasympathetic activity causes smooth muscle#N#contraction. The contraction of circular muscles constricts the pupil while#N#contraction of ciliary muscles cause accommodation for near vision.
What are the chemicals released by the axons at the nerve terminals?
Neurotransmitters. These are the chemicals released by the axons at the nerve terminals. They bind to the specific receptors present on the target tissue and initiate chemical responses. The main neurotransmitter present in the parasympathetic system is acetylcholine.
Which system stimulates the process of urination?
The process of urination is also stimulated by the parasympathetic system. The parasympathetic stimulation contracts the bladder muscles and relaxes the smooth muscles present in sphincters. The combined effect helps in voiding the bladder.
Parasympathetic Nervous System Definition
What is parasympathetic? The parasympathetic nervous system is the division of the autonomic nervous system that regulates resting and relaxation of the body. The other division of the autonomic nervous system is the sympathetic nervous system, which is important for the fight or flight response in the body.
Parasympathetic Nervous System Functions
The main function of the parasympathetic nervous system is as the "rest and digest" division. The parasympathetic nervous system is the part of the autonomic nervous system that is usual active. It controls many of our bodily functions, including digestion and relaxation.
What is the parasympathetic nervous system?
The parasympathetic nervous system is a division of the autonomic nervous system. It is involuntary, and acts with the sympathetic system to maintain body homeostasis. The actions of the parasympathetic nervous system are associated with the 'rest and digest' response. In this article, we shall look anatomy of the parasympathetic innervation to ...
Where do parasympathetic nerves originate?
The parasympathetic fibres begin in the central nervous system. The nerves supplying the head and neck are situated within four nuclei, located within the brainstem.
What muscle is responsible for constricting the pupil?
The ciliary ganglion provides innervation to the sphincter pupillae muscle, which acts to constrict the pupil. If the ciliary ganglion is damaged, there is a loss of innervation to the sphincter pupillae. This results in a permanently dilated pupil that does not constrict in the presence of light.
What are the four parasympathetic ganglia?
There are four parasympathetic ganglia located within the head – the ciliary, otic, pterygopalatine and submandibular. They receive fibres from the oculomotor, facial and glossopharyngeal nerves (the vagus nerve only innervates structures in the thorax and abdomen).
Where is the ciliary ganglion located?
The ciliary ganglion is located within the bony orbit. It is situated anteriorly to the superior orbital fissure, between the lateral rectus muscle and the optic nerve. Pre-ganglionic fibres: The ciliary ganglion is supplied by fibres from the Edinger-Westphal nucleus (associated with the oculomotor nerve).
Where is the pterygopalatine ganglion located?
The pterygopalatine ganglion (also known as sphenopalatine) is the largest of the four parasympathetic ganglia. It is located within the pterygopalatine fossa – a space located inferiorly to the base of the skull, and posteriorly to the maxilla.
Where are pre-ganglionic fibres found?
These fibres are carried within a branch of the facial nerve, the chorda tympani. This nerve hitch-hikes along the lingual branch of the mandibular nerve to reach the ganglion.