What is the pectineal line of the hip bone?
Right hip bone. External surface., with pectineal line corresponding to the "Pectineus" area demarcated in red at right. The pectineal line of the pubis (also pecten pubis) is a ridge on the superior ramus of the pubic bone. It forms part of the pelvic brim .
What is another name for the coxal bone?
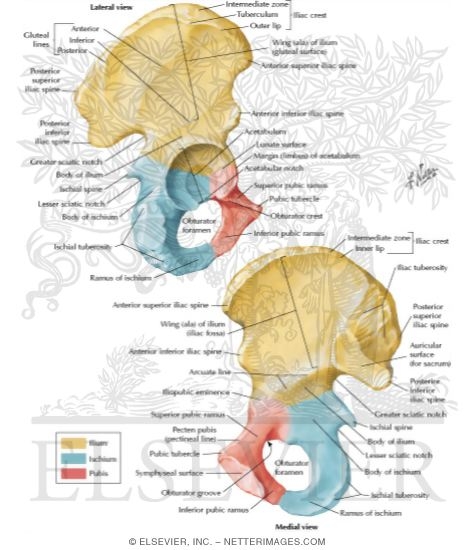
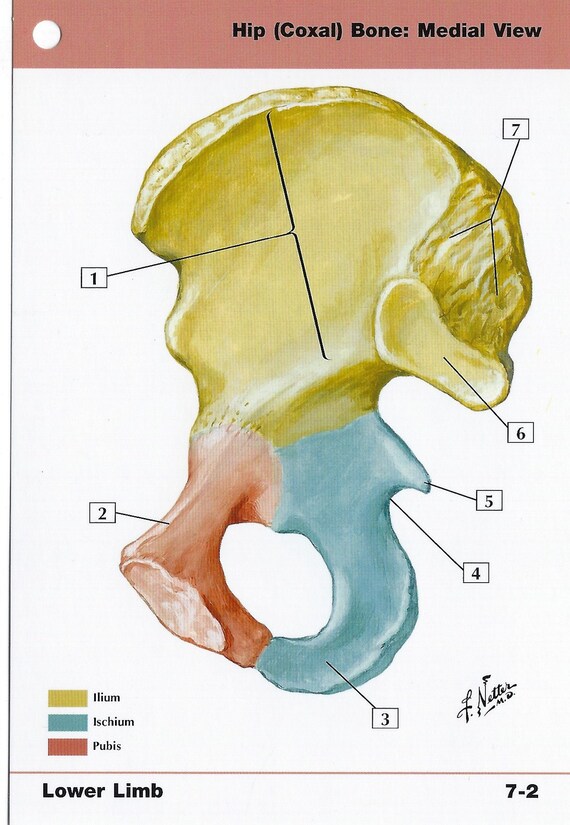
Synonyms: Coxal bone, Pelvic bone , show more... The hip bone (os coxae) is an irregularly shaped, bilateral bone of the bony pelvis which is also known as the innominate bone, pelvic bone or coxal bone. In reality, it is a compound structure which consists of three smaller bones: the ilium, ischium and pubis.
What is the pectineal line of the pubis?
The pectineal line of the pubis (also pecten pubis) is a ridge on the superior ramus of the pubic bone. It forms part of the pelvic brim .
What bone does the pectineus originate from?
The pectineus originates from the pectineal line of the pubic bone, which is also known as the pectin pubis. The pectineus muscle continues downward and in a posterolateral direction (behind and to the side) and inserts into the pectineal line of the femur (thigh bone).
Which coxal bone contains the anterior and posterior gluteal lines?
The lateral surface of the ilium has 3 rough curved lines: the posterior, anterior, and inferior gluteal lines. Medially, the ilium has an iliac fossa. Posteriorly, the medial aspect of the ilium has an auricular surface. The ischium is the inferior aspect of the pelvis.
What bone of the pelvis is the location of the Pectineal line?
The pectineal line (pecten pubis) of the pubis is a ridge on the superior ramus of the pubic bone, it passes to the pubic tubercle as a continuation of the arcuate line. The pecten pubis forms part of the pelvic brim. Lying across it are fibers of the pectineal ligament and the proximal origin of the pectineus muscle.
Which of the following bones make up the pelvic bone?
In discussing the pelvis, a distinction can be made between the "pelvic spine" and the "pelvic girdle." The pelvic girdle, also known as the os coxae, Latin for “bone of the hip,” consists of the fused bones identified individually as the ilium, ischium, and pubis.
What are the lines on the pelvis called?
The pelvic brim is defined by a line formed by the upper margin of the pubic symphysis anteriorly, and the pectineal line of the pubis, the arcuate line of the ilium, and the sacral promontory (the anterior margin of the superior sacrum) posteriorly.
What attaches to the pectineal line?
On the posterior surface of the femur, the intermediate ridge or pectineal line is continued to the base of the lesser trochanter and gives attachment to the pectineus muscle.
What does pectineal mean?
Medical Definition of pectineal : of, relating to, or located near the pubic bone.
What are the 4 bones of the pelvis?
Bones of the PelvisThere are three bones of the pelvis: the hip bone, sacrum and coccyx. ... The hip bone has three parts: the ilium, pubis and ischium. ... The sacrum is located inferiorly to the spinal vertebrae, and posteriorly within the pelvis.More items...
Which bone is not part of the pelvic girdle?
The correct answer is Incus.
Which bones are part of the pelvis quizlet?
Terms in this set (47)Two hip bones, sacrum, and coccyx. Which bones form the pelvis?Pelvis. ... Os coxae or innominate. ... ilium, ishium, and pubis. ... iliopubic and ilioishial colum. ... acetabulum. ... ASIS and iliac crest. ... 3; anterior, posterior, and superior.More items...
What is the Ilioischial line?
The ilioischial line demarcates the medial border of the posterior column. The posterior wall of the acetabulum is larger and projects more laterally than does the anterior wall.
Is Linea Terminalis same as Iliopectineal line?
f. The linea terminalis is the pronounced line separating the greater and lesser pelves, formed by the sacral promontory, the arcuate line, the pectineal line, and the pubic crest. g. The iliopectineal line is that part of the linea terminalis formed by the arcuate line and the pectineal line.
What is the hole in the hip bone called?
The big hole in the lower part of the hip bone is the obturator foramen. This is the body of the pubis, this is the superior ramus of the pubis, and this is the ischio-pubic ramus. This prominence is the pubic tubercle, to which the inguinal ligament is attached.
What is spiral line of femur?
The intertrochanteric line (or spiral line of the femur ) is a line located on the anterior side of the proximal end of the femur. Right hip-joint from the front.
Where is the linea aspera of the femur?
The linea aspera is the rough, longitudinal, irregular crest on the posterior surface of the shaft of the femur. It is formed by the joining of lateral and medial lips, which may be separated by up to 10 mm [1]. It is divided distally into medial and lateral supracondylar ridges.
Where is the inferior pubic ramus located?
pelvisThe inferior pubic ramus is a part of the pelvis and is thin and flat. It passes laterally and downward from the medial end of the superior ramus; it becomes narrower as it descends and joins with the inferior ramus of the ischium below the obturator foramen. Right hip bone.
Is pubic symphysis a bone?
The pubic symphysis is a joint sandwiched between your left pelvic bone and your right pelvic bone. It helps your pelvis absorb some of the weight from your upper body before it travels to your lower body.
Where is the coxal bone located?
The coxal bone is located between the lower abdomen and the upper part of the lower limbs.
What is the coxal bone?
The coxal bone It is a paired bone articulated posteriorly with the sacral bone of the vertebral column, and anteriorly with its contralateral counterpart through the symphysis pubis. This bone forms the pelvic girdle. It is the result of the union of three primitive bone pieces: the ilium, the ischium and the pubis; these converge in the acetabular fossa.
Where is the innominate bone?
The innominate bone is a deep bone that becomes more superficial at four points: on both sides of the iliac crest, on both sides of the anterior superior iliac spines, on the underside of the pubic spine, and on the back of the ischial tuberosity. .
What is the articular cavity called?
This articular cavity has two parts: a non-articular square, called the acetabular fossa; and an articular one that surrounds the crescent-shaped fossa, called the semilunar facet.
What are the characteristics of an innominate bone?
One of the characteristics of the innominate bone is its constitution as a true flat bone, with two sheets of compact bone covering the cancellous bone.
How many faces, edges, and angles are there in the innominate bone?
Two faces, four edges, and four angles are described in the innominate bone.
Which bone is articulated poteriorly with the acral bone of the vertebral column?
The coxal bone It i a paired bone articulated poteriorly with the acral bone of the vertebral column, and anteriorly with it contralateral counterpart through the ymphyi pubi. Thi bone form the pelvic
Which bone is the lateral aspect of the hip?
The lateral aspect of the hip bone houses the acetabulum, one of the most prominent landmarks of this bone. It bears a socket shaped articular surface that faces anteroinferiorly which articulates with the head of the femur forming the hip joint. The three components of the hip bone unit at the acetabulum, contributing to its formation.
Which bone is the largest?
The body of the ischium is the largest portion of the bone. It projects superiorly to join the ilium and the superior ramus of the pubis, and contributes to the acetabulum.
What are the components of the hip bone?
They completely fuse during puberty to form the complex and compact hip bone. The centre of this union is the acetabulum , a deep, cup-shaped socket on the lateral surface of the bone, that articulates with the femoral head at the hip joint. Anteroinferior to the acetabulum is the large obturator foramen. The right and left hip bones make up the pelvic girdle. The bony pelvis is completed posteriorly by the pelvic spine which is composed of the sacrum and coccyx. The bony pelvis connects the axial skeleton to the lower limbs, serving as a weightbearing structure. It also protects and supports the abdominopelvic viscera, provides attachment for several muscles and ligaments, and forms part of the skeletal framework of the birth canal.
What are the parts of the hip?
This bone is the smallest component of the hip bone. It is divided into three main parts: body, superior ramus, and inferior ramus. The body is located anteromedially and the two rami extend posterollatery from the body: the superior ramus extends superiorly to the acetabulum, while the inferior ramus continues inferiorly to join the ischial ramus. It should be noted that some sources consider the body of the pubis to be the superolateral part of the bone which contributes to the formation of the acetabulum, however this is not in accordance with the Terminologia Anatomica.
What is the hip bone?
The hip bone (os coxae) is an irregularly shaped, bilateral bone of the bony pelvis which is also known as the innominate bone, pelvic bone or coxal bone. In reality, it is a compound structure which consists of three smaller bones: the ilium, ischium and pubis. The ilium is the largest and most superior part of the bone, the ischium is located posteroinferiorly, and the pubis or pubic bone forms the anterior portion of the hip bone.
Where is the obturator canal located?
Located anteroinferior to the acetabulum is the obturator foramen, a large opening delimited by the pubis and ischium. Most of this foramen is covered by a flat connective tissue membrane called obturator membrane. A narrow obturator canal remains superiorly between the membrane and adjacent bone through which the obturator nerve, artery and vein pass through while travelling between the pelvic cavity and the medial compartment of the thigh.
What are the three bony surfaces of the Ilium?
The borders of the ilium bound its three bony surfaces: the gluteal, sacropelvic surfaces and iliac fossa.
Where does the pectineus receive its blood supply?
The pectineus receives its main blood supply from the medial circumflex femoral artery and contributions from the femoral and obturator arteries. 3 .
Where does the pectineus originate?
The pectineus originates from the pectineal line of the pubic bone, which is also known as the pectin pubis. The pectineus muscle continues downward and in a posterolateral direction (behind and to the side) and inserts into the pectineal line of the femur (thigh bone).
What is the function of the pectineus muscle?
The main functions of the pectineus muscle are flexion, adduction, and external rotation of the hip. The pectineus muscle both flexes and adducts the thigh at the hip joint when it contracts. Adduction is the movement of a limb or other part toward the midline of the body or toward another part. 4 . In the limbs, flexion decreases the angle ...
How does the pectineus muscle get injured?
The pectineus muscle can become injured by overstretching one or both legs too far out to the side or front of the body. Pectineus injuries can also be caused by rapid movements and the following: 2 6
What muscle is used to flex the thigh?
Treatment. The pectineus muscle, a flat, quadrangular muscle located in the middle of the thigh, helps to flex or move your leg towards your body. Running, skating, kicking a soccer ball, playing basketball, or exercising with fatigued muscles can strain or pull this muscle, resulting in a painful injury. If that happens, be patient ...
Which nerve innervates the pectineus?
Similar to the adductor magnus muscle, the pectineus frequently has dual innervation; the anterior (front) part of the muscle is innervated by the femoral nerve while the posterior (back) part is supplied by obturator nerve.
Which muscle is located on the medial side of the femur?
The pectineus muscle continues downward and in a posterolateral direction (behind and to the side) and inserts into the pectineal line of the femur (thigh bone). The pectineus muscle is a hip adductor, one of a group of five large muscles on the medial (middle) thigh that adduct the leg. The other hip adductors include the adductor longus, ...
Which part of the pubic bone is the wide, strong, medial and flat portion?
The body forms the wide, strong, medial and flat portion of the pubic bone which unites with the other pubic bone in the pubic symphysis. The fibrocartilaginous pad which lies between the symphysial surfaces of the coxal bones, that secures the pubic symphysis, is called the interpubic disc .
What is the name of the bone that is constricted in the center?
Hip bone . The hip bone ( os coxae, innominate bone, pelvic bone or coxal bone) is a large irregular bone, constricted in the center and expanded above and below. In some vertebrates (including humans before puberty) it is composed of three parts: the ilium, ischium, and the pubis .
What are the bones that make up the pelvis?
The two hip bones join at the pubic symphysis and together with the sacrum and coccyx (the pelvic part of the spine) comprise the skeletal component of the pelvis – the pelvic girdle which surrounds the pelvic cavity. They are connected to the sacrum, which is part of the axial skeleton, at the sacroiliac joint.
Where does the gluteus maximus come from?
The gluteus maximus muscle arises from the posterior gluteal line of the inner upper ilium, and the rough portion of bone including the iliac crest, the fascia covering the gluteus medius ( gluteal aponeurosis ), as well as the sacrum, coccyx, the erector spinae ( lumbodorsal fascia ), the sacrotuberous ligament.
Which pelvis is wider, the pubis or the ischium?
The ilium and ischium then become joined, and lastly the pubis and ischium, through the intervention of this Y-shaped portion. The male pelvis, formed by left and right hip bones, sacrum, and coccyx. The female pelvis is wider than the male pelvis to accommodate childbirth.
Which direction does the hip bone rotate?
In therapsids, the hip bone came to rotate counter-clockwise, relative to its position in reptiles, so that the ilium moved forward, and the pubis and ischium moved to the rear. The same pattern is seen in all modern mammals, and the thyroid fenestra and obturator foramen have merged to form a single space.
Where do hip bones join?
They join each other in a Y-shaped portion of cartilage in the acetabulum. By the end of puberty the three regions will have fused together, and by the age 25 they will have ossified . The two hip bones join each other at the pubic symphysis. Together with the sacrum and coccyx, the hip bones form the pelvis.
