Beta-1 selective blockers are a subclass of beta blockers that are commonly used to treat high blood pressure. Drugs in this class include atenolol (Tenormin), metoprolol (Lopressor), nebivolol (Bystolic) and bisoprolol (Zebeta, Monocor).
What medications are beta blockers?
These medicines can also relax blood vessels so the blood flows better. Drug Names Beta-blockers include: Acebutolol ( Sectral) Atenolol ( Tenormin) Betaxolol ( Kerlone) Bisoprolol ( Zebeta, Ziac)...
What are the side effects of beta blockers?
Side effects commonly reported by people taking beta blockers include:
- feeling tired, dizzy or lightheaded (these can be signs of a slow heart rate)
- cold fingers or toes (beta blockers may affect the blood supply to your hands and feet)
- difficulties sleeping or nightmares
- feeling sick
What are the contraindications for beta blockers?
- Beta-blockers are very effective for the symptomatic treatment of patients with effort angina or arrhythmias.
- Most evidence for the reduction of cardiovascular events by beta-blockers concerns acute coronary syndrome patients; especially in the presence of LV dysfunction.
- High-degree AV block (without a pacemaker) is an absolute contraindication.
What is the best beta blocker for hypertension?
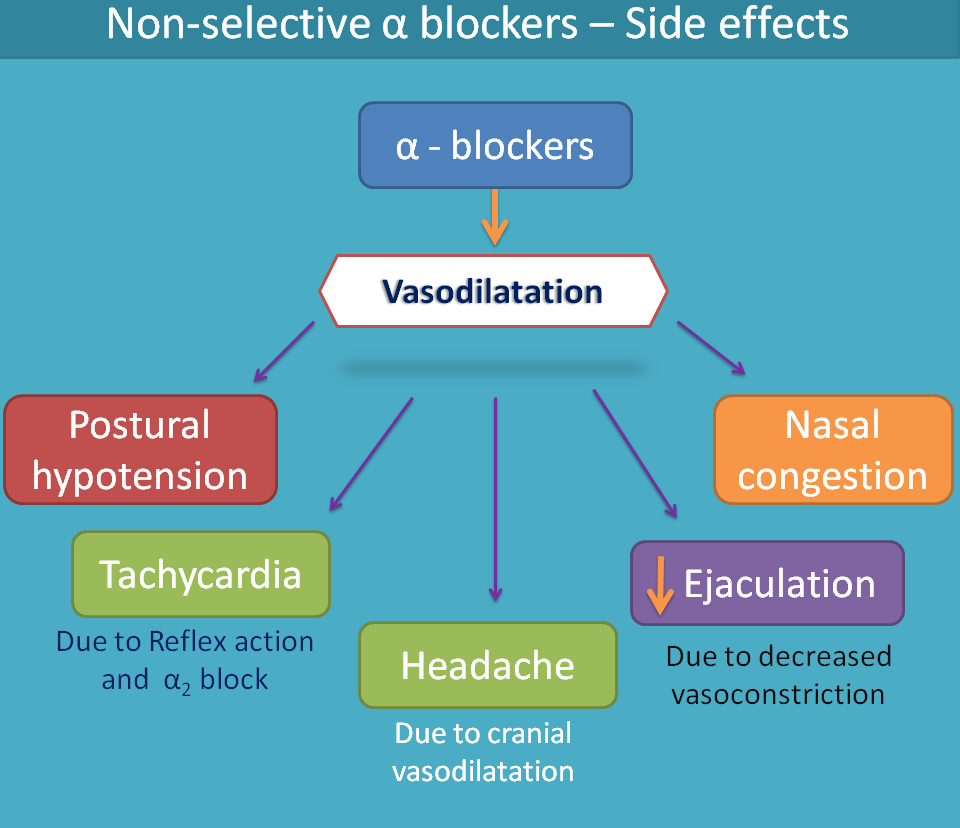
- Alpha blockers. Alpha blockers prevent the hormone norepinephrine (noradrenaline) from tightening the muscles in the walls of smaller arteries and veins, which causes the vessels to remain open and relaxed.
- Alpha-beta blockers. Alpha-beta blockers work similarly to beta blockers. ...
- Central-acting agents. ...
- Vasodilators. ...
- Aldosterone antagonists. ...

What is selective and non-selective beta-blockers?
Beta-blockers classify as either non-selective or beta-1 selective. There are also beta-blocking drugs that affect both beta-2 and/or beta-3 selectively; neither has a known clinical purpose to date. Non-selective agents bind to both beta-1 and beta-2 receptors and induce antagonizing effects via both receptors.
Which beta-blockers are not selective?
Non-selective or non-specific beta blockersPropranolol,nadolol,timolol maleate,penbutolol sulfate,sotalol hydrochloride, and.pindolol.
Are beta-blockers selective or nonselective?
Beta-1 selective blockers are preferred for therapy of heart disease, whereas the nonselective beta-blockers are preferred as therapy to prevent recurrent variceal hemorrhage in patients with cirrhosis and portal hypertension.
What are the 4 types of beta-blockers?
labetalol (also called Trandate) metoprolol (also called Betaloc or Lopresor) propranolol (also called Inderal or Angilol) sotalol.
Is propranolol selective or not?
Propranolol is a nonselective, competitive antagonist at beta adrenergic receptors. It binds with high affinity to both beta-1 and beta-2 receptor subtypes, but has lower affinity at the beta-3 subtype.
What is the difference between Cardioselective and non Cardioselective beta-blockers?
Cardioselective agents have a greater affinity for β1-adrenergic receptors located in the heart, whereas nonselective agents work on β1-adrenergic receptors and β2-adrenergic receptors located in bronchial musculature.
Is metoprolol selective or non selective?
Metoprolol is a relatively selective β1-receptor antagonist. The potency of metoprolol for β1-receptor blockade is equal to that of propranolol, but metoprolol exhibits only 1% to 2% of the effect of propranolol at β2 receptors.
Is propranolol a non selective beta-blocker?
Nonselective beta-blockers are a subclass of beta-blockers including propranolol (Inderal), nadolol (Corgard), etc.
Is metoprolol selective or non selective?
Metoprolol is a relatively selective β1-receptor antagonist. The potency of metoprolol for β1-receptor blockade is equal to that of propranolol, but metoprolol exhibits only 1% to 2% of the effect of propranolol at β2 receptors.
Is carvedilol a selective or non selective beta-blocker?
Carvedilol is a non‐selective beta‐blocker with additional intrinsic alpha1‐blocking effects, which may be superior to traditional, non‐selective beta‐blockers in reducing portal pressure and, therefore, in reducing the risk of upper gastrointestinal bleeding.
Is carvedilol a non selective beta-blocker?
Carvedilol is a non-selective beta-blocker with additional intrinsic alpha1-blocking effects, which may be superior to traditional, non-selective beta-blockers in reducing portal pressure and, therefore, in reducing the risk of upper gastrointestinal bleeding.
What is the difference between Cardioselective and non Cardioselective beta-blockers?
Cardioselective agents have a greater affinity for β1-adrenergic receptors located in the heart, whereas nonselective agents work on β1-adrenergic receptors and β2-adrenergic receptors located in bronchial musculature.
What are beta 1 blockers?
The cardio-selective beta-1-blockers include atenolol, betaxolol, bisoprolol, esmolol, acebutolol, metoprolol, and nebivolol. FDA approved uses of beta-1-selective blockers include hypertension, chronic stable angina, heart failure, post-myocardial infarction, and decreased left ventricular function after a recent myocardial infarction. Non-FDA approved uses include migraine prophylaxis, treatment of arrhythmias, tremor reduction, and the symptomatic treatment of anxiety disorders. Their use is associated with decreased morbidity and mortality post-myocardial infarction. Treatment with beta-1 blockers decreases the risk of stroke, coronary artery disease, and congestive heart failure. This activity outlines the indications, mechanisms of action, methods of administration, important adverse effects, contraindications, and monitoring, of selective beta-1 antagonists, so providers can direct patient therapy in treating indicated disorders as part of the interprofessional team, with a basis on the current knowledge for optimal utilization.
Is tremor reduction FDA approved?
Non-FDA approved uses include migraine prophylaxis, treatment of arrhythmias, tremor reduction, and the symptomatic treatment of anxiety disorders. Their use is associated with decreased morbidity and mortality post-myocardial infarction.
Does beta blocker help with stroke?
Treatment with beta-1 blockers decreases the risk of stroke, coronary artery disease, and congestive heart failure. This activity outlines the indications, mechanisms of action, methods of administration, important adverse effects, contraindications, and monitoring, of selective beta-1 antagonists, so providers can direct patient therapy in ...
Which beta receptor blockers are cardio-selective?
Beta-1 receptor-selective blockers like atenolol, bisoprolol, metoprolol, and esmolol only bind to the beta-1 receptors; therefore, they are cardio-selective. [2][3][4] Beta-blockers lower the secretion of melatonin and hence may cause insomnia and sleep changes in some patients. [5]
What are the different forms of beta blockers?
Beta-blockers are available for administration in three main forms: oral, intravenous, and ophthalmic , and the route of administration often depends on the acuity of the illness (parenteral use in arrhythmias), disease type (topical use in glaucoma), and chronicity of the disease.
What are beta blockers used for?
Indications. Beta-blockers, as a class of drugs, are primarily used to treat cardiovascular diseases and other conditions. [1] Beta receptors exist in three distinct forms: beta-1 (B1), beta-2 (B2), and beta-3 (B3). Beta-1 receptors located primarily in the heart mediate cardiac activity. Beta-2 receptors, with their diverse location in many organ ...
What is the best treatment for beta blocker overdose?
The antidote for beta-blocker overdose is glucagon. It is especially useful in beta-blocker-induced cardiotoxicity. The second line of treatment is cardiac pacing if glucagon fails.
What does alpha 1 do to the heart?
Alpha-1 receptors induce vasoconstriction and increased cardiac chronotropy; this means agonism at the alpha-1 receptors leads to higher blood pressure and an increased heart rate. In contrast, antagonism at the alpha-1 receptor leads to vasodilation and negative chronotropic, which leads to lower blood pressure and decreases heart rate. Some beta-blockers, such as carvedilol, labetalol, and bucindolol, have additional alpha-1 receptor blockage activity in addition to their non-selective beta receptor blockage. This property is clinically useful because beta-blockers that block the alpha-1 receptor have a more pronounced clinical effect on treating hypertension. [6]
Which receptors are responsible for the breakdown of fat cells?
Beta-2 receptors, with their diverse location in many organ systems, control various aspects of metabolic activity and induce smooth muscle relaxation. Beta-3 receptors induce the breakdown of fat cells and are less clinically relevant at present.
Can beta blockers cause bronchospasm?
Less commonly, bronchospasm presents in patients on beta-blockers. Asthmatic patients are at a higher risk.[7] Patients with Raynaud syndrome are also at risk of exacerbation. Beta-blockers can induce hyperglycemia and mask the hemodynamic signs, usually seen in a hypoglycemic patient, such as tachycardia.
Which beta blocker is more potent?
Beta-adrenergic blocking agents may also affect beta-2 adrenergic receptors located in the bronchial smooth muscle of the airways, which has the potential to cause bronchoconstriction (a narrowing of the breathing passages). Cardioselective beta blockers have a clinical advantage in that they are 20 times more potent at blocking beta-1 receptors ...
What are Cardioselective beta blockers?
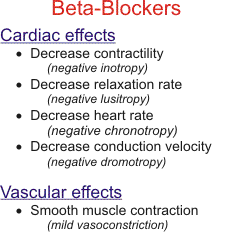
Beta-adrenergic blocking agents prevent stimulation of the beta-1 adrenergic receptors at the nerve endings of the sympathetic nervous system and therefore decrease the activity of the heart. They block sympathetic stimulation of the heart and reduce systolic pressure, heart rate, cardiac contractility and output, which in turn decreases the demand by the heart for oxygen and increases exercise tolerance. Beta-adrenergic blocking agents may also affect beta-2 adrenergic receptors located in the bronchial smooth muscle of the airways, which has the potential to cause bronchoconstriction (a narrowing of the breathing passages).
Do beta blockers cause bronchoconstriction?
Cardioselective beta blockers have a clinical advantage in that they are 20 times more potent at blocking beta-1 receptors than beta-2 receptors. They are therefore less likely to cause bronchoconstriction compared with non-selective beta-blockers; however, the danger of bronchoconstriction cannot be totally ignored, ...
Overview
Beta-blockers are a class of medicines commonly used to treat a wide range of problems involving your heart and your circulatory system. They also are sometimes used to treat conditions related to your brain and nervous system.
Recovery and Outlook
You can use beta-blockers for extended periods. In some cases, especially for adults over 65, it’s possible to use them for years or indefinitely.
When to Call the Doctor
Your healthcare provider can advise you on when you should call or schedule an appointment related to taking beta-blockers. In general, you should call or schedule an appointment if you have a sudden change in symptoms, especially ones related to your heart and circulatory system. These include:
What conditions do beta blockers treat?
Beta blockers are FDA-approved to treat many health conditions. This group of medications is one of the best treatments for certain heart problems, and some can also help treat migraines, tremors, and hyperthyroidism — a condition when your body has too much thyroid hormone.
Which beta blocker is most effective?
The best beta blocker depends on the health condition you have. Some beta blockers work better than others for certain conditions — this often depends on whether the medication is a “selective” or “non-selective” beta blocker and if it has “alpha-blocking” effects.
What should I be aware of while taking a beta blocker?
Before starting a beta blocker, you should confirm the dosage and timing with your healthcare provider. Some oral beta blockers are taken twice a day, and others are taken once a day. Depending on your condition, taking the medication at a certain time of day can help the medication work at its best.
The bottom line
Beta blockers are important medications for certain heart conditions like heart failure, arrhythmias, and after heart attacks. While these medications are most commonly used for heart conditions, they can also be used to treat migraines and tremors.
What are non selective beta blockers?
Non-selective beta-blockers, on the other hand, block the beta1, beta2, and beta3 receptors, helping to address even more physical symptoms of performance anxiety.
What is a beta blocker?
Beta-blockers are one of the most common medications and are prescribed by doctors to help with an irregular heartbeat (arrhythmias), chest pain (angina), and high blood pressure (hypertension). They’re also often prescribed for quite a few off-label uses including migraines, glaucoma, essential tremor, and performance anxiety.
What happens if you don't connect to beta receptors?
When adrenaline doesn’t connect to beta receptors, the fight-or-flight response isn’t activated. Adrenaline is like an electrical plug, a device that brings energy. Beta receptors are the electrical outlet, the thing that activates that energy. If a plug and outlet don’t connect, nothing happens.
Where are beta1 receptors located?
Selective beta-blockers are cardioselective. In other words, they “select” the beta receptors located in the heart tissue , known as your beta1 receptors.
What is the best medication for trembling hands?
This kind of medication can help slow your breathing, prevent your hands from trembling, or your palms from sweating. Common non-selective beta-blockers include nadolol, pindolol, among others.
Is propranolol a beta blocker?
Propranolol is a type of non-selective beta-blocker.
Do beta blockers work?
There are indeed. And while they generally work the same way, different types of this kind of medication prevent adrenaline from binding to different beta receptors. And by binding to different beta receptors, they affect different areas of the body. The two main types of beta-blockers are called selective and non-selective.
Which beta blockers affect the heart?
Selective or Cardioselective beta blockers. Second generation beta blockers such as Metroprolol and the following block only Beta1 receptors and so mostly affect the heart and cause a reduction in cardiac output: Cardioselective beta blockers without intrinsic sympathomimetic activity (ISA) include atenolol, metoprolol, bisoprolol, and practolol.
Is propranolol a beta blocker?
Non-selective or non-specific beta blockers. First generation beta blockers such as propranolol (and the others listed below) are non-selective or nonspecific. That means they block both beta1 and beta2 receptors and so affect the heart, lungs, vascular smooth muscles, kidneys, GI, etc. Propranolol,
Does carvedilol work the same way as labetalol?
Labetalol and carvedilol work exactly the same way!
What is the second generation beta blocker?
Second generation beta blockers such as metoprolol ( Lopressor, Toprol XL ), acebutolol hydrochloride ( Sectral ), bisoprolol fumarate ( Zebeta ), esmolol hydrochloride ( Brevibloc ), betaxolol hydrochloride ( Kerlone ), and acebutolol hydrochloride (Sectral) are selective, as they block only β 1 receptors and as such will affect mostly the heart and cause reduced cardiac output.
What are beta blockers and how do they work?
Beta blockers, also known as beta-adrenergic blocking agents, are a class of drugs that works by blocking the neurotransmitters norepinephrine and epinephrine from binding to receptors. There are three known types of beta receptors, known as beta 1 (β 1 ), beta 2 (β 2) and beta 3 (β 3 ).
What are the drug interactions?
Beta blockers [pindolol (Visken) and propranolol (Inderal, InnoPran)] should not be taken with phenothiazines [ thioridazine and chlorpromazine ( Thorazine )] as this will cause an increase in blood plasma levels of either or both classes of drugs. Due to the fact that increased levels of thioridazine could increase the risk of life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias, thioridazine is contraindicated in patients receiving pindolol and propranolol.
Which beta blocker has quinidine?
Beta blocker such as propranolol (Inderal, InnoPran), acebutolol hydrochloride (Sectral), and betaxolol hydrochloride (Kerlone) possess a quinidine-like or anesthetic -like membrane action, which affects cardiac action potential (electrical impulses within the heart that cause contractions).
What happens when neurotransmitters are blocked?
When the neurotransmitters are prevented from binding to the receptors, it in turn causes the effects of adrenaline (epinephrine) to be blocked . This action allows the heart to relax and beat more slowly thereby reducing the amount of blood that the heart must pump.
Is pindolol a beta blocker?
First generation beta blockers such as propranolol ( Inderal, InnoPran), nadolol ( Corgard ), timolol maleate ( Blocadren ), penbutolol sulfate ( Levatol ), sotalol hydrochloride ( Betapace ), and pindolol ( Visken) are non-selective in nature, meaning that they block both beta 1 (β 1) and beta 2 (β 2) receptors and will subsequently affect the heart, kidneys, lungs, gastrointestinal tract, liver, uterus, vascular smooth muscle, and skeletal muscle and as an effect, could cause reduced cardiac output, reduced renal output amongst other actions.
Which beta blocker lowers blood pressure?
Beta blockers such as labetalol hydrochloride ( Trandate, Normodyne) and carvedilol ( Coreg) have both β- and α 1 -adrenergic receptors. Blocking the α 1 -adrenergic receptors in addition to the β blocker lowers blood pressure which provides additional vasodilatory action of the arteries.