What is the function of the somatosensory association area?
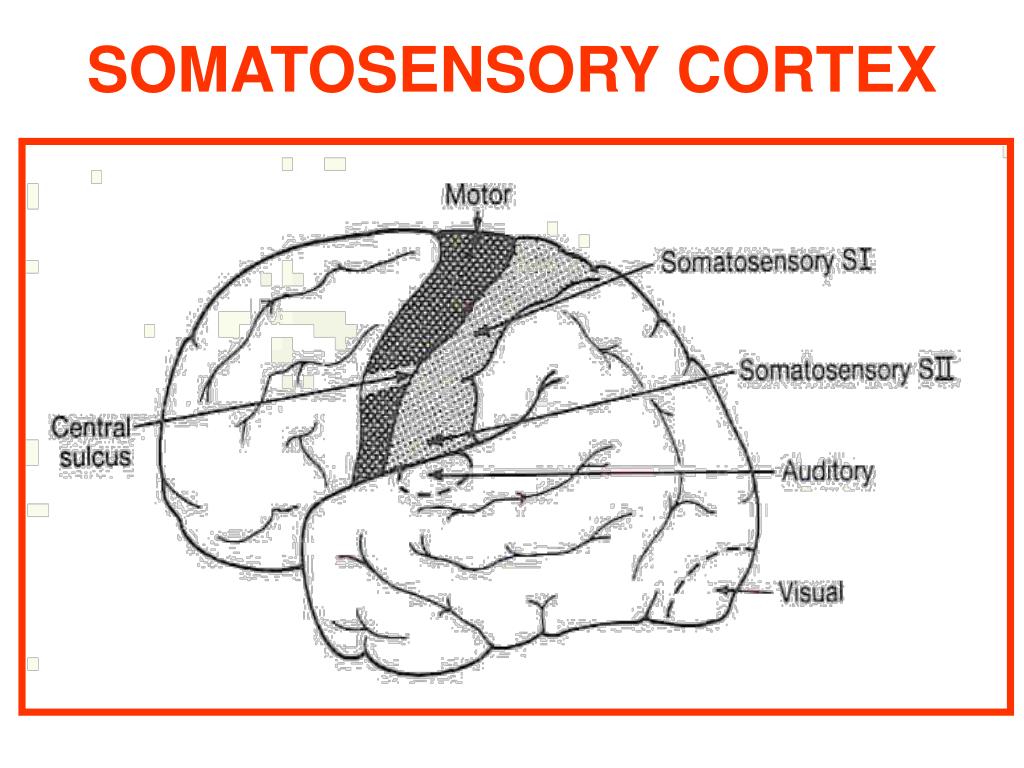
The somatosensory and somatomotor cortexes are two adjoining narrow bands of the topmost central area of the brain, stretching roughly from ear to ear. The motor cortex is partly responsible for the body’s voluntary muscle movements. The function of the somatosensory cortex is to receive and interpret most of the human sense of touch.
What is the function of the somatomotor cortex?
The somatosensory cortex is an important part of the cerebral cortex in the brain that processes sensory information from the body. Neurons from different parts of the body that receive environmental stimuli all send their information to the somatosensory cortex. The somatosensory cortex then processes the information.
What does association cortex mean?
association area, association cortex noun cortical areas that are neither motor or sensory but are thought to be involved in higher processing of information Matched Categories
How does the somatosensory system work?
The somatosensory system is also known as the somatic senses, touch or tactile perception. Anatomically speaking, the somatosensory system is a network of neurons that help humans recognize objects, discriminate textures, generate sensory-motor feedback and exchange social cues. Sensory neurons relay peripheral sensations such as pain, pressure, movement or temperature from the skin to the brain.
What is somatosensory association cortex?
The somatosensory cortex is a region of the brain which is responsible for receiving and processing sensory information from across the body, such as touch, temperature, and pain.
Where is the somatosensory cortex located and what is its function?
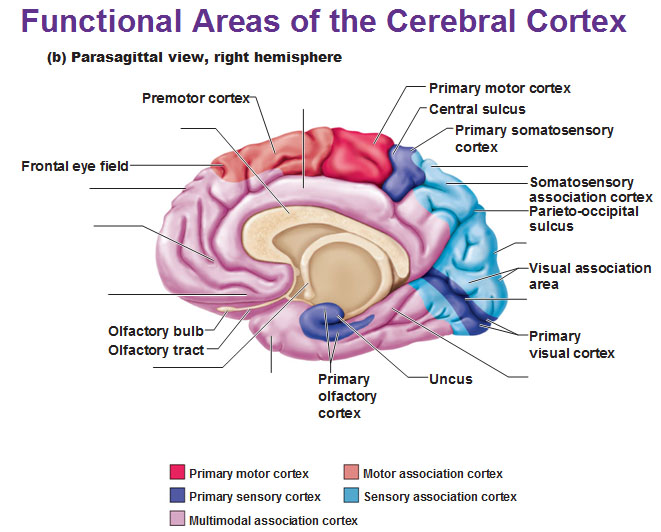
The primary somatosensory cortex is located in the post central gyrus immediately posterior to the primary motor cortex. It is also known as Brodmann areas 1, 2, 3a, and 3b. Its primary function is to detect sensory information from the body regarding temperature, proprioception, touch, texture, and pain.
What is the somatosensory association area of the brain responsible for?
The primary somatosensory cortex is responsible for processing somatic sensations. These sensations arise from receptors positioned throughout the body that are responsible for detecting touch, proprioception (i.e. the position of the body in space), nociception (i.e. pain), and temperature.
Is the somatosensory cortex in the temporal lobe?
The primary auditory cortex lies in the temporal lobe, where it includes a portion of the lower bank of the lateral sulcus. The primary somatic sensory cortex lies on the postcentral gyrus.
What is the sensory association area?
sensory association area an association area around the borders of a primary receiving area, where sensory stimuli are interpreted. silent area an area of the brain in which pathologic conditions may occur without producing symptoms.
Where is the somatosensory cortex found quizlet?
The primary somatosensory cortex is located behind and parallel to the primary motor cortex, in front of the parietal lobe. It receives and processes sensory information from the skin and body, enabling us to perceive bodily sensations.
What part of the brain is responsible for association?
Parietal Association Cortex Mediates Spatial Orientation. Theposterior parietal cortex, the part of the parietal lobe posterior to S1, is filled with association areas.
What is the difference between the primary somatosensory cortex and the somatosensory association cortex?
The primary somatosensory cortex is responsible for receiving the bulk of somatosensory inputs, including touch, temperature, vibration, pressure, and pain, etc. Whereas, the secondary somatosensory cortex is associated with spatial and tactile memory associated with sensory experiences.
Where are association areas located in the brain?
The anterior association area is in the frontal lobes. It is rostral to the postcentral gyri, Rolandic fissure, and premotor areas. It has Sylvian fissure as its posterior boundary. It is referred to as prefrontal cortex.
Which brain lobe contains the somatosensory cortex?
parietal lobeThese functions are processed by an area of your parietal lobe called the somatosensory cortex. Processing hearing information. This function is processed by an area of your temporal lobe called the auditory cortex.
Is somatosensory in parietal lobe?
The parietal lobes are responsible for processing somatosensory information from the body; this includes touch, pain, temperature, and the sense of limb position. Like the temporal lobes, the parietal lobes are also involved in integrating information from different modalities.
What lobe is the somatosensory motor cortex in?
The motor cortex comprises three different areas of the frontal lobe, immediately anterior to the central sulcus.
Which cortex is located in the temporal lobes quizlet?
~The primary auditory cortex is located in the temporal lobe.
Is the temporal lobe part of the sensory area of the brain?
The temporal lobe, which crosses both hemispheres of the brain, helps process sensory input, including pain and auditory stimuli. The brains of all mammals, including people, contain four lobes in the cortex, including the occipital, parietal, temporal, and frontal lobes.
Is the temporal lobe part of the nervous system?
The temporal lobe is a significant part of the limbic system. The limbic system is involved with motivation, emotion, learning, and memory. While the limbic system interacts with other areas of the brain, it works directly with the temporal lobe to influence the components of the limbic system.
What part of the temporal lobe controls facial recognition?
fusiform gyrusThe ability to recognize faces is so important in humans that the brain appears to have an area solely devoted to the task: the fusiform gyrus. Brain imaging studies consistently find that this region of the temporal lobe becomes active when people look at faces.
Where is the somatosensory cortex located?
The somatosensory cortex is a part of the cerebral cortex and is located in the middle of the brain. This image shows the somatosensory cortex, highlighted in red in the brain. The somatosensory cortex is highlighted in red in the brain.
What is the Somatosensory Cortex?
This is where the somatosensory cortex comes in. This part of the brain processes sensations, or external stimuli, from our environment. Before we learn more about the somatosensory cortex, we need to learn a little bit about brain anatomy and where the somatosensory cortex is located.
What part of the brain is responsible for understanding information?
Some neurons are very important and a big chunk of the somatosensory cortex is devoted to understanding their information. The senior scientist sends the most important information to our analyst, and he spends a lot of time understanding it. However, our junior scientists or volunteers gather less important information, so our analyst, or somatosensory cortex, spends less time on that data.
What part of the brain processes sensations?
This is where the somatosensory cortex comes in. This part of the brain processes sensations, or external stimuli, from our environment. Before we learn more about the somatosensory cortex, we need to learn a little bit about brain anatomy and where the somatosensory cortex is located. 4:42.
Why are hands sensitive?
This is because your hands are sensitive and your somatosensory cortex devotes more energy to interpreting information coming from them. Lesson Summary. Let's review! The somatosensory cortex is an important part of the cerebral cortex in the brain that processes sensory information from the body.
What is the name of the part of the brain that is devoted to each part of the body?
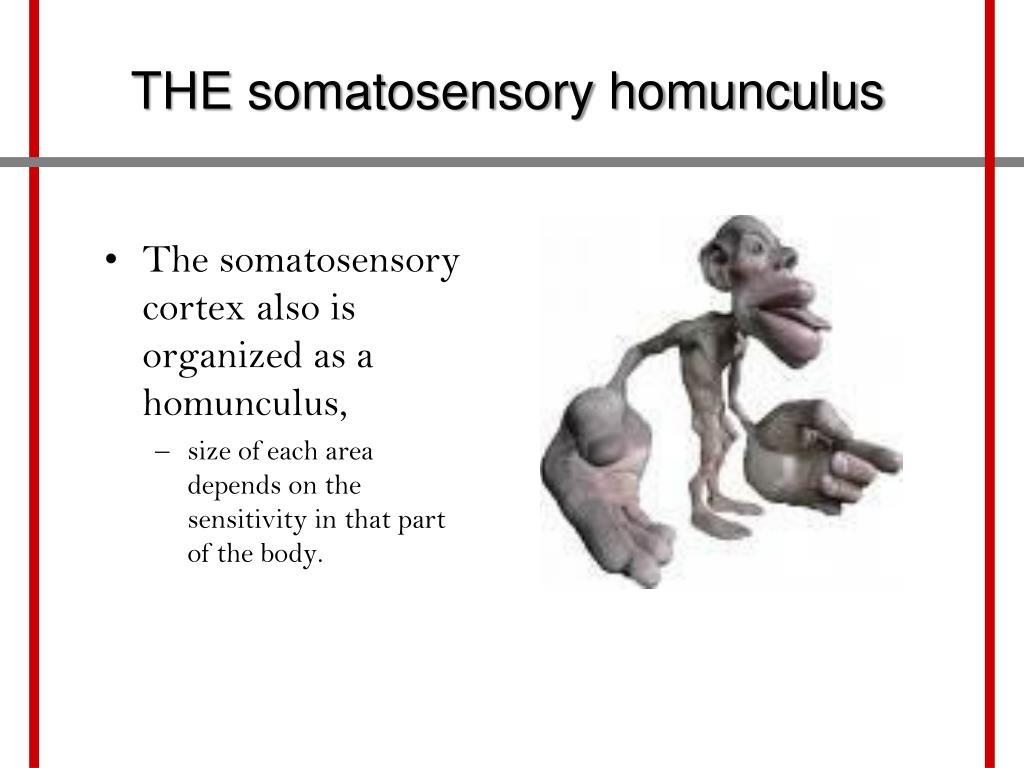
The Homunculus. Scientists have actually mapped out where neurons in each part of the body go to in the somatosensory cortex, and how much of the cortex is devoted to each part. This map of the somatosensory corte x is called a homunculus. Important and sensitive organs have a large part of the somatosensory cortex devoted to them, ...
How does the skin transmit signals to the brain?
The following diagram shows how sensations in the skin are sent through neurons to the brain for processing. The skin transmits signals through other neurons to the brain. Each neuron takes its information to a specific place in the somatosensory cortex.
What is the somatosensory cortex?
Performance focused athletes. Student learning. The somatosensory cortex is a part of your brain that receives and processes sensory information from the entire body. Other names of somatosensory cortex include somesthetic area and somatic sensory area. This part of the brain is essential for receiving.
Which lobe of the brain is the somatosensory cortex located in?
The somatosensory cortex is a part of the forebrain. It is present in the parietal lobe.
What is the cause of a somatosensory lesion?
Unilateral lesion of the somatosensory cortex causes sensory disturbances on the contralateral side of the body. The person remains unable to judge degrees of pressure, warmth, unable to localize pain and tactile stimuli accurately, and unable to judge the weights and shapes of the objects. Loss of muscle tone may also be a symptom of lesions of somatosensory cortex.
What part of the brain processes sensory information?
The somatosensory cortex is a part of your brain that receives and processes sensory information from the entire body. Other names of somatosensory cortex include somesthetic area and somatic sensory area.
Which part of the brain is responsible for the discrete localization of different sensations that arise in different parts of the?
Pinpoint the location of pain, tingling, touch, temperature, and other sensations is the function of somatosensory cortex , specifically area S1.
Where does the primary somatosensory area receive fibers?
Primary Somatosensory Cortex (S1) The primary somatosensory area receives projection fibers from the ventral posterior lateral and ventral posterior medial nuclei of thalamus. These nuclei receive fibers from the contralateral half of the body in the form of medial, trigeminal and spinal lemnisci.
Which artery supplies the lateral surfaces of the cerebral hemispheres?
The arterial supply to most of the primary somatosensory area (S1) and the secondary somatosensory area (S2) is derived from the medial cerebral artery. This artery supplies the lateral surfaces of the cerebral hemispheres.
What is the primary somatosensory cortex?
The primary somatosensory cortex of the human brain is made up of Brodmann areas 3, 1 and 2. Brodmann area, one section of the cerebral cortex is familiar with its histological structure or cytoarchitecture and organization of cells (2).
What is the somatosensory system?
The somatosensory system is made up of primary, secondary and tertiary neurons that enable touching and sensitive to temperature, position, and balance possible (3). They are distributed throughout the body and include sensory receptors neurons on the surface and deeper neurons within the central nervous system (CNS).
What is the somatic sense of pain?
Derived#N#from the Latin words "to harm or hurt", nociception is the somatic#N#sense of pain. In this case, the primary somatosensory cortex responds to#N#certain harmful or potentially harmful stimuli (1). For example, if you are cut or some#N#chili powder is poured to your eyes, nociceptors generate projections along the#N#spinal cord to the primary somatosensory cortex. These may result in a variety#N#of physiological and behavioral responses.
Which cortex is prone to a lesion?
to neurosurgeons, the primary somatosensory cortex is prone to the lesion. 1. Agraphesthesia. This is one kind of disorder of directional cutaneous kinesthesia (proprioception) or disorientation of sensation of the skin across the skin space (2).
Which part of the brain is responsible for the processing of somatic sensations?
The primary somatosensory cortex is mainly responsible for the processing of somatic sensations. According to research, somatic sensations are bodily sensations of touch, pain, temperature, vibration and proprioception (1).
Where are thalamocortical projections?
For clarity, the thalamocortical projections/radiations are fibers between the thalamus and the cerebral cortex (2). A tactile representation of the primary somatosensory cortex is ordered in an upturned style starting from the toe at the uppermost of the cerebral hemisphere to the mouth at the undermost (1).
Which hemisphere has a graphical display of the contralateral side of the body?
Nonetheless, few body parts are governed by moderately imbricated regions of the cortex. The primary somatosensory of each cerebral hemisphere has a graphical display of the contralateral side of the body (3). Moreover, the amount of primary somatosensory cortex assigned to a body part is not equivalent to the size of the body part but to the bulkiness of the cutaneous tactile report of the body part.
What parts of the brain stem from the most superior to the most inferior?
1.--------midbrain (or mesencephalon) 2.---pons------------- 3.---medulla oblongata-------------. midbrain (or mesencephalon), pons, medulla oblongata. Match the parts of the brain with their function. Choose from the list below:
What are the associated fibers that match the lobes of the cerebrum?
The associated fibers matched with their function are: Label the meninges and the spaces between them. Label the network of cavities within the brain.
Which hemisphere controls the motor function of the left side?
Cerebral hemispheres may specialized in distinct functions, for example, language centers are on the left hemisphere only. Motor functions are contralateral, the right-side controls motor functions of the left side, and vise-versa. List the motor areas of the brain, label their location and list their functions:
Where is the somatosensory cortex located?
somatosensory cortex. The primary somatosensory cortex is located in the postcentral gyrus and is part of the somatosensory system. It was initially defined from surface stimulation studies of Wilder Penfield, and parallel surface potential studies of Bard, Woolsey, and Marshall.
What is the somatosensory cortex?
Somatosensory Cortex is responsible for processing somatic sensations. These sensations arise from receptors positioned throughout the body that are responsible for detecting touch, proprioception (the position of the body in space), nociception (pain), and temperature. When such receptors detect one of these sensations, ...
What part of the brain is responsible for figuring out what information means?
Next, that part of the somatosensory cortex gets to work on figuring out what the information means. Think of it like scientists sending data to a data analyst. Each scientist, like the neuron, gathers information and sends it to a master analyzer or the somatosensory cortex.
What part of the brain processes external stimuli?
This is where the somatosensory cortex comes in. This part of the brain processes sensations, or external stimuli, from our environment.
What are the Brodmann areas?
Brodmann areas 3, 1, and 2 make up the primary somatosensory cortex of the human brain (or S1). Because Brodmann sliced the brain somewhat obliquely, he encountered area 1 first; however, from anterior to posterior, the Brodmann designations are 3, 1, and 2, respectively.
How many regions of the brain did Brodmann identify?
Brodmann identified 52 distinct regions of the brain according to differences in cellular composition, these divisions are still widely used today and the regions they form are referred to as Brodmann’s areas. Brodmann divided the primary somatosensory cortex into areas 3 (which is subdivided into 3a and 3b), 1, and 2.
Which part of the brain receives sensory input?
The somatosensory cortex receives all sensory input from the body. Cells that are part of the brain or nerves that extend into the body are called neurons. Neurons that sense feelings in our skin, pain, visual, or auditory stimuli, all send their information to the somatosensory cortex for processing.