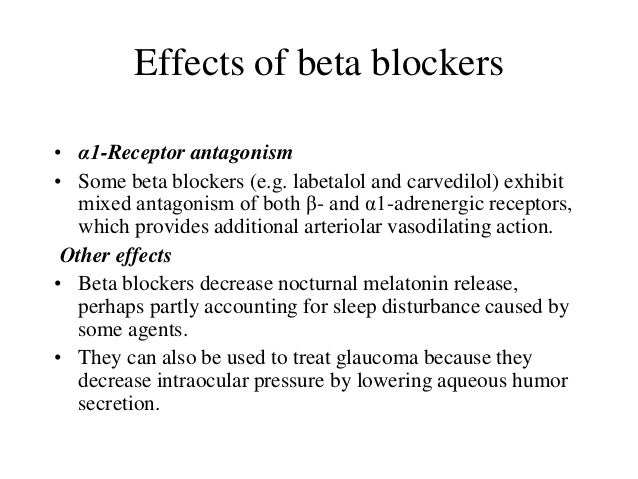
Relevance of intrinsic sympathomimetic activity for beta blockers. Intrinsic sympathomimetic activity (ISA) characterizes a group of beta blockers that are able to stimulate beta-adrenergic receptors (agonist effect) and to oppose the stimulating effects of catecholamines (antagonist effect) in a competitive way.
- Acebutolol.
- Pindolol.
- Sectral.
- Visken.
Are You taking a beta blocker?
In people who have diabetes, beta blockers may block signs of low blood sugar, such as rapid heartbeat. It's important to check your blood sugar regularly if you have diabetes and you're taking a beta blocker. Beta blockers can also affect your cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
Do beta blockers increase libido?
Tens of millions of Americans use beta blockers such as propranolol and metoprolol with great benefit to their hearts, but not necessarily their sex lives. In rare cases, even eye drops containing the beta blocker Timolol (used to treat glaucoma) can decrease libido, says Dering-Anderson. But there are many beta blockers on the market.
Do beta blockers increase contractility of the heart?
Therefore, beta-blockers cause decreases in heart rate, contractility, conduction velocity, and relaxation rate. These drugs have an even greater effect when there is elevated sympathetic activity.
Do beta blockers interfere with the function of the thyroid?
The problem as ever is balancing hypo symptoms with medication intake and having m.e makes that so much more complex to identify what is what and cause and effect. Some beta blockers are known to interfere with thyroid function. A doc put me on propanolol soon after my celiac-triggered hypothyroidism.

Which beta-blocker possesses intrinsic sympathomimetic activity?
Certain beta 1-selective blocking drugs, including acebutolol, have intrinsic sympathomimetic activity (ISA), also termed partial agonist activity. This property produces slight cardiac stimulation, which can be blocked by propranolol.
Which drug has intrinsic sympathomimetic activity?
Alprenolol. Alprenolol is an oral nonselective β-receptor blocker with intrinsic sympathomimetic activity.
Does metoprolol have intrinsic sympathomimetic activity?
Unlike some other beta-adrenoceptor antagonists, metoprolol does not display a membrane-stabilizing effect or have intrinsic sympathomimetic activity.
Does labetalol have intrinsic sympathomimetic activity?
These results indicate that the alpha- and beta-adrenergic receptor antagonist, labetalol possesses partial beta-adrenergic receptor agonist activity. This intrinsic sympathomimetic action of labetalol appears to be more sustained on cardiac than on vascular beta-adrenergic receptors.
Which of the following beta-blockers has ISA activity?
Beta blockers such as pindolol (Visken), penbutolol sulfate (Levatol), and acebutolol hydrochloride (Sectral) differ from other beta blockers as they possess intrinsic sympathomimetic activity (ISA), which means they mimic the effects of epinephrine and norepinephrine and can cause an increase in blood pressure and ...
Why do beta-blockers have intrinsic sympathomimetic activity?
Intrinsic sympathomimetic activity (ISA) characterizes a group of beta blockers that are able to stimulate beta-adrenergic receptors (agonist effect) and to oppose the stimulating effects of catecholamines (antagonist effect) in a competitive way.
Does atenolol have intrinsic sympathomimetic activity?
Atenolol does not have membrane-stabilizing or intrinsic sympathomimetic activities. It has relatively low lipid solubility. As with other beta blockers, atenolol exerts its effects primarily by blocking the action of the endogenous catecholamines, epinephrine and norepinephrine, at beta-adrenoceptors.
Does bisoprolol have ISA?
ISA: intrinsic sympathomimetic activity; MSA: membrane stabilizing activity; IV: intravenous....DrugBisoprololBeta-1 selectivityYesISANoMSANoLipophilicityModerate17 more columns
Is Carvedilol a sympathomimetic?
A synthetic antihypertensive methoxyphenoxy- 2-propanol derivative with no intrinsic sympathomimetic activity, Carvedilol acts as a nonselective beta-adrenoceptor blocking agent (S(-) enantiomer) and as an alpha 1-adrenoceptor blocker (R(+) and S(-) enantiomers).
Does Nadolol have intrinsic sympathomimetic activity?
Nadolol is a non-selective β-adrenergic antagonist that lacks intrinsic sympathomimetic activity and membrane-stabilizing properties.
Does betaxolol have intrinsic sympathomimetic activity?
Abstract. Betaxolol is a relatively cardioselective beta-adrenoceptor blocking drug, with no partial agonist (intrinsic sympathomimetic) activity and weak membrane-stabilising (local anaesthetic) activity.
What is the difference between metoprolol and labetalol?
Metoprolol also is used to prevent migraine headaches. Labetalol is a beta-blocker used to treat high blood pressure.
What are examples of sympathomimetic drugs?
Now, sympathomimetic medications include dobutamine, dopamine, norepinephrine, epinephrine, and isoproterenol. All of them are administered intravenously, while isoproterenol can also be given intramuscularly, and epinephrine can also be administered intramuscularly, as well as through endotracheal tube or inhalation.
Which drug is also known as sympathomimetic drugs?
Catecholamines are sympathomimetic drugs. Dopamine and norepinephrine are used as vasopressors (antihypotensives).
What is intrinsic activity of a drug?
Intrinsic activity is a measure of the ability of a drug once bound to the receptor to generate an effect activating stimulus and producing a change in cellular activity.
Which of these drugs is a sympathomimetic drug?
Sympathomimetic amines (epinephrine, norepinephrine, phenylephrine, dopamine, dobutamine, ephedrine, isoproterenol, metoproterenol, and isoetharine) are particularly susceptible to pharmacodynamic drug–drug interactions.
HOW ARE BETA-BLOCKERS WITH INTRINSIC SYMPATHOMIMETIC ACTIVITY USED?
Beta-blockers with intrinsic sympathomimetic activity are used to treat:
What is the effect of beta blockers on ISA?
Stimulation of beta-adrenergic receptors releases epinephrine, which is responsible for increased heart contraction and heart rate .
Does beta blocker lower heart rate?
Beta-blockers with ISA decrease blood pressure and overall resistance to blood flow while maintaining the heart rate. Some drugs may also lower heart rate and contraction along with blood pressure and resistance.
What are nonselective blockers?
Nonselective β-blockers, particularly those with intrinsic sympathomimetic activity such as pindolol and xamoterol, may have a limited place in the treatment of orthostatic hypotension despite the well-acknowledged negative chronotropy and inotropy associated with these medications.14,66,68,100 The suggested mechanism of action of these medications is the blockade of vasodilating β 2 receptors, allowing unopposed α adrenoreceptor–mediated vasoconstrictor effects to dominate. Congestive heart failure may be a serious side effect of this medication. 12,62 The pressor effect of these agents has not been demonstrated in all clinical trials. 53
What is acebutolol antagonist?
Acebutolol is a "cardioselective" beta adrenoceptor antagonist with weak intrinsic sympathomimetic activity and low membrane stabilizing effects. Acebutolol inhibits selectively beta-1 receptors with a lower affinity for beta-2 receptor subtype. Receptor-subtype selectivity diminishes at high doses. Acebutolol has low lipid solubility. As other beta blockers, acebutolol exerts its effects primarily by blocking the action of the endogenous catecholamines, epinephrine and norepinephrine, at beta adrenoceptors. The magnitude of the effect of acebutolol is dependent on the degree of sympathetic tone. Acebutolol also blocks the effects of drugs with beta adrenergic agonist activity. Acebutolol and other beta adrenoceptor antagonists are used widely to treat many cardiovascular disorders including: hypertension, angina, arrhythmias, myocardial infarction, and congestive heart failure …
How long does it take for labetalol to peak?
In addition, cardiac output is maintained because the decreased afterload compensates for reduced cardiac function. The peak hypotensive effect of labetalol occurs between 5 and 15 minutes and the duration of action is estimated to be 4–6 hours after a single intravenous dose. View chapter Purchase book.
What is the first line of treatment for CPVT?
Beta-blockers without intrinsic sympathomimetic activity combined with exercise restriction are the first line of treatment for CPVT and should be promptly initiated to prevent occurrence of ventricular tachyarrhythmias (see Fig. 31.7 ). Because of the poor prognosis of untreated CPVT, drug therapy is indicated for all clinically diagnosed patients and usually also for all silent carriers of a CPVT mutation.
How to determine beta blocker dosage?
Exercise stress testing and Holter monitoring can help determine the adequate beta-blocker dosage for arrhythmia control. It should be noted, however, that the absence of exercise-provoked arrhythmias does not completely exclude the risk of arrhythmia recurrence, and the maximal tolerated dose of beta-blockers should be prescribed to maximize control of arrhythmias with a goal to avoid the heart rate exceeding the threshold rate for CPVT. Furthermore, compliance with regular therapy is extremely important because missing even a single dose can potentially lead to arrhythmias and increase the risk of SCD. In fact, in one report, poor adherence contributed to 48% of arrhythmic events in children with CPVT.
What is a low sympathetic tone?
Conditions with low sympathetic tone (e.g., during rest/sleep) are associated with a sufficient degree of ISA and a resultant decreased reduction in heart rate and cardiac output. If the drug possesses β2 ISA, stimulation of β2 vasodilator receptors may result in less of a decrease in peripheral blood flow.
Is carteolol a sympathomimetic drug?
Carteolol, which has intrinsic sympathomimetic activity (ISA; see Pharmacology, above) has theoretically less systemic β-blockade effect and thus might have cardiovascular tolerability profiles better than the other non-selective β-blockers. 45,75 However, the theoretical advantages of ISA have not been fully substantiated in the ophthalmologic literature for topically applied carteolol; 63 neither have they been so in the medical literature for systemically administered β-blockers with potent ISA such as pindolol. Carteolol can be preferably prescribed in patients with unfavorable lipid profiles as it does not alter the lipid profile to the same extent as timolol, 45 but whether this confers a therapeutic advantage remains, to date, an open question.
Why are beta blockers banned?
Beta blockers are banned by the International Olympic Committee. In the 2008 Summer Olympics, 50-metre pistol silver medalist and 10-metre air pistol bronze medalist Kim Jong-su tested positive for propranolol and was stripped of his medals.
How low should beta blockers be given for congestive heart failure?
Therapeutic administration of beta blockers for congestive heart failure ought to begin at very low doses (1/8 of target) with a gradual escalation of the dose. The heart of the patient must adjust to decreasing stimulation by catecholamines and find a new equilibrium at a lower adrenergic drive.
What is the effect of beta blockers on heart rate?
Beta blockers are known primarily for their reductive effect on heart rate, although this is not the only mechanism of action of importance in congestive heart failure. Beta blockers, in addition to their sympatholytic β1 activity in the heart, influence the renin–angiotensin system at the kidneys.
How long does it take for beta blockers to reduce the risk of death?
Trials have shown beta blockers reduce the absolute risk of death by 4.5% over a 13-month period. In addition to reducing the risk of mortality, the numbers of hospital visits and hospitalizations were also reduced in the trials.
Which beta blockers exhibit intrinsic sympathomimetic activity?
Some beta blockers (e.g. oxprenolol, pindolol, penbutolol, labetalol and acebutolol) exhibit intrinsic sympathomimetic activity (ISA). These agents are capable of exerting low-level agonist activity at the β-adrenergic receptor while simultaneously acting as a receptor site antagonist. These agents, therefore, may be useful in individuals exhibiting excessive bradycardia with sustained beta blocker therapy.
What is the best treatment for bronchospasm?
People experiencing bronchospasm due to the β 2 receptor-blocking effects of nonselective beta blockers may be treated with anticholinergic drugs, such as ipratropium, which are safer than beta agonists in patients with cardiovascular disease. Other antidotes for beta blocker poisoning are salbutamol and isoprenaline .
What is a beta blocker?
Beta blockers ( beta-blockers, β-blockers, etc.) are a class of medications that are predominantly used to manage abnormal heart rhythms, and to protect the heart from a second heart attack ( myocardial infarction) after a first heart attack ( secondary prevention ). They are also widely used to treat high blood pressure ( hypertension ), ...
What is intrasynaptic sympathomimetic activity?
Intrinsic sympathomimetic activity is used particularly with beta blockers that can show both agonism and antagonism at a given beta receptor, depending on the concentration of the agent (beta blocker) and the concentration of the antagonized agent (usually an endogenous compound, such as norepinephrine).
Why join Researchgate?
Join ResearchGate to find the people and research you need to help your work.
Can beta blockers cause tachycardia?
Beta blockers with ISA cause less RESTING Bradycardia but are capable of reducing exercise tachycardia in similar extent to those without ISA. In addition, there may be less peripheral vasospasm-cold feet. Because of ISA, such drugs are best avoided in angina and IHD
Is amikacin a polar drug?
Amikacin is a polar drug meant for parenteral use against gm negative bacteria.In some cases,different forms of amikacin meant for local application are used but can injection amikacin is effective if applied directly on wounds?
