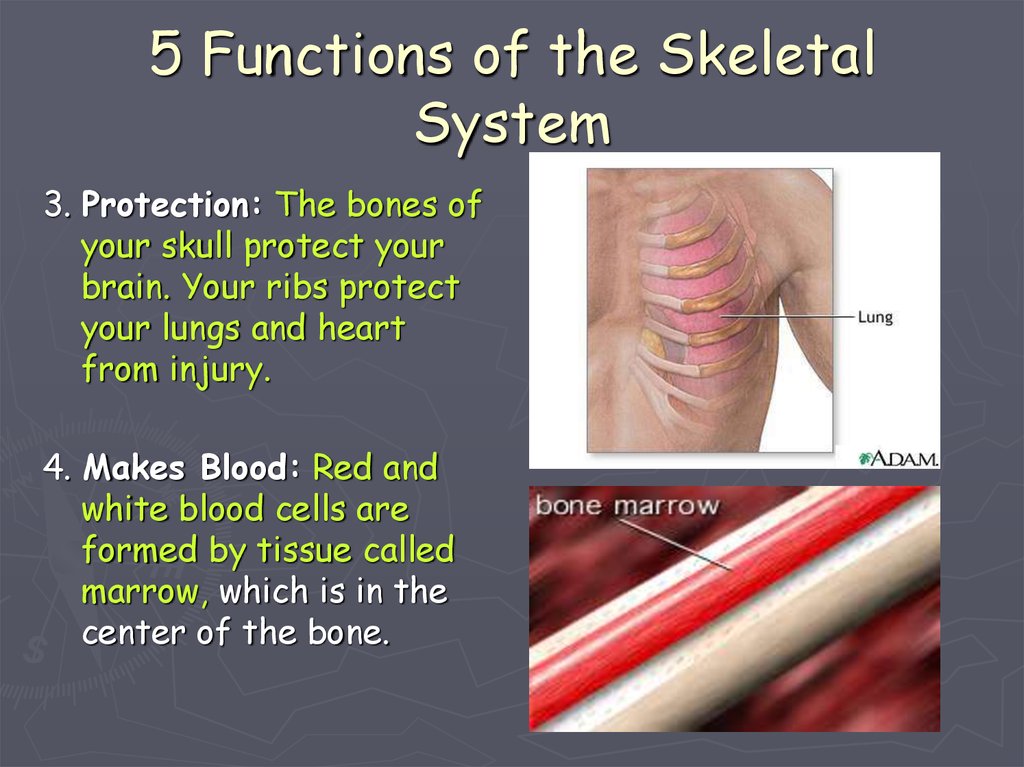
What surrounds and protects the heart and the lungs?
The thoracic cage surrounds and protects the heart and lungs in the thoracic cavity. It consists of the ribs, the sternum, and the thoracic vertebrae, to which the ribs articulate. How does the heart sit in the chest? The heart is responsible for circulating blood throughout the body. It is about the size of your clenched fist and sits in the ...
What are three bones that protect your body organs?
Which bones serve as protection?
- The skull is like a natural helmet which protects the brain.
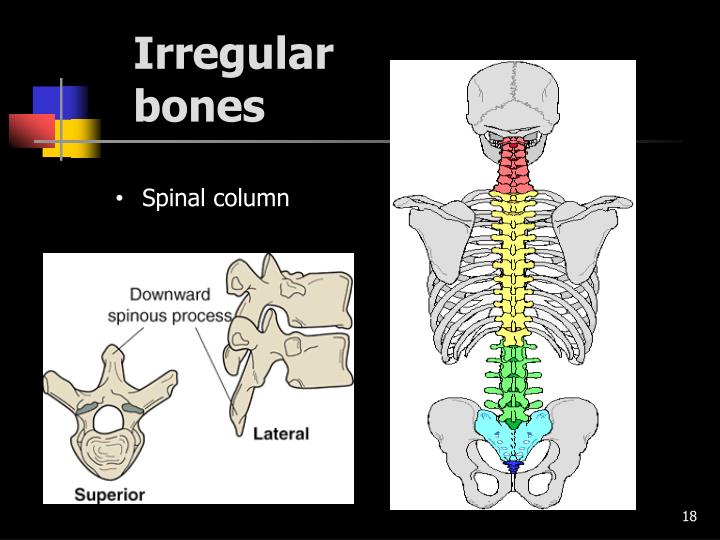
- The spine protects the nerves in the spinal column.
- The ribs make a shield around our lungs, heart and liver.
What structure protects the heart and lungs?
The thoracic cage protects the heart and lungs. It is composed of 12 pairs of ribs with their costal cartilages and the sternum. The ribs are anchored posteriorly to the 12 thoracic vertebrae. The sternum consists of the manubrium, body, and xiphoid process.
Which organs are protected by Bones?
Bones also protect internal organs from injury by covering or surrounding them. For example, your ribs protect your lungs and heart, the bones of your vertebral column (spine) protect your spinal cord, and the bones of your cranium (skull) protect your brain (Figure).
Which two bones protect the heart and lungs?
The ribs and sternum make up the ribcage. The rib cage protects major vital organs such as the heart, lungs, and liver from injury.
What ribs protect the lungs?
The sternum in front, ribs in two side and 12 thoracic vertebrae in the back form the bony cage for protection of these vital organs.
Which bones protect the lungs and heart in animals?
The rib cage surrounds the lungs and the heart, serving as an important means of bony protection for these vital organs.In total, the rib cage consists of the 12 thoracic vertebrae and the 24 ribs, in addition to the sternum.
What holds your lungs in place?
The lungs are covered by a thin tissue layer called the pleura. The same kind of thin tissue lines the inside of the chest cavity -- also called pleura. A thin layer of fluid acts as a lubricant allowing the lungs to slip smoothly as they expand and contract with each breath.