Which bones are the only ones that do not ossify? At birth, the skull and clavicles are not fully ossified nor are the junctions between the skull bone (sutures) closed. This allows the skull and shoulders to deform during passage through the birth canal.
How long does it take for bones to become fully ossified?
Bone of upper limbs and scapulae becoming completely ossified. 18 to 23 years. Bone of the lower limbs and os coxae become completely ossified. 23 to 26 years. Bone of the sternum, clavicles, and vertebrae become completely ossified. By 25 years. Nearly all bones are completely ossified.
What is the difference between ossification and osteogenesis?
Ossification. Ossification (or osteogenesis) in bone remodeling is the process of laying down new bone material by cells called osteoblasts. It is synonymous with bone tissue formation. There are two processes resulting in the formation of normal, healthy bone tissue: Intramembranous ossification is the direct laying down...
What is the difference between heterotopic ossification and calcification?
Heterotopic ossification is a process resulting in the formation of bone tissue that is often atypical, at an extraskeletal location. Calcification is often confused with ossification. ... Endochondral ossification is the formation of long bones and other bones.
When does secondary ossification occur in bones?
Secondary ossification mostly occurs after birth (except for distal femur and proximal tibia which occurs during 9th month of fetal development). The epiphyseal arteries and osteogenic cells invade the epiphysis, depositing osteoblasts and osteoclasts which erode the cartilage and build bone.
Which type of ossification forms the flat bones of the skull, mandible and hip bone?
How long does it take for bones to become ossified?
What is the process of laying down new bone material called?
What is the name of the model that describes ossification and bone loss?
When does secondary ossification occur?
What is the rare genetic condition that causes cartilage to ossify?
How did bone evolve?
See 4 more
About this website
Do all bones ossify?
All of the bones of the body, except for the flat bones of the skull, mandible, and clavicles, are formed through endochondral ossification. In long bones, chondrocytes form a template of the hyaline cartilage diaphysis. Responding to complex developmental signals, the matrix begins to calcify.
Which parts of the skull are not fully ossified at birth?
Fontanelles are membranous areas that have not yet ossified in the developing cranial vault of neonatal and juvenile animals. Fontanelles allow for rapid stretching and deformation of the cranium as the brain expands faster than the surrounding bone can grow.
Which bones ossify first?
The clavicle is the first bone to ossify in the devel- oping embryo. At approximately 5 weeks of gesta- tion, primary ossification of the clavicle proceeds by membranous ossification of two centers with no prior cartilaginous anlage. Both will soon fuse.
Which is the last bone to ossify?
Heterotopic ossification is a process resulting in the formation of bone tissue that is often atypical, at an extraskeletal location....Ossification.Time periodBones affected23 to 26 yearsBone of the sternum, clavicles, and vertebrae become completely ossified7 more rows
Which two bones are not connected by a suture?
The bones of the skull, with one pair of exceptions, are joined together by immovable fibrous joints called sutures. (See Fig. 6-7 and 6-8.) The exceptions are the jaw joints, the movable synovial joints between the mandible and the 2 temporal bones.
Which of the following bones is not a facial bone?
Answer and Explanation: The bone that is not one of the facial bones is the frontal bone. There are 14 facial bones. These are nasal (2), lacrimal (2), inferior nasal concha (2), maxilla (2), palatine (2), zygomatic (2), a mandible (1), and vomer (1).
What are the two types of bone ossification?
There are two types of bone ossification, intramembranous and endochondral. Each of these processes begins with a mesenchymal tissue precursor, but how it transforms into bone differs.
What means ossified?
ossified adjective (BODY) (of body tissue) having become hard and changed into bone: The bones in the creature's feet were only partially ossified. With increasing age the joints between the bones may become ossified.
How does the clavicle ossify?
Its lateral end is formed by intramembranous ossification while medially it is formed by endochondral ossification. It consists of a mass of cancellous bone surrounded by a compact bone shell. The cancellous bone forms via two ossification centres, one medial and one lateral, which fuse later on.
What are the 3 stages of ossification?
Abstract. The process of bone formation is called osteogenesis or ossification. After progenitor cells form osteoblastic lines, they proceed with three stages of development of cell differentiation, called proliferation, maturation of matrix, and mineralization.
What is the last bone to complete its growth?
clavicleThe clavicle (collar bone), pictured here, is the last bone to complete growth, at about age 25. Measuring the length of long bones can give an estimate of age for children, but this technique is useful only until bones have stopped growing.
Why does ossification end?
Ossification of long bones proceeds until only a thin strip of cartilage remains at either end; this cartilage, called the epiphyseal plate, persists until the bone reaches its full adult length and is then replaced with bone.
How is the fetal skull different?
The neurocranium compared to an adult's is more oval and is substantially bigger than the facial cranium. The newborn's skull has four “horns” two in the front on the frontal bone and two in the back on the parietal bone. These bumps are the thickness that the skull will eventually become.
What are the fontanelle of the fetal skull?
There are 2 fontanelles on your baby's skull. These are the skin-covered gaps where the skull plates meet. The anterior fontanelle is at the top of your baby's head, and the posterior fontanelle is located at the back of your baby's head.
What features characterize the fetal skull?
The fetal skull bones are as follows: The frontal bone, which forms the forehead. In the fetus, the frontal bone is in two halves, which fuse (join) into a single bone after the age of eight years. The two parietal bones, which lie on either side of the skull and occupy most of the skull.
Which bone does not have a sinus?
temporal boneThere are four paranasal sinuses in the head: the frontal, maxillary, sphenoid, and ethmoid sinuses. They function in lightening the skull, and creating mucous for the nasal cavity. The temporal bone does not contain a sinus.
What Is the Process of Ossification? - Reference.com
The process of ossification allows bones to form while a fetus is still in the womb. The process converts various types of connective tissue into bone. The two main processes of ossification are intra-membranous and intra-cartilaginous, depending on the area of the body in which the cartilage is located.
Ossification | definition of ossification by Medical dictionary
ossification [os″ĭ-fĭ-ka´shun] formation of or conversion into bone or a bony substance. ectopic ossification a pathological condition in which bone arises in tissues not in the osseous system and in connective tissues usually not manifesting osteogenic properties. endochondral ossification ossification that occurs in and replaces cartilage ...
Medical Definition of Ossification
Ossification: The process of creating bone, that is of transforming cartilage (or fibrous tissue) into bone. The human skeleton initially consists largely of cartilage which is relatively soft and is gradually transformed into hard bone during infant and child development.
Ossification - Bone, Cells, Osteoblasts, and Matrix - JRank Articles
Intramembranous ossification is the transformation of the mesenchyme, cells of an embryo into bone. During early development of vertebrate animals, the embryo consists of three primary cell layers: ectoderm on the outside, mesoderm in the middle, and endoderm on the inside. Mesenchyme cells constitute part of the embryo's mesoderm and develop into connective tissue such as bone and blood.
Process of Ossification in Human Body | Connective Tissues | Biology
ADVERTISEMENTS: Development of bone begins from mesoderm in the embryonic life (from sixth week) and a good number of bones of the human body continue to grow until a person reaches about twenty-fifth years. There are two processes of ossification-intramembranous and intracartilaginous (endochondral). The bones of the cranial vault and the mandible are membranous in […]
Which type of ossification forms the flat bones of the skull, mandible and hip bone?
Intramembranous ossification forms the flat bones of the skull, mandible and hip bone .
How long does it take for bones to become ossified?
18 to 23 years. Bone of the lower limbs and os coxae become completely ossified. 23 to 26 years. Bone of the sternum, clavicles, and vertebrae become completely ossified. By 25 years. Nearly all bones are completely ossified.
What is the process of laying down new bone material called?
Ossification (or osteogenesis) in bone remodeling is the process of laying down new bone material by cells named osteoblasts. It is synonymous with bone tissue formation. There are two processes resulting in the formation of normal, healthy bone tissue: Intramembranous ossification is the direct laying down of bone into ...
What is the name of the model that describes ossification and bone loss?
Dystrophic calcification. Mechanostat, a model describing ossification and bone loss. Ossicone, the horn-like (or antler-like) protuberances on the heads of giraffes and related species. Osteogenesis imperfecta, a juvenile bone disease.
When does secondary ossification occur?
Secondary ossification mostly occurs after birth (except for distal femur and proximal tibia which occurs during 9th month of fetal development). The epiphyseal arteries and osteogenic cells invade the epiphysis, depositing osteoclasts and osteoblasts which erode the cartilage and build bone, respectively.
What is the rare genetic condition that causes cartilage to ossify?
Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva, an extremely rare genetic disease which causes fibrous tissue (muscle, tendon, ligament etc.) to ossify when damaged. Primrose syndrome, a rare genetic disease in which cartilage becomes ossified.
How did bone evolve?
Several hypotheses have been proposed for how bone evolved as a structural element in vertebrates. One hypothesis is that bone developed from tissues that evolved to store minerals. Specifically, calcium-based minerals were stored in cartilage and bone was an exaptation development from this calcified cartilage.
What are some examples of bones?
Examples: most bones of the skull, the ribs, the sternum, and the bones of the pelvis.
Where do osteons originate?
originate from the blood vessels in the periosteum and travel in right angles or perpendicular to the central canals of neighboring osteons and serve to connect them with one another.
What makes bone strong and resistant to compression?
crystalline structure makes bone one of the hardest substances in the body, which makes it strong and resistant to compression.
What is the second bone texture?
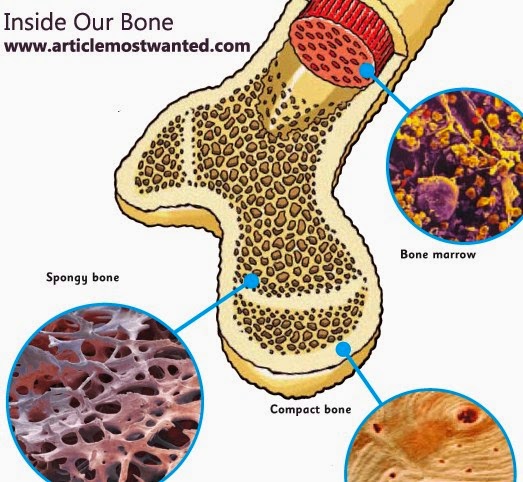
the second bone texture found inside the cortical bone, is a honeycomb-like framework of bony struts that allows long bones to resist forces from many directions and provides a cavity for bone marrow.
Where is the endosteum hole?
endosteum-lined hole found in the center of each osteon where blood vessels and nerves reside to supply the bone.
Where do cells get their oxygen and nutrients from?
cells obtain their oxygen and nutrients from the blood vessels in the bone marrow.
Which crystals enhance the hardness of bone?
align themselves with hydroxyapatite crystals, which enhance the hardness of bone.
Which type of ossification forms the flat bones of the skull, mandible and hip bone?
Intramembranous ossification forms the flat bones of the skull, mandible and hip bone .
How long does it take for bones to become ossified?
18 to 23 years. Bone of the lower limbs and os coxae become completely ossified. 23 to 26 years. Bone of the sternum, clavicles, and vertebrae become completely ossified. By 25 years. Nearly all bones are completely ossified.
What is the process of laying down new bone material called?
Ossification (or osteogenesis) in bone remodeling is the process of laying down new bone material by cells named osteoblasts. It is synonymous with bone tissue formation. There are two processes resulting in the formation of normal, healthy bone tissue: Intramembranous ossification is the direct laying down of bone into ...
What is the name of the model that describes ossification and bone loss?
Dystrophic calcification. Mechanostat, a model describing ossification and bone loss. Ossicone, the horn-like (or antler-like) protuberances on the heads of giraffes and related species. Osteogenesis imperfecta, a juvenile bone disease.
When does secondary ossification occur?
Secondary ossification mostly occurs after birth (except for distal femur and proximal tibia which occurs during 9th month of fetal development). The epiphyseal arteries and osteogenic cells invade the epiphysis, depositing osteoclasts and osteoblasts which erode the cartilage and build bone, respectively.
What is the rare genetic condition that causes cartilage to ossify?
Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva, an extremely rare genetic disease which causes fibrous tissue (muscle, tendon, ligament etc.) to ossify when damaged. Primrose syndrome, a rare genetic disease in which cartilage becomes ossified.
How did bone evolve?
Several hypotheses have been proposed for how bone evolved as a structural element in vertebrates. One hypothesis is that bone developed from tissues that evolved to store minerals. Specifically, calcium-based minerals were stored in cartilage and bone was an exaptation development from this calcified cartilage.

Overview
Endochondral ossification
Endochondral ossification is the formation of long bones and other bones. This requires a hyaline cartilage precursor. There are two centers of ossification for endochondral ossification.
The primary center
In long bones, bone tissue first appears in the diaphysis (middle of shaft). Chondrocytes multiply and form trebeculae. Cartilage is progressively eroded and replaced by hardened bone, extendin…
Intramembranous ossification
Intramembranous ossification forms the flat bones of the skull, mandible and hip bone.
Evolution
Several hypotheses have been proposed for how bone evolved as a structural element in vertebrates. One hypothesis is that bone developed from tissues that evolved to store minerals. Specifically, calcium-based minerals were stored in cartilage and bone was an exaptation development from this calcified cartilage. However, other possibilities include bony tissue evolving as an osmotic barrier, or as a protective structure.
See also
• Dystrophic calcification
• Mechanostat, a model describing ossification and bone loss
• Ossicone, the horn-like (or antler-like) protuberances on the heads of giraffes and related species
• Osteogenesis imperfecta, a juvenile bone disease