Coagulation factors and related substances
| Number and/or name (s) | Function | Associated genetic disorders |
| Factor I ( fibrinogen) | Forms fibrin threads (clot) | Congenital afibrinogenemia, Familial ren ... |
| Factor II ( prothrombin) | Its active form (IIa) activates platelet ... | Prothrombin G20210A, Thrombophilia |
| Factor III ( tissue factor, tissue ... | Co-factor of factor VIIa, which was form ... | |
| Factor IV ( calcium ion) | Required for coagulation factors to bind ... |
- Factor I - fibrinogen.
- Factor II - prothrombin.
- Factor III - tissue thromboplastin (tissue factor)
- Factor IV - ionized calcium ( Ca++ )
- Factor V - labile factor or proaccelerin.
- Factor VI - unassigned.
- Factor VII - stable factor or proconvertin.
How many factors are involved in coagulation?
There are 13 principal coagulation factors in all, and each of these has been assigned a Roman numeral, I to XIII. Coagulation can be initiated through the activation of two separate pathways, designated extrinsic and intrinsic. Both pathways result in the production of factor X.
What are the 4 groups of coagulation factors?
Nomenclature of coagulation proteins is rather complex [Table 3]. The first 4 of the 12 originally identified factors are referred to by their common names, i.e., fibrinogen, prothrombin, tissue factor (TF), and calcium and are not assigned any Roman numerals.
What are the 13 coagulation factors in the body?
There are about thirteen known clotting factors:Fibrinogen (Factor 1)Prothrombin (Factor 2)Thromboplastin (Factor 3)Calcium (Factor 4)Proaccelerin or Labile Factor (Factor 5)Stable Factor (Factor 6)Antihemophilic Factor (Factor 8)Christmas Factor (Factor 9)More items...•
What are the 3 components of blood coagulation?
Secondary hemostasis involves the clotting factors acting in a cascade to ultimately stabilize the weak platelet plug. This is accomplished by completing three tasks: (1) triggering activation of clotting factors, (2) conversion of prothrombin to thrombin, and (3) conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin.
What are the three components of coagulation?
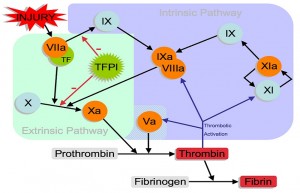
The coagulation cascade is classically divided into three pathways: the contact (also known as the intrinsic) pathway, the tissue factor (also known as the extrinsic pathway), and the common pathway. Both the contact pathway and the tissue factor feed into and activate the common pathway.
What are the 12 blood clotting factors?
Types of blood clotting factors:Fibrinogen.Prothrombin.Thrombokinase (tissue factor)Ionized calcium ( Ca++ )Labile factor.Leiden thrombophilia.Stable factor.Antihemophilic factor.More items...
What is clotting factor 10 called?
Practice Essentials. Clotting factor X, or Stuart-Prower factor, is a vitamin K–dependent serine protease that serves as the first enzyme in the common pathway of thrombus formation.
What is the 11th clotting factor?
Factor XI (FXI) is the zymogen of a serine protease enzyme in the intrinsic pathway of blood coagulation and is an important factor in the creation of a stable fibrin clot.
What are the coagulation groups?
The following are coagulation factors and their common names:Factor I - fibrinogen.Factor II - prothrombin.Factor III - tissue thromboplastin (tissue factor)Factor IV - ionized calcium ( Ca++ )Factor V - labile factor or proaccelerin.Factor VI - unassigned.Factor VII - stable factor or proconvertin.More items...
What is the name of factor 4?
Factor IV: Ionized calcium: Metal cation important in coagulation. Factor V: Proaccelerin or labile factor: Activation of prothrombin to thrombin. Factor VI: Stable factor: Initiates extrinsic pathway. Factor VII: Antihemophilic factor: Intrinsic activation factor.
Which factors are in the contact group?
1. Contact group – factors 11, 12, prekallikrein, and high molecular weight kininogen (HMWK). All of these factors are involved in the initial phase of the intrinsic system activation.
What are the four vitamin K dependent clotting factors?
Prothrombin, FVII, FIX, protein C, and protein S are vitamin K-dependent clotting factors or proteins strictly related to blood coagulation.
What are the factors that make blood clots?
The following are the clotting factors involved in the process of blood clot formation. Factor I: Clotting factor I is also known as fibrinogen. It is synthesized by the liver. Fibrinogen is the last enzyme to be activated in the process of clot formation. It is downstream of both intrinsic and extrinsic pathways.
What are the two pathways of clotting factor activation?
The cascade of clotting factor activation is traditionally viewed as being divided into two separate pathways: intrinsic pathway and extrinsic pathway.
What is the process of fibrin clot formation?
The process of fibrin clot formation also requires a cascade of enzyme activations. These enzymes are known as clotting factors, and are normally present in the blood in inactive forms. When the coagulation process begins, the clotting factors start getting activated in a linear fashion by one another.
What is the clotting factor of fibrin?
The long strands of fibrin form an interconnected meshwork that constitutes the clot. Factor II: Clotting factor II is also known as prothrombin. Like fibrinogen, prothrombin is also synthesized by the liver. Clotting factor II is a step above the clotting factor I in the cascade.
What happens when collagen is exposed to a blood clot?
Eventually, the platelet plug will get enmeshed in a fibrous protein called fibrin, resulting in a blood clot. The process of fibrin clot formation also requires a cascade of enzyme activations.
How do platelets stop bleeding?
The complex process of stopping bleeding through clot formation is set into motion when the damaged blood vessel constricts, and circulating platelets (tiny cell fragments) in the bloodstream start adhering to the damaged walls of the injured blood vessel. The platelets are attracted to the damaged site by collagen, which is a normal constituent of the walls of blood vessels, and gets exposed when a vessel gets damaged.
What is the process of clotting blood?
The clotting of blood is a very complex process, which is orchestrated by aggregation and activation of different chemicals, cells and components of blood. Disorders at any step in the clotting mechanism could lead to bleeding (hemorrhagic) disorders or abnormal clot formations (thrombosis). Either of these conditions could be lethal.
Why is it important to know about blood coagulation?
Knowing about the Blood Coagulation factors in Dentistry is very important to prevent the mishaps from occurring during or after Dental procedures. There are many Hematologic disorders which are related to these factors, which makes it essential to make note of these factors and the concerning disorders.
What is the process of coagulation?
In simple words Coagulation means Clotting which is seen when there is any injury to the body, the Liquid blood turns in gel form which is used to stop the bleeding from the injury site. The Clotting factors are Plasma proteins which are circulating in the Blood stream, they end up being a clot through Enzymatic cascade.
What is the difference between factor VI and VIII?
Factor VI – Accelerin (Does not exist as it was named initially but later on discovered not to play a part in blood coagulation) Factor VIII = Antihemophilic factor A, Antihemophilic Globulin, Antihemophilic factor. Factor IX = Plasma Thromboplastin component, Antihemophilic factor B or Christmas factor.
What are the natural proteins that help in coagulation?
Blood Coagulation or Clotting Factors are the natural proteins which help in coagulation of blood to control bleeding, they also help to maintain the flow of blood in the body and also make sure coagulation takes place in case of any injury.
What is the role of thrombin in clotting?
Most have their own role to play in Clotting, but some Factors play a major role – Thrombin (Factor II) which is a major coagulant as it converts Fibrinogen into Fibrin which forms a major chunk of the Clot in addition to the Platelets.
What factor does Accelerin not exist?
Factor VI – Accelerin (Does not exist as it was named initially but later on discovered not to play a part in blood coagulation)
What are Clotting Factors?
Clotting factors are components found in plasma that are linked to the blood clotting process. These factors are named and numbered based on their discovery. Though there are a total of 13 numerals, there are only 2 clotting factors. Factor VI was discovered to be part of another factor.
What is the role of coagulation in the repair of blood vessels?
Otherwise known as blood clotting, coagulation plays a pivotal role in the repair of blood vessels. The heart pumps blood throughout the body with the aid of the arteries, and in turn, blood goes back to the heart through the veins. When the blood vessels become injured, it will trigger the blood clotting process.
How does hemostasis work?
Hemostasis is a way of the body to stop injured blood vessels from bleeding. One of the most important parts of hemostasis is clotting of the blood. Subsequently, the body needs to control the mechanisms to control and limit clotting. These include dissolving excess clots that are not needed anymore. When there is an abnormality in any part of the system that controls bleeding, it can lead to hemorrhage or excessive clotting. These are potentially life-threatening.#N#Too much clotting can lead to stroke and heart attacks because blood clots can travel and clog the vessels. On the other hand, poor clotting can lead to severe blood loss even with just a slight injury to the blood vessels.
What happens when a blood vessel is injured?
When a blood vessel becomes injured, the coagulation factors or clotting factors in the blood are activated. The clotting factor proteins stimulate the production of fibrin, which is a strong and strand-like substance that forms a fibrin clot. For days or weeks, this fibrin clot strengthens and then dissolves when the injured blood vessel walls close and heal.
What happens when blood vessels become damaged?
When the blood vessels become injured, it will trigger the blood clotting process. This way, the body will repair the damage to stop hemorrhage or bleeding from happening. For instance, the damage happens in the lining of the blood vessels, the platelets will form an initial plug on the affected area. They will initiate the clotting process ...
Why is blood clotting important?
Blood clotting is a crucial process that can help prevent blood loss due to injury. If there is an abnormality in any part of the process, it can lead to dangerous complications such as severe blood loss. Commonly, people with clotting disorders are closely monitored to prevent injuries and bleeding.
What is the function of platelets in the body?
In response to the injury, the body activates platelets. At the same time, chemical signals are released from small sacs in the platelets to attract other cells to the area. They make a platelet plug by forming a clump together. A protein called the von Willebrand factor (VWF) helps the platelets to stick together.
What are clotting factors?
Last Modified on March 1, 2020 | No comments. Coagulation factors or Clotting Factors are proteins in the blood that help control bleeding. It has several different clotting factors in the blood. When you cut or another injury that causes bleeding, your clotting factors work together to form a blood clot.
How many factors are involved in the coagulation cascade?
The table lists 13 of 20 different coagulation factors involved in the coagulation cascade that are vital to normal blood clotting.
What is the main goal of coagulation?
The main goal of coagulation is to form a stable blood clot to stop bleeding and allow time for the tissue to be repaired.
What are the three pathways of coagulation?
Coagulation consists of three pathways, the extrinsic, intrinsic, and common path ways, that interact together to form a stable blood clot. The extrinsic and intrinsic coagulation pathways both lead into the final common pathway by independently activating factor X. The extrinsic pathway involves initiation by factor III (i.e., tissue factor) and its interaction with factor VII. Whereas, factors XII, XI, IX, and VIII are utilized in the intrinsic pathway. Then, the common pathway uses factors X, V, II, I, and XIII.
When is fibrin produced during the coagulation cascade?
Fibrin (factor Ia) is a long, thin protein with branches produced at the end of the coagulation cascade when fibrinogen (factor I) is converted to fibrin, which stabilizes the blood clot.
What are the most important facts to know about the coagulation cascade?
The coagulation cascade refers to the series of steps that occur during the formation of a blood clot after injury by activating a cascade of proteins called clotting factors . There are three pathways: intrinsic, extrinsic, and common. The intrinsic pathway is activated by factors in the blood, while extrinsic is activated by tissue factor. Both pathways result in activation of factor X leading into the common pathway, which ends with converting fibrinogen into fibrin to form a stabilized blood clot. Coagulation disorders occur when there is a deficiency in a clotting factor involved, and the most common disorders are hemophilia and vitamin K deficiency.
What is the coagulation cascade?
The coagulation cascade involves the activation of a series of clotting factors, which are proteins that are involved in blood clotting. Each clotting factor is a serine protease, an enzyme that speeds up the breakdown of another protein. The clotting factors are initially in an inactive form called zymogens. When placed with its glycoprotein co-factor, the clotting factor is activated and is then able to catalyze the next reaction. When a clotting factor becomes activated, it is denoted with an “a” following its respective Roman numeral (e.g. when activated, Factor V becomes Factor Va).
What is the most common bleeding disorder?
Von Willebrand disease is the most common bleeding disorder and is characterized by a deficiency in von Willebrand factor due to an autosomal dominant genetic mutation. The von Willebrand factor is mostly involved in primary hemostasis where it helps platelets stick together. The factor also plays a role in secondary hemostasis by helping stabilize factor VIII.
What is the common pathway?
The common pathway may result after the activation of factor X at the end of either pathway. The common pathway begins when factor Xa , Va , and calcium bind together , forming a prothrombinase complex. The prothrombinase complex then activates prothrombin (factor II) into thrombin (factor IIa). Next, thrombin cleaves fibrinogen (factor I) into fibrin (factor Ia). Afterwards, thrombin cleaves the stabilizing factor (factor XIII) into XIIIa. Factor XIIIa binds with calcium to then create fibrin crosslinks to stabilize the clot. Thrombin has several functions, including activating platelets (cell fragments involved in clot formation) and activating factors V, VIII, and IX.
