
How many answers to lower posterior part of brain (10/908716) crossword clue?
The Crossword Solver found 20 answers to the lower posterior part of the brain (10)/908716 crossword clue. The Crossword Solver finds answers to American-style crosswords, British-style crosswords, general knowledge crosswords and cryptic crossword puzzles. Enter the length or pattern for better results.
What is the posterior view of the brainstem?
Anatomy of the brainstem and related structures (posterior view) The posterior surface of the pons is intimately connected with the fourth ventricle and the cerebellum.
What is the posterior parietal cortex?
The posterior parietal cortex comprises the region of the parietal cortex that is posterior to the primary somatosensory cortex and its adjacent sulcus, the postcentral sulcus. The posterior parietal cortex itself is divided into an upper and lower portion: the superior parietal lobule and inferior parietal lobule, respectively.
Where is the posterior cerebral artery located in the body?
It is located on the left and right sides of the head and is relatively short. The posterior cerebral arteries branch off from the basilar artery. The left and right PCAs form the longest sections of the circle of Willis. The internal carotid arteries are located in the front of the neck.
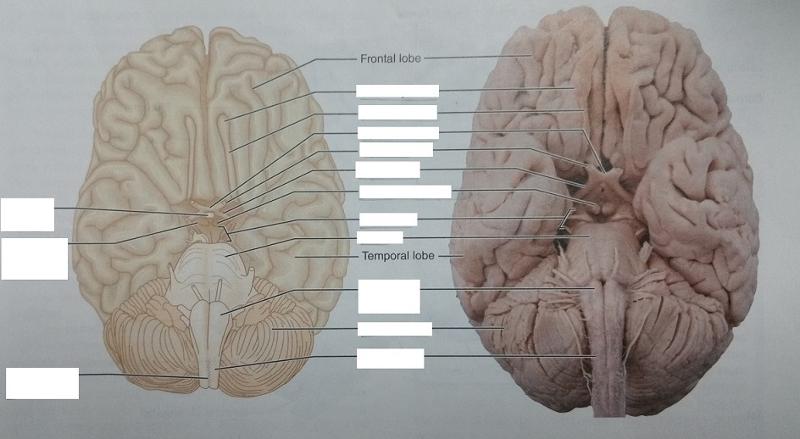
What part of the brain is posterior?
Posterior cortex usually means the posterior (back) part of the complete cerebral cortex and includes the occipital, parietal, and temporal cortices. In other words, the posterior cortex includes all the cerebral cortex without the frontal cortex.
What does the posterior brain control?
The posterior parietal cortex is also believed to be involved in some aspects of motor function, such as planning movements and integrating visual information with movement to facilitate actions like reaching and grasping.
Which side of the brain controls memory?
rightOur brains have two sides, or hemispheres. In most people, language skills are in the left side of the brain. The right side controls attention, memory, reasoning, and problem solving. RHD may lead to problems with these important thinking skills.
What part of the brain controls memory?
HippocampusHippocampus. A curved seahorse-shaped organ on the underside of each temporal lobe, the hippocampus is part of a larger structure called the hippocampal formation. It supports memory, learning, navigation and perception of space.
What does the posterior association area do?
The multimodal posterior association area receives inputs from the visual and auditory systems and from the hippocampus. They result from an inability to perceive objects despite normally functioning sensory systems.
Which lobe of the brain is responsible for breathing?
medulla oblongataThe medulla oblongata controls breathing, blood pressure, heart rhythms and swallowing.
What happens if the right parietal lobe is damaged?
Damage to the right parietal lobe can result in neglecting part of the body or space (contralateral neglect), which can impair many self-care skills such as dressing and washing. Right side damage can also cause difficulty in making things (constructional apraxia), denial of deficits (anosagnosia) and drawing ability.
What lobe is responsible for language comprehension?
posterior superior temporal lobeWernicke's area is a critical language area in the posterior superior temporal lobe connects to Broca's area via a neural pathway. Wernicke's area is primarily involved in the comprehension. Historically, this area has been associated with language processing, whether it is written or spoken.
What are the parts of the brain?
Parts of the Brain: Structures, Anatomy and Functions. The human brain is one of the largest and most complex organs in the body. It controls your emotions, thoughts, speech, memory, creativity, breathes, movement, and stores information from the outside world. This article discusses the different parts of the brain and the function ...
What is the largest part of the brain?
The cerebrum is the largest part of the human brain. It has a rough surface (cerebral cortex) with gyri and sulci. It can also be divided into 2 parts: the left hemisphere and the right hemisphere.
How many lobes are there in the brain?
There are 3 main parts of the brain include the cerebrum, cerebellum, and brain stem. The Cerebrum can also be divided into 4 lobes: frontal lobes, parietal lobes, temporal lobes, and occipital lobes. The brain stem consists of three major parts: ...
Which lobe of the brain controls facial expressions?
The occipital lobe is located at the rear of our brain. This lobe is responsible for our visual awareness, including visual attention, optical recognition, and spatial awareness. It also controls our ability to interprets body language like facial expressions, gestures, and body postures.
What is the function of the cerebellum?
The function of the cerebellum also includes maintaining posture, equilibrium, body balance, and even speech. 3. Brainstem. The brain stem is the posterior part of the brain that connects the brain with the spinal cord.
What is the role of the midbrain?
It plays a key role in controlling voluntary motor function and transferring messages. In addition, it controls eye movement and processes auditory, visual information, and eye movement.
Where is the cerebellum located?
The cerebellum, also known as the little brain, is located in the back of the brain. It sits just below the occipital lobes and on top of the pons. Just like the cerebrum, the cerebellum has two equal hemispheres and a wrinkly surface. Although the cerebellum is small, it contains numerous neurons.
Where is the cerebellum located?
The cerebellum (“little brain”) is a fist-sized portion of the brain located at the back of the head, below the temporal and occipital lobes and above the brainstem. Like the cerebral cortex, it has two hemispheres. The outer portion contains neurons, and the inner area communicates with the cerebral cortex.
Which part of the brain controls movement?
The largest part of the brain, the cerebrum initiates and coordinates movement and regulates temperature. Other areas of the cerebrum enable speech, judgment, thinking and reasoning, problem-solving, emotions and learning. Other functions relate to vision, hearing, touch and other senses.
What is the brain made of?
Weighing about 3 pounds in the average adult, the brain is about 60% fat. The remaining 40% is a combination of water, protein, carbohydrates and salts. The brain itself is a not a muscle. It contains blood vessels and nerves, including neurons and glial cells.
How does the brain work?
The brain sends and receives chemical and electrical signals throughout the body. Different signals control different processes, and your brain interprets each. Some make you feel tired, for example, while others make you feel pain.
Where is the spinal cord located?
The spinal cord extends from the bottom of the medulla and through a large opening in the bottom of the skull. Supported by the vertebrae, the spinal cord carries messages to and from the brain and the rest of the body.
How many halves are there in the cerebral cortex?
The cerebral cortex is divided into two halves, or hemispheres. It is covered with ridges (gyri) and folds (sulci). The two halves join at a large, deep sulcus (the interhemispheric fissure, AKA the medial longitudinal fissure) that runs from the front of the head to the back.
Which hemisphere controls the left side of the body?
The right hemisphere controls the left side of the body, and the left half controls the right side of the body. The two halves communicate with one another through a large, C-shaped structure of white matter and nerve pathways called the corpus callosum. The corpus callosum is in the center of the cerebrum.
What is the role of the posterior communicating artery?
The artery connects the internal carotid and the posterior cerebral arteries. Its role is to provide blood supply to the brain. The posterior communicating artery is a location where aneurysms can potentially occur.
Which artery supplies blood to the occipital and temporal lobes?
The posterior cerebral arteries provide blood to the occipital and temporal lobes, midbrain, thalamus, and choroid plexus. The internal carotid supplies the head and brain with blood.
What is the location of an aneurysm?
Aneurysm. The posterior communicating artery is a potential location of aneurysms. An aneurysm is a bulging area in an artery. Although aneurysms in the circle of Willis most commonly occur in the anterior communicating artery, those in the posterior circulation account for 15% to 20% of all intracranial aneurysms. 1.
Where is the PCOM located?
The PCOM is located in the back of the head at the back end of the circle of Willis. It is located on the left and right sides of the head and is relatively short. The posterior cerebral arteries branch off from the basilar artery. The left and right PCAs form the longest sections of the circle of Willis.
How to tell if you have a TBI?
TBIs are usually diagnosed by a CT scan or MRI. Treatment may include medication or surgery to temporarily remove part of the skull to accommodate swelling.
What is the term for a blockage of blood flow in the brain?
Stroke. A stroke occurs when there is an interruption of blood flow in an artery. This blockage keeps blood from reaching its destination in the brain, resulting in a loss of function in the affected region.
Overview
Posterior cortical atrophy is a rare, degenerative brain and nervous system (neurological) syndrome that results in gradually declining vision. Common symptoms include difficulties with reading, judging distances, and recognizing objects and familiar faces.
Products & Services
Crutch SJ, et al. Consensus classification of posterior cortical atrophy. Alzheimer's and Dementia. 2017;13:870.
What is the cerebellum and brainstem?
The cerebellum and brainstem are a testament to the fact that good things do come in small packages, so this article is an overview of their anatomy. Occupying only a fraction of the volume of the cerebrum, these structures are responsible for simplifying every second of your life and keeping you alive.
Which structure houses the majority of the cranial nerve nuclei?
Cranial nerve nuclei. Now that we’ve clarified the external structure of the brainstem, let’s take a closer look at its internal structure. The brainstem houses the majority of the cranial nerve nuclei, except those involved with olfaction ( olfactory nerve (CN I)) and vision ( optic nerve (CN II) ).
What are the three pairs of peduncles that connect the cerebellum to the brain?
The cerebellum is connected to the brainstem by three pairs of cerebellar peduncles: the superior peduncle with the midbrain, the middle peduncle with the pons, and the inferior peduncle with the medulla oblongata.
What are the features of the Medulla Oblongata?
These include the posterior medial sulcus, cuneate and gracile fasciculi, cuneate and gracile tubercles (respective nuclei), trigeminal tubercle ( spinal nucleus of the trigeminal nerve ), lateral funiculus (lateral white matter fibers), inferior half of the rhomboid fossa (floor of the fourth ventricle ), and the obex. The arterial supply of the medulla oblongata is provided by the anterior and posterior inferior cerebellar arteries, together with the anterior spinal artery.
How many lobes does the cerebellum have?
The cerebellum consists of two large hemispheres united in the middle by the vermis. Numerous transverse fissures divide the cerebellum into three lobes (anterior, posterior, and flocculonodular) and many lobules. The flocculonodular lobe consists of a flocculus and a nodule.
Which part of the brain is responsible for the cardiac, respiratory, reflex, and vasomotor functions?
The medulla oblongata is the most inferior portion of the brain stem, sitting in the posterior cranial fossa. It is continuous with the spinal cord from below and the pons above. The medulla oblongata is responsible for various autonomic functions and contains the cardiac, respiratory, reflex, and vasomotor centers.
Where are the nuclei of the reticular formation located?
The nuclei of the reticular formation are located deep within the brainstem and are divided into median, medial, and lateral groups. The afferent and efferent pathways associated with the reticular formation are the spinothalamic, dorsal column-medial lemniscus, reticulobulbar, and reticulospinal tracts.
Which part of the brain contains the thalamus, hypothalamus, and pituitary gland?
Tetanus. The posterior part of the brain that contains the thalamus, hypothalamus, and pituitary gland is the: Diencephalon. X is a disorder in the brain in which certain parts of the brain are overactive, producing convulsive seizures and possible loss of consciousness. Epilepsy.
What is the bridge that connects the spinal cord with the brain and parts of the brain with each other?
X is a bridge that connects the spinal cord with the brain and parts of the brain with each other. Pons Varolii. The thin membrane that lines the eyelids and covers part of the eye is called: Conjunctiva.
What is the X of the midbrain?
The X of the midbrain is a reflex center that controls movement of the head and eyeballs in response to visual stimuli and the head and trunk in response to auditory stimuli. Dorsal Tectum. A (n) X is an enlargement or dilation of a blood vessel wall, commonly referred to as ballooning. Aneurysm.
Which lobe of the brain is responsible for the transmission of sound waves?
The ear is adapted to pick up sound waves and transmit them to the auditory center of the brain located in the X lobe.
Which lobe of the brain is responsible for coordinating complex skeletal muscular movements?
Olfactory signals are transmitted to the X lobe. Frontal. The X is the second largest portion of the brain and functions as a reflex center in coordinating complex skeletal muscular movements, maintaining proper body posture, and keeping the body balanced. Cerebellum.
Where is the X in the ear?
The X is the snail-shaped structure in the inner ear where sound vibrations are converted into nerve impulses.
Which gland produces tears?
Tears are produced by the X gland.
