What are the four lobes of the temporal lobe?
Temporal Lobe The brains of all mammals, including people, contain four lobes in the cortex, including the occipital, parietal, temporal, and frontal lobes. Located just beneath the lateral fissure and crossing both fissures of the brain is the temporal lobe. This vital structure helps process sensory input, including pain and auditory stimuli.
What is the function of the temporal lobe Quizlet?
Temporal Lobe: Function, Location and Structure The temporal lobe, which crosses both hemispheres of the brain, helps process sensory input, including pain and auditory stimuli.
What is the difference between the occipital and temporal lobe?
The occipital lobe sits just behind it. These structures also span other lobes. For example, Wernicke’s area extends into the parietal lobe, and Broca’s area is part of the frontal lobe. The function of the temporal lobe centers around auditory stimuli, memory, and emotion. The temporal lobe contains the primary auditory complex.
What are the areas associated with vision in the temporal lobe?
The areas associated with vision in the temporal lobe interpret the meaning of visual stimuli and establish object recognition. The ventral part of the temporal cortices appear to be involved in high-level visual processing of complex stimuli such as faces ( fusiform gyrus) and scenes ( parahippocampal gyrus ).
See more
What are three functions of the temporal lobe?
The main functions of the temporal lobes include understanding language, memory acquisition, face recognition, object recognition, perception and processing auditory information. Alike to the other lobes of the brain, there are left and right temporal lobes, situated in both hemispheres of the cerebrum.
What is located in the temporal lobe of the brain?
The temporal lobe is involved in primary auditory perception, such as hearing, and holds the primary auditory cortex. The primary auditory cortex receives sensory information from the ears and secondary areas process the information into meaningful units such as speech and words.
What are the symptoms of temporal lobe damage?
Kolb & Wishaw (1990) have identified eight principle symptoms of temporal lobe damage: 1) disturbance of auditory sensation and perception, 2) disturbance of selective attention of auditory and visual input, 3) disorders of visual perception, 4) impaired organization and categorization of verbal material, 5) ...
What would happen if the temporal lobe was damaged?
The temporal lobe is responsible for interpreting and assigning meaning to various sounds. As a result, damage to the left temporal lobe often leads to problems understanding language, also known as receptive aphasia or Wernicke's aphasia.
What causes damage to temporal lobe?
As is the case with other traumatic brain injuries, damage to the temporal lobe most often occurs as a result of vehicle crashes, falls, and firearms. Taking steps to prevent these injuries could save you or a loved one a lifetime of the added stress that accompanies traumatic brain injuries.
What is the key function of the temporal lobe?
The temporal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cortex. It is primarily responsible for interpreting sounds from the ears and plays a significant role in recognizing and using language. The temporal lobe also helps with object recognition and interacts with other structures to create new and long term memories.
What would a tumor on the temporal lobe affect?
Location of the tumour temporal lobe – may cause memory loss (amnesia) language problems (aphasia), and seizures. parietal lobe – may cause aphasia, numbness or weakness in one side of the body, and co-ordination problems (dyspraxia), such as difficulty dressing.
Can you live without temporal lobe?
Can You Live Without a Temporal Lobe? Theoretically speaking, you can live without your temporal lobe, but it will in most cases cause a disruption in your daily life. There is a type of surgery called a lobectomy, in which a part of a person's temporal lobe is removed.
How do I keep my temporal lobe healthy?
4 Ways to Improve Learning and MemoryRhythmic Movement. The temporal lobes are involved with processing and producing rhythms, chanting, dancing, and other forms of rhythmic movements can be healing. ... Listen to Healing Music. Listen to a lot of great music. ... Use Toning and Humming to Tune Up Your Brain.
What is temporal lobe syndrome?
Temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE) is epilepsy that starts in the temporal lobe area of your brain. You have two temporal lobes, one on each side of your head behind your temples (by your ears and in alignment with your eyes). TLE is the most common localized (also called “focal”) type of epilepsy.
Is the thalamus in the temporal lobe?
No. It is located above the brainstem and below the thalamus.
Is the hippocampus in the temporal lobe?
Hippocampus is a complex brain structure embedded deep into temporal lobe. It has a major role in learning and memory. It is a plastic and vulnerable structure that gets damaged by a variety of stimuli.
What would a tumor on the temporal lobe affect?
Location of the tumour temporal lobe – may cause memory loss (amnesia) language problems (aphasia), and seizures. parietal lobe – may cause aphasia, numbness or weakness in one side of the body, and co-ordination problems (dyspraxia), such as difficulty dressing.
Is the amygdala part of the temporal lobe?
The amygdala comprises several nuclei on the medial aspect of the temporal lobe, mostly anterior the hippocampus and indenting the tip of the temporal horn. The amygdala receives input from the olfactory bulb and from association cortex for other modalities of sensation.
What are the temporal lobes?
Essentially, the temporal lobes interact with, and depend upon input, which can be from other brain regions, as well as from sensory input from the environment. The temporal lobes can convert sounds into visual images in the mind. We also would not be able to understand someone talking to us without the use of our temporal lobes helping us to make sense of language.
What is the outer surface of the temporal lobes called?
The outer surface of the temporal lobes is called the neocortex. There are many substructures within the temporal lobes which have specific functions. The most inner part of the temporal lobes, is the older part of the cortex, also known as the limbic system, which includes the hippocampus and the amygdala . The main functions of the temporal lobes ...
What is the test for temporal lobe function?
There are also some common tests which are used to test for temporal lobe function. There is the Rey-Complex Figure which is a test for visual memory. The Wechsler Memory Scale- Revised is also a common test used to assess the verbal memory of an individual.
Why is temporal lobe damage common?
A common cause of temporal lobe damage is epilepsy, so a discussion of previous seizure activity can be discussed. A referral to a neuropsychologist may be necessary to enable an understanding of the precise nature of the problem and to help with managing the condition.
How to diagnose temporal lobe damage?
In order to diagnosis damage to the temporal lobes, a thorough history of the symptoms being experienced need to be investigated. This assessment can be accompanied by someone who knows the patient well and has witnessed the problems at hand.
Where is the gyrus located?
The superior temporal gyrus is situated at the top of the temporal lobes, located somewhat above the ears. The superior temporal gyrus is an area of the temporal lobe which contains other areas with specialized functions. Some areas of the superior temporal gyrus are vital in ...
Where is the auditory cortex located?
The auditory cortex, the main area responsible for processing auditory information, is located within the temporal lobe. The auditory cortex is a part of the superior temporal gyrus which essentially receives input from the ears and analyses it.
Where is the temporal lobe?
The temporal lobe sits at the bottom middle portion of the brain, just behind the temples within the skull, which is also where it gets its name. It also sits above the brain stem and cerebellum. The frontal and parietal lobes are above the temporal lobe. The occipital lobe sits just behind it.
What are the structures of the temporal lobe?
Key structures that are part of the temporal lobe include: 1 Wernicke’s area 2 Broca’s area 3 limbic system
What is the limbic system?
The limbic system is involved with motivation, emotion, learning, and memory. While the limbic system interacts with other areas of the brain, it works directly with the temporal lobe to influence the components of the limbic system. The limbic system itself contains important structures, including the amygdala and hippocampus.
What is the term for a condition that affects the front and temporal lobe?
Pick’s disease. Pick’s disease, or frontotemporal dementia, is a less common form of dementia, that damage or atrophy in the front and temporal lobe causes. The condition may include changes to states such as mood, attention levels, or irritated or aggressive behaviors.
Where is schizophrenia found in the brain?
There is a link between schizophrenia and deficit or damage in the temporal lobe, within the primary auditory cortex in the left temporal lobe.
Which lobe of the brain is responsible for interpreting information in the form of sounds from the ears?
The temporal lobe contains the primary auditory complex. This is the first area responsible for interpreting information in the form of sounds from the ears. The temporal lobe receives different frequencies, sounds, and pitches from the ears, and gives them meaning.
Which lobe is the limbic system?
Key structures that are part of the temporal lobe include: Wernicke’s area. Broca’s area. limbic system. These structures also span other lobes. For example, Wernicke’s area extends into the parietal lobe, and Broca’s area is part of the frontal lobe.
Where is the temporal lobe located?
Temporal lobe Location- The temporal lobe is positioned toward the base of the center of the cortex, just behind the temples. Though every temporal lobe has an alike structure, the experiences presented in each person’s temporal lobe are uniquely their individual.
What is the temporal lobe?
This function includes understanding sounds, empowering meaning to those sounds, and recalling sounds. Paramount of the auditory functioning of the temporal lobe is processed within the superior temporal gyrus, a temporal lobe arrangement that takes sound input quickly from the ear. Remarkable of its additional functions comprise:
Why is temporal lobe damage important?
If temporal lobe damage of the brain can hold global outcomes for essentially every bodily function considering much of what we do depends on emotions and the sensory input.
Which lobe of the brain is responsible for automatic emotional responses?
The limbic lobe of the brain truly converges with several lobes but combines directly with the temporal lobe to control the limbic system, including automatic emotional responses such as the fight-or-flight response. The limbic lobe is addressing key memory, learning, and attention processing structures such as the amygdala and the hippocampus.
Which lobe of the brain is responsible for long term memory?
The temporal lobe consists of edifices that are essential for declarative or long-term memory. Declarative or explicit memory is understanding memory classified into semantic memory (facts) and episodic memory (events). The temporal lobe is important for long-term memory to involve the hippocampus, accompanying the surrounding hippocampal region consisting of the perirhinal, parahippocampal, and the entorhinal neocortical regions. The hippocampus is significant for memory formation, and the encompassing medial temporal cortex is currently theorized to be significant for memory storage. The prefrontal and visual cortices are similarly committed in explicit memory.
What is the cause of seizures in the temporal lobe?
Temporal lobe epilepsy cause seizures that produce uncontrolled electrical activity in the brain that can lead to seizures. Damage to Broca’s region does prevent the ability to speak, while injury to Wernicke’s area can prevent the ability to understand speech.
Which lobe is responsible for the generation of long-term memories?
The generation of visual memories, including long-term memories. In combination with the amygdala and hippocampus, the temporal lobe is important for the formation of conscious memories.
What is the temporal lobe?
The temporal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The temporal lobe is located beneath the lateral fissure on both cerebral hemispheres of the mammalian brain. The temporal lobe is involved in processing sensory input into derived meanings for the appropriate retention of visual memory, ...
What is temporal lobe epilepsy?
Temporal lobe epilepsy is a chronic neurological condition characterized by recurrent seizures; symptoms include a variety of sensory (visual, auditory, olfactory, and gustation) hallucinations, as well as an inability to process semantic and episodic memories.
What lobe is affected by savant syndrome?
Damage specifically to the anterior portion of the left temporal lobe can cause savant syndrome.
What is the most common symptom of inferior temporal lobe damage?
The most common symptom of inferior temporal lobe damage is visual agnosia, which involves impairment in the identification of familiar objects. Another less common type of inferior temporal lobe damage is prosopagnosia which is an impairment in the recognition of faces and distinction of unique individual facial features.
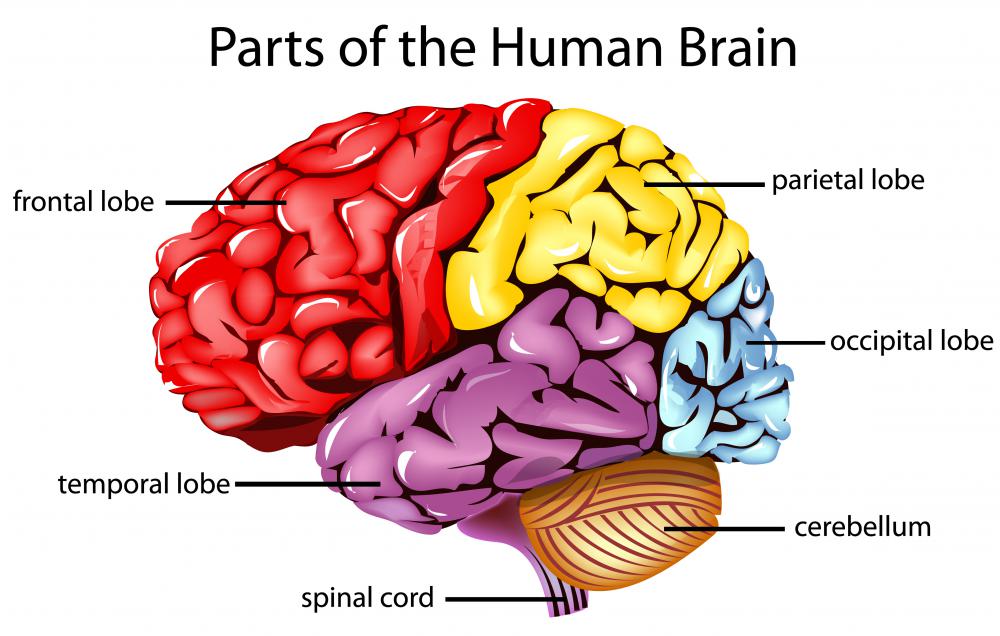
What are the four lobes of the brain?
One of the four lobes of the mammalian brain. Temporal lobe . Frontal lobe. Temporal lobe. Parietal lobe. Occipital. lobe. Lobes of the human brain (temporal lobe is shown in green) Section of brain showing upper surface of temporal lobe.
Which lobe of the brain is responsible for language comprehension?
The temporal lobe holds the primary auditory cortex, which is important for the processing of semantics in both language and vision in humans. Wernicke's area, which spans the region between temporal and parietal lobes, plays a key role (in tandem with Broca's area in the frontal lobe) in language comprehension, whether spoken language or signed language. FMRI imaging shows these portions of the brain are activated by signed or spoken languages. These areas of the brain are active in children's language acquisition whether accessed via hearing a spoken language, watching a signed language, or via hand-over-hand tactile versions of a signed language
Which lobe of the brain is responsible for processing auditory information?
Adjacent areas in the superior, posterior, and lateral parts of the temporal lobes are involved in high-level auditory processing. The temporal lobe is involved in primary auditory perception, such as hearing, and holds the primary auditory cortex. The primary auditory cortex receives sensory information from the ears and secondary areas process the information into meaningful units such as speech and words. The superior temporal gyrus includes an area (within the lateral fissure) where auditory signals from the cochlea first reach the cerebral cortex and are processed by the primary auditory cortex in the left temporal lobe.
What is the temporal lobe?
The temporal lobe subdivides further into the superior temporal lobe, the middle temporal lobe, and the inferior temporal lobe. It houses several critical brain structures including the hippocampus and the amygdala. The temporal lobe of the brain is often referred to as the neocortex. It forms the cerebral cortex in conjunction with ...
How to understand temporal lobe?
In order to fully comprehend the temporal lobe, it is best to analyze it also through its functional connectivity, not just its gross structure. The idea that certain parts of the brain perform certain functions is called localizationism. Localizationism does not always correspond to predictions of functions. Connections define functions. On the other hand, without understanding function, connections of structures are useless. Hence, in order to see the whole picture, structure, connections, and functions must be correlated. [1][2]
What are the three areas of the temporal gyrus?
Temporal area 1 anterior (TE1a), middle (TE1m) and posterior (TE1p) are found in the MTG. All three areas have functional connectivity to different parcellations of the frontal, temporal and parietal lobes. TE1a has additional functional connectivity to some STS areas, temporal gyrus ventral (TGv), entorhinal cortex (EC), and hippocampus. All three areas have white matter connections (structural connectivity) to "u" fibers of the occipitotemporal system and arcuate/SLF. TE1a has an additional white matter connection to inferior longitudinal fasciculus (ILF). These areas are primarily responsible for processing visual information, including working memory for short term visual maintenance of information. [3][5]
Where is the superior temporal gyrus located?
Superior temporal gyrus region 'a' (STGa) is found on the superior temporal gyrus at its anterior superior surface. It is functionally connected to different parcellations of the insula opercular region and temporal lobe. It has white matter connections (structural connectivity) to inferior longitudinal fasciculus and local parcellations. STG areas are functionally involved in perceptual and conceptual acoustic sound processing. [6]
Where is the area pres located?
Area PreS is located on the posterosuperior surface of the parahippocampal gyrus. It has functional connectivity to the hippocampus, numerous parcellations in the frontal lobe, parietal lobe and occipital lobe and local functional connectivity to PHA1 and PHA2. Area PreS has white matter connections to the cingulum, precuneus and occipital lobe, as well as EC and PeEc. Its function is mainly involved in spatial information processing. [3]
Where is the PHT located?
Area PHT is located on the subcentral gyrus and involves the operculum and Sylvian Fissure. It has functional connectivity to numerous parcellations in the frontal lobe, insula opercular area, temporal, parietal and occipital lobes. It has white matter connections to the arcuate/SLF. The part that lies on the posterior MTG is useful in conscious retrieval of conceptual knowledge while the anterior part is for automatic retrieval of semantic information. [3]
Which lobe has two social areas?
Social - two areas in the temporal lobe
Which lobe is the most anterior?
The frontal lobe forms the most anterior portion of the cerebral hemisphere and is separated from the parietal lobe posteriorly by the central sulcus, and from the temporal lobe posteroinferiorly by the lateral sulcus (Sylvian fissure). The most anterior portion of the frontal lobe is known as the frontal pole.
What is the anterior border of the parietal lobe?
The anterior border of the parietal lobe is demarcated by the central sulcus, and the posterior border is formed by an imaginary line that extends between the parietooccipital sulcus (superiorly) and the preoccipital notch (inferiorly). The inferior border is formed by the lateral sulcus (Sylvian fissure), while the superior boundary of the parietal lobe is formed by the medial longitudinal fissure that separates the two cerebral hemispheres.
How many lobes are there in the cerebral cortex?
The cerebral cortex is divided into six lobes: the frontal, temporal, parietal, occipital , insular and limbic lobes. Each lobe of the cerebrum exhibits characteristic surface features that each have their own functions. These lobes are not anatomically separated from one another by any barriers, but are physically continuous with each other, or interconnected via neural pathways in order to work together to process and synthesize information.
Which part of the brain is responsible for processing emotional information?
The most rostral portion of the frontal cortex is known as the prefrontal cortex, which encompasses the superior, middle and inferior frontal gyri of the frontal lobe. It plays a crucial role in the processing of intellectual and emotional information, including aggression, and facilitates judgement and decision-making.
Which lobe of the brain is the largest?
The frontal lobe is the largest lobe of the brain comprising almost one-third of the hemispheric surface. It lies largely in the anterior cranial fossa of the skull, leaning on the orbital plate of the frontal bone .
What are the three outpouchings of the neural tube?
Early on in development, the neural tube forms three outpouchings called the primary brain vesicles. The prosencephalon, mesencephalon, and rhombencephalon will form the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain, respectively. Shortly after these form, in the fifth week of gestation, the prosencephalon and rhombencephalon undergo further divisions, ...
What is the brain?
The brain is a complex organ with many layers and components that play their roles, in one way or another, in almost every function performed by the body. To complicate matters, an otherwise uniform-looking region can contain sub-regions responsible for performing vastly different functions.