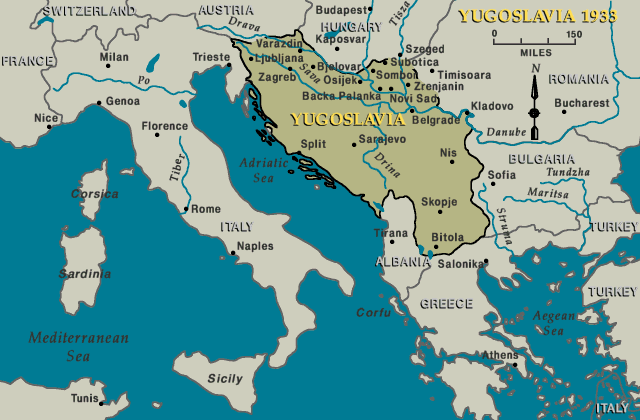
Which countries was Yugoslavia divided into?
Yugoslavia was divided between Germany, Italy, Hungary, and Bulgaria. On the territory of Croatia and Bosnia and Herzegovina, a puppet Independent State of Croatia was formed, headed by Ante Pavelic, who carried out mass repressions against Serbs, Jews, Gypsies and anti-fascists.
What country is now the former Yugoslavia?
What Is Yugoslavia Called Now? Former Yugoslavia is now the six nations of Serbia, Montenegro, Slovenia, Croatia, Macedonia and Kosovo. The six states that are now independent nations began to break away from Yugoslavia in the early 1990s.
What countries did Yugoslavia break up to?
The Breakup of Yugoslavia. Over the course of just three years, torn by the rise of ethno-nationalism, a series of political conflicts and Greater Serbian expansions, , the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia disintegrated into five successor states: Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Macedonia, Slovenia, and the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (later known as Serbia and Montenegro).
What were the major cities of Yugoslavia?
in the three major cities in Yugoslavia: Belgrade, Ljubljana and Zagreb. In the mid-1970s the universities in Zagreb and Ljubljana and the students’ cultural centres in Belgrade and Ljubljana...
See more
.jpg)
What is the old Yugoslavia called now?
of Serbia and MontenegroIn 2003, the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia was reconstituted and re-named as a State Union of Serbia and Montenegro.
Which country left Yugoslavia first?
SloveniaSlovenia was the first to declare “sovereignty” in 1990, issuing a parliamentary declaration that Slovenian law took precedence over Yugoslav law.
Was Croatia previously Yugoslavia?
In June 1991, Croatia and Slovenia – two of the component republics of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia – declared their independence.
What was Croatia called before?
the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and SlovenesHistorical Backgound It was known as the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes. In 1929, the name of this new nation was changed to Yugoslavia. After World War II, the former prewar kingdom was replaced by a federation of six equal republics.
What 7 countries made up Yugoslavia?
After the Allied victory in World War II, Yugoslavia was set up as a federation of six republics, with borders drawn along ethnic and historical lines: Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia, and Slovenia.
What was Serbia called before?
From 1815 to 1882, the official name for Serbia was the Principality of Serbia. From 1882 to 1918, it was renamed to the Kingdom of Serbia, later from 1945 to 1963, the official name for Serbia was the People's Republic of Serbia. This was again renamed the Socialist Republic of Serbia from 1963 to 1990.
Why is Croatia split in two?
When Yugoslavia broke up in 1991, the newly independent Croatia was now split in two. Twelve miles of Bosnia-Herzegovinian coastline separate the Dubrovnik region from the rest of Croatia to the north. The Neum corridor gives Bosnia and Herzegovina a shorter coastline than any other nation on earth aside from Monaco.
What language is spoken in Yugoslavia?
Official languages Serbo-Croatian, pluricentric language and dialect continuum of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Montenegro and Serbia, split into four national standard varieties used in respective countries after the breakup of Yugoslavia: Bosnian, Croatian, Montenegrin and Serbian.
Why was Albania not part of Yugoslavia?
Answer and Explanation: Although it is part of the Balkan Peninsula, Albania was never part of Yugoslavia. This is likely because Albania is, in fact, not a Slavic country.
What happened to Yugoslavia and Czechoslovakia?
Both federal states faced rising economic and nationalist challenges in late 1980's, issues that culminated in the violent Breakup of Yugoslavia in what is known as the Yugoslav Wars-a situation that contrasted sharply with the peaceful Dissolution of Czechoslovakia.
What was Serbia called before?
From 1815 to 1882, the official name for Serbia was the Principality of Serbia. From 1882 to 1918, it was renamed to the Kingdom of Serbia, later from 1945 to 1963, the official name for Serbia was the People's Republic of Serbia. This was again renamed the Socialist Republic of Serbia from 1963 to 1990.
When did Yugoslavia separate?
June 25, 1991 – April 28, 1992Breakup of Yugoslavia / Period
Where is Yugoslavia located?
Full Article. Yugoslavia, former federated country that was situated in the west-central part of the Balkan Peninsula. This article briefly examines the history of Yugoslavia from 1929 until 2003, when it became the federated union of Serbia and Montenegro (which further separated into its component parts in 2006).
What was the first Yugoslavia?
The first Yugoslavia. After the Balkan Wars of 1912–13 ended Ottoman rule in the Balkan Peninsula and Austria-Hungary was defeated in World War I, the Paris Peace Conference underwrote a new pattern of state boundaries in the Balkans.
How big was Yugoslavia in square miles?
The postwar Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (Socijalistička Federativna Republika Jugoslavija) covered 98,766 square miles (255,804 square km) and had a population of about 24 million by 1991.
What was the Balkans' new state?
The major beneficiary there was a newly created Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes, which comprisedthe former kingdoms of Serbia and Montenegro (including Serbian-held Macedonia), as well as Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Austrian territory in Dalmatiaand Slovenia, and Hungarian land north of the Danube River. Great difficulty was experienced in crafting this multinational state. Croats favoured a federal structure that would respect the diversityof traditions, while Serbs favoured a unitary statethat would unite their scattered population in one country. The unitarist solution prevailed. The 1921 constitution established a highly centralized state, under the Serbian Karadjordjević dynasty, in which legislative power was exercised jointly by the monarchy and the Skupština (assembly). The king appointed a Council of Ministers and retained significant foreign policyprerogatives. The assembly only considered legislation that had already been drafted, and local government acted in effect as the transmission belt for decisions made in Belgrade.
What happened after 1945?
After 1945 the communist government nationalized large landholdings, industrial enterprises, public utilities, and other resources and launched a strenuous process of industrialization. After a split with the Soviet Union in 1948, Yugoslavia had by the 1960s come to place greater reliance on market mechanisms.
What countries are part of Yugoslavia?
It included the current countries of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, North Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia, Slovenia, and the partially recognized country of Kosovo. Learn more about Yugoslavia in this article.
What was the name of the country that was changed to Yugoslavia?
After a decade of acrimonious party struggle, King Alexander I in 1929 prorogued the assembly, declared a royal dictatorship, and changed the name of the state to Yugoslavia. The historical regions were replaced by nine prefectures ( banovine ), all drafted deliberately to cut across the lines of traditional regions.
What was the name of the new Yugoslavia after WWII?
When WWII ended, the Partisans, led by Tito, took control of Yugoslavia and proclaimed the establishment of a new Yugoslavia, called the Federal People’s Republic of Yugoslavia. The new communist federation was comprised of 6 republics: Serbia, Montenegro, Macedonia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and Slovenia.
How many republics were there in the Yugoslavia?
There were six republics in the federation: Serbia, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, and Slovenia. At first, Yugoslavia was a constitutional monarchy, but it then became a communist state under the leadership of Josip Broz Tito. After Tito died, the unity of the federation began to falter.
What was the name of the federation of states in which Southern Slavic languages were dominant?
Yugoslavia was a federation of states in which Southern Slavic languages were dominant.
Why did participatory democracy not take shape in Yugoslavia?
Although workers controlled industries in Yugoslavia in theory, the reality was that full participatory democracy in the workplace was not able to take shape because of the monopoly of the Yugoslav Communist Party.
Who was the leader of Yugoslavia during the Cold War?
As the ruler of Yugoslavia, Josip Tito steered the country on a course that was independent of the Soviet Union and the other communist states of the Cold War-era Eastern Bloc. In fact, at times, his relations with the USSR were quite frosty.
When did Serbia and Montenegro become a country?
In 1992, Serbia and Montenegro proclaimed the establishment of a new Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, composed only of their two countries. Shortly thereafter, Yugoslavia was expelled from the United Nations and suspended from the Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE).
When did the idea of a Southern Slavic federation begin?
The Formation Of Yugoslavia. Map of the former republic of Yugoslavia. The idea of a Southern Slavic federation began to take shape in the early 20th century, as the two empires that had dominated the region of the Southern Slavs, the Austro-Hungarian Empire and the Ottoman Empire, were on the decline. The last hurrah of these two empires was World ...
What was the name of the republic that was formed after the dissolution of Yugoslavia?
The Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. What remained of Yugoslavia after its dissolution was initially referred to as the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. This republic was comprised of Serbia and Montenegro.
What was the role of Yugoslavia in World War II?
A prominent ally to the Soviet Union during World War II, Yugoslavia came to resent the USSR's growing desire to dominate its economy and land. Subordinate Yugoslavia turned the tables in an infamous alliance rupture with Josip Tito and Joseph Stalin on either side. Tito ousted the Soviet Union and was consequently "excommunicated" by Stalin ...
Why did Serbia and Montenegro split?
Montenegro. Montenegro and Serbia split into two separate countries in response to a referendum for Montenegro's independence in June 2006. The creation of Montenegro as an independent country resulted in landlocked Serbia losing access to the Adriatic Sea.
Why is Macedonia called Macedonia?
For geographical and cultural reasons, Greece feels that "Macedonia", named after the Greek kingdom of Macedon, was appropriated and should not be used. Because Greece is so strongly opposed to the use of the ancient Greek region as an external territory, Macedonia was admitted to the United Nations under the name "the former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia".
Why did Yugoslavia develop diplomatic relations with Western European governments?
When Soviet blockades and sanctions were established, Yugoslavia got creative and developed diplomatic relationships with western European governments in order to trade, despite the fact that Yugoslavia was technically a communist country. After the death of Stalin, relations between the USSR and Yugoslavia improved.
What is the melting pot of Bosnia?
The almost landlocked "cauldron of conflict" of four million inhabitants is a melting pot of Muslims, Serbs, and Croats. While the Winter Olympics of 1984 were held in Bosnia-Herzegovina's capital city of Sarajevo, the country has since been devastated by war. The mountainous region has been trying to rebuild its infrastructure since its 1995 peace agreement with Croatia and Serbia, on whom the small country relies for imports such as food and materials.
When did Serbia and Montenegro regain their independence?
Although the rogue state of the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia was exiled from the United Nations in 1992, Serbia and Montenegro regained recognition on the world stage in 2001 after the arrest of Slobodan Milosevic, former Serbian president. The Federal Republic of Yugoslavia was dissolved and rebranded.
How long did Yugoslavia last?
This first Yugoslavia lasted until the Second World War when Axis forces invaded in 1941. The Regency had been moving closer to Hitler, but an anti-Nazi coup brought the government down and the wrath of Germany onto them.
What was the political history of the Second Yugoslavia?
The political history of the Second Yugoslavia is basically a struggle between the centralized government and the demands for devolved powers for the member units, a balancing act that produced three constitutions and multiple changes over the period.
How many federations of Balkan nations are there?
The Origins of Yugoslavia. There have been three federations of Balkan nations called Yugoslavia. The first originated in the aftermath of the Balkan Wars and World War One. At the end of the nineteenth century, the two empires which previously dominated the region – Austria-Hungary and the Ottomans – began to undergo changes ...
When did the Serbs become king?
He was key in declaring the Kingdom of the Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes, becoming king in 1921. However, years of frustration at the political infighting made him declare a dictatorship in early 1929, creating Yugoslavia.
Who led the communist partisans fighting in Yugoslavia during World War 2?
Tito led the communist partisans fighting in Yugoslavia during World War 2 and emerged as the leader of the new second Yugoslavian federation. He held the country together and was notable for differing markedly with the USSR, which dominated the other communist nations of Eastern Europe.
Who was the Yugoslav president in 1975?
9th May 1975: Yugoslav statesman and president, Marshal Tito (1892 - 1980) salutes as troops march past at a military parade at Belgrade to mark the 30th anniversary of liberation. Keystone / Getty Images
Who was the king of Yugoslavia in 1921?
Key People from the History of Yugoslavia. Born to the King of Serbia, Alexander lived some of his youth in exile before leading Serbia as regent during World War 1. He was key in declaring the Kingdom of the Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes, becoming king in 1921.
What was the name of the new Yugoslav state?
The name of the new Yugoslav state was: " Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes " ( Serbo-Croatian: Kraljevina Srba, Hrvata i Slovenaca / Краљевина Срба, Хрвата и Словенаца; Slovene: Kraljevina Srbov, Hrvatov in Slovencev) or its abbreviated form " Kingdom of SHS " ( Kraljevina SHS / Краљевина СХС).
Who was the first king of Yugoslavia?
The state was ruled by the Serbian dynasty of Karađorđević, which previously ruled the Kingdom of Serbia under Peter I from 1903 (after the May Coup) onward. Peter I became the first king of Yugoslavia until his death in 1921. He was succeeded by his son Alexander I, who had been regent for his father.
What was the name of the country in the early 1900s?
The Kingdom of Yugoslavia ( Serbo-Croatian: Kraljevina Jugoslavija / Краљевина Југославија; Slovene: Kraljevina Jugoslavija) was a state in Southeast and Central Europe that existed from 1918 until 1941.
How many Banovinas were there in the Yugoslavia?
In 1929, the Kingdom of Yugoslavia was subdivided into nine banovinas. This became eight in 1939, when two were merged to form the Banovina of Croatia.
Why did the commercial potential of Yugoslavia's Adriatic ports go to waste?
The commercial potential of Yugoslavia's Adriatic ports went to waste because the nation lacked the capital or technical knowledge to operate a shipping industry. On the other hand, the mining industry was well developed due to the nation's abundance of mineral resources, but since it was primarily owned and operated by foreigners, most production was exported. Yugoslavia was the third least industrialized nation in Eastern Europe after Bulgaria and Albania .
When did Yugoslavia sign the Tripartite Pact?
Fearing an invasion by the Axis powers, Yugoslavia signed the Tripartite Pact on 25 March 1941 , pledging cooperation with the Axis. Massive anti-Axis demonstrations followed in Belgrade .
When was the Kingdom of Serbia formed?
The preliminary kingdom was formed in 1918 by the merger of the provisional State of Slovenes, Croats and Serbs (itself formed from territories of the former Austria-Hungary, encompassing Bosnia and Herzegovina and most of Croatia and Slovenia) and Banat, Bačka and Baranja (that had been part of the Kingdom of Hungary within Austria-Hungary) with the formerly independent Kingdom of Serbia. In the same year, the Kingdom of Montenegro also proclaimed its unification with Serbia, whereas the regions of Kosovo and Vardar Macedonia had become parts of Serbia prior to the unification.
Where did the Yugoslavia come from?
The establishment of Yugoslavia took place in the region after the end of Ottoman rule. It continued its existence from the north of the Balkans to the southeast and from 1918 to 2003 in the southeast of Europe. The neighboring countries of Yugoslavia, with a surface area of 255,804 km², were Italy, Austria, Hungary, Bulgaria, Greece, and Romania.
What countries were part of Yugoslavia?
The neighboring countries of Yugoslavia, with a surface area of 255,804 km², were Italy, Austria, Hungary, Bulgaria, Greece, and Romania. The formation of Yugoslavia is based on the political developments in the Balkan wars and World War I years, during the last period of the Ottoman rule. As in the aftermath of the Balkan wars, Serbia became one ...
What happened to the Yugoslavia government after the occupation?
The king and government of Yugoslavia left the country after the occupation. With the occupation of Yugoslavia, the people, especially the Muslims, suffered a great deal of pain and the country was under great destruction. On the other hand, the government in Yugoslavia was still in exile and this government was accepted as an official member ...
What happened to Serbia and Bulgaria?
Serbia and Bulgaria were attacked by Germany and Bulgaria. After the war, however, the Austro-Hungarian Empire disintegrated, and the unification of the Slavs, which left the empire, with Serbia, laid the foundation for the foundation of Yugoslavia. As a result of this merger, on December 1, 1918, the state, which was ruled by the constitution, ...
How many states did Kosovo leave?
Finally, with the independence of Kosovo, seven states emerged as a result of the disintegration of Yugoslavia. These states; Serbia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, Croatia, Slovenia, Macedonia, ...
When did Kosovo start a debt reform?
The increasing debt burden necessitated deep-rooted reforms after 1983, in line with the economic stabilization program. Political demonstrations and actions that began in Kosovo in 1981 have spread to other republics over time.
Which country was the first to leave Yugoslavia?
Serbia began its attacks against the separatist elements in Yugoslavia, led by Milosevic, who held the Yugoslavian army. As a result, Slovenia was the first state to leave Yugoslavia in 1991, and in June 1991 Croatia, under the leadership of Franjo Tudman, decided for independence. Serbia, which does not accept Croatia’s independence, ...
Who was the first president of Yugoslavia?
The birth of Yugoslavia is in some ways attributable to US President Woodrow Wilson who, at the Versailles Peace Conference in 1919, actively supported the formation of the Kingdom of the Slovenes, Croats, and Serbs—the predecessor of Yugoslavia. During the Bosnian War of 1992-1995, the United States, under President Clinton, gave decisive leadership to ending that conflict in 1995 with the Dayton Peace Accords. The United States continues to have a special attachment to the seven states that were formerly part of Yugoslavia and enjoys close relations with these seven states. Today, like the United States, the area of Yugoslavia is multiculturally diverse and widely engaged with the international and regional communities in order to improve the lives of its citizens.
When did Croatia occupy Slovenia?
These four years of struggle ended in 1995. In 1998, Croatia was able to occupy all of eastern Slovenia.
What is the history of Kosovo?
The area is rich with Serbian history. The World Factbook states that “during the medieval period, Kosovo became the center of a Serbian Empire and saw the construction of many important Serb religious sites.” 5 It was also here that the Serbs suffered a major defeat by the Ottoman Turks in the Battle of Kosovo in 1389. The Albanian presence continued to grow and, by the end of the 19th century, Albanians had become the dominant ethnic group in Kosovo. 6
When did Slovenia become independent?
In 1991, driven by the goal of full freedom from the Serb majority, Slovenia declared its independence after a ten-day struggle. Slovenia is the most flourishing of the former member states of Yugoslavia, enjoying strong economic benefits from a stable political system.
Who was the leader of Serbia in 1989?
He led Yugoslavia until his death in 1980. After almost a decade of weak internal leadership, Slobodan Milosevic became President of Serbia in 1989. An ultra-nationalist, Milosevic advocated Serb domination which led to the violent breakup of Yugoslavia in 1991.
When did Montenegro become a member of the United Nations?
It began transitioning to full independence despite a loose state union in 2003 known as “Serbia and Montenegro.” The 14 years of transition passed peacefully and in June 2006, following a decade of negotiations, Montenegro became the 192nd member state of the United Nations. The United States played a significant role in the negotiations that led to Montenegrin independence in 2006, and the bilateral relationship remains favorable today.
Is Bosnia a sovereign state?
Bosnia and Herzegovina was confirmed as a sovereign state. Today, the country is slightly smaller than West Virginia and has a population of over four and a half million. 1. However, the political solution that ended the war is complex. There are two tiers of government.
Where did Yugoslavia live?
Yugoslavia occupied a significant portion of the Balkan peninsula, including a strip of land on the east coast of the Adriatic Sea, stretching southward from the Bay of Trieste in Central Europe to the mouth of Bojana as well as Lake Prespa inland, and eastward as far as the Iron Gates on the Danube and Midžor in the Balkan Mountains, thus including a large part of Southeast Europe, a region with a history of ethnic conflict.
What countries were part of Yugoslavia?
After the Allied victory in World War II, Yugoslavia was set up as a federation of six republics, with borders drawn along ethnic and historical lines: Bosnia and Herzegovina, Croatia, Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia, and Slovenia. In addition, two autonomous provinces were established within Serbia: Vojvodina and Kosovo. Each of the republics had its own branch of the League of Communists of Yugoslavia party and a ruling elite, and any tensions were solved on the federal level. The Yugoslav model of state organisation, as well as a "middle way" between planned and liberal economy, had been a relative success, and the country experienced a period of strong economic growth and relative political stability up to the 1980s, under dictatorial rule of Josip Broz Tito. After his death in 1980, the weakened system of federal government was left unable to cope with rising economic and political challenges.
Why did the Croatian Serbs in Knin try to gain access to weapons?
Croatian Serbs in Knin, under the leadership of local police inspector Milan Martić, began to try to gain access to weapons so that the Croatian Serbs could mount a successful revolt against the Croatian government. Croatian Serb politicians including the Mayor of Knin met with Borisav Jović, the head of the Yugoslav Presidency in August 1990, and urged him to push the council to take action to prevent Croatia from separating from Yugoslavia, because they claimed that the Serb population would be in danger in Croatia which was ruled by Tuđman and his nationalist government.
How many ethnic Serbs died in Bosnia?
Of that number, 330,000 to 390,000 ethnic Serbs perished from all causes in Croatia and Bosnia. These same historians also established the deaths of 192,000 to 207,000 ethnic Croats and 86,000 to 103,000 Muslims from all affiliations and causes throughout Yugoslavia.
What was the Yugoslav model?
The Yugoslav model of state organisation, as well as a "middle way" between planned and liberal economy, had been a relative success, and the country experienced a period of strong economic growth and relative political stability up to the 1980s, under dictatorial rule of Josip Broz Tito.
How did the Croats and Slovenes reform Yugoslavia?
In turn, the Croats and Slovenes sought to reform Yugoslavia by delegating even more power to six republics, but were voted down continuously in every motion and attempt to force the party to adopt the new voting system. As a result, the Croatian delegation, led by Chairman Ivica Račan, and Slovene delegation left the Congress on 23 January 1990, effectively dissolving the all-Yugoslav party. Along with external pressure, this caused the adoption of multi-party systems in all the republics.
What were the two autonomous provinces of Serbia?
In addition, two autonomous provinces were established within Serbia: Vojvodina and Kosovo. Each of the republics had its own branch of the League of Communists of Yugoslavia party and a ruling elite, and any tensions were solved on the federal level.

The Fall of Yugoslavia
The Federal Republic of Yugoslavia
- What remained of Yugoslavia after its dissolution was initially referred to as the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. This republic was comprised of Serbia and Montenegro.
Slovenia
- Slovenia, the most homogeneous and prosperous region of what was once Yugoslavia, was the first to secede from the diverse kingdom. This country now has its own language and capital city, Ljubljana (also a primate city). Slovenia is mostly Roman Catholic and has a compulsory education system. Slovenia was able to avoid much of the bloodshed induced...
Macedonia
- Macedonia's claim to fame is its rocky relationship with Greece, a longstanding dispute caused by the very name Macedonia that existed before Yugoslavia even fell apart. For geographical and cultural reasons, Greece feels that "Macedonia", named after the Greek kingdom of Macedon, was appropriated and should not be used. Because Greece is so strongly opposed to the use of the a…
Croatia
- In January 1998, Croatia assumed control of its entire territory, some of which had been under the control of Serbs. This also marked the end of a two-year United Nations peacekeeping mission there. Croatia's declaration of independence in 1991 caused Serbia, unwilling to cede, to declare war. Croatia is a boomerang-shaped country of over four million with extensive coastline along t…
Bosnia and Herzegovina
- The almost landlocked "cauldron of conflict" of four million inhabitants is a melting pot of Muslims, Serbs, and Croats. While the Winter Olympics of 1984 were held in Bosnia-Herzegovina's capital city of Sarajevo, the country has since been devastated by war. The mountainous region has been trying to rebuild its infrastructure since its 1995 peace agreement with Croatia and Ser…
Sources
- Chapman, Bert. “Yugoslav-Soviet Split.” Purdue Libraries e-Pubs, 16 Oct. 2014.
- Harris, Emily. “Former Yugoslavia 101: The Balkans Breakup.” NPR, All Things Considered, 18 Feb. 2008.
- Kästle, Klaus. "Serbia and Montenegro".One World Nations Online.
- “The Breakup of Yugoslavia.” Remembering Srebrenica, Scotland, 16 Nov. 2014.
The Origins of Yugoslavia
The First Kingdom
- Ten years of political infighting between the many different parties followed, largely because the kingdom was dominated by Serbs, who had expanded their governing structures to run it, rather than by anything new. Consequently, King Aleksander I shut the parliament and created a royal dictatorship. He renamed the country Yugoslavia, (literally ‘Land of the South Slavs’) and create…
War and The Second Yugoslavia
- This first Yugoslavia lasted until the Second World War when Axis forces invaded in 1941. The Regency had been moving closer to Hitler, but an anti-Nazi coup brought the government down and the wrath of Germany onto them. Warensued, but not one as simple as pro-Axis versus anti-Axis, as communist, nationalist, royalist, fascist and other factions all fought in what was effecti…
War and The Third Yugoslavia
- Throughout his rule, Tito had to tie the federation together against growing nationalism. After his death, these forces began to increase rapidly and tore Yugoslavia apart. As Slobodan Milosevic took control first of Serbia and then the collapsing Yugoslavia’s military, dreaming of a Greater Serbia, Slovenia and Croatia declared their independence to escape him. Yugoslav and Serbian …
Key People from The History of Yugoslavia
- King Alexander / Aleksander I 1888 - 1934 Born to the King of Serbia, Alexander lived some of his youth in exile before leading Serbia as regent during World War 1. He was key in declaring the Kingdom of the Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes, becoming king in 1921. However, years of frustration at the political infighting made him declare a dictatorship in early 1929, creating Yugoslavia. He …