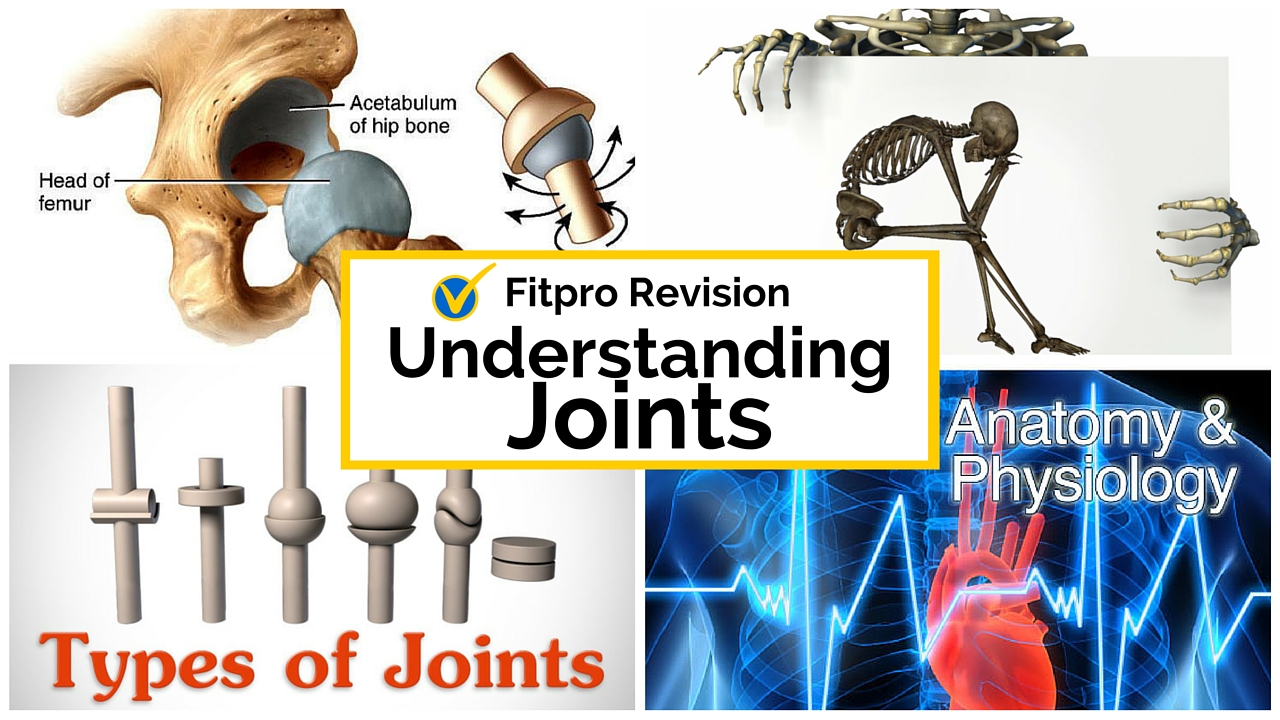
Where is the condylar joint located?
What is the sacroiliac joint?
What is a polyaxial joint?
What is ball and socket joint?
Which type of joint is a synovial joint that is flat or slightly curved?
What are the five types of joints?
What is the joint between the femur, patella, and tibia?
See 4 more
About this website

Where are Synarthrodial joints located?
The joint that connects bones by fibrous tissue and allows only little or no movement. This type of joint connects bones by tough fibrous tissue. Examples are the sutures between the bones of the skull, and synchrondrosis.
What are the Synarthrodial joints in the body?
A synarthrodial joint is one in which the two bones are separated only by an intervening membrane, such as the cranial sutures.
What is another name for Synarthrodial joint?
In fibrous joints (synarthrodial joint) the bones are joined by fibrous tissue, namely dense fibrous connective tissue, and no joint cavity is present.
Which body part has an Amphiarthrodial joint?
Slightly movable joints, i.e., amphiarthrodial joints. Example: tibia and the fibula joint.
Is the knee Synarthrodial?
The knee joint is a synovial joint that connects three bones; the femur, tibia and patella. It is a complex hinge joint composed of two articulations; the tibiofemoral joint and patellofemoral joint.
What are the 3 main joints in the human body?
Histologically the three joints in the body are fibrous, cartilaginous, and synovial. Functionally the three types of joints are synarthrosis (immovable), amphiarthrosis (slightly moveable), and diarthrosis (freely moveable).
What are the 4 main types of joints?
What are the different types of joints?Ball-and-socket joints. Ball-and-socket joints, such as the shoulder and hip joints, allow backward, forward, sideways, and rotating movements.Hinge joints. ... Pivot joints. ... Ellipsoidal joints.
What are the 4 types of synarthroses?
joints. Synarthroses are divided into three classes: fibrous, symphysis, and cartilaginous.
What is function of Bursa?
Bursae are small fluid-filled sacs that reduce friction between moving parts in your body's joints.
What are the 6 main joints?
The six types of freely movable joint include ball and socket, saddle, hinge, condyloid, pivot and gliding. Common causes of joint pain include inflammation (pain and swelling), infection and injury.
What is an example of an amphiarthrosis joint?
Amphiarthrosis. An amphiarthrosis is a joint that has limited mobility. An example of this type of joint is the cartilaginous joint that unites the bodies of adjacent vertebrae. Filling the gap between the vertebrae is a thick pad of fibrocartilage called an intervertebral disc (Figure 9.3).
Is the elbow amphiarthrosis?
A uniaxial diarthrosis, such as the elbow, is a joint that only allows for movement within a single anatomical plane.
What are the 4 types of synarthroses?
joints. Synarthroses are divided into three classes: fibrous, symphysis, and cartilaginous.
What is it synarthrosis 4 types of synarthroses?
A synarthrosis is a type of joint which allows no movement under normal conditions. Sutures and gomphoses are both synarthroses. Joints which allow more movement are called amphiarthroses or diarthroses. Syndesmoses joints are considered to be amphiarthrotic, because they allow a small amount of movement.
What is an example of a Synarthrotic joint?
A synarthrosis is an immobile or nearly immobile joint. An example is the manubriosternal joint or the joints between the skull bones surrounding the brain.
What are the four types of immovable joints?
There are three types of immovable joints: sutures, syndesmosis, and gomphosis.
Synarthrosis | definition of synarthrosis by Medical dictionary
joint [joint] the site of the junction or union of two or more bones of the body; its primary function is to provide motion and flexibility to the frame of the body. Some are immovable, such as the sutures where segments of bone are fused together in the skull. Others, such as those between the vertebrae, are gliding joints and have limited motion ...
What is an amphiarthrosis joint?
An amphiarthrosis is a joint that has limited mobility. An example of this type of joint is the cartilaginous joint that unites the bodies of adjacent vertebrae. Filling the gap between the vertebrae is a thick pad of fibrocartilage called an intervertebral disc ( [link] ). Each intervertebral disc strongly unites the vertebrae but still allows for a limited amount of movement between them. However, the small movements available between adjacent vertebrae can sum together along the length of the vertebral column to provide for large ranges of body movements.
What is the classification of a joint?
The functional classification of joints is determined by the amount of mobility found between the adjacent bones. Joints are thus functionally classified as a synarthrosis or immobile joint, an amphiarthrosis or slightly moveable joint, or as a diarthrosis, which is a freely moveable joint (arthroun = “to fasten by a joint”). Depending on their location, fibrous joints may be functionally classified as a synarthrosis (immobile joint) or an amphiarthrosis (slightly mobile joint). Cartilaginous joints are also functionally classified as either a synarthrosis or an amphiarthrosis joint. All synovial joints are functionally classified as a diarthrosis joint.
What is a freely mobile joint?
A freely mobile joint is classified as a diarthrosis. These types of joints include all synovial joints of the body, which provide the majority of body movements. Most diarthrotic joints are found in the appendicular skeleton and thus give the limbs a wide range of motion. These joints are divided into three categories, based on the number of axes of motion provided by each. An axis in anatomy is described as the movements in reference to the three anatomical planes: transverse, frontal, and sagittal. Thus, diarthroses are classified as uniaxial (for movement in one plane), biaxial (for movement in two planes), or multiaxial joints (for movement in all three anatomical planes).
Where is the condylar joint located?
condylar joint ( condyloid joint) one in which an ovoid head of one bone moves in an elliptical cavity of another, permitting all movements except axial rotation; this type is found at the wrist, connecting the radius and carpal bones, and at the base of the index finger. See illustration. diarthrodial joint synovial joint.
What is the sacroiliac joint?
sacroiliac jointthe joint between the sacrum and ilium in the lower back; see also sacroiliac joint.
What is a polyaxial joint?
Called also polyaxial or spheroidal joint. bicondylar joint a condylar joint with a meniscus between the articular surfaces, as in the temporomandibular joint. cartilaginous joint a type of synarthrosis in which the bones are united by cartilage, providing slight flexible movement; the two types are synchondrosis and symphysis. ...
What is ball and socket joint?
ball-and-socket joint a synovial joint in which the rounded or spheroidal surface of one bone (the “ball”) moves within a cup-shaped depression (the “socket”) on another bone, allowing greater freedom of movement than any other type of joint. See illustration. Called also polyaxial or spheroidal joint.
Which type of joint is a synovial joint that is flat or slightly curved?
gliding jointa synovial jointin which the opposed surfaces are flat or only slightly curved, so that the bones slide against each other in a simple and limited way. The intervertebral joints are this type, and many of the small bones of the wrist and ankle also meet in gliding joints. Called also arthrodial jointand plane joint.
What are the five types of joints?
The majority of the body's joints are of this type. They are divided into five types according to structure and motion: ball and socket, gliding, saddle, hinge, and pivot. Joints. trochoid joint pivot joint.
What is the joint between the femur, patella, and tibia?
knee joint the compound joint between the femur, patella, and tibia. pivot joint a synovial joint in which one bone pivots within a bony or an osseoligamentous ring, allowing only rotary movement; an example is the joint between the first and second cervical vertebrae (the atlas and axis). See illustration.