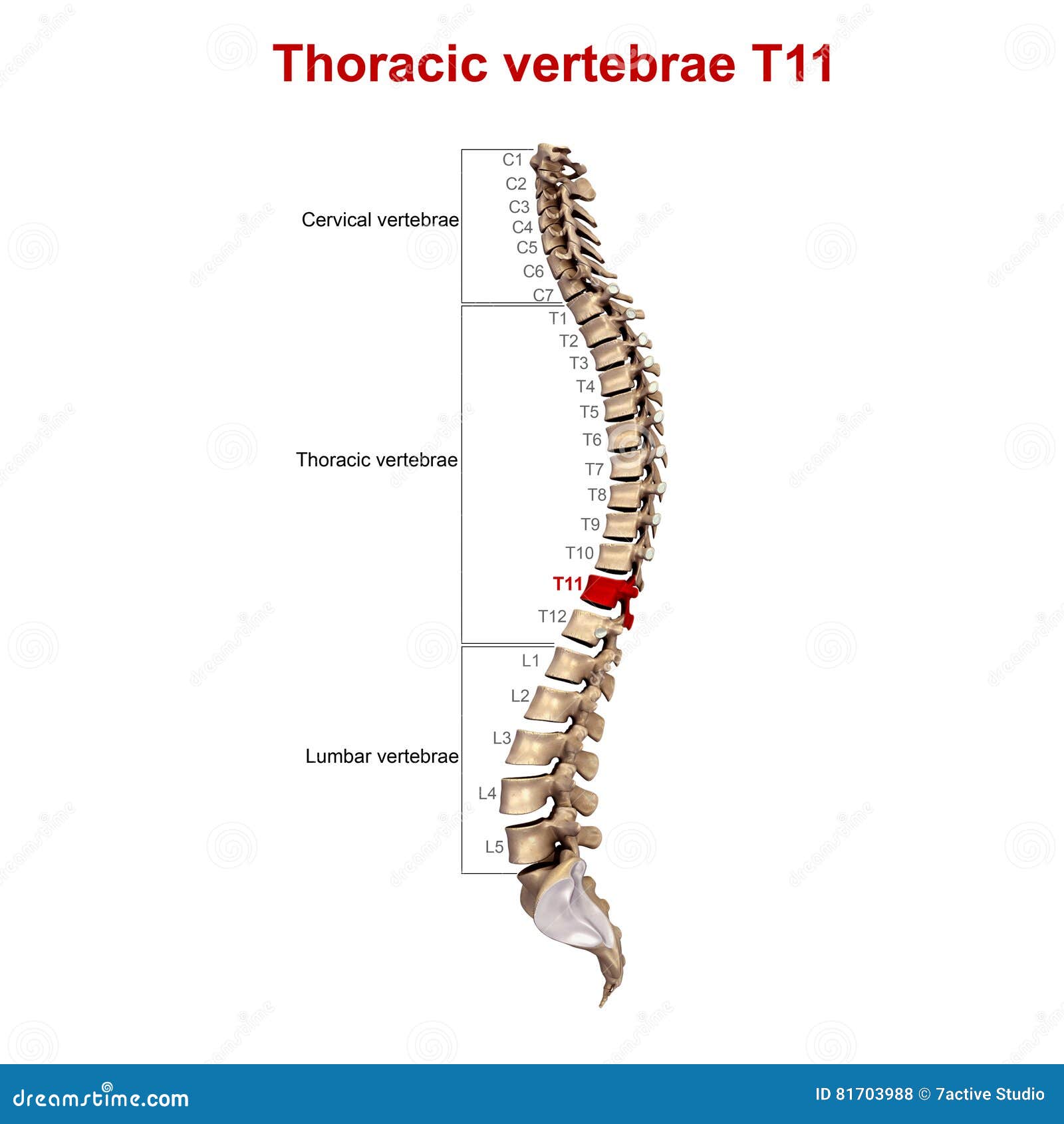
The eleventh thoracic vertebra (T11) is located near the bottom of the thoracic spine. Generally, the spinal bones are larger and heavier the further down they are located. This helps each vertebra to support the weight of the vertebrae above it, as well as the weight of the skull and brain.
Where is T11 located?
The eleventh thoracic vertebra (T11) is located near the bottom of the thoracic spine. Like all of its spinal counterparts, T11 protects the spinal cord by encasing it in bone. The T11 vertebra articulates into the rib bones, but they are not designated as true ribs, since they do not connect to the chest's sternum.
What does the T11 vertebra control?
What does t11 nerve control? Like all of its spinal counterparts, T11 protects the spinal cord by encasing it in bone. The T11 vertebra articulates into the rib bones, but they are not designated as true ribs, since they do not connect to the chest's sternum.
What is T11 wood siding?
What is t11 wood? T1-11 is an exterior wood siding product made from plywood, wood composite or oriented strand board, which is a layered board made of compressed wood chips. If treated with chemicals that fight decay and rot, the siding will be noted as a treated wood siding product—an important requirement for outdoor use.
Where is T12 spine?
The thoracic region of your spinal cord is divided into 12 segments that innervate the muscles in your trunk. T12 spinal cord injury patients generally have full function in their upper limbs and trunk. The T12 nerve roots innervate the very lower abdominal muscles.

What part of the body does T12 affect?
The T12 nerve roots innervate the very lower abdominal muscles. Therefore, individuals with T12 SCIs will focus on rehabilitation for the lower half of their body. Your spinal cord relays messages between your brain and body.
What is a T11 and T12 fracture?
Thoracic Compression Fracture Definition Compression fractures of the spine usually occur at the bottom part of the thoracic spine (T11 and T12) and the first vertebra of the lumbar spine (L1). Compression fractures of the spine generally occur from too much pressure on the vertebral body.
Where is T11 in your spine?
The T11 is one of the two lowest vertebrae in your spinal thoracic region. Like the other thoracic vertebrae, they are attached to your ribcage, which helps to protect them from direct harm, though they can be subject to damage from compression fractures.
What does T12 spine control?
The region of your spinal cord protected by this vertebra controls your abdominal muscles, lower back, stability and support. Unfortunately, pain from a T12 injury can be tricky to diagnose as it can radiate to other areas of your body and not be centered where the injury actually is.
Can you walk with a T12 fracture?
All the patients with L1 fractures and 70.9% of the patients with T12 fractures were able to walk independently with or without walking aids, but unfortunately, all the patients with T10 and T11 fractures didn't regain the walking ability even 12 months after surgery.
How long does a fractured T12 vertebrae take to heal?
A spinal fracture takes between six and 12 weeks to heal. During the healing process, spinal bones don't return to their normal shape. They heal in their new compressed shape.
What nerves does T11 and T12 control?
At the T1 through T11 levels, the ventral ramus eventually becomes an intercostal nerve that travels along the same path as the ribs (specifically between the innermost and internal intercostal muscles that connect adjacent ribs). At T12, the ventral ramus becomes a subcostal nerve that travels beneath the twelfth rib.
Is a T12 fracture serious?
This is the most severe type of spinal fracture because it can result in compressing the nerves, leading to neurological complications.
What does a fractured T11 feel like?
If the fracture is caused by a sudden, forceful injury, you will probably feel severe pain in your back, legs, and arms. You might also feel weakness or numbness in these areas if the fracture injures the nerves of the spine.
What does the T11 nerve control?
T-1 through T-5 nerves affect muscles, upper chest, mid-back and abdominal muscles. These nerves and muscles help control the rib cage, lungs, diaphragm and muscles that help you breathe.
How do you sleep with a T12 fracture?
Sleep on your back with a pillow under your knees. This will decrease pressure on your back. You may also sleep on your side with 1 or both of your knees bent and a pillow between them. It may also be helpful to sleep on your stomach with a pillow under you at waist level.
Can a T12 fracture cause paralysis?
Thoracic spinal cord injury T1-T12 Thoracic injuries can cause paralysis or weakness of the legs (paraplegia) along with loss of physical sensation, bowel, bladder, and sexual dysfunction. In most cases, arms and hands are not affected.
Is a T12 fracture serious?
This is the most severe type of spinal fracture because it can result in compressing the nerves, leading to neurological complications.
What can be done for a T12 compression fracture?
Treatment of compression fractures may include medicine, rest, a back brace, or physical therapy. Sometimes, surgery is needed. The risk of new fractures can be reduced by doing regular weight-bearing exercises that increase strength, and balance exercises that reduce the risk for falls.
Can a T12 fracture cause paralysis?
Thoracic spinal cord injury T1-T12 Thoracic injuries can cause paralysis or weakness of the legs (paraplegia) along with loss of physical sensation, bowel, bladder, and sexual dysfunction. In most cases, arms and hands are not affected.
Is a fractured vertebrae the same as a broken back?
Overview. A “broken back” is another term to describe a spinal fracture — a break in one or more vertebrae, the 33 bones that form your backbone and protect your spinal cord. A broken back injury can be worrying, but it doesn't necessarily mean that there's damage to the spinal cord.
What is the role of T11 in the spinal cord?
Like all of its spinal counterparts, T11 protects the spinal cord by encasing it in bone .
How many vertebrae are in the thoracic spine?
T11. The thoracic spinal vertebrae consist of 12 total vertebrae and are located between the cervical vertebrae (which begin at the base of the skull) and the lumbar spinal vertebrae.
Is the T11 a spinous process?
Also, unlike other thoracic vertebrae, T11 features a spinous process that is relatively short, and it tends to be horizontal, featuring only a slight curvature. The eleventh thoracic spinal nerve extends from beneath the vertebra. Last medically reviewed on January 20, 2018.
Where is the T10 Vertebra Located?
The T10 vertebrae location can be found between the T9 and T11 vertebrae within the torso.
Why are T9 and T12 considered transitional vertebrae?
Sections T9 - T12 are known as transitional vertebrae because of their proximity and similarity to the lumbar vertebrae. The spinal cord and nerves’ correlation to these levels, along with the rest of the thoracic spine, aid in controlling the trunk of the body. The completeness of the spinal cord damage will determine how severe an injury truly is ...
What is the T9 Vertebra?
The ninth thoracic vertebra is also known as T9. It is a segment of the thoracic level of the spinal column and is the first of the four transition vertebrae. The T9 vertebra directly communicates to the adrenal glands through nerves.
Why do thoracic vertebrae fracture?
Thoracic Vertebrae Fractures. Thoracic vertebrae fractures are usually due to accidents with hard falls and physical trauma, or conditions such as osteoporosis. This injury occurs when the vertebrae spine collapses in its weakened state due to pressure.
What is the eleventh thoracic vertebra?
The eleventh thoracic vertebra (T11) is one of the last thoracic spinal vertebrae. It’s the first of the transitional vertebra that is not attached to a true rib, meaning a rib bone that connects to the chest’s sternum.
What are the symptoms of a T11 injury?
A T11 injury will demonstrate itself by severe back and leg pain. If the nerves in the T11 vertebrae are damaged, common symptoms include weakness and numbness in these areas.
What happens if you get a T10 vertebrae?
An injury to the T10 vertebra will likely result in a limited or complete loss of use of the lower abdomen muscles, as well as the buttocks, legs, and feet. A minor injury will result in minor symptoms such as weakness, numbness, as well as partial or complete lack of muscle control over only one side of the body. Severe damage to this vertebra can result in complete paraplegia .
What are the joints in the T11 and T12?
The joints formed between T11 and T12 are classified as planar joints , and allow the bones to glide along a plane relative to one another. At the bottom of T12, a pair of inferior articular processes descends to meet the superior articular processes of the L1 vertebra.
Where is the T12 located?
The T12 vertebra is located in the spinal column of the thoracic (or trunk) region inferior to the T11 vertebra and superior to the first lumbar (L1) vertebra. Continue Scrolling To Read More Below...
What is the name of the joint that forms a joint with the 12th pair of ribs?
A pair of strong pedicles extends posteriorly from the vertebral body to begin the arch. Each pedicle contains a smooth, oval-shaped articular facet that forms a joint with the 12th pair of ribs. Posterior to the pedicles are the transverse processes that extend laterally from the vertebral arch.
What are the two pairs of articular processes that extend vertically from the vertebral arch?
Extending vertically from the vertebral arch are two pairs of articular processes that form joints with the neighboring vertebra and help to stabilize the spine. The superior articular processes extend superiorly to meet the inferior articular processes of the T11 vertebra.
What is inside the vertebral arch?
Inside the vertebral arch is a hollow vertebral foramen that contains the spinal cord and spinal nerves. The strong bony tissue of the vertebral arch protects the delicate nervous tissue as it passes through the vertebral canal.
Which process is a thin rectangle of bone that provides muscle attachment points for the muscles that stabilize, flex, extend?
The thin laminae continue the vertebral arch posteriorly from the transverse processes until they unite at the body’s midline to form the spinous process. The spinous process extends posteriorly toward the surface of the back and can be felt through the skin. It is a thin rectangle of bone that provides muscle attachment points for the muscles that stabilize, flex, extend, and rotate the spine. The spinous process is considerably shorter, straighter, and thicker in T12 than it is in the superior thoracic vertebrae, closely resembling the spinous process of the lumbar vertebrae below.
Which thoracic vertebra is the strongest?
The twelfth thoracic vertebra (or the T12 vertebra) is the largest and most inferior of the thoracic vertebrae. T12 bears the most weight of any thoracic vertebra, making it the strongest thoracic vertebra, but also the most susceptible to stress-related injuries. In many ways, the T12 is a hybrid vertebra with the anatomical features ...
Where are the thoracic vertebrae located?
The thoracic vertebrae are located in the middle section of the vertebral column, specifically inferior to the cervical vertebrae and superior to the lumbar vertebrae. These vertebrae span the large majority of the chest cavity area.
What is the body of a thoracic vertebra?
The body of a thoracic vertebra is somewhat “heart-shaped,” and is larger than the cervical but smaller than the lumbar vertebrae in size. The body also has small, smooth, and somewhat concave costal facets for the attachment of the ribs. Ribs are generally inserted between two vertebrae, such that each vertebra contributes to articulating with half of the articular surface. Each vertebra therefore has a pair of superior articular facets that face posteriorly and a pair of inferior articulating facets that face anteriorly (except for T12). This means that the rib will articulate with the inferior costal facet of the upper vertebrae and the superior costal facet of the lower vertebrae. Transverse processes arise from the arch found behind he superior articular processes and pedicles, and are thick and strong with a clubbed end and a small concave surface for the articulation with the tubercle of a rib. These processes are directed obliquely backward towards the spinous process and lateralward.
How many vertebrae are there in the thoracic spine?
Two muscles also interact with those twelve vertebrae, these being the spinalis and longissimus.
How long is the reading time for the thoracic vertebrae?
Last reviewed: May 31, 2021. Reading time: 15 minutes. The twelve thoracic vertebrae are strong bones that are located in the middle of the vertebral column, sandwhiched between the cervical ones above and the lumbar vertebrae below. Like typical vertebrae, they are separated by intervertebral discs. However, they are various anatomical features ...
What is the difference between vertebrae and vertebrae?
The vertebrae are separated by intervertebral discs of fibrocartilage, which are flexible cartilage discs located between the bodies of two adjacent vertebrae that allow movement in the spine and have a shock absorbing or cushioning function as well. An intervertebral disc consists of an inner gelatinous nucleus pulposus surrounded by a ring of fibrocartilage, the annulus fibrosus.
Why do thoracic vertebrae increase in size?
Thoracic vertebrae increase in size as they descend towards the lumbar vertebrae; this is because the lower vertebrae must be able to support more of the body’s weight when a person is standing due to the effects of gravity. To summarize, the main anatomical components of a thoracic vertebra are: Body. Spinous process.
How many discs are there in the human body?
In total, the adult human body typically has 23 discs, with the first found between cervical vertebrae 2 and 3, and the last one is found between the lumbar vertebra and the sacrum.
Where is the spinal cord located?
The spinal cord is the main bundle of nerves that runs from the base of the brain all the way down through the cervical spine and thoracic spine before splitting into a bundle of nerve roots (cauda equina) in the lumbar spine. The brain exchanges electrical signals with the rest of the body via the spinal cord.
How many nerve roots are there in the thoracic spine?
Thoracic Spinal Nerves. The thoracic spine has 12 nerve roots (T1 to T12) on each side of the spine that branch from the spinal cord and control motor and sensory signals mostly for the upper back, chest, and abdomen. The thoracic spine (highlighted) spans the upper and mid-back. It includes twelve vertebrae named T1 through T12.
How many thoracic nerves are there?
Each thoracic spinal nerve is named for the vertebra above it. For example, the T3 nerve root runs between the T3 vertebra and T4 vertebra. There are 12 thoracic spinal nerve root pairs (two at each thoracic vertebral level), starting at vertebral level T1-T2 and going down to T12-L1.
What nerves feed into the ventral ramus?
After branching from the spinal cord and traveling through the foramen, a thoracic nerve root branches into two different nerve bundles that feed into the nerves at the front (ventral ramus) and back (dorsal ramus) of the body. At the T1 through T11 levels, the ventral ramus eventually becomes an intercostal nerve that travels along ...
What is spinal cord injury?
Spinal cord injuries are usually classified based on the spinal nerve root level where function is reduced or completely lost. For example, a T6 spinal cord injury would impair or lose function at the T6 nerve root level and below.
What nerve travels between the ribs?
At the T1 through T11 levels, the ventral ramus eventually becomes an intercostal nerve that travels along the same path as the ribs (specifically between the innermost and internal intercostal muscles that connect adjacent ribs). At T12, the ventral ramus becomes a subcostal nerve that travels beneath the twelfth rib.
What is the hole in the spinal canal called?
Each thoracic nerve root exits the spinal canal through a bony hole, called an intervertebral foramen. This bony hole is formed by two adjacent vertebrae, and its size and shape can slightly shift as the vertebrae move.
How many segments are there in the T12?
Photo Credit: Ralf Stephan. The thoracic region of your spinal cord is divided into 12 segments that innervate the muscles in your trunk. T12 spinal cord injury patients generally have full function in their upper limbs and trunk. The T12 nerve roots innervate the very lower abdominal muscles. Therefore, individuals with T12 SCIs will focus on ...
What is the treatment for T12 spinal cord injury?
Rehabilitation after a T12 spinal cord injury primarily consists of physical and occupational therapy. These rehabilitative therapies will assess your functional abilities and strive towards maximizing your mobility and independence.
What are the functions of T12?
T12 Spinal Cord Injury: Functions Affected and Recovery Outlook. A T12 spinal cord injury affects lower body functions such as walking and bowel and bladder functions. Fortunately, individuals with T12 spinal cord injuries generally have normal, full functioning of their upper bodies, which allows a great deal of independence.
What is the function of the spinal cord?
Your spinal cord relays messages between your brain and body. After a spinal cord injury, these messages may not be able to make a connection past the site of injury.
What happens to the more spared neural pathways at the site of injury?
The more spared neural pathways there are at the site of injury, the more functions will be preserved.
Is spinal cord injury rehabilitation easy?
Incomplete spinal cord injury rehabilitation isn’t easy, but it’s possible to improve your mobility with targeted therapy.
Can you forget to change positions after spinal cord injury?
However, after a spinal cord injury, you may not be able to feel these sensations, which makes it easier to forget to change positions. Prolonged pressure on the body can cut off circulation, causing tissues to become inflamed and skin to gradually break down, with risk of infection.
