
What are the types of bursae around the knee?
[ 4] Bursae around the knee can be grouped as those that occur around the patella and those that occur elsewhere. [ 1] Bursae around the patella include the prepatellar bursa, the superficial and deep infrapatellar bursae, and the suprapatellar bursa.
Do Bursa bursae in the knee show up on MRI?
Bursae about the knee may or may not communicate with the joint, and with a few exceptions normally contain minimal or no fluid, such that they may not be detectable on MRI.
Which bursae are not anatomically close to the patella?
Bursae that are not anatomically close to the patella include the pes anserine bursa, the iliotibial bursa, the tibial and fibular collateral ligament bursae and the gastrocnemius-semimembranosus bursa. On MRI imaging, bursitis appears as an oblong fluid collection in its expected anatomical location.
What is a bursa?
A bursa is a fluid-filled structure that is present between the skin and tendon or tendon and bone. The main function of a bursa is to reduce friction between adjacent moving structures. Typically, bursae are located around large joints such as the shoulder, knee, hip, and elbow.[1] Inflammation of this fluid-filled structure is called bursitis.
Does the Popliteus bursa communicate with the knee joint?
Lateral and Posterolateral Bursa It routinely communicates with the knee, may extend caudally deep to the popliteus myotendinous junction, and may communicate with the proximal tibiofibular joint in 10% of adults.
Does prepatellar bursa communicate with knee joint?
Normally, the prepatellar bursa does not communicate with the joint space and contains a minimal amount of fluid; when it becomes inflamed, however, there is a marked increase of fluid within its space.
What is the function of Suprapatellar bursa?
Suprapatellar bursa is located between the distal femur (leg bone) and the quadriceps tendon. It permits free movement of the quadriceps tendon over the distal femur. It allows for full flexion (bending) and extension (straightening) of the knee. It can be irritated by a direct blow or from repeated stress or motions.
Which bursa is most frequently aggravated by falling on your knee?
Sports that result in direct blows or frequent falls on the knee — such as wrestling, football and volleyball — can increase your risk of knee bursitis. Runners can develop pain and inflammation in the pes anserine bursa, situated on the inner side of your knee below the joint.
What is a communicating bursa?
When a bursa is located adjacent to a joint, the synovial membrane of the bursae may communicate with the joint. [2] This bursa is termed a communicating bursa. Some examples are the iliopsoas bursa lateral to the hip and the gastrocnemius-semimembranosus bursa posteromedial to the knee.
How many bursae are in the knee joint?
The knee joint is surrounded by three major bursae. At the tip of the knee, over the kneecap bone (patella), is the prepatellar bursa. This bursa can become inflamed (prepatellar bursitis) from direct trauma to the front of the knee.
What are the 4 bursae of the knee joint?
Bursae around the knee can be grouped as those that occur around the patella and those that occur elsewhere. [1] Bursae around the patella include the prepatellar bursa, the superficial and deep infrapatellar bursae, and the suprapatellar bursa.
What is the largest bursa in the knee?
The prepatellar bursa is located at the front of the knee, in between the skin and the patella bone (kneecap). It is one of the bursae most likely to develop bursitis.
What does Suprapatellar bursitis feel like?
Suprapatellar bursitis symptoms dull, achy pain or tenderness. swelling or redness. warmth. loss or reduction in motion.
Why is knee bursitis worse at night?
The levels of your natural anti-inflammatory hormone, cortisol, are naturally lower at night. Staying still in the same position will also cause your knee joints to stiffen up.
Why is knee bursitis so painful?
Knee bursitis can occur in any part of the knee—above, below, or in the kneecap. Bursas are small fluid-filled sacs found in the knee joint. They prevent the various knee tissues from rubbing against each other, which can cause immobility and excruciating pain.
Should you wrap a knee with bursitis?
Use of a compressive wrap or knee sleeve can help reduce swelling. Elevate your knee. Prop your affected leg on pillows to help reduce swelling in your knee.
Which bursa is affected in clergyman's knee?
Superficial infrapatellar bursitis, also called clergyman's knee, is due to inflammation and fluid accumulation resulting from chronic stress. Clinically, there is a palpable swelling inferior to the patella.
Is prepatellar bursitis serious?
It's not as common, but it's a serious condition that needs immediate medical treatment. Having rheumatoid arthritis and/or gout: Although it's not as common, both rheumatoid arthritis and gout can cause prepatellar bursitis.
Why is it called housemaid knee?
Recurrent minor injury to the knee This usually happens after spending long periods of time kneeling down, putting pressure on the kneecap (patella). Historically, this was typical of housemaids who spent long periods of time on their knees scrubbing floors; hence, the term housemaid's knee.
Does prepatellar bursitis ever go away?
Prepatellar bursitis that is caused by an injury will usually go away on its own. The body will absorb the blood in the bursa over several weeks, and the bursa should return to normal. If swelling in the bursa is causing a slow recovery, a needle may be inserted to drain the blood and speed up the process.
Which bursa communicates with the synovial cavity?
lateral gastrocnemius bursa: between the capsule and lateral head of gastrocnemius; may communicate with the synovial cavity in some people. popliteus bursa: between popliteus tendon and posterior tibia and fibula; communicates with the synovial cavity 1. pes anserinus bursitis. bursitis.
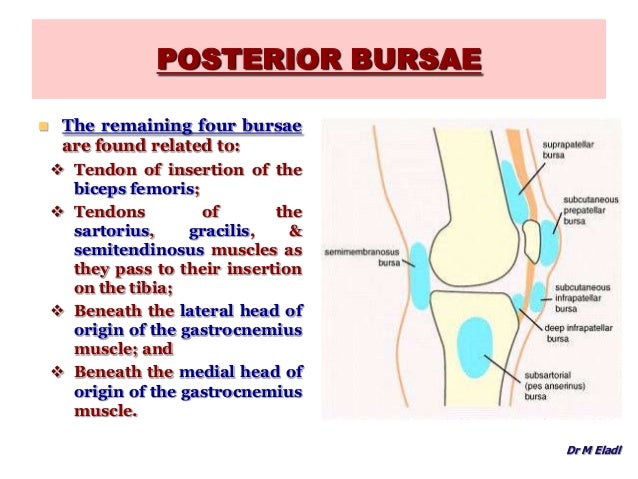
Which bursae are posterior to the knee joint?
There are four bursae posterior to the knee joint: between the capsule and medial head of gastrocnemius; communicates with the synovial cavity. semimembranosus bursa : between semimembranosus and the medial head of gastrocnemius; may communicate with the bursa under the medial head of the gastrocnemius and thereby the synovial cavity.
How many bursae are there in the knee?
There are four bursae anterior to the knee joint:
Where is the suprapatellar bursa located?
There are four bursae anterior to the knee joint: suprapatellar bursa: located between the femur and quadriceps femoris, it is attached to the articularis genu muscle and usually communicates with the synovial cavity. subcutaneous prepatellar bursa: between the skin and patella.
What is the sac around the knee joint?
Knee bursae are sacs surrounding the knee joint that are filled with synovial fluid. They facilitate movement and reduce friction where tendons or muscles pass over bony prominences. The knee bursae can be either communicating or non-communicating with the knee joint itself.
What are the bursae around the knee?
Bursae around the knee can be grouped as those that occur around the patella and those that occur elsewhere.[1] Bursae around the patella include the prepatellar bursa, the superficial and deep infrapatellar bursae, and the suprapatellar bursa. Bursae that are not anatomically close to the patella include the pes anserine bursa, the iliotibial bursa, the tibial and fibular collateral ligament bursae and the gastrocnemius-semimembranosus bursa. On MRI imaging, bursitis appears as an oblong fluid collection in its expected anatomical location.
What is the function of the bursa?
The main function of a bursa is to reduce friction between adjacent moving structures. Typically, bursae are located around large joints such as the shoulder, knee, hip, and elbow.[1] Inflammation of this fluid-filled structure is called bursitis. Trauma, infection, overuse, and hemorrhage are some of the common causes for inflammation.[2] Other causes include systemic illness like collagen vascular disease and inflammatory arthropathy; in some instances the cause is unknown.[3] Some cases of bursitis are associated with certain occupations and are named accordingly; for instance, prepatellar bursitis is also known as housemaid's knee and superficial infrapatellar bursitis is synonymous with clergyman's knee.[4]
What is the bursa of the tibial collateral ligament?
The pes anserine bursa separates the pes anserine tendons, consisting of the distal sartorius, gracilis, and semitendinosus tendons, from the subjacent distal portion of the tibial collateral ligament and the bony surface of the medial tibial condyle.[9] Anserine bursitis results from overuse, especially in runners.[3]
What is the swelling of clergyman's knee?
Superficial infrapatellar bursitis, also called clergyman's knee, is due to inflammation and fluid accumulation resulting from chronic stress. Clinically, there is a palpable swelling inferior to the patella.[6] On MRI, it appears as a loculated collection that projects exophytically, anterior to the patellar tendon, forming a swelling [Figure 2]. On imaging, it should be differentiated from subcutaneous edema: edema is seen as a diffuse fluid collection seen all over the anterior aspect of the knee, whereas bursitis appears as a localized collection with well-defined borders.
Where is iliotibial bursitis located?
On MRI [Figure 8] iliotibial bursitis appears as a fluid collection near the insertion of the iliotibial tract in its distal part, close to the lateral aspect of the tibia. It must be differentiated from iliotibial tendinitis. On MRI, iliotibial tendinitis appears as a fluid collection encircling the tendon, whereas bursitis appears as a localized oblong fluid collection adjacent to the tendon.[1]
What is the purpose of a bursa?
The main function of a bursa is to reduce friction between adjacent moving structures. Bursae around the knee can be classified as those around the patella and those that occur elsewhere. In this pictorial essay we describe the most commonly encountered lesions and their MRI appearance.
Where is the prepatellar bursa located?
The prepatellar bursa is located between the patella and the overlying subcutaneous tissue. Chronic trauma in the form of prolonged or repeated kneeling leads to inflammation and hemorrhagic bursitis. Clinically, patients may present with pain and swelling over the patella.[5]
What is anatomic bursa?
Anatomic or primary bursae are synovial lined periarticular structures, which occur normally developmentally, contain variable amounts of fluid, and serve to reduce motion or pressure induced friction between adjacent anatomic periarticular structures, often between bone and the overlying soft tissues. An adventitial bursa describes an acquired fluid filled soft tissue abnormality that develops at a pathologic or iatrogenic site of increased friction between two structures, often between bone or hardware and the overlying soft tissues. The latter may not be synovial lined.
What is the bursal distension of the knee?
Bursal distension and other cystic lesions about the knee are frequently encountered findings on MR imaging of the knee. It is important for those interpreting MRI of the knee to be familiar with the normally occurring anatomic bursa of the knee, potential clinical presentations, usual and variable imaging appearances, and differential diagnostic considerations. The aim of this web clinic is to review the anatomy of bursa of the knee and to discuss commonly occurring soft tissue cystic lesions around the knee.
What is a distended semimembranosus gastrocnemius bursa?
A distended semimembranosus-gastrocnemius bursa is the most commonly encountered fluid collection about the knee 1, 28 The term “Baker’s cyst” is now often used to describe distension of this anatomic bursa, after clinical observations in 8 patients with popliteal fossa swelling were described by William M. Baker in 1877. 29 In adults these bursae frequently communicate with the knee joint and are most likely to occur in knees with an effusion due to traumatic or degenerative internal derangement, osteoarthritis, inflammatory or crystal deposition related arthropathy or other diseases of the synovium including PVNS and primary synovial osteochondromatosis. 26 The reported prevalence of distension of this bursa varies, dependent upon the age and nature of the study population, defining criteria and imaging modality utilized, ranging from 5-32% of adults being evaluated for suspected internal derangement by MRI and arthrography, respectively. Higher detection rate using arthrography has been postulated to be due to iatrogenic distension of previously collapsed bursae. 30 In an MRI evaluation of 102 asymptomatic knees, Tschirch et al. found prevalence of Sm-Gb of 19%, with the majority having a maximal size of 30 mm or less. In contradistinction, the majority of cases of semimembranosus-gastrocnemius bursal distension in pediatric patients, excluding those with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis (JRA), are not associated with effusion and intra-articular pathology and are thought to occur spontaneously due to local trauma or irritation involving the bursa. 31, 32 Pediatric patients with JRA and an effusion commonly develop semimembranosus- gastrocnemius bursal cysts. 33
What is suprapatellar bursa?
The Suprapatellar bursa or recess is an anterior midline structure located deep to the distal quadriceps and superficial to the pre-femoral fat pad and distal femur. This communicates widely with the knee joint in most adults functioning as a recess due to the involution of an embryonic septum that exists between the bursa and the remaining joint, which occurs at about the third fetal month. 1, 2 A suprapatellar plica is often seen, representing a shelf-like membranous remnant of part of that septum. In approximately 16% of adults, an isolated suprapatellar bursa may be present due to failure of the embryonic septum to involute leaving a complete septum. Distension of this bursa may mimic a mass in the pre-femoral region. 3 A persistent partial septum or suprapatellar plica may trap chondral or osteochondral bodies in the suprapatellar recess. 4 See Figure 15.
Where is the semimembranosus bursa located?
The Semimembranosus-gastrocnemius bursa or recess (Sm-Gb) arises between the semimembranosus tendon and the medial head of the gastrocnemius, within the posteromedial popliteal fossa, cranial to the joint line at the level of the upper medial femoral condyle. They most often extend caudally, though they may extend in any direction. 12 The bursa communicates with the knee joint in most adults and thus is sometimes referred to by many as a recess, being comprised of a distal gastrocnemius bursa and a proximal semimembranosus bursa, which sometimes are partially separated by a septum. 13 The reported prevalence of this communication has varied dependent upon the population being studied, and the mode of investigation. It has been reported as occurring in 30-50% of cadaveric dissections, 50% in arthrograms of normal knees, 55% in open surgical excision, and 37% in diagnostic arthroscopies. 14, 15, 16, 17 Lindgren et al. studied 80 cadaver knee joints and concluded that communication of the Sm-Gb with the knee joint is acquired, due to degeneration of the capsule, occurring with greater frequency in older individuals, in more than 50% of those over the age of 50 years and in no patient under 10 years of age. The communication occurs via a slit-like defect in the posteromedial capsule most often measuring 15-20 mm, where the medial gastrocnemius tendon exits the joint. 17, 18 Various studies have shown unidirectional flow of fluid from the knee joint into the Sm-Gb, though the precise nature of that valvular mechanism is controversial with some proposing a Bunsen or ball valve mechanism and others theorizing that the dynamic actions of the semimembranosus, semitendinosus and gastrocnemius myotendinous units in flexion and extension contribute to a functional unidirectional communication. 17, 19, 20
Where is the semimembranosus tibial collateral bursa located?
The Semimembranosus-tibial collateral bursa is located along the posteromedial joint line, cranial to the pes anserine bursa, and was found to be consistently present in a cadaveric analysis of 50 knees. 10, 11 It has an inverted U or J configuration with a superficial distal arm and a deep proximal arm that drapes around the distal semimembranosus tendon.
Where is the Pes Anserine Bursa located?
The pes anserine bursa is located anteromedially, about 3-4 cm caudal to the joint line and does not typically communicate with the joint. It is interposed between the distal tibial collateral ligament insertion and the distal sartorius, gracilis and semitendinosus tendons. The combined insertions of these tendons have a webbed configuration, which has been likened to that of a goose’s foot, from which is derived their Latin name, pes anserinus tendons. 7 The Tibial collateral or MCL bursa has been found to be present in 90% of adults and in cadaveric specimens, separate femoral and tibial portions of the bursa were frequently seen. 8 Distension of the MCL bursa typically appears as a vertically oriented well defined fluid collection extending along the medial aspect of the femoral and tibial cortices, being centered deep to the superficial MCL (tibial collateral ligament) between it and the deep MCL (the meniscofemoral and meniscotibial ligaments), typically occurring in association with medial compartment and or medial capsuloligamentous pathology. 8, 9 Distinction between fluid in the MCL bursa and a medial parameniscal cyst may be difficult, though usually medial parameniscal cysts are centered more posteriorly, and usually communication of a parameniscal cyst with a meniscal tear or focus of intra-meniscal degeneration is present. 8 Additionally, parameniscal cysts are often more loculated and sometimes contain more inspissated contents.
Why do bursas sit on the knee?
They sit between two surfaces, usually muscle and bone, to reduce friction, a bit like ball bearings. This allows everything to move smoothly preventing inflammation. Sometimes the knee bursa get damaged, known as bursitis, which can cause pain.
Which side of the tibia is the bursa?
Medially - inner side: medial gastrocnemius bursa, the bursa between semitendinosus tendon and the head of the tibia and occasionally there is a bursa between the tendons of semimembranosus and semitendinosus. Laterally - outer side: lateral gastrocnemius, fibular, fibulopopliteal and the subpopliteal bursae.
What is the term for a knee that is prone to inflammation?
Inflammation is known as prepatellar bursitis, or Housemaids Knee, but today is more common in trades such as roofers and carpet fitters. 2.
What causes a bursa knee to hurt?
1. Inflamed: i.e. swollen known as bursitis or. 2. Dried out: i.e. they lose the fluid inside them. This results in more friction on the bone and muscles/tendons leading to bursa knee pain. Usually a combination of strengthening and stretching exercises, medication and injections helps them to recover.
How many infrapatellar knee bursa are there?
There are actually two infrapatellar knee bursa, known as the deep and superficial infrapatellar bursa.
Why is my knee swollen?
This is ususally caused by excess fluid in the knee, usually from an injury or arthritis, which leaks back into the bursa causing it to swell. A lump forms behind the knee, like a squashy orange.
Where are the bursas located?
The other bursa knee locations are: 1 Anteriorly - front of the knee: pretibial and deep infrapatellar bursa 2 Medially - inner side: medial gastrocnemius bursa, the bursa between semitendinosus tendon and the head of the tibia and occasionally there is a bursa between the tendons of semimembranosus and semitendinosus 3 Laterally - outer side: lateral gastrocnemius, fibular, fibulopopliteal and the subpopliteal bursae
How many bursae are there in the knee?
X-ray of the knee of a 12 year old male, with knee effusion extending into the suprapatellar bursa. In front there are five bursae: the suprapatellar bursa or recess between the anterior surface of the lower part of the femur and the deep surface of the quadriceps femoris.
What is the bursae of the joint?
The bursae are thin-walled, and filled with synovial fluid. They represent the weak point of the joint, but also provide enlargements to the joint space. They can be grouped into either communicating and non-communicating bursae or, after their location – frontal, lateral, or medial.
What ligament allows for movement of the skin over the tibia?
It allows for movement of the patellar ligament over the tibia. the subcutaneous [or superficial] infrapatellar bursa between the patellar ligament and skin. the pretibial bursa between the tibial tuberosity and the skin. It allows for movement of the skin over the tibial tuberosity.
How many bursae are there in the medial tibial ligament?
Medial. Medially, there are five bursae: the anserine bursa between the medial (tibial) collateral ligament and the pes anserinus – the conjoined tendons of the sartorius, gracilis, and semitendinosus muscles. the bursa semimembranosa between the medial collateral ligament and the tendon of the semimembranosus.
How many bursae are there in the lateral biceps?
Laterally there are four bursae: the lateral gastrocnemius [subtendinous] bursa between the lateral head of the gastrocnemius and the joint capsule. the fibular bursa between the lateral (fibular) collateral ligament and the tendon of the biceps femoris.
What is the distension of the bursa?
A distension of this bursa is therefore generally an indication of knee effusion. the prepatellar bursa between the patella and the skin It allows movement of the skin over the underlying patella. the deep infrapatellar bursa between the upper part of the tibia and the patellar ligament.
Where is the bursa semimembranosa?
the bursa semimembranosa between the medial collateral ligament and the tendon of the semimembranosus. there is one between the tendon of the semimembranosus and the head of the tibia. and occasionally there is a bursa between the tendons of the semimembranosus and semitendinosus.
Which bursa communicates directly with knee joint?
There are four bursae anterior to the knee joint: suprapatellar bursa: located between the femur and quadriceps femoris, it is attached to the articularis genu muscle and usually communicates with the synovial cavity. subcutaneous prepatellar bursa: between the skin and patella.
Does the Suprapatellar bursa communicate with the knee joint?
Gross anatomy There are four bursae anterior to the knee joint: suprapatellar bursa: located between the femur and quadriceps femoris, it is attached to the articularis genu muscle and usually communicates with the synovial cavity.
Where does the knee joint communicate?
The knee joint is composed of two articulations: Tibiofemoral articulation, where the articular surface of the medial and lateral condyles of the femur articulate with the articular surface of the superior medial and lateral condyles of the tibia.
What are the names of the bursae associated with the knee?
There are five primary bursae that protect the knee joint. They are the: prepatellar, infrapatellar, suprapatellar, Pes Anserine, and the semimembranosus bursae. The prepatellar bursa is located in front of the knee cap. Pre means before in Latin and patella is the medical term for knee cap.

Diagnosis
Introduction
- Bursal distension and other cystic lesions about the knee are frequently encountered findings on MR imaging of the knee. It is important for those interpreting MRI of the knee to be familiar with the normally occurring anatomic bursa of the knee, potential clinical presentations, usual and variable imaging appearances, and differential diagnostic considerations. The aim of this web cli…
Bursae of The Knee: Function and Anatomy
- Definition and Function Anatomic or primary bursae are synovial lined periarticular structures, which occur normally developmentally, contain variable amounts of fluid, and serve to reduce motion or pressure induced friction between adjacent anatomic periarticular structures, often between bone and the overlying soft tissues. An adventitial bursadescribes an acquired fluid fille…
Bursae of The Knee: Clinical Presentations and MRI Appearance
- Bursae about the knee may or may not communicate with the joint, and with a few exceptions normally contain minimal or no fluid, such that they may not be detectable on MRI. Small amounts of fluid may be seen within some bursae and recesses in the absence of symptoms, particularly the semimembranosus gastrocnemius bursa, the deep infrapatellar burs...
Differential Considerations
- Synovial cystrefers to any synovial lined periarticular or peritendinous fluid collection. The term has been used in the literature synonymously with bursa, though most use it to describe synovial lined fluid collections that are acquired rather than being uniformly present developmentally. Ganglia describes benign periarticular, intra-articular, subchondral or periosteal cystic structure…
Treatment
- Many periarticular and intraarticular fluid collections, particularly those that are small, are asymptomatic requiring no treatment. Symptomatic bursae occurring in the setting of athletic overuse may be treated with rest, non-steroidal medication, corrective training measures, shoe wear or orthotics. Identification and treatment of treatable associated intraarticular pathology is i…
Conclusion
- Cystic lesions and bursal distension about the knee joint are commonly occurring findings. While some lesions are asymptomatic, others may be associated with swelling, limited range of motion, pain due to impingement upon adjacent structures, or symptoms related to associated intraarticular pathology. MRI aids in characterization and treatment of symptomatic periarticular …