How are vitamins absorbed by the GI tract?
GI Vitamin Absorption Overview Beyond nutrients, water, and important electrolytes the alimentary tract must absorb a variety of critical small molecule vitamins. Hydrophobic fat soluble vitamins (Vitamins A, D, E, K) are absorbed together with other lipids using general mechanisms of GI Lipid Absorption.
Where are micronutrients absorbed in the small intestine?
Fat-soluble micronutrients including vitamin A and carotenoids are assumed to follow the fate of lipids in the upper gastrointestinal tract [5], and their absorption presumably occurs in the upper half of the small intestine.
How is vitamin B12 absorbed?
Most water-soluble vitamins are absorbed through secondary active transport via vitamin-specific Na-Vitamin symporters in the small intestine. However, Vitamin B12 has a unique mechanism for absorption which will be described in a Vitamin B12 page, once it is written.
Where are nutrients absorbed?
All of the nutrients that come from food and supplements don't get absorbed in the same place; they're absorbed in various places in your gastrointestinal tract.
Is vitamin A absorbed in the duodenum?
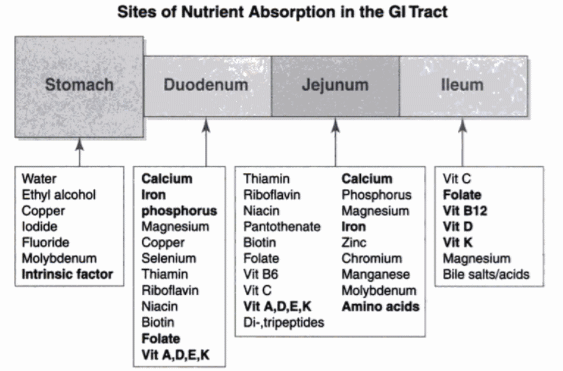
Removing portions of the digestive tract can cause deficiencies in the nutrients those organs would normally absorb, as listed below. Duodenum: Absorbs Vitamin A, D, E, and K. Jejunum: Absorbs protein, carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals. Ileum: Passes food to the colon and absorbs Vitamin B12.
Is vitamin A absorbed in the stomach?
Essentially all vitamin absorption occurs in the small intestine.
How is vitamin A digested and absorbed?
Mechanisms involved in the digestion and absorption of dietary vitamin A require the participation of several proteins. Dietary retinyl esters are hydrolyzed in the intestine by the pancreatic enzyme, pancreatic triglyceride lipase, and intestinal brush border enzyme, phospholipase B.
How is vitamin A absorb?
The various forms of vitamin A are solubilized into micelles in the intestinal lumen and absorbed by duodenal mucosal cells [5]. Retinyl esters and provitamin A carotenoids are converted to retinol after uptake into the lumen (for retinyl esters) or absorption (for provitamin A carotenoids).
Where is Vit A stored in the body?
the liverVitamin A is also fat-soluble, meaning that any amount not immediately needed by the body is absorbed and stored in fat tissue or the liver.
Which vitamins are absorbed in the large intestine?
The bacteria in the colon produce substantial amounts of vitamins by fermentation. Vitamin K and B vitamins, including biotin, are produced by the colonic bacteria. These vitamins are then absorbed into the blood.
What vitamins are absorbed in the stomach?
It is well established now that intestinal absorption of the water-soluble vitamins ascorbate, biotin, folate, niacin, pantothenic acid, pyridoxine, riboflavin and thiamin is via specific carrier-mediated processes.
What form of vitamin A is best absorbed?
Therefore, preformed vitamin A is the best-absorbed form, but since it is derived from animal sources, some people prefer the “Provitamin A Carotenoid” or plant-based form.
What vitamin helps you absorb vitamin A?
Adding one whole avocado to your meal may even double the amount of vitamin A you can absorb. Get enough zinc. You need to have enough zinc in your diet in order to fully absorb vitamin A. Women need at least 8mg every day (up to 10 or 11mg if pregnant or breastfeeding), and adult men need 11mg daily.
Where do nutrients get absorbed?
All of the nutrients that come from food and supplements don't get absorbed in the same place; they're absorbed in various places in your gastrointestinal tract. Below are the rest stations where nutrients get absorbed along the body's GI tract. Because food pulls over at various spots in the intestinal tract, disease in these areas can cause ...
Which part of the small intestine contains fat, sucrose, lactose, and folic acid
Jejunum: Middle part of the small intestine: Fat, sucrose, lactose, fat-soluble vitamins A and D, water-soluble vitamins like folic acid, proteins and amino acids, glucose. Ileum: Last part of the small intestine (leads to large bowel): Proteins and amino acids, water-soluble vitamins like folic acid, vitamin B12.
What are the parts of the digestive system that are affected by food pulls over?
Because food pulls over at various spots in the intestinal tract, disease in these areas can cause nutritional deficiencies, even if we are eating the right foods. Stomach: Alcohol. Duodenum: First part of the small intestine (takes off from the stomach): Calcium, magnesium, iron, fat-soluble vitamins A and D, glucose.
What are the different parts of the digestive system?
Where along the gastrointestinal tract do different nutrients get absorbed? 1 Stomach: Alcohol. 2 Duodenum: First part of the small intestine (takes off from the stomach): Calcium, magnesium, iron, fat-soluble vitamins A and D, glucose. 3 Jejunum: Middle part of the small intestine: Fat, sucrose, lactose, fat-soluble vitamins A and D, water-soluble vitamins like folic acid, proteins and amino acids, glucose. 4 Ileum: Last part of the small intestine (leads to large bowel): Proteins and amino acids, water-soluble vitamins like folic acid, vitamin B12. 5 Colon: (also known as the large bowel): Water, potassium, sodium chloride, fatty acids from fiber digestion.
Where are minerals stored in the body?
While minerals are stored in your body only few of vitamins also stay as our guests in liver ( fat-soluble are stored in fatty tissues also) . These are fat-soluble vitamins and vitamin B12, as an exception.
Where does hydrochloric acid go when you swallow?
Once you swallow it travels to your stomach where hydrochloric acid and other digestive enzymes are dealing with solid parts, shredding them and sends to small intestines where further digestion and nutrient absorption occurs. In the upper regions of small intestine begins the final part of digestion. Bile and pancreas enzymes give us fine ...
How does the body process food?
Our body is clever, it acts like a machine that crushes food, processes, uses and stores vitamins and minerals. This process starts in mouth by chewing food . Saliva is responsible for chemical breakdown and allows next step – swallowing. Once you swallow it travels to your stomach where hydrochloric acid and other digestive enzymes are dealing with solid parts, shredding them and sends to small intestines where further digestion and nutrient absorption occurs. In the upper regions of small intestine begins the final part of digestion. Bile and pancreas enzymes give us fine particles able to pass between intestinal cells wall. This is called absorption and now through capillaries vitamins go to bloodstream. Journey continues by sending nutrients in liver to be used immediately or stored or sent to kidneys for elimination through urine.
What is the role of vitamin K in the body?
K – main role is in blood clotting. Also, reduce risk of heart disease, high concentration of calcium in the blood…. Dietary sources : kale, liver, butter, spinach, eggs. If this vitamin is missing it can cause bleeding and reduced bone density that can lead to fractures.
What is the role of B6 in the body?
Pantothenic acid is the key for various metabolic functions. Vitamin B6 helps red blood cell formation, energy metabolism, synthesis of several neurotransmitters. Biotin as well as the others uses chemical reactions for fatty acid synthesis, glucose formation and amino acid metabolism. Vitamin B9 is necessary for the cell growth, ...
What is the process of bile and pancreas enzymes?
Bile and pancreas enzymes give us fine particles able to pass between intestinal cells wall. This is called absorption and now through capillaries vitamins go to bloodstream. Journey continues by sending nutrients in liver to be used immediately or stored or sent to kidneys for elimination through urine.
Is it unhealthy to take fat soluble vitamins?
Fat-soluble vitamins. There is a common belief that fats are unhealthy. If you are convinced in it too I must break it to you. It´s opposite, fats are necessary for usage of vitamin A, D, E and K. The whole process wouldn´t have been possible if fats are missing and the body would just eliminate this group of vitamins.
