
Is the dermis in the subcutaneous tissue?
The epidermis is the thin outer layer of skin, the dermis is the thicker inner layer of skin. Beneath the dermis, lies a layer of loose connective tissue called subcutaneous tissue or the hypodermis deeper tissues including muscles, tendon, ligament, joint capsule and bone lie beneath the subcutaneous tissue layer.
What is the subcutaneous layer of the skin?
Your skin has three main layers:
- The hypodermis (subcutaneous tissue) is the innermost layer of skin in your body.
- The dermis is the middle layer.
- The epidermis is the outermost layer.
What does subcutaneous mean in medical terms?
The term "cutaneous" refers to the skin. Subcutaneous means beneath, or under, all the layers of the skin. For example, a subcutaneous cyst is under the skin. Gawkrodger DJ, Ardern-Jones MR. Microanatomy of the skin.
What is the function of the subcutaneous layer?
What functions does the subcutaneous layer have?
- Insulation. The subcutaneous layer consists primarily of fat, allowing it to act as the body’s insulator. ...
- Thermoregulation. The blood vessels in the hypodermis dilate to cool the body down. ...
- Shock absorption. Besides insulation, the large proportion of fat in the subcutaneous layer also helps with shock absorption.
- Structural support. ...
- Energy reserve. ...

Where is the subcutaneous tissue found quizlet?
3rd layer of the skin,it lies just beneath the dermis. the hypodermis, super fascia, or subcutaneous fascia.
Where is the subcutaneous tissue What is its function what tissue is there?
Subcutaneous tissue is the deepest layer of your skin. It's made up mostly of fat cells and connective tissue. The majority of your body fat is stored here. The subcutaneous layer acts as a layer of insulation to protect your internal organs and muscles from shock and changes in temperature.
Where is the subcutaneous tissue in relation to the dermis?
Subcutaneous Tissue (Fat) Beneath the dermis lies the panniculus, with lobules of fat cells or lipocytes separated by fibrous septa composed of collagen and large blood vessels (Fig. 1.8). The collagen in the septa is continuous with the collagen in the dermis.
What is under subcutaneous tissue?
The subcutaneous tissue, also known as the hypodermis or superficial fascia, is the layer of tissue that underlies the skin. The terms originate from subcutaneous in Latin and hypoderm in Greek, both of which mean “beneath the skin,” as it is the deepest layer that rests just above the deep fascia.
Which layer of the skin is the subcutaneous fat layer?
Subcutaneous tissue, also known as the hypodermis, is the innermost layer of skin. It's made up of fat and connective tissues that house larger blood vessels and nerves. It acts as an insulator to help regulate body temperature.
What layer of skin is subcutaneous injection?
A subcutaneous injection is a way to give certain medications using a needle. The subcutaneous tissue, also known as the hypodermis, is the innermost (deepest) layer of skin. It is made up of fat and connective tissue and helps the body control temperature.
How far down is subcutaneous tissue?
The body stores fat in the subcutaneous layer. Other components include collagen-rich connective tissue and a network of blood vessels and nerves. In the body's abdominal area, which often has more fat, the subcutaneous layer reaches up to 3 centimeters in depth.
What is found in the subcutaneous layer quizlet?
The subcutaneous layer consists of areolar and adipose connective tissue. One of the functions of the subcutaneous layer is thermal insulation.
What kind of cells are found in the subcutaneous layer?
The types of cells found in the layer are fibroblasts, adipose cells, and macrophages. The subcutaneous tissue is derived from the mesoderm, but unlike the dermis, it is not derived from the mesoderm's dermatome region.
Where do you give a subcutaneous injection?
Choose Your Injection Site At least 3 inches (7.5 centimeters) below your shoulder and 3 inches (7.5 centimeters) above your elbow, on the side or back. Outer side of upper thighs. Belly area. Below your ribs and above your hip bones, at least 2 inches (5 centimeters) away from your belly button.
What does subcutaneous mean in medical terms?
Subcutaneous means beneath, or under, all the layers of the skin. For example, a subcutaneous cyst is under the skin. A subcutaneous injection is administered under the skin.
What is the function of the subcutaneous layer of the skin?
The subcutaneous layer protects the body and keeps it warm. It provides insulation and protection for vital tissues such as muscles, bones, blood vessels, and organs. This article looks at subcutaneous tissue, its functions, and conditions that can affect this essential skin layer.
Where is adipose tissue found?
Where is my adipose tissue? Adipose tissue is commonly known as body fat. It is found all over the body. It can be found under the skin (subcutaneous fat), packed around internal organs (visceral fat), between muscles, within bone marrow and in breast tissue.
What is found in the subcutaneous layer quizlet?
The subcutaneous layer consists of areolar and adipose connective tissue. One of the functions of the subcutaneous layer is thermal insulation.
What kind of cells are found in the subcutaneous layer?
The types of cells found in the layer are fibroblasts, adipose cells, and macrophages. The subcutaneous tissue is derived from the mesoderm, but unlike the dermis, it is not derived from the mesoderm's dermatome region.
Where is subcutaneous fat located?
Subcutaneous fat is the fat located in the subcutaneous layer. Adipocytes, or fat cells, hold the fat in specialized connective tissue called adipose tissue.
How deep is the subcutaneous layer?
In the body’s abdominal area, which often has more fat, the subcutaneous layer reaches up to 3 centimeters in depth. The thickness depends on someone’s overall body fat composition.
What are the drawbacks of subcutaneous injections?
Subcutaneous injections have some drawbacks. People may experience abscesses, which are areas of pus under the skin. Anyone who needs frequent injections may experience an accumulation of fat under the skin called lipohypertrophy. People can avoid this by varying the injection site, as it typically happens when an individual has multiple injections in the same area.
What is the term for a disease that affects the subcutaneous layer?
Panniculitis is an umbrella term for a variety of diseases concerning subcutaneous tissue. The signs of panniculitis include inflammation in the subcutaneous layer and possible scarring of the subcutaneous tissue. This condition is most often associated with autoimmune disorders. It can also be caused by infection and trauma.
What are the two classifications of burns that affect the subcutaneous layer?
The two classifications of burns that affect the subcutaneous layer are third degree and fourth degree burns. Third degree burns destroy the entire epidermis and dermis and may impact. Trusted Source. the subcutaneous tissue. These burn sites may appear either white or blackened.
Why is subcutaneous injection so slow?
The slow absorption rate is because compared with muscle, the subcutaneous tissue has far fewer blood vessels.
What are the possible damage to the subcutaneous layer?
Possible damage to the subcutaneous layer includes third or fourth degree burns, abscesses, pressure ulcers, tumors, and panniculitis.
Where does subcutaneous tissue accumulate?
The location and thickness of subcutaneous tissue differ by gender. 4 Men tend to accumulate more around the abdomen and the shoulders, while women tend to accumulate it around the thighs, hips, and buttocks.
What is the function of subcutaneous tissue?
The epidermis' adipose tissue acts as an energy reserve. 5 Once the body uses up energy that's acquired from consuming carbohydrates, it turns to adipose tissue as a fuel source, which can lead to weight loss.
How does the subcutaneous tissue regulate body temperature?
Subcutaneous tissue also regulates body temperature by making sure that your internal temperature isn't too high or too low. 6 The hypodermis essentially insulates the body, allowing you to go outside on a cold day without getting hypothermia (a dangerous condition that, if allowed to go on for too long, can result in freezing to death).
What is the innermost layer of the skin?
His research has been published in the New England Journal of Medicine. Subcutaneous tissue, which is also known as the hypodermis , is the innermost layer of skin. It's made up of fat and connective tissues that house larger blood vessels and nerves, and it acts as an insulator to help regulate body temperature.
Why are subcutaneous injections used?
Since the subcutaneous tissue contains a limited network of blood vessels, medications injected here are absorbed gradually over time. 7 This makes them an ideal route for many drugs. That's why may medications are injected into the hypodermis. Examples of medications that may be given by subcutaneous injection include epinephrine for allergic reactions, some vaccinations, insulin, some fertility drugs, some chemotherapy medications, morphine, growth hormone, and anti-arthritis drugs. 8 The parts of the body that have greater concentrations of subcutaneous tissue make them ideal injection sites. These include:
Why is subcutaneous tissue more sensitive to cold?
This weakened layer of insulation makes the body more sensitive to the cold because less tissue makes it harder to stay warm.
What are the cells that attach to the dermis?
Collagen and elastin fibers (these attach the dermis to muscles and bones) Fat cells. Blood vessels. Sebaceous glands. Nerve endings. Hair follicle roots. The hypodermis is largely composed of adipose tissue (fat tissue), which is made up of adipocytes, or fat cells. 3 The amount of adipose tissue varies throughout the body.
What is the hypodermis responsible for?
Together with your other layers of skin, the hypodermis protects your skeletal system, organs, muscles and tissues from harm.
Where is the hypodermis located?
The hypodermis is the bottom layer of your skin, located below the epidermis (top layer) and dermis (middle layer) in your skin.
What color is the hypodermis?
The hypodermis is yellowish. Depending on how much of the pigment called carotene is in your hypodermis, it can be dark yellow or light yellow.
How big is the hypodermis?
The hypodermis varies in thickness across your body. It’s thinnest over your eyelids and external genitals, where it may be less than 1 millimeter thick. It’s thickest in your abdomen and butt, where it may be over 3 centimeters thick.
What are common signs or symptoms of hypodermis conditions?
Some common signs or symptoms of conditions that can affect your hypodermis include:
What are common tests to check the health of your hypodermis?
Your healthcare provider will conduct a physical exam to check for any possible symptoms or conditions. They may also perform the following tests:
What are common treatments for conditions of your hypodermis?
Some common treatments for conditions that affect your hypodermis include:
What is subcutaneous tissue?
The subcutaneous tissue is composed of subcutaneous fat and various other types of cells. It is thickest in areas of the body such as the buttocks, palms, and soles of the feet. Subcutaneous fat is the most widely distributed layer of subcutaneous tissue and is made up of adipocytes.
Why is subcutaneous tissue important?
The subcutaneous tissue is essential because of its role in padding the body. This enables it to protect the bones, muscles, and organs under the skin from physical damage. It does this by storing excess fat around the body in the subcutaneous layer, to cushion the body and protect it from injury. Additionally, the subcutaneous tissue helps ...
What is the layer of skin that underlies the skin?
The subcutaneous tissue, also known as the hypodermis or superficial fascia, is the layer of tissue that underlies the skin. The terms originate from subcutaneous in Latin and hypoderm in Greek, both of which mean “beneath the skin,” as it is the deepest layer that rests just above the deep fascia.
What connects the dermis to the lymphatic system?
Collagen and elastin fibers: to connect the subcutaneous tissue to the dermis. Lymphatic vessels : to connect the dermis to the lymphatic system. Nerves: to connect the dermis and free nerve endings in the subcutaneous tissue to the nervous system. Blood vessels: to connect the dermis to the circulation of blood.
Where is fat found in the body?
Fat is present in all areas of the body, except the eyelids, clitoris, scrotum, penis and much of the pinna. Other components of the subcutaneous tissue include: Fibrous bands: to anchor the skin to the deep fascia. Collagen and elastin fibers: to connect the subcutaneous tissue to the dermis.
How do adipocytes form lobules?
The adipocytes group together to form lobules, which are separated by connective tissue. The number of adipocytes in the subcutaneous tissue varies with the area of the body, whereas the size of the individual cells depends on the nutrition of the person.
What is the function of subcutaneous tissue?
It provides support to the blood vessels, nerves, and glands of the body and connects the dermis (middle layer of the skin) to muscles and bones. In essence, subcutaneous tissue is the padding of the body, acting as a protective layer.
What would happen if the body didn't have subcutaneous tissue?
As you can imagine, subcutaneous tissue disorders can cause many problems that interfere with the natural defenses of the body.
What is skin abscess?
Skin abscess: This is a fluid collection of purulent material or puss. A Simple incision should drain such a medical case.
Which tissue is made up of many veins and blood vessels?
The subcutaneous tissue, which is made up of many veins and blood vessels, has much importance and functionality.
Do subcutaneous skin conditions heal?
Some subcutaneous skin conditions will often resolve and not require specific treatment. The underlying healing condition will simply scar over time.
Can subcutaneous tissue be a problem?
To reach this area for treatment can often mean a minor or possibly major procedure. As such, subcutaneous tissue disorders can become a serious problem.
Where is adipose tissue found?
Adipose tissue can be found in a number of different places throughout the body. White adipose tissue is the most abundant type of fat in humans. It is distributed within subcutaneous fat, visceral fat, and bone marrow fat. Subcutaneous fat is found throughout the whole body, in the spaces between the skin and underlying muscles. Visceral fat is predominantly found around the organs in the abdominal cavity, such as the liver, intestines and kidneys, as well as in the peritoneum (a serous membrane that lines the outside of the abdominal organs). White adipose tissue is also present in the bone marrow (a sponge-like tissue present in the central cavity of bones). In addition, white adipose tissue can be found in the pericardium surrounding the heart, or cushioning other parts of the body, like the soles of the feet, eyeballs, and certain blood vessels.
Where is brown fat found in the body?
In newborns, brown adipose tissue is mainly located on the back, along the upper half of the spine, in between the shoulders, and surrounding the kidneys.
What is adipose tissue?
Adipose tissue, also known as fat tissue or fatty tissue, is a connective tissue that is mainly composed of fat cells called adipocytes. Adipocytes are energy storing cells that contain large globules of fat known as lipid droplets surrounded by a structural network of fibers.
What is the function of adipose tissue?
The main function of white adipocytes is to store excess energy in the form of fatty molecules, mainly triglycerides. Fat storage is regulated by several hormones, including insulin, glucagon, catecholamines ( adrenaline and noradrenaline), and cortisol. Depending on the body ’s immediate energy requirements, these hormones can either stimulate adipose tissue formation and storage (i.e. lipogenesis) or initiate the release of fat from adipose tissue (i.e. lipolysis ). Under the influence of insulin, for instance, adipocytes can increase the uptake of blood glucose and transform it into fatty molecules, thereby increasing fat storage.
What are the most important facts to know about adipose tissue?
Accordingly, adipose tissue can be classified as white adipose tissue, composed primarily of white and beige adipocytes, and brown adipose tissue, composed of brown adipocytes. White adipose tissue is the predominant type of fat in the human body. It can be found beneath the skin ( subcutaneous fat ), around internal organs (visceral fat), and in the central cavity of bones (bone marrow fat), as well as cushioning various parts of the body. Its main role is to serve as an energy storing reservoir, but it also insulates the body from extreme temperatures, cushions vital organs, and secretes hormones and biological factors. On the other hand, brown adipose tissue is mostly present during fetal life and in infants. It is mainly located in the upper back, above the clavicles, around the vertebrae, and in the mediastinum. The main role of brown adipose tissue is to generate heat through non-shivering thermogenesis; a process that’s especially important to prevent hypothermia in newborns.
What is the most common type of fat in the human body?
Accordingly, adipose tissue can be classified as white adipose tissue, composed primarily of white and beige adipocytes, and brown adipose tissue, composed of brown adipocytes. White adipose tissue is the predominant type of fat in the human body.
What is the difference between brown and white adipose tissue?
Based on the type of adipocytes, adipose tissue can be classified into two functionally different tissues: white adipose tissue, composed primarily of white and beige adipocytes, and brown adipose tissue, composed of brown adipocytes. The increased concentration of iron-containing mitochondria in brown adipocytes gives brown adipose tissue its ...
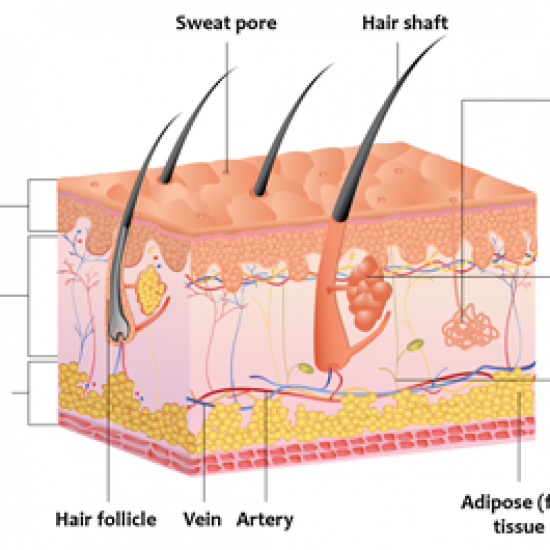
Subcutaneous Tissue Structure
Functions
- Subcutaneous tissue has several functions in the body. It helps provide insulation, regulate temperature, and store fat. Because subcutaneous tissue is the deepest layer of the skin, it attaches the other skin layers to tissues under the skin, like bones and muscles.
Subcutaneous Injection
- Since the subcutaneous tissue contains a limited network of blood vessels, medications injected here are absorbed gradually over time.7This makes them an ideal route for many drugs. That's why many medications are injected into the hypodermis. Medications that may be given by subcutaneous injection include:8 1. Epinephrine for allergic reactions 2. Some vaccinations 3…
Effect of Age
- As you age, subcutaneous tissue starts to thin out. This weakened layer of insulation makes the body more sensitive to the cold because less tissue makes it harder to stay warm. The loss of subcutaneous tissue due to aging also causes the body to sweat less, making it harder to stay cool in warm weather.9It can also affect the body's reaction to certain medications that are abs…