
What is trigeminal neuralgia, and how is it treated?
Trigeminal neuralgia is a condition that causes episodes of stinging or shock-like pain in the face. It is caused by damage or pressure on the trigeminal nerve, which provides feeling to the face. Certain medications and surgical procedures can help to improve the pain of trigeminal neuralgia. PeopleImages/E+ via Getty Images.
Can people with trigeminal neuralgia drink coffee?
Trigeminal neuralgia is more common among women than men, and it is more likely to occur in people over 50. People with trigeminal neuralgia should avoid drinking coffee because coffee contains a lot of caffeine which will stimulate nerves and trigger arteriolar spasm, causing the deterioration of the disease. Besides, people with trigeminal neuralgia should avoid greasy or spicy foods, limit alcohol drinking and smoking.
What is the main cause of trigeminal neuralgia?
What causes trigeminal neuralgia? TN is associated with a variety of conditions. TN can be caused by a blood vessel pressing on the trigeminal nerve as it exits the brain stem. This compression causes the wearing away or damage to the protective coating around the nerve (the myelin sheath).
How rare is trigeminal neuralgia?
Trigeminal neuralgia is a rare neurological condition that causes chronic and severe facial pain. While an exact number is unknown, researchers estimate that between 10,000 to 15,000 new cases of TN are diagnosed every year. Not many physicians have experience diagnosing and treating the condition.
Where do you feel trigeminal nerve pain?
Trigeminal neuralgia usually affects one side of the face. In some cases it can affect both sides, although not usually at the same time. The pain can be in the teeth, lower jaw, upper jaw or cheek. Less commonly the pain can also be in the forehead or eye.
What parts of the body does the trigeminal nerve affect?
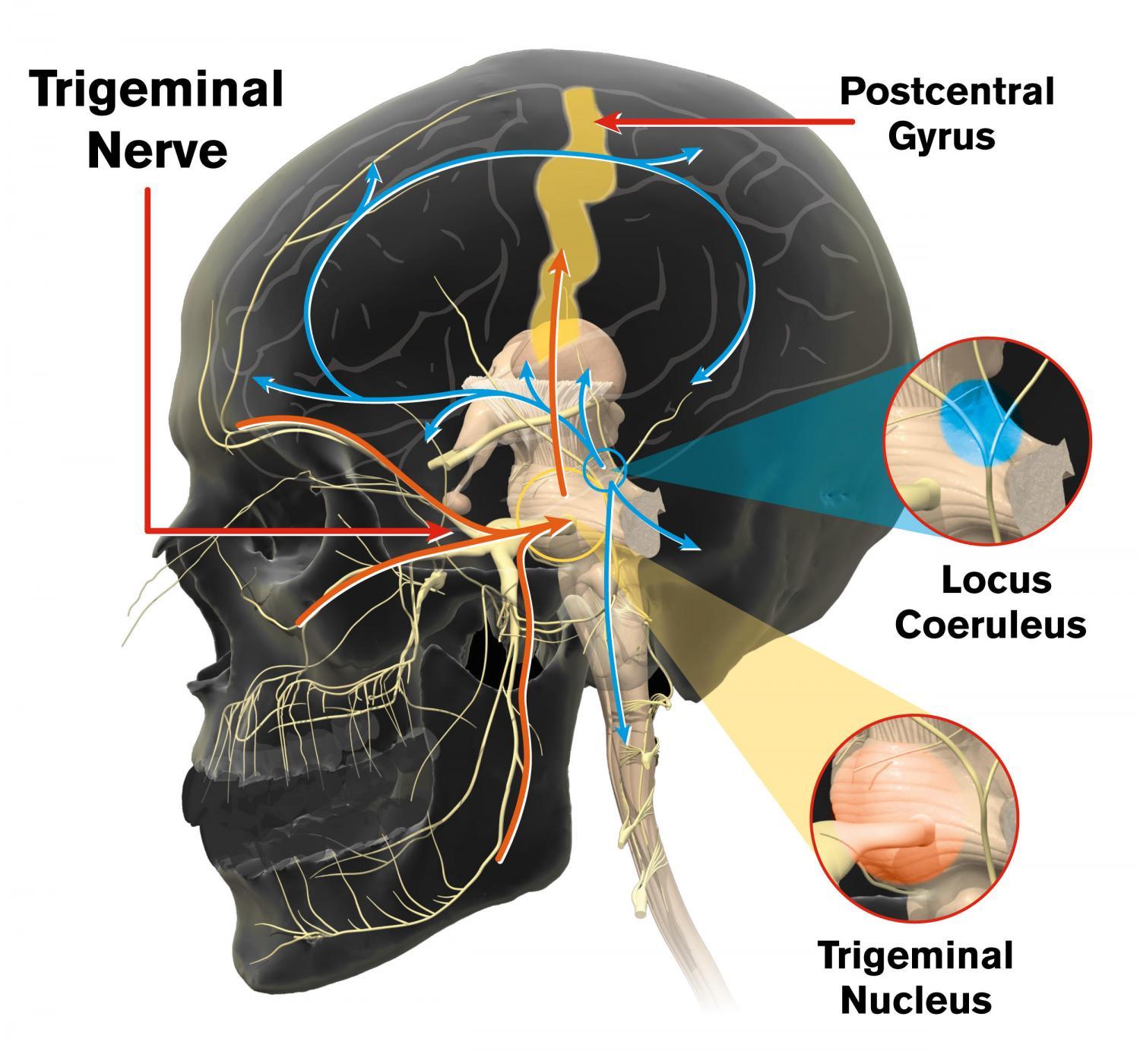
The trigeminal nerve is one of 12 pairs of nerves that are attached to the brain. The nerve has three branches that conduct sensations from the upper, middle, and lower portions of the face, as well as the oral cavity, to the brain.
Is the trigeminal nerve on the left or right?
The trigeminal nerve is one set of the cranial nerves in the head. It is the nerve responsible for providing sensation to the face. One trigeminal nerve runs to the right side of the head, while the other runs to the left.
What part of the brain does trigeminal neuralgia affect?
The exact cause of trigeminal neuralgia is not known, but it's often thought to be caused by compression of the trigeminal nerve, or by another medical condition that affects this nerve. The trigeminal nerve – also called the fifth cranial nerve – provides sensation to the face.
What can irritate the trigeminal nerve?
TriggersShaving.Touching your face.Eating.Drinking.Brushing your teeth.Talking.Putting on makeup.Breeze lightly blowing over your face.More items...•
Does brain MRI show trigeminal nerve?
Advanced MRI techniques are capable of demonstrating neurovascular compression with morphologic changes of the trigeminal nerve root. Facial and intraoral territories of innervation of the 3 trigeminal branches (ophthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular).
Can Covid vaccine trigger trigeminal neuralgia?
From the literature search, apart from our case, there are 2 additional cases of trigeminal neuralgia with COVID-19 vaccination.
How do I calm my trigeminal nerve?
To treat trigeminal neuralgia, your doctor usually will prescribe medications to lessen or block the pain signals sent to your brain. Anticonvulsants. Doctors usually prescribe carbamazepine (Tegretol, Carbatrol, others) for trigeminal neuralgia, and it's been shown to be effective in treating the condition.
How do you check trigeminal nerves at home?
1:413:03Cranial Nerve 5 | Trigeminal Nerve Assessment for PhysiotherapistsYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipPlace one index finger on the chin and tap it with a reflex hammer. Normally you would observeMorePlace one index finger on the chin and tap it with a reflex hammer. Normally you would observe slight closure on no reflex at all.
What does a neurosurgeon do for trigeminal neuralgia?
Surgical Management The surgical options for trigeminal neuralgia include peripheral nerve blocks or ablation, gasserian ganglion and retrogasserian ablative (needle) procedures, craniotomy followed by microvascular decompression (MVD), and stereotactic radiosurgery (Gamma Knife®).
What diseases cause trigeminal neuralgia?
Causes of Trigeminal Neuralgia Trigeminal neuralgia usually occurs spontaneously, but is sometimes associated with facial trauma or dental procedures. The condition may be caused by a blood vessel pressing against the trigeminal nerve, also known as vascular compression.
What is the best drug to take for trigeminal neuralgia?
The anti-convulsant drug most commonly prescribed for trigeminal neuralgia is carbamazepine (Tegretol), which can provide at least partial pain relief for up to 80 to 90 percent of patients. Other anti-convulsants prescribed frequently for trigeminal neuralgia include: Phenytoin (Dilantin)
What muscle is controlled by the trigeminal nerve?
The only branch of the trigeminal nerve that has a motor component in the mandibular nerve (V3). This branch supplies motor innervation to the facial muscles involved in mastication which include the masseter, temporalis muscle, and the lateral and medial pterygoids.
Does the trigeminal nerve affect the neck?
Pain in the head and neck is mediated by sensory (afferent) nerve fibers in the trigeminal nerve, glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves, and the upper cervical roots via the occipital nerves.
What does the trigeminal nerve detect?
In neuroanatomy, the trigeminal nerve (lit. triplet nerve), also known as the fifth cranial nerve, cranial nerve V, or simply CN V, is a cranial nerve responsible for sensation in the face and motor functions such as biting and chewing; it is the most complex of the cranial nerves.
Does the trigeminal nerve affect the ear?
Disruptions of the trigeminal nerve caused by neuralgia may also induce or contribute to tinnitus by affecting the vasculature of the inner ear. The trigeminal nerve is the source of innervation for blood vessels around the spiral modiolus and the stria vascularis of inner ear [31, 38].
What is the trigeminal nerve?
As the name suggests, the trigeminal nerve is a tripartite entity made up of distinct terminal divisions. Each component of the nerve is responsible for a specific region of the face, and transmits specific impulses. The three divisions of the trigeminal nerve are:
How do axons form the mesencephalic tract?
As the myelinated axons leave the mesencephalic nucleus, they coalesce to form the mesencephalic tract. The individual axon s then split into central and peripheral branches. The central branches convey impulses from the neuromuscular spindles within the muscles of mastication, and from the bite force reflex arcs, to the motor neuron of the trigeminal nerve. Other central fibers also integrate with the reticular formation and the sensory trigeminal nerve. Others also gain access to the cerebellum by way of the superior cerebellar peduncle. This interplay between the proprioceptive and motor divisions of the trigeminal nerve helps to regulate the activity of the stretch muscles; and by extension, the process of mastication.
How many nuclei does the trigeminal nerve have?
Unlike the other cranial nerves, the trigeminal nerve is quite large. It has four nuclei that send fibers to form its tracts and is associated with three separate branches. Key facts about the trigeminal nerve (CN V) Type. Mixed (motor and sensory) Nuclei. Motor nucleus of trigeminal nerve.
What nerve is CN V?
Trigeminal nerve (CN V): want to learn more about it?
What does MOM mean in medical terms?
The acronym MOM can be used to recall the three branches of the trigeminal nerve.
Where does the ophthalmic nerve receive its meningeal tributary?
Once formed, the ophthalmic nerve also receives its meningeal tributary from the dura of the anterior cranial fossa. Key facts about the ophthalmic branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V1) Branches. Nasociliary nerve.
Which nerve is responsible for the motor, sensory, and autonomous functions of the head and neck?
Trigeminal nerve (CN V) The principal regulator of the sensory modalities of the head is the trigeminal nerve. This is the fifth of twelve pairs of cranial nerves that are responsible for transmitting numerous motor, sensory, and autonomous stimuli to structures of the head and neck . While the trigeminal nerve (CN V) is largely a sensory nerve, ...
How many nerves does the trigeminal ganglion have?
The trigeminal ganglion splits into three trigeminal nerve branches. These branches travel along each side of your head to different parts of your face.
What nerves help with pain?
The trigeminal nerves play essential roles in helping your face feel pain, touch, warmth or cold. The mandibular branches of the trigeminal nerves help you bite, chew and swallow. In some cases, people develop numbness or other signs of trigeminal neuropathy from an accident, dental procedure or facial surgery. Trigeminal neuralgia can cause stabbing, shock-like facial pain or a constant burning sensation. Talk to your provider about finding relief from these trigeminal nerve conditions.
What is the name of the condition that affects only one side of the face?
Trigeminal neuralgia tends to affect only one side of your face. Some people develop facial twitches (tics) after the pain subsides.
What is the name of the condition where an artery wraps around the trigeminal nerve and causes irritation?
Primary trigeminal neuralgia occurs when an artery or vein wraps around the trigeminal nerve and causes irritation.
What is the pain on one side of the face?
Trigeminal neuralgia is a type of trigeminal neuropathy brought on by nerve damage. The condition causes sudden, intense facial pain on one side of your face. The pain can feel like an electrical shock. Approximately 150,000 people develop trigeminal neuralgia every year. It's also called tic douloureux.
What is the fifth cranial nerve?
The trigeminal nerve, also called the cranial nerve V (that's the Roman numeral five), is the fifth of 12 cranial nerves.
How many nuclei are there in the trigeminal nerve?
The trigeminal nerves begin within four nuclei — or collections of nerve cell bodies — in your brain. Three of these nuclei control the functioning of your senses. The fourth controls motor function (or your movement).
What is the most common problem associated with the trigeminal nerve?
A condition called trigeminal neuralgia is the most common problem associated with the trigeminal nerve. There are also several other medical problems that can involve the trigeminal nerve or its branches.
What is the trigeminal nerve?
The trigeminal nerve is most commonly associated with trigeminal neuralgia, a condition characterized by severe facial pain. Since it is large and has several divisions, the trigeminal nerve or its branches can also be affected by a number of medical conditions including infections, trauma, and compression from tumors or blood vessels.
What causes nerve pain in the trigeminal nerve?
It can occur without any specific cause, and sometimes it can be triggered by an injury or inflammation of the trigeminal nerve. This condition often causes pain that is severe in intensity. Medications used for pain management include antidepressants and anticonvulsants, both of which are frequently used for nerve pain.
What can be done to prevent permanent deficits of the trigeminal nerve?
Treatment with antibiotics and anti-inflammatory medication, if started in a timely manner, can prevent permanent deficits of the trigeminal nerve in the setting of infection.
Where are the trigeminal nerve roots located?
Location. The trigeminal nerve roots and ganglion, like those of other cranial nerves, are located right outside the brainstem. The brainstem is the lower part of the brain that serves as the physical connection between the spinal cord and the cerebral cortex of the brain. All 12 cranial nerves (12 in each side) emerge from the brainstem.
Which nerve is smaller than the sensory nerve?
The motor nerve branch of the trigemin al nerve is smaller than the sensory branches ...
Which nerves are located in the head?
Ophthalmic. The frontal nerve, the lacrimal nerve, and the nasociliary nerves converge in the ophthalmic nerve. These nerves and their small branches are located in and around the eye, forehead, nose, and scalp. The ophthalmic nerve enters into the skull through a small opening called the superior orbital fissure before it converges in ...
What nerve is irritated in the face?
Trigeminal Neuralgia Pain. The trigeminal nerve splits off into three branches: ophthalmic, maxillary and mandibular. Each branch provides sensation to different areas of the face. Depending on which branch and which part of the nerve is irritated, trigeminal neuralgia pain can be felt anywhere in the face.
How does a rhizotomy for trigeminal neuralgia work?
The surgeon inserts a long needle through the cheek on the affected side of the face and uses an electrical current (heat) or a chemical (glycerin or glycerol) to deaden the pain fibers of the trigeminal nerve. For those undergoing trigeminal neuralgia rhizotomy for the first time, the chemical approach is typically recommended. Those who have the procedure repeated often benefit from both the chemical and the heat treatment delivered in the same session.
How long does a trig neuralgia pain last?
The pain travels through the face in a matter of seconds, but as the condition progresses, the pain can last minutes and even longer. Trigeminal neuralgia is sometimes known as tic douloureux, ...
What causes trigeminal neuralgia?
The condition may be caused by a blood vessel pressing against the trigeminal nerve , also known as vascular compression.
What causes facial pain?
Trigeminal neuralgia is the most common cause of facial pain and is diagnosed in approximately 15,000 people per year in the United States. Trigeminal neuralgia pain is exceptionally severe. Although the condition is not life-threatening, the intensity of the pain can be debilitating. Trigeminal neuralgia relief is possible: Medical ...
How many nerves are there on each side of the face?
We have two trigeminal nerves for each side of our face, but trigeminal neuralgia pain most commonly affects only one side. The pain of trigeminal neuralgia is unlike facial pain caused by other problems.
How long does it take to recover from MVD?
It is suitable for people in good health who can tolerate surgery and general anesthesia, and whose lifestyles can accommodate a recovery period of four to six weeks. The goal of the MVD surgery is to separate the blood vessel from the trigeminal nerve by placing a cushion made of Teflon between them.
Does TMJ Trigger All Migraines?
Based on how unevenly people respond to migraine treatments, it seems likely that there are many different causes of migraines. For many people, TMJ treatment works great, and it involves no drugs and has few side effects. It’s a great treatment option, and people who haven’t tried it should consider it, especially if they have other symptoms associated with TMJ like tinnitus, neck pain, and damage or excessive wear on teeth.
What is the number to call for TMJ in Savannah?
If you would like to learn whether TMJ is responsible for your trigeminal nerve migraines in Savannah, please call (912) 234-8282 for an appointment with a TMJ dentist at Beyond Exceptional Dentistry. By Dr. Rod Strickland, DDS | June 15th, 2020 | Headaches. |.
What nerve causes migraines?
It’s National Migraine Awareness Month, so we decided to do our part by focusing on the nerve that serves as the origin point of migraines: the trigeminal nerve. At Beyond Exceptional Dentistry in Savannah, GA, we want our patients to experience migraine-free lives. Without knowing what might trigger your frequent migraines, there’s no way to find relief. Learn if you’re suffering from trigeminal nerve migraines and if TMJ is the cause.
Why does my TMJ hurt?
One potential cause of overstimulation of the trigeminal nerve, then, is excessive feedback from the jaw system. In TMJ, the muscles are unable to find a comfortable, relaxed position. Instead, they struggle, reposition, and grind. You may experience damage to your teeth and jaw pain.
Why do I get migraines?
Irregularities in the blood vessels in your brain, typically when the blood vessels swell, cause migraines by putting pressure on the brain. The blood vessels don’t expand spontaneously. Often abnormal stimuli in the trigeminal nerve trigger this swelling.
What muscles are involved in chewing?
Tensor tympani. Except for the tensor tympani , all of these muscles are involved in biting, chewing, and swallowing. The first four are known as the muscles of mastication, because they’re our primary chewing muscles. One potential cause of overstimulation of the trigeminal nerve, then, is excessive feedback from the jaw system.
Which branch of the trigeminal nerve is responsible for the pain in the upper jaw?
The maxillary branch covers the area of the upper jaw, including the lower part of the nose and up to the area right below the eye. The ophthalmic branch takes sensory data from the nose, eyes, and scalp–until ⅔ of the way back on the head. Another potential source of overstimulation of the trigeminal nerve is a pain in any of these areas, ...
