
Who is the father of additive color?
What is additive mixing?
What is subtractive color?
How does additive mixing work?
What is the gamut of color?
Who created the first color photograph?
See 3 more
About this website

Is CMYK additive color?
CMYK is a color model most often used in printing. Also known as the "four-color process", it stands for Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and Key (or black) and is a subtractive color model, as opposed to an additive color model like RGB. In printing, CMYK reduces the brightness, or reflected light, from a white background.
Is CMYK subtractive or additive?
The CMYK color model (also known as process color, or four color) is a subtractive color model, based on the CMY color model, used in color printing, and is also used to describe the printing process itself. CMYK refers to the four ink plates used in some color printing: cyan, magenta, yellow, and key (black).
Is RGB subtractive or additive?
Additive PrimariesRGB—Additive Primaries By mixing red, green and blue (the additive primaries) in different combinations and at varying levels of intensity, we can simulate the full range of colors in nature. If the reflected light contains a mix of pure red, green, and blue light, the eye perceives white.
Is RGB color additive?
The RGB model is as an "additive" model: as colors are added, in the form of light, the result becomes lighter. For instance, the full combination of red, green and blue produces white. An alternative model to the RGB model is the CMYK model, which is used for color printing.
Why is RGB called additive color?
The RGB color model is additive in the sense that the three light beams are added together, and their light spectra add, wavelength for wavelength, to make the final color's spectrum.
Why is RGB additive and CMYK subtractive?
In the RGB model notice that the overlapping of additive colors (red, green and blue) results in subtractive colors (cyan, magenta and yellow). In the CMYK model notice that the overlapping of subtractive colors (cyan, magenta and yellow) results in additive colors (red, green and blue).
Why is CMYK subtractive color?
The CMYK model works by partially or entirely masking colors on a lighter, usually white, background. The ink reduces the light that would otherwise be reflected. Such a model is called subtractive because inks “subtract” the colors red, green, and blue from white light.
Is paint color additive or subtractive?
This is because paint, like printing ink, doesn't generate light and make additive colours, instead it selectively reflects and absorbs wavelengths. This is called subtractive colour. Say you have a red ink. It doesn't shine with red light, it reflects it.
What is RGB vs CMYK?
RGB is an additive color model, while CMYK is subtractive. RGB uses white as a combination of all primary colors and black as the absence of light. CMYK, on the other hand, uses white as the natural color of the print background and black as a combination of colored inks.
What is CMYK used for?
The CMYK acronym stands for Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and Key: those are the colours used in the printing process. A printing press uses dots of ink to make up the image from these four colours. 'Key' actually means black. It's called Key because it's the main colour used to determine the image outcome.
What does CMYK stand for?
CMYK is a scheme for combining primary pigments. The C stands for cyan (aqua), M stands for magenta (pink), Y for yellow, and K for Key. The key color in today's printing world is black but it has not always been.
Is CMYK a primary color?
CMYK refers to the primary colors of pigment: Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and Black. These are the inks used on the press in “4-color process printing”, commonly referred to as “full color printing” or “four color printing”.
Why is CMYK a subtractive model?
The CMYK model works by partially or entirely masking colors on a lighter, usually white, background. The ink reduces the light that would otherwise be reflected. Such a model is called subtractive because inks “subtract” the colors red, green, and blue from white light.
What is difference between CMYK and RGB?
Simply put, CMYK is the color mode intended for printing with ink, such as business card designs. RGB is the color mode intended for screen displays. The more color added in CMYK mode, the darker the result. The more color added to RGB, the lighter the result.
What is CMYK color mixing?
Printing Cyan + Magenta creates Blue. Printing Cyan + Yellow creates Green. Printing Yellow + Magenta creates Red. Printing Cyan + Magenta + Yellow in equal quantities blocks all colors to create Black. As more ink is added, the color becomes darker.
What is an example of subtractive color?
The subtractive colors are cyan, yellow, magenta and black, also known as CMYK.
Additive Color Mixing - GSU
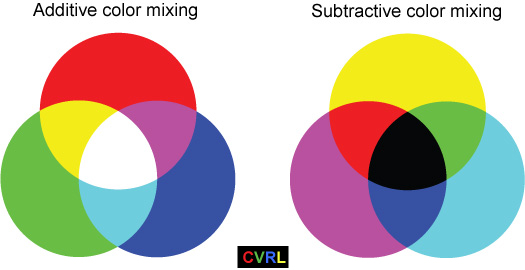
Additive color mixing is the kind of mixing you get if you overlap spotlights in a dark room, as illustrated at left. The commonly used additive primary colors are red, green and blue, and if you overlap all three in effectively equal mixture, you get white light as shown at the center. Additive color mixing is conceptually simpler than the subtractive color mixing you get with paints and ...
Additive and Subtractive Color Mixing - Hanover College
Background. There are two main types of color mixing: additive color mixing and subtractive color mixing. Additive color mixing is creating a new color by a process that adds one set of wavelengths to another set of wavelengths.
Additive Color: Theory & Definition - Video & Lesson Transcript - Study.com
Discover color additive theory, its properties, and origins. Explore why red, green, and blue are primary colors in this theory instead of red,...
What are additive colors?
Also known as RGB color, additive colors are created by mixing different amounts of light colors, primarily red, green, and blue (the primary colors of the visible light spectrum). Mixing different amounts of red, green, and blue produces three secondary colors: yellow, cyan, and magenta – the primary colors of the subtractive color mode.
What color is used in additive RGB?
TVs, computer monitors, and other electronics use additive color – every pixel starts as black, and take on colors that are expressed as percentage values of red, green, and blue ( hence “RGB”). So when you create a design on your computer, you’re using the additive RGB color mode.
How are subtractive colors created?
Subtractive Color (CMYK) Additive colors are created by adding colored light to black. On the other hand, subtractive colors are created by completely or partially absorbing (or subtracting) some light wavelengths and reflecting others. Subtractive colors begin as white. As you add filters to the white light, such as ink, ...
How do colors gain their appearance?
The colorful objects we see in everyday life also gain the appearance of color using a subtractive process: an object, such as a flower or a printed sheet of paper, uses colorants such as pigments, dyes, or inks to absorb portions of the white light that illuminates the object, while reflecting other portions that we then perceive as color.
What is part 2 of color theory?
In Part 2 of our ongoing blog series about color theory, we took a look at active and passive colors and how to incorporate them into your creative designs. Part 3 will examine color from a different perspective by exploring the differences between additive and subtractive color.
What are the two methods of producing color?
There are two methods of producing color: additive and subtractive. The additive color mode is primarily used when shades of light are used to create colors, while the subtractive mode is used when white light, such as sunlight, reflects off an object. Confused yet?
How many shades of color can a monitor display?
A good monitor can display “true” color, or about 16,000,000 shades and tints of every visible color, but the color output for printed materials is limited to a comparatively small portion of the visible light spectrum. When you print your design, the ink acts as a filter to subtract or absorb portions of white light, or allow that light to pass through and reflect off your paper in order to create perceptible colors.
Why is it important to differentiate color modes?
As a designer, it’s important to differentiate the color modes so you can optimize each stage of your design process. If you use the correct color mode in your design, you will also help get your message and tone across. In this lesson, we’ll define common color modes and help you understand when to use them in your designs. You’ll never have to fear these acronyms again.
What is the color mode of a lab?
The color mode consists of one channel for Lightness (L) and two channels for Color (A and B). The Lightness channel (L) ranges from 0 to 100 and the Green-Red Axis channel (A) and Blue-Yellow Axis channel (B) range from +127 to -128.
What is RGB color?
The RGB color mode consists of Red, Green and Blue hues that combine to create extensive variations of colors. This color mode exists exclusively in digital formats to include computer monitors, mobile devices and television screens. Even though RGB is present across most electronic devices, the color elements vary across systems and models. An image you see on your MacBook may display differently on your friend's Dell.
What is greyscale in print?
The Greyscale mode consists of different shades of grey within an image. This color mode may be used in both digital and print formats. In digital formats, every pixel within a greyscale image contains a value that ranges from 0 ( black) to 255 ( white ). In print formats, the greyscale values are measured by the percentage of black ink that ranges from 0% ( white) to 100% ( black ).
Why use LAB in color management?
Color management systems use LAB as a color reference to predictably transform a color from one color space to another color space. You can also use LAB to make the colors in your images look more vibrant and natural.
Why use LAB color?
LAB color is considered device-independent, which means that it’s easier for you to achieve exactly the same color across different types of media. If your organization wants you to design a branded t-shirt, coffee mug or banner, it would be a good idea to use LAB color as it will ensure that the colors look exactly the same.
Why is index color important?
Although its palette of colors is limited, index color can reduce file size yet maintain the visual quality needed for digital presentations, websites and mobile applications. Therefore, Index color mode is ideal for image optimization. As limited editing is available in this mode, you should convert temporarily to RGB mode for extensive editing.
Who is the father of additive color?
For his experimental work on the subject, James Clerk Maxwell is sometimes credited as being the father of additive color. He had the photographer Thomas Sutton photograph a tartan ribbon on black-and-white film three times, first with a red, then green, then blue color filter over the lens.
What is additive mixing?
Additive color or additive mixing is a property of a color model that predicts the appearance of colors made by coincident component lights, i.e.
What is subtractive color?
Instead, subtractive color is used to model the appearance of pigments or dyes, such as those in paints, inks . The combination of two of the common three additive primary colors in equal proportions produces an additive secondary color — cyan, magenta or yellow.
How does additive mixing work?
Additive color or additive mixing is a property of a color model that predicts the appearance of colors made by coincident component lights, i.e. the perceived color can be predicted by summing the numeric representations of the component colors. Modern formulations of Grassmann's laws describe the additivity in the color perception of light mixtures in terms of algebraic equations. Additive color predicts perception and not any sort of change in the photons of light themselves. These predictions are only applicable in the limited scope of color matching experiments where viewers match small patches of uniform color isolated against a grey or black background.
What is the gamut of color?
In chromaticity space, a gamut is a plane convex polygon with corners at the primaries. For three primaries, it is a triangle .
Who created the first color photograph?
The first permanent color photograph, taken by Thomas Sutton, under the direction of James Clerk Maxwell in 1861. Systems of additive color are motivated by the Young–Helmholtz theory of trichromatic color vision, which was articulated around 1850 by Hermann von Helmholtz, based on earlier work by Thomas Young.
A Bit of Background
Additive vs. Subtractive Color
- There are two methods of producing color: additive and subtractive. The additive color mode is primarily used when shades of light are used to create colors, while the subtractive mode is used when white light, such as sunlight, reflects off an object. Confused yet? Let’s jump in.
Additive and Subtractive Colors in The Printing Process
- The differences between additive and subtractive color may seem subtle and unimportant for your everyday life – after all, color is color, right? Most of the time this is correct, but they are an important consideration when you’re designing for print. When you design something on your computer, your screen will display your design in an additive RGB color mode, but offset printing …
Adding It All Up
- Understanding additive and subtractive color may not help you decide which colors to use in your next creative project, but knowing how these two color modes differ is critical when you’re designing for print.
What Is Subtractive Color (CMY and Cmyk)?
- This color model is also referred to as the CMY and CMYK mode and involves creating new color by removing wavelengths — thus subtractive. When paints, dyes or pigments mix, each colored material absorbs all the wavelengths it did previously. The result is only the wavelengths that both mixed paintsreflect. Certain wavelengths are subtracted or dele...
How Is Subtractive Color used?
- The objects we see in everyday life gain the appearance of color using a subtractive process. However, industries mainly use the subtractive color model in inkjet color printing to produce photos, magazines and any printed material. Subtractive color mixing also occurs when mixing paints, dyes, pigments and other colored material.
How to Measure Additive and Subtractive Color
- Instead of using three filters to measure the RGB values of the color, spectrophotometers have upwards of 31 filters so they can measure the full-color spectrum — whether it’s an additive or subtractive color. Spectrophotometers provide colors with three-dimensional numeric values that can precisely define an object’s color.