Medication
Which classes of drugs are used in the treatment of angina pectoris?
- Aspirin. Aspirin and other anti-platelet medications reduce the ability of your blood to clot, making it easier for blood to flow through narrowed heart arteries.
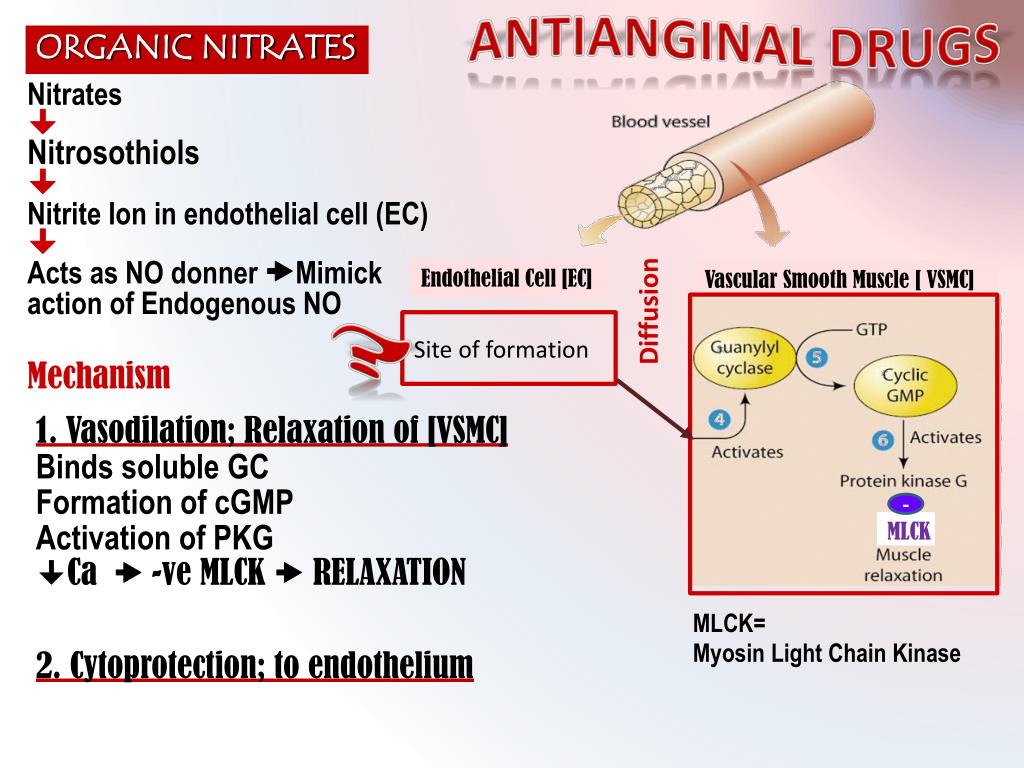
- Nitrates.
- Beta blockers.
- Statins.
- Calcium channel blockers.
- Ranolazine (Ranexa).
Procedures
Treating Angina at Home
- Lifestyle changes. These are among the most crucial steps you can take in responding to your angina. ...
- Citrus. Vitamin C helps the body control its cholesterol levels and sufficient levels can slow the accumulation of arterial plaque.
- Onions. ...
- Turmeric. ...
- Meditate. ...
- Lower your sodium. ...
- Basil. ...
Self-care
Treatment to Prevent Worsening of CAD. Antiplatelet therapy: To reduce the risk of ACS, anyone with angina should be on treatment to reduce blood clotting. For most people this means daily aspirin therapy (75 to 325 mg/day). Plavix (clopidogrel) can be used in people who are allergic to aspirin.
Nutrition
Over the past century, nitroglycerin, also known as “nitro,” has been used to treat angina. In addition to helping patients with CAD regain their physical activity, nitroglycerin is also useful for treating other conditions. Both stable and unstable angina can be relieved of discomfort by nitroglycerin.
Specialist To Consult
What is the drug most often used to treat angina?
How to treat angina naturally?
How do medications treat stable angina?
Can angina be relieved with nitroglycerin?

What is the best drug for angina pectoris pain?
Nitrates are often used to treat angina. Nitrates relax and widen the blood vessels so more blood flows to the heart. The most common form of nitrate used to treat angina is nitroglycerin. The nitroglycerin pill is placed under the tongue.
Which drug groups are most often used to treat patients with angina?
Overall, three drug classes are typically used in the treatment and prevention of angina: organic nitrates, calcium channel blockers and beta-blockers. nitroglycerin is recommended as first-line treatment.
Which group of drugs are first-line choice for treating angina?
Beta blockers are first-line therapy to reduce angina and improve exercise tolerance by limiting the heart rate response to exercise.
What are the 4 types of angina pectoris?
Types of AnginaStable angina.Unstable angina.Microvascular Angina.Vasospastic or variant angina.
What are the 3 types of angina?
There are three types of angina:Stable angina is the most common type. It happens when the heart is working harder than usual. ... Unstable angina is the most dangerous. It does not follow a pattern and can happen without physical exertion. ... Variant angina is rare. It happens when you are resting.
Which classes of medication are most effective in relieving ischemia and angina?
β-adrenergic receptor blockers (beta-blockers) and calcium-channel blockers are considered to be first-line anti-anginal drugs and have been shown in many studies to prevent angina and myocardial ischaemia.
What is the first line treatment for unstable angina?
Patients with unstable angina require admission to the hospital for bed rest with continuous telemetry monitoring. One should obtain intravenous (IV) access, and provide supplemental oxygen if evidence of desaturation is noted.
What is the most common cause of angina pectoris?
Coronary artery disease (CAD): This is the most common cause of angina. It happens when plaque (a fatty, waxy substance) builds up in your coronary arteries, which supply blood to your heart. These arteries narrow or harden (atherosclerosis), reducing blood flow to your heart.
What is angina pectoris and how is it classified?
Angina, also known as angina pectoris, is chest pain or pressure, usually caused by insufficient blood flow to the heart muscle (myocardium). It is most commonly a symptom of coronary artery disease. Angina is typically the result of obstruction or spasm of the arteries that supply blood to the heart muscle.
Is Class 3 angina unstable angina?
Owa et al10 found that unstable angina class III was associated with both a higher incidence of coronary thrombi on angiography and an increased risk of clinical progression to myocardial infarction.
Which classification of antihypertensive drugs is the first choice therapy for treating hypertension and angina in clients with known coronary artery disease?
The Antihypertensive and Lipid-Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial ALLHAT study recommended thiazide diuretics as the first line of treatment for hypertension unless there are contraindications.
Which of the following drugs is the first line choice for treatment of hypertension?
There are three main classes of medication that are usually in the first line of treatment for hypertension: 1. Calcium Channel Blockers (CCB) 2. Angiotensin Converting Enzyme inhibitors (ACE inhibitors or ACE-I) and Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARBs) 3.
What is the first medication a paramedic should administer to a patient with angina?
The initial treatment consists of administration of oxygen, aspirin, nitroglycerin, morphine, and a beta-blocker. Given an altered, yet nondiagnostic ECG and no contraindications, further treatment with heparin (low-molecular weight or unfractionated), clopidogrel, or other antiplatelet agents may be initiated.
Which medication class is most commonly used as a first line treatment of heart failure?
1.3 Beta-adrenergic receptor blocker (beta-blocker) Beta-blockers are part of the first line therapy in the treatment of HFrEF, as they have been proven to improve survival and decrease hospitalizations in this population of patients, in a number of large clinical trials.
Drugs used to treat Angina
The following list of medications are in some way related to, or used in the treatment of this condition.
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.
How long does nitroglycerin last?
Every 6 months, the nitroglycerin prescription should be refilled and the old tablets safely discarded. Nitroglycerin has a longer shelf life than 1 or 3 months but does not have a shelf life as long as 1 year.
Can ACE inhibitors be used in combination with statins?
ACE inhibitors and statins are often combined to treat angina pectoris. Antidysrhythmics and platelet active agents are not used in combination to treat angina because angina does not typically result in rhythm disturbances. Vasoconstrictors would exacerbate angina and are not used with diuretics. Analgesics and thrombolytics are not used in combination to treat angina because angina is not caused by a clot, so thrombolytics are not necessary.
What is the best treatment for angina pectoris?
Current ESC guidelines on the treatment of stable angina pectoris [4] recommend the use of renin-angiotensin system (RAS) blockers since they may favourably alter prognosis, as well as the use of calcium channel blockers (CCBs), beta-blockers and long-acting nitrates for symptom relief. We have to bear in mind, however, that RAS blockers, as well as CCBs and beta-blockers, represent agents with significant antihypertensive effects. In effect, these agents are four of the five antihypertensive drug classes proposed by the current ESH/ESC guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension [5]. Thus, in patients with stable angina in need of antihypertensive treatment, ESH/ESC guidelines also suggest the use of these agents since, in addition to blood pressure (BP) decrease, these drugs also present other auxiliary properties (in terms of prognosis or symptom relief).
What is the best drug for diabetics with angina?
When treating diabetic patients with angina, drugs that have a positive or at least a neutral metabolic profile have to be preferred. Ranolazine is an antianginal drug with favourable effects in reduction of HbA1c levels [11].
Which beta blocker is best for angina?
Therefore, agents such as ranolazine or vasodilating beta-blockers with their favourable metabolic profile, or agents such as ivabradine, nicorandil, CCBs and probably trimetazidine with their neutral profile, should be preferred in patients with angina and DM for symptom relief.
Can antianginal drugs be combined?
Thus, in the majority of studies various antianginal drugs were administered on top of other antianginal drugs [4,10]. However, not all antianginal drugs can be combined.
Can PCI cause recurrent angina?
Despite modern percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) and coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) techniques, a significant percentage of stable coronary artery disease (SCAD) patients will continue to experience or will develop recurrent angina symptoms. Several randomised studies and meta-analyses [1-3] have shown that approximately 30% of patients revascularised for SCAD continue to experience angina symptoms, regardless of the procedure (PCI or CABG). Thus, the use of antianginal drugs represents a common treatment in those patients. Current ESC guidelines suggest the use of first- and second-line classes of drugs for the management of stable angina [4]; however, these patients often, if not always, have several concomitant risk factors or comorbidities which, on the one hand, alter the therapeutic approach and, on the other hand, may have in practice led to the development of their coronary artery disease. In this article, we are going to summarise the evidence in stable angina treatment recommendations in order to individualise patients’ treatment according to their particular characteristics and comorbidities.
Is stable angina a therapeutic approach?
Management of stable angina is often challenging. Despite several therapeutic approaches, including revascularisation, many patients are symptomatic and their daily activities and quality of life are affected. Current ESC and ACC guidelines suggest a step-by-step approach for the medical treatment of stable angina, categorising antianginal drugs as first- or second-line therapy. Nevertheless, they do not provide many suggestions to guide choice within each step, or among steps. The purpose of this article is to suggest a systematic therapeutic approach tailored to patients’ cardiovascular profiles and drug characteristics, taking into account their risk factors and comorbidities.
Does atrial fibrillation cause angina?
Atrial fibrillation may aggravate angina symptoms since it increases heart rate and thus myocardial oxygen consumption. Hence, in patients with stable angina and atrial fibrillation, heart rate-lowering antianginal drugs such as beta-blockers and non-DHP CCBs should be preferred.
What is the third type of angina?
A third type of angina—unstable or crescendo angina , also known as acute coronary syndrome —is characterized by increased frequency and severity of attacks that result from a combination of atherosclerotic plaques, platelet aggregation at ...
What is Vasospastic Angina?
It involves reversible spasm of coronaries, usually at the site of an atherosclerotic plaque. Spasm may occur at any time, even during sleep. Vasospastic angina may deteriorate into unstable angina.
What is an atheroclerotic angina?
It is associated with atheromatous plaques that partially occlude one or more coronary arteries. When cardiac work increases (eg, in exercise), the obstruction of flow and inadequate oxygen delivery results in the accumulation of acidic metabolites and ischemic changes that stimulate myocardial pain endings. Rest usually leads to complete relief of the pain within 15 min. Atherosclerotic angina constitutes about 90% of angina cases.
What is the best medication for angina?
Aspirin and other anti-platelet medications reduce the ability of your blood to clot, making it easier for blood to flow through narrowed heart arteries. Nitrates. Often used to treat angina, nitrates relax and widen your blood vessels, allowing more blood to flow to your heart muscle.
How to treat angina?
The best treatment for your angina depends on the type of angina you have and other factors. If your angina is stable, you might be able to control it with lifestyle changes and medicines. Unstable angina requires immediate treatment in a hospital, which could involve medicines and surgical procedures.
How to treat angina with nitrates?
Several medications can improve angina symptoms, including: 1 Aspirin. Aspirin and other anti-platelet medications reduce the ability of your blood to clot, making it easier for blood to flow through narrowed heart arteries. 2 Nitrates. Often used to treat angina, nitrates relax and widen your blood vessels, allowing more blood to flow to your heart muscle. Nitrates in pills or sprays act quickly to relieve pain during an event. There are also long-acting nitrate pills and skin patches. 3 Beta blockers. These block the effects of the hormone epinephrine, also known as adrenaline. They help your heart beat more slowly and with less force, decreasing the effort your heart makes and easing the angina pain. 4 Statins. Statins lower blood cholesterol by blocking a substance your body needs to make cholesterol. They might also help your body reabsorb cholesterol that has accumulated in the buildup of fats (plaques) in your artery walls, helping prevent further blockage in your blood vessels. 5 Calcium channel blockers. Also called calcium antagonists, these drugs relax and widen blood vessels by affecting the muscle cells in the arterial walls. This increases blood flow in your heart, reducing or preventing angina. 6 Ranolazine (Ranexa). This anti-angina medication might be prescribed with other angina medications, such as beta blockers. It can also be used as a substitute if your symptoms don't improve with the other medications.
What to do if your angina is not working?
For most people, first steps include medications and lifestyle changes. If those don't work for you, angioplasty and stenting can be another option. Talk to your doctor if you think your treatment isn't controlling your angina well enough. May 21, 2021. Show references.
How do statins help with angina?
They help your heart beat more slowly and with less force, decreasing the effort your heart makes and easing the angina pain. Statins. Statins lower blood cholesterol by blocking a substance your body needs to make cholesterol.
How to get rid of angina after exercise?
Talk to your doctor about starting a safe exercise plan. If your angina is brought on by exertion, pace yourself and take rest breaks. Excess weight. If you're overweight, find a way to achieve and maintain a healthy weight by balancing what and how much you eat with how much physical activity you get.
What is the procedure that increases blood flow through a blocked artery and decreases angina?
Angioplasty, also known as percutaneous coronary intervention, increases blood flow through a blocked artery and decreases angina.