What is the function of vWf?
- Factor Xa converts Prothrombin to thrombin
- Thrombin converts Factor V to Factor Va, which assists in converting prothrombin to thrombin
- Thrombin converts Fibrinogen to fibrin
- Thrombin converts Factor XIII to Factor XIIIa
What is the role of thrombin in coagulation?
The covalent bonds increase the stability of the fibrin clot. Thrombin interacts with thrombomodulin. As part of its activity in the coagulation cascade, thrombin also promotes platelet activation and aggregation via activation of protease-activated receptors on the cell membrane of the platelet.
What causes the conversion of pro-thrombin to thrombin?
Second, the pro-thrombin activator, in the presence of sufficient amounts of ionic Ca++, causes conversion of pro-thrombin to thrombin (Figure 36–2). Third, the throm-bin causes polymerization of fibrinogen molecules into fibrin fibers within another 10 to 15 seconds.
Is prothrombin a clotting factor?
Clotting factor II, or prothrombin, is a vitamin K–dependent proenzyme that functions in the blood coagulation cascade. Factor II deficiency is a rare, inherited or acquired bleeding disorder with an estimated incidence of one case per 2 million population. Is fibrinogen a clotting factor?
What is the mechanism of action of anticoagulants on prothrombin?
Manipulation of prothrombin is central to the mode of action of most anticoagulants. Warfarin and related drugs inhibit vitamin K -dependent carboxylation of several coagulation factors, including prothrombin. Heparin increases the affinity of antithrombin to thrombin (as well as factor Xa ).

What factor converts prothrombin to thrombin?
prothrombinaseProthrombin is transformed into thrombin by a clotting factor known as factor X or prothrombinase; thrombin then acts to transform fibrinogen, also present in plasma, into fibrin, which, in combination with platelets from the blood, forms a clot (a process called coagulation).
Does factor Xa convert prothrombin to thrombin?
Factor Xa, produced by both the extrinsic tenase and intrinsic tenase complexes, represents the point of convergence of the extrinsic and intrinsic pathways of the coagulation cascade and converts prothrombin into thrombin (Figure 1)—the serine protease responsible for fibrin formation and the subsequent growth and ...
Does heparin convert prothrombin to thrombin?
Heparin is an anticoagulant, which prevents the conversion of prothrombin into thrombin.
What is Factor 4 in blood coagulation?
Platelet factor-4 (PF4/CXCL4) is an orphan chemokine released in large quantities in the vicinity of growing blood clots. Coagulation of plasma supplemented with a matching amount of PF4 results in a translucent jelly-like clot.
Is prothrombinase and thrombokinase same?
Answer: Answer: prothrombinase is (biochemistry) a complex consisting that catalyzes the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin in the presence of calcium ions while thrombokinase is (enzyme) a proteolytic enzyme, that converts prothrombin into thrombin during the clotting of blood.
What is the role of Factor XIII?
Factor XIII, also known by the name fibrin stabilizing factor, is a key clotting factor in the coagulation cascade known for stabilizing the formation of a blood clot.
Which is the Stuart prower factor?
FACTOR X (Stuart-Prower Factor) DEFICIENCY The factor X protein plays an important role in activating the enzymes that help to form a clot. It needs vitamin K for synthesis, which is produced by the liver. Factor X is an ultra-rare bleeding disorder.
Which anticoagulant inhibits the conversion of prothrombin to thrombin?
Heparin is an injectable anticoagulant that activates antithrombin III, which inhibits thrombin and factor Xa, factors necessary in the final stages of blood clotting cascade.
Which anticoagulant prevents conversion of prothrombin to thrombin?
HeparinHeparin is an anticoagulant, which prevents the conversion of prothrombin into thrombin.
What is factor 7 used for?
Factor VII, also called proconvertin, is one such clotting factor produced by the liver. It requires vitamin K for its production. Along with other clotting factors and blood cells, it promotes blood clotting at the site of an injury. It forms normal blood clots and closes the wound to prevent blood loss.
How is factor 12 activated?
In vivo, factor XII is activated by contact to polyanions. Activated platelets secrete inorganic polymers, polyphosphates. Contact to polyphosphates activates factor XII and initiates fibrin formation by the intrinsic pathway of coagulation with critical importance for thrombus formation.
What is factor 9 in the blood?
Factor IX is a protein produced naturally in the body. It helps the blood form clots to stop bleeding. Injections of factor IX are used to treat hemophilia B, which is sometimes called Christmas disease. This is a condition in which the body does not make enough factor IX.
What is the function of prothrombin?
Prothrombin is one of the proteins in constant circulation in the blood. It is manufactured by the liver and requires vitamin K. Since the body is constantly plugging small tears throughout the system everyday, prothrombin is rapidly used up. If the liver does not produce thrombin for one or two days, blood clotting is compromised. As explained above the extrinsic and intrinsic pathways yield Prothrombin Activator. This converts prothrombin into thrombin. Thrombin is essentially an enzyme that then converts fibrinogen into fibrin.
How many factors are involved in the coagulation process?
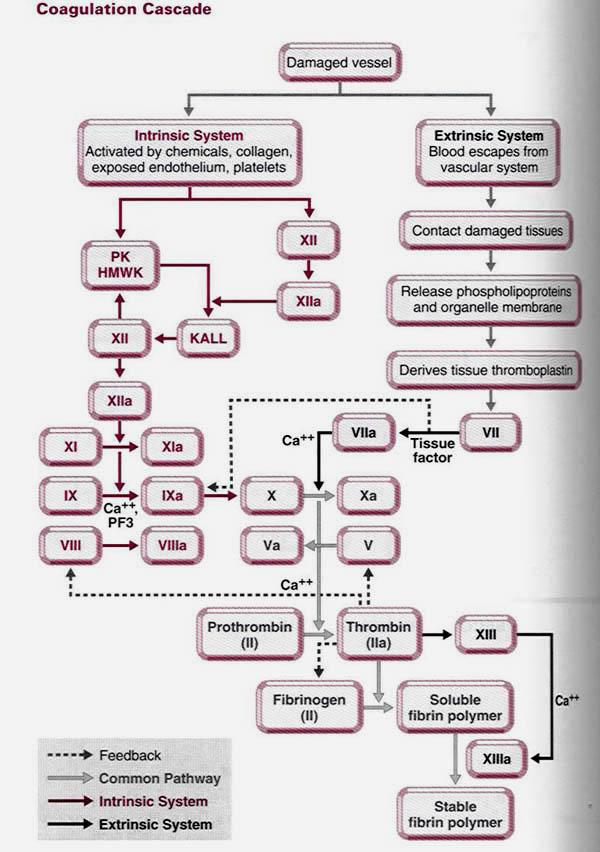
The coagulation process involves 12 clotting factors (11 different specialized chemicals and calcium) which act on each other to lead to clot formation and this is known as the coagulation cascade.
What happens if the liver does not produce thrombin?
If the liver does not produce thrombin for one or two days, blood clotting is compromised. As explained above the extrinsic and intrinsic pathways yield Prothrombin Activator. This converts prothrombin into thrombin. Thrombin is essentially an enzyme that then converts fibrinogen into fibrin.
What are the steps of the blood clot process?
The two pathways achieve three essential steps : Initiating a number of chemicals known as prothrombin activator. Conversion of prothrombin into thrombin by prothrobin activator. Conversion of fibrinogen into fibrin by thrombin.
What is the mechanism of blood loss?
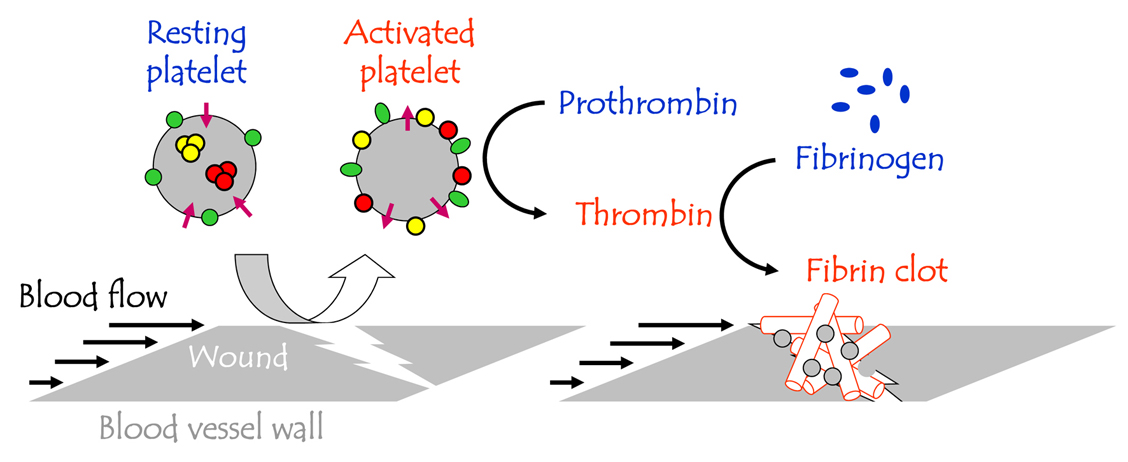
Blood Coagulation Cascade, Prothrombin and Fibrinogen. Hemostasis is the mechanism to prevent blood loss. It is a fast acting system that has multiple steps to reduce blood loss, temporarily and then permanently plug the leak until the integrity of the blood vessel is restored. There are four main phases to hemostasis with ...
What is the function of fibrinogen?
Fibrinogen is a protein formed by the liver. When thrombin acts on it, fibrinogen is converted into a lighter protein known as fibrin. Many fibrin molecules can attach to each other to form long fibrin strands. These strands are then laid down over the platelet plug (second phase of hemostasis) to secure the platelets, trap blood cells and more firmly seal the area. This is essentially a blood clot.
How does fibrinogen convert into fibrin?
Conversion of fibrinogen into fibrin by thrombin. Fibrin are long strands of protein which then form a mesh network securing the platelets laid down in the previous phases of hemostasis and trapping other blood cells and components to form a blood clot.
How is thrombin produced?
Thrombin is produced by the enzymatic cleavage of two sites on prothrombin by activated Factor X (Xa). The activity of factor Xa is greatly enhanced by binding to activated Factor V (Va), termed the prothrombinase complex. Prothrombin is produced in the liver and is co-translationally modified in a vitamin K -dependent reaction that converts 10-12 glutamic acids in the N terminus of the molecule to gamma-carboxyglutamic acid (Gla). In the presence of calcium, the Gla residues promote the binding of prothrombin to phospholipid bilayers. Deficiency of vitamin K or administration of the anticoagulant warfarin inhibits the production of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid residues, slowing the activation of the coagulation cascade.
What is the function of thrombin?
Thrombin in turn acts as a serine protease that converts soluble fibrinogen into insoluble strands of fibrin, as well as catalyzing many other coagulation-related reactions.
What is prothrombin complex concentrate?
Prothrombin complex concentrate and fresh frozen plasma are prothrombin-rich coagulation factor preparations that can be used to correct deficiencies (usually due to medication) of prothrombin. Indications include intractable bleeding due to warfarin .
What are the effects of gla residues on prothrombin?
In the presence of calcium, the Gla residues promote the binding of prothrombin to phospholipid bilayers. Deficiency of vitamin K or administration of the anticoagulant warfarin inhibits the production of gamma-carboxyglutamic acid residues, slowing the activation of the coagulation cascade.
What is fibrinogen used for?
Thrombin, combined with fibrinogen, is sold under the brand name Fibrimex for use as a binding agent for meat. Both proteins in Fibrimex derives from porcine or bovine blood. According to the manufacturer it can be used to produce new kinds of mixed meats (for example combining beef and fish seamlessly).
What is thrombin in blood?
Thrombin is implicated in the physiology of blood clots. Its presence indicates the existence of a clot. In 2013 a system for detecting the presence of thrombin was developed in mice. It combines peptide-coated iron oxide attached to "reporter chemicals".
How much antithrombin is in the blood?
In human adults, the normal blood level of antithrombin activity has been measured to be around 1.1 units/mL. Newborn levels of thrombin steadily increase after birth to reach normal adult levels, from a level of around 0.5 units/mL 1 day after birth, to a level of around 0.9 units/mL after 6 months of life.
Overview
History
Physiology
Structure
- * It is important to note that Factor V is only activated by thrombin. Therefore initially the Prothrombin Activator complex is still capable of converting prothrombin into thrombin even with the inactive Factor V component but becomes much more efficient once the Factor V is activated.
Gene
Role in disease
Applications
Thrombin (EC 3.4.21.5, fibrinogenase, thrombase, thrombofort, topical, thrombin-C, tropostasin, activated blood-coagulation factor II, blood-coagulation factor IIa, factor IIa, E thrombin, beta-thrombin, gamma-thrombin) is a serine protease, an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the F2 gene. Prothrombin (coagulation factor II) is proteolytically cleaved to form thrombin in the clotting process. Thrombin in turn acts as a serine protease that converts soluble fibrinogen int…
See also
After the description of fibrinogen and fibrin, Alexander Schmidt hypothesised the existence of an enzyme that converts fibrinogen into fibrin in 1872.
Prothrombin was discovered by Pekelharing in 1894.