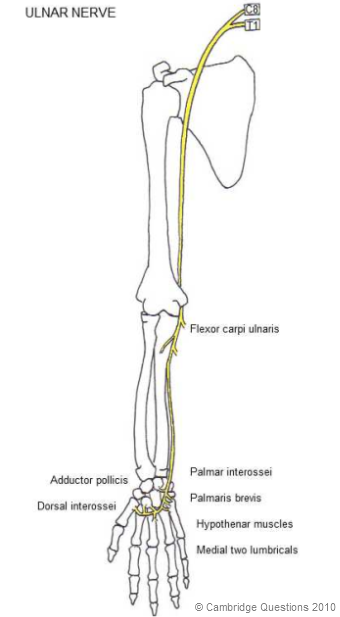
What are the symptoms of ulnar nerve damage?
SymptomsAbnormal sensations in the little finger and part of the ring finger, usually on the palm side.Weakness, loss of coordination of the fingers.Clawlike deformity of the hand and wrist.Pain, numbness, decreased sensation, tingling, or burning sensation in the areas controlled by the nerve.
Where is ulnar nerve pain felt?
The ulnar nerve is also responsible for sensation in the fourth and fifth fingers (ring and little fingers) of the hand, part of the palm and the underside of the forearm. Ulnar nerve entrapment can cause pain, numbness and tingling in the forearm and the fourth and fifth fingers.
How do you relieve ulnar nerve pain?
Home remediesicing the affected area for 10 to 15 minutes.applying topical creams, such as menthol.stopping activities that cause pain.taking regular breaks when doing repetitive tasks.wearing a splint or brace.using relaxation exercises.keeping the affected area warm.elevating the affected area.More items...•
Where is the ulnar nerve most likely to be damaged?
The most common site of ulnar nerve injury is near the elbow. Nerve pathology can be caused by anatomic damage from fracture of the medial epicondyle, osteophyte infection, soft tissue mass, or synovitis at the elbow joint.
What does ulnar nerve entrapment feel like?
Ulnar nerve entrapment can present symptoms like pain, weakness, numbness, and tingling sensations involving the little finger, ring finger, and hypothenar eminence. Mild cases may resolve spontaneously. Treatment options include pain medications, physical therapy, and immobilization.
Is ulnar nerve pain serious?
Ulnar nerve entrapment is an extremely common injury to a nerve that runs through the arm into the fingers on the outside of the hand. While ulnar nerve entrapment is usually not serious, it can have permanent consequences without prompt treatment, including paralysis and loss of feeling in the affected hand or arm.
How long does a ulnar nerve take to heal?
Ulnar Nerve Release Estimated Recovery Timeline Recovery from cubital tunnel release surgery varies from patient to patient, taking anywhere from several weeks to several months. Symptoms such as numbness or tingling may improve quickly or may take up to six months to go away.
Does MRI show ulnar nerve?
Abstract. Objective: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the ulnar nerve is being increasingly employed in the diagnosis of ulnar neuropathy at the elbow (UNE).
What happens if ulnar nerve entrapment is left untreated?
If left untreated this condition could escalate to muscle weakness and permanent injury to the arm or hand. Ulnar nerve entrapment can be caused by: Leaning on your elbow for long periods of time. Repetitive movement or exercise.
How do you test for ulnar nerve damage?
Ultrasound. Your doctor may use an ultrasound to evaluate the ulnar nerve and the soft tissue of the cubital tunnel, which allows the ulnar nerve to travel behind the elbow. During an ultrasound scan, high-frequency sound waves bounce off parts of the body and capture the returning “echoes” as images.
Can ulnar nerve damage be repaired?
The injured ulnar nerve is repaired at the injured site (primary or graft repair), and then the branch of the pronator quadratus muscle is transposed to the deep branch of the ulnar nerve at the wrist level (via end-to-end or end-to-side anastomosis). Red arrows indicate where nerve repair is being performed.
Does ulnar nerve entrapment cause shoulder pain?
Nerve entrapments in the shoulder do not normally cause any long-term effects if they are properly diagnosed and appropriately treated. If not, they can lead to ongoing pain in the shoulder, muscle wastage and a prolonged lay-off from participation in sporting activities.
Does ulnar nerve entrapment cause shoulder pain?
Nerve entrapments in the shoulder do not normally cause any long-term effects if they are properly diagnosed and appropriately treated. If not, they can lead to ongoing pain in the shoulder, muscle wastage and a prolonged lay-off from participation in sporting activities.
How do you test for ulnar nerve entrapment?
Ultrasound. Your doctor may use an ultrasound to evaluate the ulnar nerve and the soft tissue of the cubital tunnel, which allows the ulnar nerve to travel behind the elbow. During an ultrasound scan, high-frequency sound waves bounce off parts of the body and capture the returning “echoes” as images.
How do you test ulnar nerve?
0:103:31How to examine the ulnar nerve - watch orthohub ... - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipToday we're here to examine the ulnar nerve. And this is a nerve essentially of sensation from theMoreToday we're here to examine the ulnar nerve. And this is a nerve essentially of sensation from the hand the hypothenar eminence little finger and ring finger. And then extrinsic. And intrinsic muscles
What does nerve pain feel like in wrist?
Occasional shock-like sensations that radiate to the thumb and index, middle, and ring fingers. Pain or tingling that may travel up the forearm toward the shoulder. Weakness and clumsiness in the hand — this may make it difficult to perform fine movements such as buttoning your clothes.
What nerve causes pain in the elbow?
The ulnar nerve is responsible for the pain, or ‘funny bone’, sensation that occurs if the elbow bone is suddenly struck. Continual pressure on the elbow or inner forearm may cause damage. Injury can also occur from elbow fractures or dislocations. Damage to the ulnar nerve causes problems with sensation and mobility in the wrist and the hand.
What nerve is responsible for movement of the hand?
Ulnar nerve. Medically reviewed by the Healthline Medical Network — Written by the Healthline Editorial Team — Updated on January 19, 2018. The ulnar nerv e is a nerve that travels from the wrist to the shoulder. This nerve is mainly responsible for movement of the hand; despite passing through the forearm, it is only responsible for one ...
Where is the nerve in the hand located?
Its primary role is to provide nerve function to the hand. It is located near the skin surface of the body, particularly at the elbow.
What is the function of the ulnar nerve?
Motor Functions. The ulnar nerve innervates muscles in the anterior compartment of the forearm, and in the hand. Anterior Forearm. In the anterior forearm, the muscular branch of the ulnar nerve supplies two muscles: Flexor carpi ulnaris - flexes and adducts the hand at the wrist.
What nerve pierces the flexor carpi ulnaris?
In the forearm, the ulnar nerve pierces the two heads of the flexor carpi ulnaris, and travels deep to the muscle, alongside the ulna. Three main branches arise in the forearm: Muscular branch - innervates two muscles in the anterior compartment of the forearm.
What are the two motor functions of the forearm?
Motor functions: Two muscles of the anterior forearm – flexor carpi ulnaris and medial half of flexor digitorum profundus. Intrinsic muscles of the hand (apart from the thenar muscles and two lateral lumbricals) Sensory functions: Medial one and half fingers and the associated palm area.
Which nerve travels superficially to the flexor retinaculum?
Dorsal cutaneous branch - innervates the dorsal surface of the medial one and a half fingers, and the associated dorsal hand area. At the wrist, the ulnar nerve travels superficially to the flexor retinaculum, and is medial to the ulnar artery.
Which nerve innervates the medial half of the palm?
Sensory Functions. There are three branches of the ulnar nerve that are responsible for its sensory innervation. Two of these branches arise in the forearm, and travel into the hand: Palmar cutaneous branch – innervates the medial half of the palm.
Where does the ulnar nerve originate?
The ulnar nerve arises from the brachial plexus within the axilla region. It is a continuation of the medial cord and contains fibres from spinal roots C8 and T1. After arising from the brachial plexus, the ulnar nerve descends in a plane between the axillary artery (lateral) and the axillary vein (medial). It proceeds down the medial aspect of the ...
What is the ulnar nerve?
The ulnar nerve is a major peripheral nerve of the upper limb. In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the ulnar nerve – its anatomical course, motor and sensory functions, and its clinical correlations.
Overview
The ulnar nerve helps you move your forearm, hand and certain fingers. Your forearm extends from the elbow to the hand. The ulnar nerve also sends sensory information like touch, temperature and pain to the brain.
Function
The ulnar nerve controls nearly all of the small muscles in the hand. Although the ulnar nerve begins at the armpit, it doesn’t perform a function until it enters the forearm.
Anatomy
The ulnar nerve is one of five nerve branches of the brachial plexus. This nerve bundle sends sensory information and helps you move your shoulders, arms and hands.
Conditions and Disorders
Ulnar nerve entrapment is the most common ulnar nerve problem. Pressure on the ulnar nerve in the elbow or wrist causes a pinched nerve, nerve (neuropathic) pain and neuropathy (nerve damage).
What is the funny bone?
The funny bone is the name people use to describe contusion injuries to the ulnar nerve behind the elbow. In this location, the ulnar nerve wraps behind the arm bone (humerus) just underneath the skin. There is very little soft-tissue protection around the ulnar nerve in this location and, as a result, striking this part of the elbow against an object often causes sharp pain, tingling, and numbness along the ulnar nerve. 7 This is the sensation that people describe when they say they "hit their funny bone."
What is the name of the nerve that compresses the ulnar nerve behind the elbow?
Cubital tunnel syndrome is the name used to describe chronic compression of the ulnar nerve behind the elbow. 4 The actual location of compression of the ulnar nerve in people with cubital tunnel syndrome can vary and has been described as compression coming from a number of different structures behind the elbow.
What is the name of the nerve in the wrist that is compressed?
Guyon's Canal Syndrome (Handlebar Palsy) Guyon's canal, also called the ulnar tunnel, is a location within the wrist that contains the ulnar nerve. 12 Compression of the ulnar nerve in this location can occur as a result of fractures to the small bones of the wrist or ganglion cysts forming within the wrist.
What causes ulnar nerve damage?
9 Sometimes injuries occur as an acute injury, in which there is a sudden traumatic injury that causes damage to the nerve. Other times, nerve problems can be the result of a chronic, long-standing condition that causes gradual deterioration ...
Why is the ulnar nerve important?
The ulnar nerve is one of the major nerves of the upper extremity and is of critical importance to providing information to the forearm and hand muscles from your brain, as well as returning information about sensations from the extremity. Abnormalities of ulnar nerve function can occur for a variety of reasons. Determining the source of damage to the ulnar nerve is important in order to allow for proper treatment.
Where is the ulnar nerve located?
The ulnar nerve is formed by the coalescence of several major nerve fibers in an area around the shoulder blade called the brachial plexus. 2 Upon exiting the brachial plexus, the ulnar nerve travels down the arm, supplying information to some ...
What are the causes of trauma?
Traumatic injuries occur as the result of sudden, often violent damage to the nerve. Some of the more common mechanisms include nerve contusion (bruising, lacerations, and concussive injuries. Nerve contusions typically occur after a fall or motor vehicle collision. 13
What nerve is in the elbow when the arm flexes?
In some people, the ulnar nerve does not stay in its proper position and can shift across a bump of bone in the elbow when the arm flexes, referred to as a subluxing nerve. Repeated shifting can cause irritation of the ulnar nerve.
How to tell if you have ulnar nerve neuropathy?
Symptoms of ulnar nerve neuropathy may include: Weakness or tenderness in the hand. Tingling in the palm and fourth and fifth fingers. Sensitivity to cold. Tenderness in the elbow joint.
What nerve causes tingling in the forearm?
The ulnar nerve is also responsible for sensation in the fourth and fifth fingers (ring and little fingers) of the hand, part of the palm and the underside of the forearm. Ulnar nerve entrapment can cause pain, numbness and tingling in the forearm and the fourth and fifth fingers.
What is the best way to treat ulnar nerve entrapment?
Surgery for Ulnar Nerve Entrapment. When physical therapy and other forms of nonoperative treatment fail to control pain and restore function, nerve release surgery may be the best option to address symptoms. There are two types of ulnar nerve release surgery: At the elbow.
What nerve is entrapped in the elbow?
Ulnar nerve entrapment at the elbow can occur when there is prolonged stretching of the nerve by keeping the elbow fully bent or when there is direct pressure on the nerve from leaning the elbow against a solid surface.
What is ulnar nerve entrapment?
Ulnar nerve entrapment is also known as: Bicycler’s neuropathy or handlebar palsy. Guyon’s canal syndrome. Tardy ulnar palsy.
What is the difference between an EMG and an NCS?
An EMG measures ongoing muscle activity and response of the muscle to its nerve stimulation. An NCS measures the amount and speed of conduction of an electrical impulse through a nerve. The doctor may also order any of the following imaging techniques: MRI. Ultrasound.
What is the first line of treatment for ulnar nerve pain?
Certain medical conditions, particularly those that cause nerve problems or increased inflammation in the body. Nonoperative management with rest, activity modification, anti-inflammatory medications, and elbow pads/braces are typically considered as the first line of treatment for patients with ulnar nerve problems.
What causes cubital tunnel syndrome?
Cubital tunnel syndrome or ulnar nerve problems can occur involving a number of different mechanisms: Decreased space in the cubital tunnel (can occur for a number of different reasons) Swelling of the nerve, especially the portion that passes through the cubital tunnel. Repetitive use of the elbow. Prior injury to the inside part of the elbow.
What nerve crosses the elbow?
Ulnar Nerve/Cubital Tunnel Syndrome. The ulnar nerve is one of the three large nerves that crosses the elbow (the others are the median and radial nerves). The ulnar nerve passes across the elbow on the medial (inside) side. It lies very near to the medial ulnar collateral ligament. As it crosses the elbow joint, ...
What causes ulnar nerve pain in elbow?
There are a number of factors that increase your risk of ulnar nerve problems at the elbow: History of elbow injury. Arthritis in the elbow and/or neck. Sports or occupations that require repetitive elbow motion such as throwing, hammering, etc. Certain medical conditions, particularly those that cause nerve problems or increased inflammation in ...
What is the term for releasing the cubital tunnel?
This typically consists of releasing the tight cubital tunnel that is compressing the nerve, and this is referred to as “nerve decompression. ”.
Where does the ulnar nerve pass?
The ulnar nerve passes across the elbow on the medial (inside) side. It lies very near to the medial ulnar collateral ligament. As it crosses the elbow joint, it enters a small tunnel referred to as the cubital tunnel. This tunnel is made up of bone on one side and ligament on the other. Because this space is tight, ...
What is it called when a nerve is unstable?
This is referred to as a “nerve transposition.”.
What is the cubital tunnel?
Another common compression location of the ulnar nerve is within the elbow region. It’s called the Cubital Tunnel. Compression of the ulnar nerve in this location is called Cubital Tunnel Syndrome. The Cubital Tunnel is composed of bony borders and a soft tissue roof.
What is the procedure for wasting hands?
Some surgical options are: Cubital tunnel release – decompression of the ulnar nerve at the wrist. Ulnar nerve anterior transposition – moving the nerve to the other side of the elbow. Medial epicondylectomy – decompression of the ulnar nerve at the elbow.
Why does my ulnar entrapment swell?
This is known of the area of entrapment. Some common reasons for nerve swelling leading to ulnar entrapment are: Compression of the nerve at the neck, shoulder, elbow or wrist. Leading too much on a table or armrest. Swelling in the elbow or wrist from local trauma. Bony arthritis.
How to tell if you have ulnar nerve entrapment?
Common symptoms of ulnar nerve entrapment include: Intermittent numbness of the pinky and ring finger. Weakness of the hand. Feeling like the pinky and ring finger are falling asleep . Waking up at night with pinky and ring finger numbness. Loss of dexterity of the hand ( playing piano, guitar, buttoning shirts)
What nerves are involved in the hand?
Other major nerves in the region are the median and radial nerves. The ulnar nerve is composed of a collection of multiple spinal nerve roots. The ulnar nerve provides sensory to sections of the hand and motor control of many muscles used to move the hand and fingers. Ulnar Nerve Entrapment Causes.
Why is the Ulnar nerve entrapped?
The ulnar nerve can become entrapped for a variety of reasons, yet a common finding between all of the reasons is the fact that the nerve swells. Swelling of the nerve creates a sticking point within a bony tunnel or soft tissue tunnel. This is known of the area of entrapment.
Why do we grab the skin above the cubital tunnel?
This is where we grabbed the skin above or below the cubital tunnel in an effort to “lift the skin off of the nerve” so it can decompress. Surprisingly, a simple decompression of the skin from the ulnar nerve reduces numbness in almost half the people with a confirmed ulnar nerve compression at the Cubital Tunnel.
Overview
Ulnar nerve entrapment is the most common ulnar nerve problem. Ulnar nerve entrapment occurs when something puts pressure on your ulnar nerve in your elbow or wrist. Nerve entrapment is a type of nerve compression syndrome.
Symptoms and Causes
Activities that stretch your ulnar nerve at your elbow, or put a lot of pressure on your elbow, can lead to cubital tunnel syndrome. Sleeping with your elbows bent for long periods can cause or worsen symptoms of ulnar nerve entrapment.
Diagnosis and Tests
Your healthcare provider may perform several tests during your physical exam to evaluate your symptoms. These tests seem simple, but they help your healthcare provider assess finger and hand strength. They include:
Prevention
These steps can lower your risk of developing ulnar nerve entrapment, or ease symptoms: