What is the set-point for temperature control?
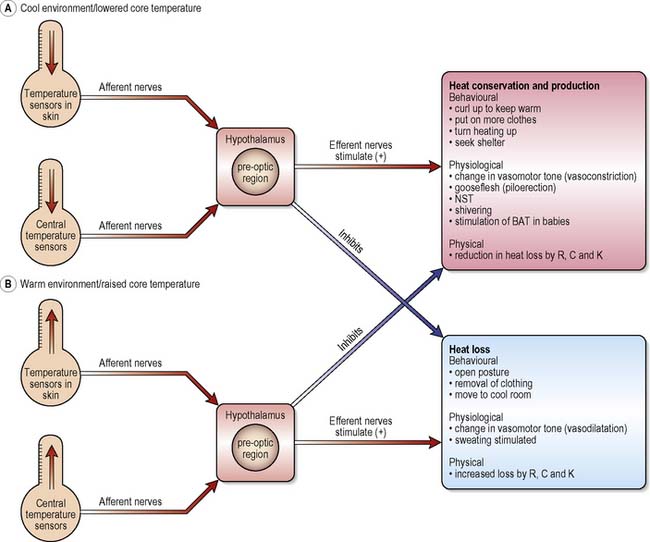
Where is the set point for body temperature controlled? Our internal body temperature is regulated by a part of our brain called the hypothalamus. The hypothalamus checks our current temperature and compares it with the normal temperature of about 37°C. If our temperature is too low, the hypothalamus makes sure that the body generates and maintains heat.
What is a set point in Physiology?
Apr 06, 2022 · Skin Temperature Can Slightly Alter the Set-Point for Core Temperature Control. The critical temperature set-point in the hypothalamus above which sweating begins and below which shivering begins is determined mainly by the degree of activity of the heat temperature receptors in the anterior hypothalamic-preoptic area. However, temperature signals from the …
What is the critical temperature set-point in the hypothalamus?
At temperatures below this level, the rate of heat production is greater than that of heat loss, so the body temperature rises and again approaches the 37.1°C level. This crucial temperature level is called the “set-point” of the temperature control mechanism. That is, all the temperature control mechanisms con-tinually attempt to bring ...
What is thermoregulation around a new set-point?
The subjects left hand was placed outside the bath for the local application of thermal stimuli between 20 degrees and 45 degrees C, subjects reporting the most pleasant temperature. The lower oral temperatures and lower levels of skin temperature rated as pleasant by obese women as compared with women of normal body weight or less suggests that in obesity the set-point …
What is the normal temperature of the human body?
The normal temperature of the human body is considered to be 37 degrees C ...
What are the effects of high temperature on the body?
Adverse effects of high temperature: The pathological effects observed in a person who died of hyperpyrexia are local hemorrhages and parenchymatous degeneration of cells all through the whole body, however particularly in the brain.
What are the effects of fever?
The effects of fever: 1 Metabolic effects:#N#Increased need for oxygen#N#Increases heart rate#N#Increases respiration#N#Increased use of body proteins as an energy source#N#During fever body switches from using glucose (an excellent medium for bacterial growth) to metabolism based on protein and fat breakdown 2 Enhances immune function#N#Increases motility and activity of WBC#N#Stimulates interferon production and activation of T cells 3 Inhibits growth of certain microbial agents#N#Many microbial agents that cause infection to grow at normal body temperatures
What is fever in the body?
Fever is the elevation of an individual's core body temperature above a 'set-point' that is normally regulated by the body's thermoregulatory center in the hypothalamus. This increase in the body's 'set point' temperature is often secondary to a pathological process that involves the release ...
What is the difference between fever and hyperthermia?
In fever, there is an increase in the 'set-point' temperature brought about by the hypothalamus, which enables the body to maintain a controlled 'increase' of the core temperature and general functionality of all organ systems. In hyperthermia, however, the increase of the body's core temperature is beyond the confines of ...
Is pyrogen endogenous or exogenous?
A pyrogen is a substance that physiologically induces fever in the body [6]. Pyrogen s can be classified as endogenous or exogenous depending on whether they originate from inside the body or a fever triggering component from outside the body (e.g., toxins). [7] .
What causes fever in the body?
Fever occurs when there is an elevation in the body's thermoregulatory set-point either by endogenous or by exogenous pyrogen. In hyperthermia, the set-point is unaltered, and the body temperature becomes elevated in an uncontrolled fashion due to exogenous heat exposure or endogenous heat production.
What is the set point of temperature?
The idea of a "Set-Point" for temperature control is that at a basic core body temperature of about 37.1 degrees C (98.8 degrees F), intense changes happen in the paces of both heat loss and heat production. At temperatures over this level, the pace of heat loss is more prominent than that of heat production, so the internal heat level falls and approaches the 37.1 degrees C level.
What is the most important component of fever?
The most crucial component initiating fever in the human body is the presence of a pyrogen. A pyrogen is a substance that physiologically induces fever in the body [6]. Pyrogens can be classified as endogenous or exogenous depending on whether they originate from inside the body or a fever triggering component from outside the body (e.g., toxins). [7]
What are the cytokines that are released when bacteria are digested?
Cytokines are released when these bacterial products are digested as part of the immune responses . Interleukin-1 is the most significant cytokines in causing fever, likewise called endogenous or leukocyte pyrogen. [3] [4]
Does fever increase with heat stroke?
Most patients with raised body temperature have a fever ; there are a few instances where an increased temperature refers to hyperthermia. These include heat stroke, specific metabolic ailments, and the impacts of certain medications that affect the thermoregulation. [1] In contradiction to fever, the thermoregulatory set-point stays unaltered at normothermic levels during hyperthermia while body temperature elevates in an uncontrolled manner and beyond the capacity to lose heat. [2] Exogenous heat exposure and endogenous heat production are methods by which hyperthermia can bring about hazardously high body temperatures.
What is set point in homeostasis?
A set point is the physiological value around which the normal range fluctuates. Click to see full answer. Furthermore, what does set point mean in homeostasis? Introduction to Homeostasis A set point is the physiological value around which the normal range fluctuates. A normal range is the restricted set of values that is optimally healthful ...
What are the components of homeostatic control?
Homeostatic control mechanisms have at least three interdependent components: a receptor, integrating center, and effector. The integrating center, generally a region of the brain called the hypothalamus, signals an effector (e.g. muscles or an organ ) to respond to the stimuli.
What is the tendency to maintain a stable, relatively constant internal environment called?
The tendency to maintain a stable, relatively constant internal environment is called homeostasis . The body maintains homeostasis for many factors in addition to temperature. For instance, the concentration of various ions in your blood must be kept steady, along with pH and the concentration of glucose.
How does temperature affect the brain?
Humans have a similar temperature regulation feedback system that works by promoting either heat loss or heat gain (Figure 1b). When the brain’s temperature regulation center receives data from the sensors indicating that the body’s temperature exceeds its normal range, it stimulates a cluster of brain cells referred to as the “heat-loss center.” This stimulation has three major effects: 1 Blood vessels in the skin begin to dilate allowing more blood from the body core to flow to the surface of the skin allowing the heat to radiate into the environment. 2 As blood flow to the skin increases, sweat glands are activated to increase their output. As the sweat evaporates from the skin surface into the surrounding air, it takes heat with it. 3 The depth of respiration increases, and a person may breathe through an open mouth instead of through the nasal passageways. This further increases heat loss from the lungs.
What hormones are released during shivering?
The muscle contractions of shivering release heat while using up ATP. The brain triggers the thyroid gland in the endocrine system to release thyroid hormone, which increases metabolic activity and heat production in cells throughout the body.
Why does the brain shiver?
This arrangement traps heat closer to the body core and restricts heat loss. If heat loss is severe, the brain triggers an increase in random signals to skeletal muscles, causing them to contract and producing shivering. The muscle contractions of shivering release heat while using up ATP.
What happens when blood sugar drops?
As glucose concentration in the bloodstream drops, the decrease in concentration—the actual negative feedback—is detected by pancreatic alpha cells, and insulin release stops. This prevents blood sugar levels from continuing to drop below the normal range.
How does blood flow to the skin affect the body?
As blood flow to the skin increases, sweat glands are activated to increase their output.
Which gland releases oxytocin?
These nerve cells send messages to the brain, which in turn causes the pituitary gland at the base of the brain to release the hormone oxytocin into the bloodstream.
Why is water concentration important?
Water concentration in the body is critical for proper functioning. A person’s body retains very tight control on water levels without conscious control by the person. Watch this video to learn more about water concentration in the body.
