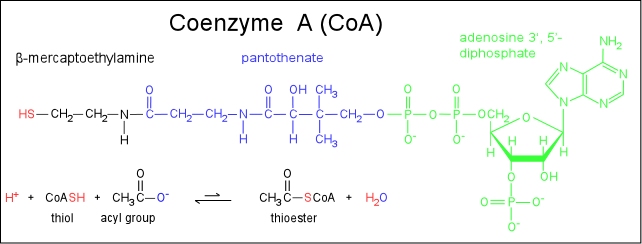
What is a thioester in organic chemistry?
Thioesters are organic compounds having the general chemical formula R-C (=O)-SR’. These compounds are analogous to carboxylate esters and differ from them due to the presence of a sulfur atom where the linking oxygen atom occurs in carboxylate ester. A thioester forms when a thiol reacts with a carboxylic acid.
How do you make thioester?
The most typical route to thioester involves the reaction of an acid chloride with an alkali metal salt of a thiol: Another common route entails the displacement of halides by the alkali metal salt of a thiocarboxylic acid.
What is the role of thioesters in ATP production?
In other words, thioesters could have actually played the role of ATP in a "thioester world" initially devoid of ATP. Eventually, [these] thioesters could have served to usher in ATP through its ability to support the formation of bonds between phosphate groups.
Why are thioesters more reactive towards amine nucleophiles than thiolates?
The carbonyl center in thioesters is more reactive toward amine nucleophiles to give amides : In a related reaction, but using a soft-metal to capture the thiolate, thioesters are converted into esters. Thioesters provide useful chemoselectivity in the synthesis of biomolecules.
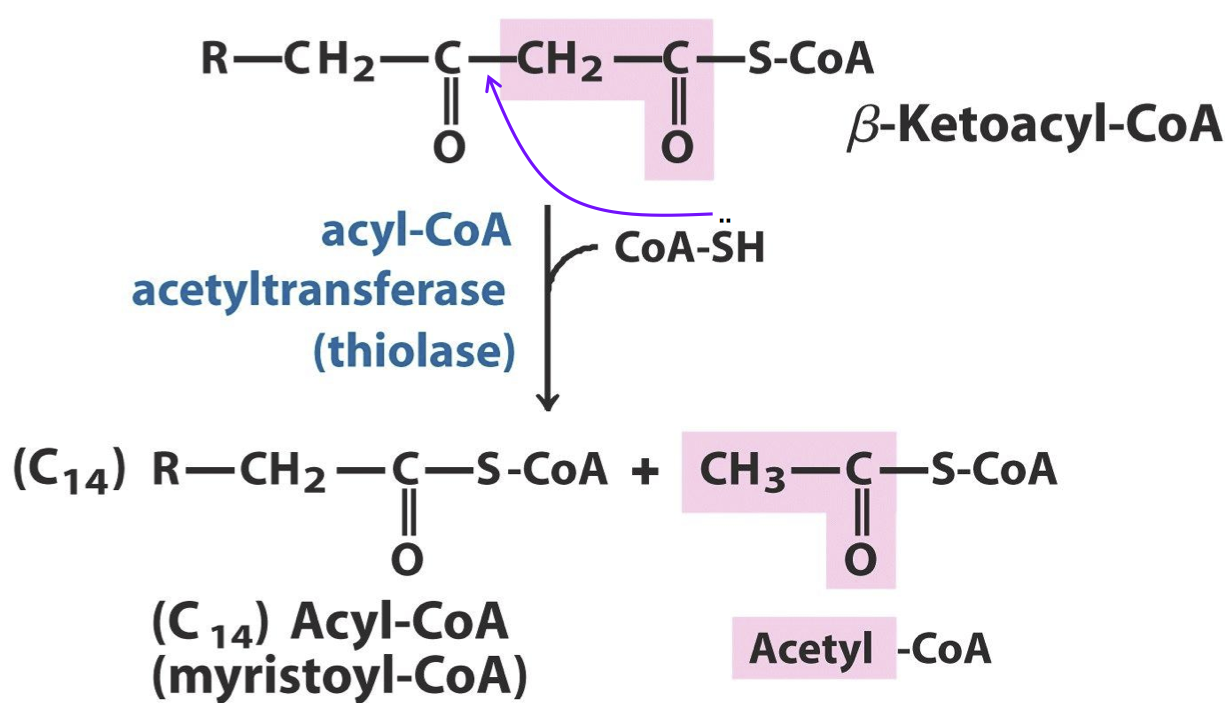
What is an example of thioester?
Thioesters are common intermediates in many biosynthetic reactions, including the formation and degradation of fatty acids and mevalonate, precursor to steroids. Examples include malonyl-CoA, acetoacetyl-CoA, propionyl-CoA, cinnamoyl-CoA, and acyl carrier protein (ACP) thioesters.
Is acetyl co AA thioester?
Acyl-coenzyme A (CoA) thioesters are key metabolites in numerous anabolic and catabolic pathways, including fatty acid biosynthesis and β-oxidation, the Krebs cycle, and cholesterol and isoprenoid biosynthesis.
What is the general formula of thioester?
Thioester | C19H12BrN3O2S - PubChem.
Is CoA a thioester?
The reaction in which a fatty acid acyl group is linked to glycerol represents the conversion of a thioester (fatty acyl CoA) to an ester.
What is meant by acetyl coenzyme A?
Acetyl coenzyme A: An important metabolic intermediate, derived from various pathways, such as glycolysis, fatty acid oxidation, and degradation of some amino acids. It also represents a key intermediate in lipid biosynthesis. Commonly referred to as acetyl CoA.
What are coenzyme A?
Coenzyme A (CoA, SHCoA, CoASH) is a coenzyme, notable for its role in the synthesis and oxidation of fatty acids, and the oxidation of pyruvate in the citric acid cycle.
How do you name a thioester?
Thioesters are named as if the alkyl chain from the alcohol is a substituent. No number is assigned to this alkyl chain. This is followed by the name of the parent chain from the carboxylic acid part of the thioester named as an alkane with the ending –thiooate.
Does ATP have a thioester bond?
The thioester bond is what biochemists call a high-energy bond, equivalent to the phosphate bonds in adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is the main supplier of energy in all living organisms. ...
What is the role of thioester in glycolysis?
Thioester is involved in the formation of the first glycolysis intermediate with an acyl-phosphate group, which is part of the slow step of glycolysis e. Thioester is involved in the formation of the first glycolysis intermediate with an acyl-phosphate group, which posses a ΔG for hydrolysis that is highly endergonic.
How is a thioester bond formed?
A thioester is formed between the carboxyl of the terminal glycine residue of Ub and a cysteine residue of the activating enzyme, or E1.
What is the role of thioester?
Thioesters play a prominent role in metabolism. This is especially true of fatty acid metabolism. The central metabolite acetyl CoA is a thioester that is produced mainly by oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate or by fatty acid degradation.
Is thioester a good leaving group?
A thioester is more reactive than an ester, for example, because a thiolate (RS-) is a weaker base and better leaving group than an alcoxide (RO-). Recall from chapter 7 that the pKa of a thiol is about 10, while the pKa of an alcohol is 15 or higher: a stronger conjugate acid means a weaker conjugate base.
What is the role of thioester in glycolysis?
Thioester is involved in the formation of the first glycolysis intermediate with an acyl-phosphate group, which is part of the slow step of glycolysis e. Thioester is involved in the formation of the first glycolysis intermediate with an acyl-phosphate group, which posses a ΔG for hydrolysis that is highly endergonic.
Which coenzyme is used for the decarboxylation of α keto acids?
In biological systems, enzymes utilize cofactors such as thiamin pyrophosphate to facilitate α-carbonyl decarboxylation reactions.
How does Acetyl-CoA form ATP?
The citric acid cycle, where acetyl CoA is modified in the mitochondria to produce energy precursors in preparation for the next step. Oxidative phosphorylation, the process where electron transport from the energy precursors from the citric acid cycle (step 3) leads to the phosphorylation of ADP, producing ATP.
Is acyl and acetyl the same?
The acyl and the acetyl groups are just a part of the molecules. A part of a molecule is called a moiety. The acetyl group is the name given to a specific type of moiety while the acyl group is the name given to a group of moieties.
What compound is used to treat thioketone 635?
Treatment of thioketone 635 with α-diazo carbonyl compounds in the presence of Rh 2 (OAc) 4 gives 3-aminothiophenes 637. Condensation of the ketene acetal with carbenoids, derived from diazo compounds, produces the intermediates 636, which undergo an intramolecular cyclization and subsequent aromatization to afford 637 ( Scheme 95) <2002J (P1)2414, 2002OL873>.
What reacts with arylidenecyanothio-acetamides 624?
Sulfonium ylides, generated from sulfonium bromides 625, react with arylidenecyanothio-acetamides 624 providing 4,5-dihydrothiophenes 627 via a cyclization of the intermediates 626 ( Scheme 93) <1997S623>. Similar cyclizations of 628 or 629 afford the dihydrothiophenes 630 <2001SC1647>.
Which model reaction supports the above mechanism?
A model reaction that supports the above mechanism is the glycolytic substrate-linked phosphorylation, which proceeds via a thiol ester prior to the formation of the phosphorylated intermediate ( Chapter 13 ). Although the chemical hypothesis is consistent with the substrate-linked phosphorylation mechanism, it is deficient in explaining the oxidative phosphorylation in mitochondria for two reasons:
Is an antibody required for the activation of the alternative pathway?
Antibody is not required for the activation of the alternative pathway, and, thus, the alternative pathway is generally viewed as an important mechanism of natural immunity. 3 Antibody can participate functionally, however, in the activation of the alternative pathway by a variety of particles, including virus-infected cells and bacteria. Thus, in some instances, the alternative pathway may participate in acquired immunity.
Is C a ligand?
where A and B represent the known redox pair, C is a hypothetical ligand, and A ∼ C is a hypothetical high-energy intermediate. The above mechanism can be modified to include other phosphorylated intermediates.
What are thioester-containing proteins?
The thioester-containing proteins (TEPs) are accessory proteins of the complement system, homologous to proteins such as C3, C4, a2M and CD109s. TEPs promote the opsonization of microorganisms and their elimination by phagocytosis in some invertebrates by activating the Toll signaling pathway (Bou et al., 2011; Dostálová et al., 2017). Seven TEP genes have been functionally characterized through molecular cloning in scallops, such as CfTEP and CfA2M in C. farreri ( Zhang et al., 2007a; Xue et al., 2017) and PyC3, PyA2M, PyTEP1, PyTEP2 and PyCD109 in Patinopecten yessoensis ( Liao et al., 2018). The family of TEPs in invertebrates is diverse and the difference between variants makes this family a potential model to explore the functional divergence in bivalve immunity. Recently, the structural analysis of several scallop TEPs showed the existence of a highly variable central region produced by the splicing of six exons, which has an important impact in the specificity of the immune response since the number of produced isoforms differs according to the immune challenge (Zhang et al., 2009a ). In C. farreri, it was further demonstrated that CfTEP, like a C3 protein, undergoes fragmentation due to the action of endogenous serum proteases ( Xue et al., 2017 ).
Which protein removes thioester linked palmitate?
Thioester linked palmitate is removed from proteins by acyl protein thioesterases, which include APT1 and APT2 as well as the α/β hydrolase domain containing proteins ABHD17A, B, and C (Won et al., 2018).
What is the role of thiol ester in biochemistry?
The central role of thiol ester compounds in nutritional biochemistry is illustrated by considering some features of the mechanisms of the reactions catalyzed by citrate synthase and acetyl-CoA carboxylase. A brief background on the properties of the thiol ester bond is first presented. This material has been simplified and is intended only to clarify why the reactions employ thiol esters of carboxylic acids, rather than oxygen esters or the free, unesterified carboxylic acid.
What is the thiol ester linkage?
The thiol ester linkage is an important concern to those studying the mechanisms of action of acetyl-CoA carboxylase, citrate synthase, propionyl-CoA carboxylase, and HMG-CoA synthase.
How is acetyl-coa produced?
Acetyl-CoA is generated either by oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate from glycolysis, which occurs in mitochondrial matrix, by oxidation of long-chain fatty acids, or by oxidative degradation of certain amino acids. Acetyl-CoA then enters in the TCA cycle where it is oxidized for energy production. In the cytosol, the initial step of de novo lipid biogenesis consists in conversion of citrate to acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetate by the enzyme ATP-citrate lyase using the energy of ATP hydrolysis [59]. Cytosolic/nuclear acetyl-CoA is also produced by two acetyl-CoA synthetase enzymes that condense acetate and thiol. Furthermore, downregulation of enzymes required for the synthesis of acetyl-CoA from acetate or citrate reduces acetylation of specific protein and histone substrates [58,59]. Accordingly, serum starvation or glucose deprivation induces a marked decrease in global histone acetylation levels [59].
Is there resonance in thiol ester?
FIGURE 4.76. No resonance in a thiol ester.
Which structural elements are responsible for the unusual active center conformation and the extremely low esterolytic activity of resting?
In conclusion, the mutational studies identified some of the structural elements responsible for the unusual active center conformation and the extremely low esterolytic activity of resting-state factor D. They include unique residues lining the specificity pocket (Lys 192, Thr 214, Ser 215, Arg 218, and Val 219 ), residues forming the surface loop 184−188 (Glu 184, Ser 185, Asn 186, Arg 187, Arg 188 ), and Ser 94. Results of esterolytic assays indicate that these residues act synergistically.
What is Thioester?
Thioesters are organic compounds having the general chemical formula R-C (=O)-SR’. These compounds are analogous to carboxylate esters and differ from them due to the presence of a sulfur atom where the linking oxygen atom occurs in carboxylate ester. A thioester forms when a thiol reacts with a carboxylic acid. In the field of biochemistry, coenzyme-A derivatives such as acetyl-CoA are well-known thioesters.
What is the Difference Between Ester and Thioester?
The key difference between ester and thioester is that ester compounds contain carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms whereas thioester compounds contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and sulfur atoms. Moreover, esters occur naturally and can be produced using different routes such as esterification of carboxylic acids with alcohols while the most typical route for thioesters is the reaction between an acid chloride and an alkali metal salt of a thiol.
What is the most common route of reaction for thioesters?
When considering the preparation of thioesters, the most typical route is the reaction between an acid chloride and an alkali metal salt of a thiol. Another common route is the displacement of halides by the alkali metal salt of a thiocarboxylic acid. There is a carbonyl centre in a thioester that is reactive towards the nucleophiles, ...
What is the formula for esters?
Esters are organic compounds having the general chemical formula R-C (=O)-OR’. These chemical compounds are derived from either organic or inorganic acid compounds in which at least one hydroxyl group is replaced by an alkoxy group. Typically, esters originate from the substitution reaction of carboxylic acids and alcohols.
What are the applications of thioesters?
There are different applications of thioesters including the synthesis of all esters, participating in the synthesis of a number of other cellular components including peptides, fatty acids, sterols, terpenes, etc.
Is a thioester reactive?
There is a carbonyl centre in a thioester that is reactive towards the nucleophiles, including water. Therefore, these chemical compounds are common intermediates of the conversion of alkyl halides into alkyl thiols. Moreover, a thioester can combine with an amine to give an amide.
What is the conversion of an amide to a high-energy thioester?
Conversion of an amide to a high-energy thioester by Staphylococcus aureus sortase A is powered by variable binding affinity for calcium. Thioesters are key intermediates in biology, which often are generated from less energy-rich amide precursors.
What is the purpose of Staphylococcus aureus sortase A?
Staphylococcus aureus sortase A (SrtA) is an enzyme widely used in biotechnology for peptide ligation. The reaction proceeds in two steps, where the first step involves the conversion of an amide bond of substrate peptide into a thioester intermediate with the enzyme.
