What are the major plasma proteins and their functions?
What are the three major plasma proteins and their functions?
- Protein Nutrition.
- Osmotic Pressure and water balance.
- Buffering action.
- Transport of Lipids.
- Transport of other substances.
- Blood Coagulation.
What are the plasma proteins found in highest concentrations?
β-Globulin – 13.4% (β1-transferrin, β-lipoprotein, etc) ¥-Globulin – 11.0% (Antibodies, etc) Fibrinogen – 6.5%. 1. Albumin. This is the most abundant class of plasma protein (2.8 to 4.5 gm/100ml) with the highest electrophoretic mobility. It is soluble in water and is precipitated by fully saturated ammonium sulfate.
What plasma protein is the most plentiful?
What are the three main groups of plasma proteins and which is most abundant?
- Albumin is the most abundant of the plasma proteins. …
- The second most common plasma proteins are the globulins. …
- The least abundant plasma protein is fibrinogen.
Which of proteins can be found in plasma?
There are peripheral proteins on the exterior of the membrane that bind elements of the extracellular matrix. Carbohydrates, attached to lipids or proteins, are also found on the exterior surface of the plasma membrane. These carbohydrate complexes help the cell bind substances that the cell needs in the extracellular fluid.

What are the 4 major plasma proteins?
Total protein consists of albumin, globulins, and fibrinogen (in plasma only). Proteins function to control oncotic pressure, transport substances (hemoglobin, lipids, calcium), and promote inflammation and the complement cascade.
What are examples of plasma proteins?
Plasma proteins, such as albumin and globulin, that help maintain the colloidal osmotic pressure at about 25 mmHg. Electrolytes like sodium, potassium, bicarbonate, chloride, and calcium help maintain blood pH. Immunoglobulins help fight infection and various other small amounts of enzymes, hormones, and vitamins.
How many types of plasma proteins are there?
You have two main types of plasma proteins in your blood: albumin, which has many important roles, such as providing amino acids for your body tissues and stopping fluid leaks. globulin, which helps support your immune system, blood clotting, and other vital functions.
What are plasma proteins called?
The proteins in plasma include the antibody proteins, coagulation factors, and the proteins albumin and fibrinogen which maintain serum osmotic pressure. Each of these can be separated using different techniques so that they form various blood products, which are used to treat different conditions.
Which is not a plasma protein?
So, the correct option is 'Heparin'.
Is albumin plasma protein?
Albumin is a constitutional plasma protein, with several functions. In inflammatory states like trauma, disease, infection and states where the organism grows, increased capillary permeability leads to escape of albumin and other plasma solutes into the interstitium.
What is the most common plasma protein?
Plasma ProteinsAlbumin is the most abundant of the plasma proteins. Manufactured by the liver, albumin molecules serve as binding proteins—transport vehicles for fatty acids and steroid hormones. ... The second most common plasma proteins are the globulins. ... The least abundant plasma protein is fibrinogen.
Which are the 5 blood proteins?
The five main blood proteins that are found in blood plasma are albumin, globulin, immunoglobulin, prothrombin, and fibrinogen.
What are types of plasma?
Examples of three forms of plasmaAstrophysical plasmaTerrestrial plasmaAll stars Solar wind Interstellar nebulae Space between planets, star systems and galaxiesLightning Auroras Ionosphere Extremely hot flamesApr 29, 2014
Is fibrinogen a protein?
Fibrinogen and fibrin are multifunctional proteins. Fibrinogen is indispensable for platelet aggregation; it also binds to several plasma proteins, however, the biological function of this interaction is not completely understood.
Is fibrinogen a plasma protein?
Fibrinogen is the major plasma protein coagulation factor. Low plasma fibrinogen concentrations are therefore associated with an increased risk of bleeding due to impaired primary and secondary haemostasis.
What are the 3 major plasma proteins and their functions?
Albumins regulate the osmotic pressure of the blood (and hence moderate the osmotic pressure of body fluids) Globulins participate in the immune system (i.e. immunoglobulins) and also act as transport proteins. Fibrinogens are involved in the clotting process (soluble fibrinogen can form an insoluble fibrin clot)
What is the most common plasma protein?
Plasma ProteinsAlbumin is the most abundant of the plasma proteins. Manufactured by the liver, albumin molecules serve as binding proteins—transport vehicles for fatty acids and steroid hormones. ... The second most common plasma proteins are the globulins. ... The least abundant plasma protein is fibrinogen.
What are 3 types of plasma proteins and their functions?
What plasma protein is essential in body defense?Blood ProteinsNormal levelFunctionAlbumins3.5-5.0 g/dlcreate and maintain oncotic pressure; transport insoluble moleculesGlobulins2.0-2.5 g/dlparticipate in the immune systemFibrinogen0.2-0.45 g/dlBlood coagulationRegulatory proteinsRegulation of gene expression1 more row•Apr 28, 2022
What are the 3 major plasma proteins and their functions?
Albumins regulate the osmotic pressure of the blood (and hence moderate the osmotic pressure of body fluids) Globulins participate in the immune system (i.e. immunoglobulins) and also act as transport proteins. Fibrinogens are involved in the clotting process (soluble fibrinogen can form an insoluble fibrin clot)
What are plasma proteins quizlet?
What are the three plasma proteins? albumin, globulins, and fibrinogen.
Albumin Characteristics
The globular protein is made up of a single polypeptide chain and has 610 amino acids.
Albumin Functions
70-80% of the total colloidal osmotic pressure in the vessel is maintained by albumin, which is a macromolecular organic compound and out of the 25-30 mm Hg COP range, albumin alone contributes to the 22 mm Hg COP range.
Albumin Clinical significances
When the serum albumin concentration becomes lower than 2.5g% then it leads to the formation of edema in the body, due to which the fluid start migrating from the vascular compartment to the interstitial spaces.
Globulin Characteristics
Electrophoresis is used to differentiate it into alpha, beta, and gamma globulin.
What is plasma protein?
Plasma protein tests are blood tests that detect the amount of proteins in the blood. This lab work is usually ordered as part of a comprehensive metabolic panel (CMP) during a physical exam. The tests can help your doctor determine your overall health. Plasma protein tests are also known as a total protein test.
What are the two main types of plasma proteins?
Types of plasma proteins. You have two main types of plasma proteins in your blood: albumin, which has many important roles, such as providing amino acids for your body tissues and stopping fluid leaks. globulin, which helps support your immune system, blood clotting, and other vital functions.
What tests are done to detect abnormal protein levels?
liver enzyme tests to detect related diseases and inflammation. protein electrophoresis to look for underlying bone marrow disorders. If your tests indicate that your abnormal protein levels are caused by any of the following serious conditions, your doctor will recommend treatments to address them: heart disease.
How do you know if you have low protein?
Symptoms of abnormal protein levels. Certain symptoms may indicate whether you have high or low protein levels in your blood. Symptoms of low protein levels can include: bruising easily. slow clotting of blood after an injury. fatigue. brittle or ridged nails. hair loss. rashes.
Why do doctors order plasma protein tests?
Doctors order plasma protein tests to measure the amounts of specific proteins in the blood. Total protein levels may be higher or lower than average in the case of certain disorders, including: bone marrow disorders. edema (fluid buildup in the tissues) hepatitis (liver infection) HIV. inflammatory bowel disease.
What are the symptoms of high protein levels?
Symptoms of high protein levels can include: pain in your bones. numbness or tingling in your hands, feet, or legs. loss of appetite. weight loss. excessive thirst. frequent infections. Symptoms may vary depending on the condition causing your abnormal plasma protein levels.
What does low protein mean in a protein test?
Lower-than-normal plasma protein levels may indicate: severe malabsorption of nutrients and malnutrition. kidney or liver disease. bowel problems. In addition to albumin levels, your protein test may also detect blood levels of globulin. This is called an A/G ratio.
What are the functions of blood proteins?
They serve many different functions, including transport of lipids, hormones, vitamins and minerals in activity and functioning of the immune system. Other blood proteins act as enzymes, complement components, protease inhibitors or kinin precursors.
What is the role of albumin in plasma?
Serum albumin accounts for 55% of blood proteins, is a major contributor to maintaining the oncotic pressure of plasma and assists, as a carrier, in the transport of lipids and steroid hormones. Globulins make up 38% of blood proteins and transport ions, hormones, and lipids assisting in immune function.
What is the function of fibrinogen?
Fibrinogen comprises 7% of blood proteins; conversion of fibrinogen to insoluble fibrin is essential for blood clotting. The remainder of the plasma proteins (1%) are regulatory proteins, such as enzymes, proenzymes, and hormones. All blood proteins are synthesized in liver except for the gamma globulins.
Is haemoglobin a protein?
Other blood proteins act as enzymes, complement components, protease inhibitors or kinin precursors. Contrary to popular belief, haemoglobin is not a blood protein, as it is carried within red blood cells, rather than in the blood serum .
Which Plasma Proteins Are Involved In Blood Clotting
A liquid called plasma makes up about half of the content of blood. Plasma contains proteins that help blood to clot, transport substances through the blood, and perform other functions. Blood plasma also contains glucose and other dissolved nutrients.
What Are The Proteins Involved In Blood Clotting?
The proteins involved in a clot include prothrobin, thrombin, fibrinogen, thromboplastin, and fibrin. The clot forms by creating thread like structures that trap RBC’s and platelets that will eventually begin to plug the wound.
What Are Coagulants And Plasma Proteins?
It mainly comprises of: Coagulants, mainly fibrinogen, aid in blood clotting Plasma proteins, such as albumin and globulin, that help maintain the colloidal osmotic pressure at about 25 mmHg Electrolytes like sodium, potassium, bicarbonate, chloride, and calcium help maintain blood pH
What Are Plasma Proteins?
Plasma proteins are proteins found in the blood plasma, the clear, protein-rich fluid which is left behind when platelets, red blood cells, and white blood cells are removed from the blood.
What Are The 21 Proteins Involved In Blood Coagulation?
Proteins involved in Blood Coagulation. The information on 21 proteins involved in blood coagulation pathway is as follows: Fibrinogen (factor I) consists of three polypeptide chains – alpha, beta and gamma. It is converted to fibrin (factor Ia) by thrombin (factor IIa).
What Are The Steps In Blood Clot Formation?
What are the steps in clot formation? 1) Constriction of the blood vessel. 2) Formation of a temporary platelet plug. 3) Activation of the coagulation cascade. 4) Formation of fibrin plug or the final clot. What causes clot formation? Blood clots form when certain parts of your blood thicken, forming a semisolid mass.
What Is The Mechanism Of Blood Clotting?
Vaccine-induced immune thrombotic thrombocytopenia (VITT), blood clotting, is a condition very rarely seen … an important step in unraveling the mechanism underlying VITT,” co-author Alan Parker (Cardiff University) clarified.
What plasma proteins help maintain colloidal osmotic pressure?
Plasma proteins, such as albumin and globulin, that help maintain the colloidal osmotic pressure at about 25 mmHg
What are immunoglobulins used for?
Immunoglobulins: Immunoglobulins protect the body against invading bacteria and viruses and play a key role in the body’s defense. Certain immunological disorders like congenital or acquired primary immune deficiency occur when the body cannot produce antibodies or experience the adverse effects of cancer treatments that harm the antibodies. Both disorders benefit greatly from immunoglobulin infusions. Immunoglobulins also play a major role in passive immunization. Antidotes to diseases such as chickenpox, rabies, hepatitis, and tetanus are the initial treatment after suspected exposure to limit disease progression. Such specific immunoglobulins are derived when patients who have been previously affected by a disease donate plasma, for example, chickenpox. This plasma contains high amounts of circulating antibodies against chickenpox that can be collected and stored after fractionation for use as post-exposure vaccines for varicella.
What is plasma in biology?
Plasma, also known as blood plasma, appears light-yellowish or straw-colored. It serves as the liquid base for whole blood. Whole blood minus erythrocytes (RBCs), leukocytes (WBCs), and thrombocytes (platelets) make up the plasma. Serum, sometimes mistakenly considered synonymous with plasma, consists of plasma without fibrinogen. Plasma contains 91% to 92% of water and 8% to 9% of solids. It mainly comprises of:
What is plasmapheresis used for?
Plasmapheresis: Plasmapheresis is an effective temporary treatment in many autoimmune diseases. In therapeutic plasmapheresis, the patient’s venous blood is withdrawn, blood cells are separated, and a replacement colloid solution and blood cells are infused in its place.[16] A 4% to 5% human serum albumin solution in saline is the preferred replacement solution in most cases. The following are common conditions where plasmapheresis is utilized:
How is plasma separated from whole blood?
It can be separated from whole blood by the process of centrifugation, i.e., spinning whole blood with an anticoagulant in a centrifuge. Plasma is lighter, forming the upper yellowish layer while the denser blood cells fall to the bottom. The plasma collected is frozen within 24 hours to preserve the functionality of the various clotting factors and immunoglobulins; it is thawed before use and has a shelf life of 1 year. Interestingly, while O- is the preferred universal donor for blood, the plasma of AB blood groups is the most preferred because their plasma does not contain antibodies, making it acceptable for everyone without fear of an adverse reaction.
What is albumin used for?
Albumin: Albumin is the main protein that controls oncotic pressure and serves as the transporter of multiple endogenous and exogenous substances (e.g., drugs) throughout the body. Infusion of albumin is used in the treatment of burns and hemorrhagic shock. Studies have also shown marked improvement in the prognosis of cirrhotic patients.[10] In patients with liver cirrhosis, albumin infusions have decreased mortality in patients with spontaneous bacterial peritonitis and improved outcomes in large volume paracentesis. [11][12] Albumin is also useful in the management of hepatorenal syndrome.
How much osmotic pressure is maintained?
Maintenance of Osmotic Pressure: the colloidal osmotic pressure is maintained at around 25 mmHg by the plasma proteins like albumin synthesized by the liver.
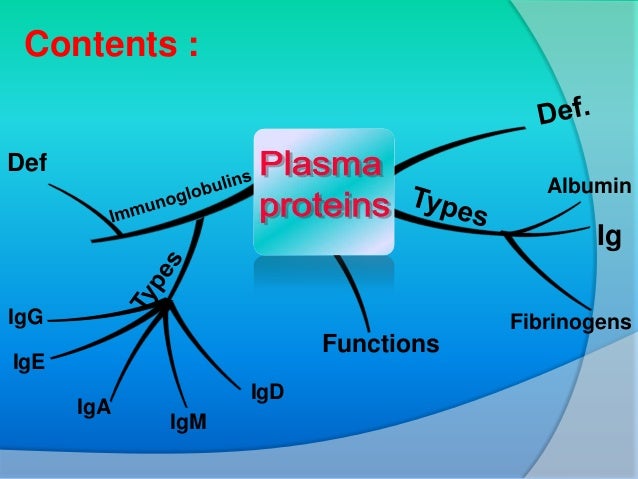
Classification of Plasma Proteins
- 1. Albumin 2. Globulin 1. Alpha 1 globulin 1.1. Alpha 1: acid glycoprotein 1.2. Alpha 1 fetoglobulin 1.3. Alpha 1 antitrypsin 2. Alpha 2 globulin 2.1. Ceruloplasmin 2.2. Haptoglobin 3. Beta globulin 3.1. Transferrin 3.2. C- reactive protein 3.3. Hemopexin 3. Other important plasma 1. Bence-jones protein 2. Fibrinogen
Albumin
- Albumin Characteristics
1. The globular protein is made up of a single polypeptide chain and has 610 amino acids. 2. Molecular weight: 69,000 3. Comprise 60-70% of plasma protein 4. Isoelectric PH: 4.7 5. Synthesized in liver 6. Full saturation of ammonium sulfate is required for its precipitation. 7. 3.… - Albumin Functions
1. 70-80% of the total colloidal osmotic pressure in the vessel is maintained by albumin, which is a macromolecular organic compound and out of the 25-30 mm Hg COP range, albumin alone contributes to the 22 mm Hg COP range. 2. To draw the water inside the plasma from interstitia…
Globulin
- Globulin Characteristics
1. Globular protein 2. Water-insoluble 3. Molecular weight: 90,000- 1,300,000 4. Electrophoresis is used to differentiate it into alpha, beta, and gamma globulin.
Other Important Plasma Proteins
- a. Bence-jones protein
Characteristics 1. During malignancy, an antibody is formed from a rapid division of monoclonal plasma cells known as paraprotein, thus bence-jones protein is a type of paraprotein. 2. Molecular weight: 45,000 3. Formed from light chain either kappa or lambda abnormal immunoglobulin 4. … - b. Fibrinogen
Characteristics 1. Aka clotting factor is a soluble plasma protein 2. It is inactivated form of fibrin that is required for blood clotting. 3. Place of synthesis: liver 4. Serum concentration: 200-400 mg/100mL 5. Molecular weight: 350,000-450,000. Clinical significance 1. Blood clotting factor 2…
Functions of Plasma Proteins
- Acid-base regulation: plasma protein being amphoteric can act as a buffer to maintain the balance between the acid-base of blood and other bodily fluids.
- Colloidal osmotic pressure: aka oncotic pressure is maintained by plasma proteins, which are essential for the distribution of water in blood vessels and interstitial spaces.
- Blood clotting:plasma proteins such as fibrinogen, prothrombin, and other blood clotting fact…
- Acid-base regulation: plasma protein being amphoteric can act as a buffer to maintain the balance between the acid-base of blood and other bodily fluids.
- Colloidal osmotic pressure: aka oncotic pressure is maintained by plasma proteins, which are essential for the distribution of water in blood vessels and interstitial spaces.
- Blood clotting:plasma proteins such as fibrinogen, prothrombin, and other blood clotting factors are present in an inactive form in plasma. During the injury, they got activated and help in blood c...
- Provide immunity: B lymphocytes form immunoglobulins which are present in plasma and provide immunity against pathogens
References
- Gupta, A. (2018). Plasma Proteins. Comprehensive Biochemistry for Dentistry, 67–75. doi:10.1007/978-981-13-1035-5_4
- Alberti KGMN (ed) (1978) Recent advances in clinical biochemistry. Churchill Livingstone, London
- Baron DN (1982) A short textbook of chemical pathology, 4th edn. Wiley, New York Conn EE, …
- Gupta, A. (2018). Plasma Proteins. Comprehensive Biochemistry for Dentistry, 67–75. doi:10.1007/978-981-13-1035-5_4
- Alberti KGMN (ed) (1978) Recent advances in clinical biochemistry. Churchill Livingstone, London
- Baron DN (1982) A short textbook of chemical pathology, 4th edn. Wiley, New York Conn EE, Stump PK (1969) Outline of biochemistry, 2nd edn. Wiley, New Delhi
- https://biochemden.com/plasma-proteins/