
Does ulnar nerve entrapment go away by itself?
Ulnar nerve injuries happen all the time. Sometimes, it may go away on its own, but if the problems persist for several weeks, treatment is very important: ulnar entrapment could wear away or stiffen the muscles in severe cases, sometimes even causing the hand to atrophy into a claw
Which arteries supply blood to the ulnar nerve?
- A nterior ulnar recurrent
- P osterior ulnar recurrent
- C ommon interosseous
- D orsal carpal branch
- D eep palmar branch
- P almar carpal branch
What vein runs with right marginal artery?
The right marginal vein is a small vein that drains blood from the heart. It passes along the inferior margin of the heart and joins the small cardiac vein (sometimes known as the right coronary vein) in the coronary sulcus, or opens directly into the right atrium.
How is ulnar artery thrombosis diagnosed and treated?
- Pain at the little finger side of your wrist
- clicking or popping noise in the wrist linked with sharp pain with the movement
- Loss of movement at the wrist particularly with rotation of your forearm and with lateral movement of your wrist towards the pinky side (ulnar deviation)
- Loss of strength in your hand while gripping strongly, linked with pain
What is the ulnar artery?
Which artery divides to give the ulnar and radial arteries?
How long is the palmar canal?
What is the name of the tunnel that passes through the hamate?
Which artery runs down the forearm?
Which artery forms a network of collateral circulation around the elbow joint?
Which artery separates the ulnar artery from the median nerve?
See more

What does the right ulnar artery supply?
Supply. The ulnar artery supplies the periarticular anastomoses of the elbow via the anterior and posterior ulnar recurrent arteries. It also supplies the medial and central forearm muscles, the median and ulnar nerves, and the common flexor sheath 1.
Is the ulnar artery important?
Although the muscles of the forearm and hand may have vascular contributions from more than one source, the ulnar artery plays a significant role in the blood supply to the following muscles: flexor carpi ulnaris, palmaris longus, flexor carpi radialis, flexor digitorum superficialis, flexor digitorum profundus, and ...
What happens if the ulnar artery is blocked?
Patients with ulnar artery thrombosis at the wrist may present with pain at night or with repetitive activity and cold intolerance. Exquisite tenderness is present at the site of pathology. Eventually, patients may have dependent rubor or ulceration of the ring finger and the tips of the little fingers.
Where do you palpate ulnar artery?
wristUlnar artery is located below the 5th digit at the proximal skin crease of the wrist 3. Compress both radial and ulnar arteries firmly using three fingers or thumb 4. Ask the patient to clench and unclench their fist 10 times, then open the hand into a relaxed, slightly flexed position.
What is the ulnar artery function?
The ulnar artery, along with the radial artery, is responsible for the arterial supply to the forearm and hand. The ulnar artery arises in the cubital fossa and traverses through the medial (ulnar) side of the forearm and ends within the medial portion of the hand as the superficial palmar arch.
What fingers does ulnar artery supply?
It brings blood supply to the index finger along its thumb side. The other side (ulnar side) of the index finger is supplied by a branch of a common digital artery.
Which artery is the most common to have blockage?
Importance in cardiovascular diseases: The LAD artery is the most commonly occluded of the coronary arteries. It provides the major blood supply to the interventricular septum, and thus bundle branches of the conducting system.
What does a blocked artery in your arm feel like?
Heaviness. Cramps. Skin that feels colder than usual. A weaker pulse in your arm.
What are the signs of artery blockage?
At other times, especially when the artery is blocked by 70% or more, the buildup of arterial plaque may cause symptoms that include:Chest pain.Shortness of breath.Heart palpitations.Weakness or dizziness.Nausea.Sweating.
How do you assess ulnar artery?
0:291:39How to Perform a Modified Allen's Test - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAsk the patient to make a tight clenching fists for about 30 seconds. Apply firm pressure over theMoreAsk the patient to make a tight clenching fists for about 30 seconds. Apply firm pressure over the ulnar and the radial arteries occluding both of them.
Where is your artery in your wrist?
Where is the radial artery? The radial artery runs on the inside of the forearm from the elbow to the thumb. The artery lies just under the surface of the skin. You may be able to see the blue or purple vein inside your wrist where the artery brings blood to the thumb.
What is ulnar artery thrombosis?
Thrombosis of the distal ulnar artery is an uncommon, often unrecognized complication of trauma to the hand. The diagnosis is often missed or delayed. Other names for this disease include hypothenar hammer syndrome, posttraumatic digital ischemia, and pneumatic tool disease.
What is the ulnar artery?
Ulnar artery. The upper limb is crucial to the basic functions we need in our daily lives. As such, its vascular supply is important knowledge to have, both for anatomy examinations and clinical practice. The word ‘ulna’ means elbow in Latin, which relates to the prominent olecranon process of the ulna.
Which artery divides to give the ulnar and radial arteries?
The brachial artery descends down the arm (first medial to the medial nerve and then lateral at the elbow ), passes deep to the bicipital aponeurosis and once it reaches the elbow, divides to give the ulnar and radial artery. The ulnar artery is rarely a branch of the axillary artery.
How long is the palmar canal?
The length of the canal is usually around 4cm in length with the distal end limited by the aponeurotic arch of the hypothenar muscles. Superficial palmar arch is the primary blood supply to the fingers and is the direct continuation of the ulnar artery once it enters the hand.
What is the name of the tunnel that passes through the hamate?
It does pass in its own tunnel, known as Guyon’s canal, with the artery passing laterally to the nerve. The superficial palmar carpal ligament forms the roof of Guyon’s canal and the hypothenar muscles and flexor retinaculum form the floor. The tunnel is bound medially by the pisiform, laterally by the hamate, and the floor by ...
Which artery runs down the forearm?
Forearm. The ulnar arter y then gives off the common interosseus artery which then divides to give the anterior and posterior interosseous arteries. These run down the forearm either side of the interosseus membrane that connects both the forearm bones.
Which artery forms a network of collateral circulation around the elbow joint?
The brachial artery forms a network of collateral circulation around the elbow joint via the superior and inferior ulnar collaterals that are renamed the anterior and posterior ulnar recurrent arteries when they pass anterior and posterior to the medial epicondyle respectively.
Which artery separates the ulnar artery from the median nerve?
The ulnar head of pronator teres separates the ulnar artery from the median nerve (which passes between the two heads of pronator teres). The ulnar artery lies between flexor digitorum superficialis and flexor carpi ulnaris along most of its length and gives perforating branches to the muscles on the ulnar side of the forearm.
Where is the Ulnar artery?
Ulnar artery. The ulnar artery branches off from the brachial artery below the bend of the elbow, at the area known as the cubital fossa. It runs the length of the forearm and ends at the superficial palmar arch. Here, it joins with the radial artery .
What are the branches of the ulnar arteries?
These are known as the common palmar digital arteries. Other branches of the ulnar arteries include the posterior and anterior ulnar recurrent arteries.
What is the superficial palmar arch?
The superficial palmar arch is also known as the superficial volar arch. The ulnar artery, like its radial counterpart, delivers oxygenated blood to the forearm and the smaller arteries in the hand. These arteries should not be confused with veins. The similarly-named veins drain oxygen-depleted blood away from the forearm and hands.
Where does the ulnar artery originate?
below the elbow, but more frequently higher, the brachial being more often the source of origin than the axillary.
Where is the ulnar vein?
The ulnar artery, the larger of the two terminal branches of the brachial, begins a little below the bend of the elbow in the cubital fossa, and, passing obliquely downward, reaches the ulnar side of the forearm at a point about midway between ...
What is the median nerve?
The median nerve is in relation with the medial side of the artery for about 2.5 cm.
Which branch of the ulnar artery passes through the hypothenar muscles to anastomos
Hand: Deep palmar branch of ulnar artery which passes through the hypothenar muscles to anastomose with the deep palmar arch which is formed predominantly by the radial artery and the terminal branch of the ulnar artery is then to form the superficial palmar arch .
Which artery is the main blood vessel of the medial aspect of the forearm?
The ulnar artery is the main blood vessel, with oxygenated blood, of the medial aspects of the forearm. It arises from the brachial artery and terminates in the superficial palmar arch, which joins with the superficial branch of the radial artery.
What is the palm of the right hand?
Palm of (corrected) right hand, showing position of skin creases and bones, and surface markings for the volar arches. Front of right upper extremity, showing surface markings for bones, arteries, and nerves. The ulnar artery is the main blood vessel, with oxygenated blood, of the medial aspects of the forearm.
Which nerve is on the medial side of the lower two-thirds of the artery?
It is accompanied by two venæ comitantes, and is overlapped in its middle third by the Flexor carpi ulnaris; the ulnar nerve lies on the medial side of the lower two-thirds of the artery, and the palmar cutaneous branch of the nerve descends on the lower part of the vessel to the palm of the hand.
Where is the ulna located?
In other words, the ulna can be found between the proximal carpal row and the upper arm bone humerus, running parallel to the other lower arm bone radius [3, 5].
What is the ulna?
Ulna (plural: ulnae; pronunciation: úl-nu) is one of the two primary bones forming the forearms in humans, the other one being the radius. There is one ulna bone in each arm. It is a long bone [1] and is vital in the formation of both the wrist and elbow joints [2]. Ulna.
What are the four bony landmarks of the proximal end of the ulna?
At the proximal end of ulna, there are four important bony landmarks, the olecranon process, coronoid process, trochlear notch, and the radial notch [7]. Another notable prominence is the tuberosity of ulna.
How many bones are in the ulna?
The ulna articulates with only two bones, joining with the humerus and the proximal end of the radius on its proximal end, and the distal end of the radius on its distal end [2]. 1. Proximal or Upper End.
What is the shaft of the ulna?
Shaft. The shaft or body is the long middle part of the ulna bone. Moving down toward the distal side, the shaft tapers gradually [8] and has three prominent surfaces and three borders ― the anterior, posterior, interosseous borders and the anterior, posterior, medial surfaces [3]. The upper part of the shaft is somewhat pyramidal in shape, ...
Which artery supplies the primary blood supply?
Primary blood supply is provided by the ulnar artery, as well as its branch the common interosseous artery, which then further branches into the volar and posterior interosseous arteries, still supplying the ulna [6].
Where is the interosseous border of the ulna?
There is a prominent ridge, known as the interosseous border of the ulna, running down the length of the lateral side of the shaft. This is where the interosseous membrane of the forearm, the thin fibrous sheet of tissue that holds the radius and ulna together, attaches to the ulna [5]. 3. Distal or Lower End.
What is the radial artery?
The radial artery is a major artery in the human forearm. It is close to the surface of the underside of the forearm; when the palm of the hand is pointing upwards, so is the radial artery. The radial artery supplies the arm and hand with oxygenated blood from the lungs. Due to the size of the radial artery, and its proximity to the surface of the arm, this is the most common artery used to measure a patient’s pulse. The pulse is checked at the wrist, where the radial artery is closest to the surface. The radial artery is also commonly used when drawing arterial blood for ‘Arterial Blood Gas’ (ABG) measurement. This is done for three reasons: firstly, it is not the only supplier of blood to the arm. If the radial artery is damaged, the ulnar artery will take over. Secondly, it is easy to access. Thirdly, the radial artery is a superficial artery; this means that damage is easily repaired and rarely endangers the patient.
Where is the pulse checked?
The pulse is checked at the wrist, where the radial artery is closest to the surface. The radial artery is also commonly used when drawing arterial blood for ‘Arterial Blood Gas’ (ABG) measurement. This is done for three reasons: firstly, it is not the only supplier of blood to the arm.
Is the radial artery superficial?
Secondly, it is easy to access. Thirdly, the radial artery is a superficial artery; this means that damage is easily repaired and rarely endangers the patient. Last medically reviewed on February 11, 2015.
Overview
The radial artery is a blood vessel that supplies blood to the forearm (lower part of the arm) and hand. Arteries carry blood out to the body. This blood is oxygenated (carrying oxygen from your lungs to other body parts).
Function
As part of the circulatory system, the radial artery supplies blood from the heart to the forearm. There are many radial artery branches. They supply oxygenated blood to the:
Anatomy
The radial artery runs on the inside of the forearm from the elbow to the thumb. The artery lies just under the surface of the skin. You may be able to see the blue or purple vein inside your wrist where the artery brings blood to the thumb.
Conditions and Disorders
The radial artery is a superficial artery, meaning it is nearer the surface. It isn’t prone to plaque buildup that causes narrowed arteries (atherosclerosis) like some major blood vessels.
Care
These steps can keep the radial artery and the rest of your circulatory system healthy:
What is the ulnar artery?
The ulnar artery is a terminal branch of the brachial artery, arising at the proximal aspect of the forearm. Along with the radial artery, it is one of the main arteries of the forearm.
What are the branches of the ulnar artery?
The main branches of the ulnar artery include the anterior and posterior ulnar recurrent arteries, the common interosseous, the palmar carpal arch, the superficial palmar arch, and the dorsal carpal branch 1.
Which artery terminates at the hand?
The ulnar artery terminates at the hand via its branches; the palmar carpal arch, the superficial palmar arch, and the dorsal carpal branch 1 .
What is the ulnar artery?
Ulnar artery. The upper limb is crucial to the basic functions we need in our daily lives. As such, its vascular supply is important knowledge to have, both for anatomy examinations and clinical practice. The word ‘ulna’ means elbow in Latin, which relates to the prominent olecranon process of the ulna.
Which artery divides to give the ulnar and radial arteries?
The brachial artery descends down the arm (first medial to the medial nerve and then lateral at the elbow ), passes deep to the bicipital aponeurosis and once it reaches the elbow, divides to give the ulnar and radial artery. The ulnar artery is rarely a branch of the axillary artery.
How long is the palmar canal?
The length of the canal is usually around 4cm in length with the distal end limited by the aponeurotic arch of the hypothenar muscles. Superficial palmar arch is the primary blood supply to the fingers and is the direct continuation of the ulnar artery once it enters the hand.
What is the name of the tunnel that passes through the hamate?
It does pass in its own tunnel, known as Guyon’s canal, with the artery passing laterally to the nerve. The superficial palmar carpal ligament forms the roof of Guyon’s canal and the hypothenar muscles and flexor retinaculum form the floor. The tunnel is bound medially by the pisiform, laterally by the hamate, and the floor by ...
Which artery runs down the forearm?
Forearm. The ulnar arter y then gives off the common interosseus artery which then divides to give the anterior and posterior interosseous arteries. These run down the forearm either side of the interosseus membrane that connects both the forearm bones.
Which artery forms a network of collateral circulation around the elbow joint?
The brachial artery forms a network of collateral circulation around the elbow joint via the superior and inferior ulnar collaterals that are renamed the anterior and posterior ulnar recurrent arteries when they pass anterior and posterior to the medial epicondyle respectively.
Which artery separates the ulnar artery from the median nerve?
The ulnar head of pronator teres separates the ulnar artery from the median nerve (which passes between the two heads of pronator teres). The ulnar artery lies between flexor digitorum superficialis and flexor carpi ulnaris along most of its length and gives perforating branches to the muscles on the ulnar side of the forearm.
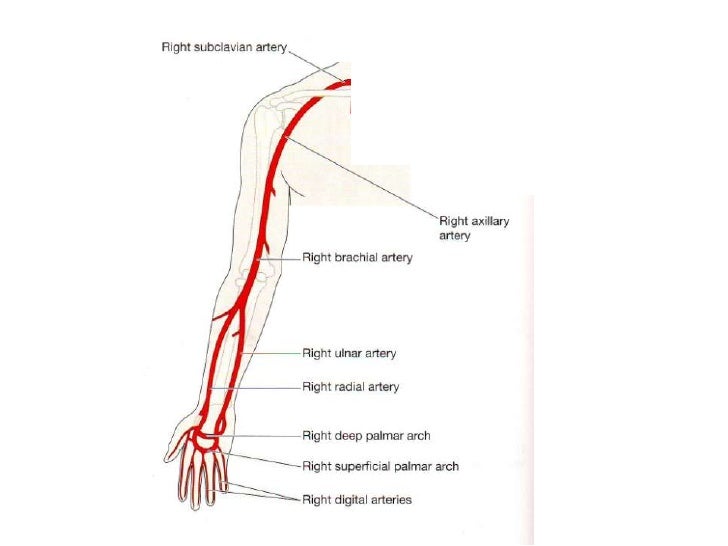
Overview
The ulnar artery is the main blood vessel, with oxygenated blood, of the medial aspects of the forearm. It arises from the brachial artery and terminates in the superficial palmar arch, which joins with the superficial branch of the radial artery. It is palpable on the anterior and medial aspect of the wrist.
Along its course, it is accompanied by a similarly named vein or veins, the ulnar vein or ulnar veins.
Branches
Forearm: Anterior ulnar recurrent artery, Posterior ulnar recurrent artery, Common interosseous is very short, around 1 cm, and gives rise to the anterior, posterior, and recurrent interosseous arteries and close to the wrist it gives off the palmar carpal branch which is the ulnar contribution to the palmar carpal arch and it also gives a dorsal carpal branch which is the ulnar contribution to dorsal carpal arch.
Relations
In its upper half, it is deeply seated, being covered by the Pronator teres, Flexor carpi radialis, Palmaris longus, and Flexor digitorum superficialis; it lies upon the Brachialis and Flexor digitorum profundus.
The median nerve is in relation with the medial side of the artery for about 2.5 cm. and then crosses the vessel, being separated from it by the ulnar head of the Pronator teres.
Peculiarities
The ulnar artery varies in its origin in the proportion of about one in thirteen cases; it may arise about 5 to 7 cm. below the elbow, but more frequently higher, the brachial being more often the source of origin than the axillary.
Variations in the position of this vessel are more common than in the radial. When its origin is normal, the course of the vessel is rarely changed.
See also
• Allen test
External links
• Ulnar_artery at the Duke University Health System's Orthopedics program
• lesson4artofforearm at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University)