Where is the superior tibiofibular joint?
The proximal tibiofibular articulation (also called superior tibiofibular joint) is an arthrodial joint between the lateral condyle of the tibia and the head of the fibula. Right knee-joint, from the front, showing interior ligaments.
Where is the proximal tibiofibular joint located?
The proximal tibiofibular joint (PTFJ) is an arthrodial sliding joint located between the lateral tibial condyle and the fibular head. 1, 2 It is a synovial joint with hyaline cartilage articulation.
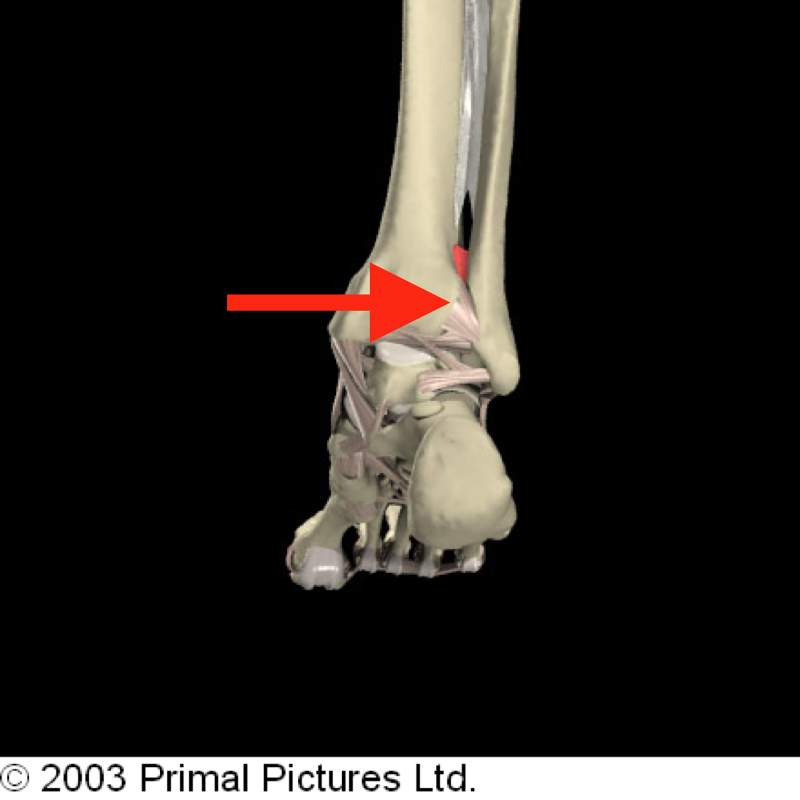
Where is the distal tibiofibular joint located?
The syndesmotic articulation of the distal tibiofibular joint occurs between the convex surface of the distal tip of the fibula and the concave fibular notch of the distal tibia. The stability of the syndesmosis is crucial to proper dynamic ankle and lower extremity function.
What type of joint is the tibiofibular joint?
plane type synovial jointThe proximal tibiofibular joint (PTFJ) is a plane type synovial joint. The primary function of the PTFJ is dissipation of torsional stresses applied at the ankle and the lateral tibial bending moments besides a very significant tensile, rather than compressive weight bearing.
Is the proximal tibiofibular joint part of the knee?
Because the proximal tibiofibular joint can be contiguous with the knee joint, either joint may be affected when the joint pressure is elevated, and thus the proximal tibiofibular joint has been construed as the “fourth compartment” of the knee joint [1].
Is tibiofibular joint part of knee joint?
The superior tibiofibular joint is the joint between the shin bone (tibia) and the smaller bone (fibula) that runs alongside it. The superior tibiofibular joint is located on the outside surface of the leg, just below the knee joint.
What kind of joint is found between the distal tibia and fibula?
syndesmosisThe distal joint between the tibia and fibula is an example of a syndesmosis.
What is between the fibula and tibia?
The interosseous ligament lies between the tibia and fibula. (Interosseous means between bones.) The interosseus ligament is a long sheet of connective tissue that connects the entire length of the tibia and fibula, from the knee to the ankle.
What joints are formed at proximal and distal tibia?
Proximally, the tibia articulates with the femur to form the tibial-femoral joint of the knee. Distally, the tibia articulates with the talus to form the talocrural joint of the ankle.
What is tibiofibular pain?
Description of Proximal Tibiofibular Joint Pain Typically, the proximal tibiofibular joint is injured in a fall when the ankle is plantar-flexed, with the stress being brought through the fibula, will cause the proximal fibula to sublux (partial dislocation) out of place over the lateral aspect of the knee joint.
What holds tibia and fibula together?
The interosseous membrane holds the fibula and tibia together. This membrane also stabilizes any posterolateral bowing of the fibula that may occur with weight bearing.
What is the ankle joint called?
Talocrural jointThe ankle joint, or Talocrural joint, is a large synovial joint. It is a hinge joint that allows plantarflexion and dorsiflexion, moving the foot up and down.
What joints are formed at proximal and distal tibia?
Proximally, the tibia articulates with the femur to form the tibial-femoral joint of the knee. Distally, the tibia articulates with the talus to form the talocrural joint of the ankle.
What makes up the distal tibiofibular joint?
It is formed between the distal tibia(concave surface) and fibula(convex surface), with no articular capsule or synovial membrane as a fibrous joint, and attached by the interosseous ligament (IOL), the anterior-inferior tibiofibular ligament (AITFL), the posterior-inferior tibiofibular ligament (PITFL), and the ...
What kind of joint is found between the distal tibia and fibula?
syndesmosisThe distal joint between the tibia and fibula is an example of a syndesmosis.
What is the articulatio tibiofibularis?
The proximal tibiofibular articulation (also called superior tibiofibular joint) is an arthrodial joint between the lateral condyle of the tibia and the head of the fibula . The contiguous surfaces of the bones present flat, oval facets covered with cartilage and connected together by an articular ...
What is the clinical significance of proximal tibiofibular dislocation?
Clinical significance. Injuries to the proximal tibiofibular joint are uncommon and usually associated with other injuries to the lower leg. Dislocations can be classified into the following five types: Superior dislocation (uncommon, associated with shortened tibia fractures or severe ankle injuries)
What are the contiguous surfaces of bones?
The contiguous surfaces of the bones present flat, oval facets covered with cartilage and connected together by an articular capsule and by anterior and posterior ligaments.
What is inferior dislocation?
Inferior dislocations are exceptional as they usually only occur in avulsion (traumatic amputation) injuries. Subluxation may also occur in diseases with ligamentous laxity (e.g., Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome ), muscle weakness (e.g., muscular dystrophy ), or secondarily to degeneration (e.g., in rheumatoid arthritis ).
What is a superior tibiofibular joint injury?
The superior tibiofibular joint is the joint between the shin bone (tibia) and the smaller bone (fibula) that runs alongside it. The superior tibiofibular joint is located on the outside surface of the leg, just below the knee joint. A superior tibiofibular joint injury occurs when the joint or its supporting structures are damaged. Physiotherapy is important in the rehabilitation of a superior tibiofibular joint injury.
What causes a tibiofibular joint to twist?
An injury to the superior tibiofibular joint can be caused by direct trauma to the joint or if the leg is twisted. A twisting injury often occurs when pivoting or suddenly changing direction whilst running and often occurs with a knee or ankle injury.
How long does it take for a tibiofibular joint to heal?
The most important time in the initial treatment of a superior tibiofibular joint injury is the first 24–48 hours. This is because the majority of the bleeding and swelling around the injured joint occurs within this time. To control the amount of swelling and, therefore, accelerate your recovery, the injured leg should be rested and iced.
Where is pain in the lower leg?
Pain is felt on the outside of the leg, just below the knee if the superior tibiofibular joint is injured. Pain is usually worsened by activities that require rotation of the lower leg, such as pivoting or changing direction whilst running. Other symptoms may include:
Where is the superior tibiofibular joint located?
This joint is located between the flat articular facet on the fibular head and a similar articular facet situated posterolaterally on the lateral tibial condyle. As expected, the superior tibiofibular joint is also surrounded by a joint capsule, which attaches to the margins of the articular surfaces of the fibula and tibia.
Which bones are connected by a superior tibiofibular joint?
Right below the knee joint, there are the leg bones, namely the tibia and fibula, which are connected by a superior tibiofibular joint, and an inferior tibiofibular joint, which is a component of the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis, as it is the distal end of the syndesmotic - or fibrous - connection between the tibia and fibula.
What is the syndesmosis of the tibia?
The tibiofibular syndesmosis, on the other hand, is a compound fibrous joint. Basically, it represents the fibrous union of the tibia and fibula by means of the interosseous membrane, which unites the shaft of the bones, and the inferior tibiofibular joint, which unites the distal ends of the bones.
What are the two joints of the leg?
Now, everyone knows about the famous hip joint and knee joint, but not many people like to talk about the lesser known tibiofibular joints. The tibiofibular joints are two joints of the leg, one superior and one inferior.
Articulating structures of superior tibiofibular joint
The articular surfaces of the superior tibiofibular joint include the following:
Joint capsule and ligaments
Both articular structures are surrounded by the fibrous joint capsule. Besides the capsule, this joint is strengthened with two ligaments - the anterior and posterior ligaments of the fibular head.
What is the cartilage of the proximal tibiofibular joint?
The articular surfaces of the proximal tibiofibular joint are lined with hyaline cartilage and contained within a joint capsule.
What are the proximal and distal tibiofibular joints?
The proximal and distal tibiofibular joints refer to two articulations between the tibia and fibula of the leg. These joints have minimal function in terms of movement but play a greater role in stability and weight-bearing.
What is the interosseous membrane?
Interosseous membrane - a fibrous structure spanning the length of the tibia and fibula. Anterior and posterior inferior tibiofibular ligaments. Inferior transverse tibiofibular ligament - a continuation of the posterior inferior tibiofibular ligament. As it is a fibrous joint, the distal tibiofibular joint does not have a joint capsule ...
What is the difference between inferior and distal tibiofibular joints?
Articulating Surfaces. The distal (inferior) tibiofibular joint consists of an articulation between the fibular notch of the distal tibia and the fibula. It is an example of a fibrous joint, where the joint surfaces are by bound by tough, fibrous tissue.
What nerve innervates the tibiofibular joint?
The joint is innervated by branches of the common fibular nerve and the nerve to the popliteus (a branch of the tibial nerve). The distal (inferior) tibiofibular joint consists of an articulation between the fibular notch of the distal tibia and the fibula.
What is the distal joint?
The distal (inferior) tibiofibular joint consists of an articulation between the fibular notch of the distal tibia and the fibula.
What are the clinical features of a fibular head?
Common clinical features include inability to weight-bear, lateral knee pain and tenderness/ prominence of the fibular head.
Where does iliotibial band pain go?
Inflammation and irritation of the thick fibrous iliotibial band which runs from the pelvis to the tibia on the outside of the leg. Usually pain is felt on the outside of the leg, but may transfer to the outer side of the hip.
Where should the kneecap be on the thigh?
The kneecap should track smoothly in the groove on the lower end of the thigh bone. If this does not happen, the cartilage on the two surfaces may wear away and the bones come into contact with each other causing pain due to arthritis.
What is the condition that affects the underside of the kneecap and the trochlear groove in the?
Patellofemoral Arthritis. This affects the underside of the kneecap (patella) and the trochlear groove in the femur in which it moves. When the articular cartilage covering the surfaces of the bone wears away and becomes inflamed the bones come into contact with each other resulting in pain.
How many plicae are there in each knee?
There are usually four in each knee, at the embryonic stage, and help to bend the joints easily. About 50% of the population loose their plicae by absorption at the foetal stage. If a plica becomes inflamed because of injury or overuse it can cause pain, swelling or locking of the knee joint.
What is the pain at the front of the thigh above the knee?
Pain at the front above the knee. This is the location of the quadriceps tendon which attaches the four large muscles of the front of the thigh to the knee cap.
What is the structure of the knee?
The knee is a complex structure consisting of bone, cartilage, muscle, tendon, ligament, synovial fluid and nerves. Knee pain could be the result of a problem with any one of these components, or a combination of several. You may be experiencing knee pain and want to know the possible causes. The diagram, below, is a handy guide to ...
What is the pain in the front of the knee called?
Patellofemoral pain syndrome. This is a general term used for a dull pain in the vicinity of the kneecap and front of the knee. Sometimes known as runner’s knee. Various causes including overuse or misalignment of the kneecap.
Which side of the body is the tibiofibular joint?
Lateral view of the tibiofibular joints on the right side of the body.
Where is the syndesmosis fibrous joint located?
This is a syndesmosis fibrous joint located between the medial side of the lateral malleolus of the fibula and the fibular notch of the distal tibia.
Which part of the foot is responsible for dorsiflexion and plantarflexion?
The superior/inferior glide of the fibula is functionally important for dorsiflexion and plantarflexion of the foot at the ankle joint.
