
Potassium sparing diuretics list
- Amiloride hydrochloride (Midamar)
- Spironolactone (Aldactone)
- Triamterene (Dyrenium)
- Amiloride (Midamor)
- Eplerenone (Inspra)
- Spironolactone (Aldactone, Carospir)
- Triamterene (Dyrenium)
Which of the following is a potassium sparing diuretic?
Potassium-sparing diuretics. Potassium sparing diuretics examples. There are four potassium-sparing diuretics. They are: Amiloride; Triamterene; Eplerenone; Spironolactone
Do diuretics cause low potassium?
Potassium-sparing diuretics are commonly used to help reduce the amount of water in the body. Unlike some other diuretics, these medicines do not cause your body to lose potassium. Amiloride and spironolactone are also used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension).
Is amiloride a potassium sparing diuretic?
Amiloride Amiloride is a potassium-sparing diuretic used in the management of hypertension and congestive heart failure. Potassium-sparing diuretics are diuretic drugs that do not promote the secretion of potassium into the urine.
Is Triamterene a potassium sparing diuretic?
Potassium-sparing diuretics are diuretic drugs that do not promote the secretion of potassium into the urine. Triamterene (trade names Dyrenium, Maxzide, Dyazide) is a potassium-sparing diuretic used in combination with thiazide diuretics for the treatment of hypertension and edema.

Which diuretics are not potassium sparing?
A thiazide diuretic used to treat hypertension as well as edema due to congestive heart failure....Non Potassium Sparing Diuretics.DrugTargetTypeFurosemide6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase, decarboxylatingenzymeFurosemideCarbonic anhydrase 2targetFurosemideUDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1-1enzymeFurosemideThyroxine-binding globulincarrier51 more rows
Is furosemide potassium wasting or sparing?
Loop diuretics, such as furosemide, are widely used to reduce fluid overload in patients and are well known for their renal K-wasting effects that often produce hypokalemia (11, 12, 22).
Is Hydrochlorothiazide a potassium-sparing diuretics?
The combination potassium-sparing diuretics are: Aldactazide (spironolactone/hydrochlorothiazide)
Which diuretic is potassium sparing and does not cause hypokalemia?
Medications called potassium-sparing diuretics don't lower potassium levels. Examples include spironolactone (Aldactone, Carospir), eplerenone (Inspra) and triamterene (Dyrenium). Treatment of low potassium may include: Changing to a potassium-sparing diuretic.
Is spironolactone a potassium sparing?
Spironolactone is a potassium-sparing diuretic (water pill). It prevents your body from absorbing too much salt and keeps your potassium levels from getting too low. This medicine is also used to treat or prevent hypokalemia (low potassium levels in the blood).
Which diuretic is best for kidneys?
A loop diuretic is generally the diuretic of choice in patients with renal insufficiency. Although a thiazide-type diuretic will initiate diuresis in patients with mild renal insufficiency, the response in patients with a GFR of <50 ml/min/1.73 m2 is less than that seen with a loop diuretic.
Is losartan a potassium-sparing drug?
Taking a potassium-sparing diuretic at the same time as an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor or an angiotensin receptor antagonist medicine (eg, valsartan, losartan) can also cause very high blood potassium levels.
Which diuretic causes hyperkalemia?
Potassium-sparing diuretics such as spironolactone, amiloride, and triamterene all have the potential to cause hyperkalemia. This risk is increased when used in association with potassium supplements and salt substitutes, as previously noted.
Which diuretic is best for hypertension?
One of the most commonly prescribed thiazide-like diuretics is chlorthalidone. Studies show that it may be the best diuretic to control blood pressure and prevent death.
Is mannitol potassium sparing or wasting?
Conclusion: In patients receiving neurocritical care for cerebral edema, the adjunct of a potassium sparing diuretic (canrenone) to mannitol therapy reduces potassium urinary loss, prevents hypokalemia, and reduces the incidence of new cardiac arrhythmias.
What are the 3 types of diuretics?
There are three types of diuretics:Loop-acting diuretics, such as Bumex®, Demadex®, Edecrin® or Lasix®. ... Potassium-sparing diuretics, such as Aldactone®, Dyrenium® or Midamor®. ... Thiazide diuretics, such as Aquatensen®, Diucardin® or Trichlorex®.
Does furosemide cause potassium loss?
Diuretics. Diuretic therapy causes renal loss of potassium and is the most common cause of hypokalemia. It can occur with both thiazide-type diuretics and loop diuretics such as furosemide.
Does furosemide cause potassium loss?
Diuretics. Diuretic therapy causes renal loss of potassium and is the most common cause of hypokalemia. It can occur with both thiazide-type diuretics and loop diuretics such as furosemide.
How does furosemide affect potassium?
Furosemide is mainly used to treat hyperkalemia, which brings about its desired effect by removing the excess serum potassium through its action on loop of Henle. [23] This property of furosemide resulted in an increased urinary potassium levels in experimental rats.
Is furosemide sodium sparing?
Furosemide is a loop diuretic that inhibits the Na+/K+/2Cl- cotransporter in the ascending thick loop of Henle. It is often called a high-ceiling diuretic because it is more effective than other diuretics. Furosemide decreases the sodium, chloride, and potassium reabsorption from the tubule.
Does Lasix cause potassium wasting?
Thiazide diuretics, such as chlorothiazide (Diuril), chlorthalidone (Hygroton), and hydrochlorothiazide (Esidrix, HydroDiuril, Microzide) tend to deplete potassium levels. So do loop diuretics, such as bumetanide (Bumex) and furosemide (Lasix).
How do potassium-sparing diuretics work?
As more fluid is passed out by the kidneys, less fluid remains in the bloodstream. So any fluid which has built up in the tissues of the lungs or body is drawn back into the bloodstream to replace the fluid passed out by the kidneys. This eases symptoms such as fluid retention in the legs (oedema) and breathlessness caused by excess fluid on the lungs. As well as increasing the amount of water that you pass out from your kidneys, potassium-sparing diuretics also help your kidneys keep (retain) potassium in the body. They do this by blocking the channels that potassium would pass through.
How many potassium diuretics are there?
There are four potassium-sparing diuretics. They are:
What is thiazide used for?
Thiazide diuretics (for example, bendroflumethiazide).These are mainly used for treating high blood pressure (hypertension) and fluid on the legs (oedema). See the separate leaflet called Thiazide Diuretics for more information.
How do potassium diuretics help the kidneys?
As well as increasing the amount of water that you pass out from your kidneys , potassium-sparing diuretics also help your kidneys keep (retain) potassium in the body. They do this by blocking the channels that potassium would pass through.
What is the name of the medicine that increases the amount of fluid removed from the body when we pass urine?
In this series. In this series: Dietary Potassium. Diuretics are medicines which increase the amount of fluid removed from the body when we pass urine. Potassium-sparing diuretics are one type of diuretic. They are weak diuretics usually prescribed in combination with other types of diuretics. They are used to increase the amount ...
What is a diuretic pill?
A diuretic is a medicine which increases the amount of urine that you pass out from your kidneys. A diuretic causes an increase in urine (a diuresis). So, they are sometimes called 'water' tablets. There are three main types of diuretics: Loop diuretics (for example, furosemide).
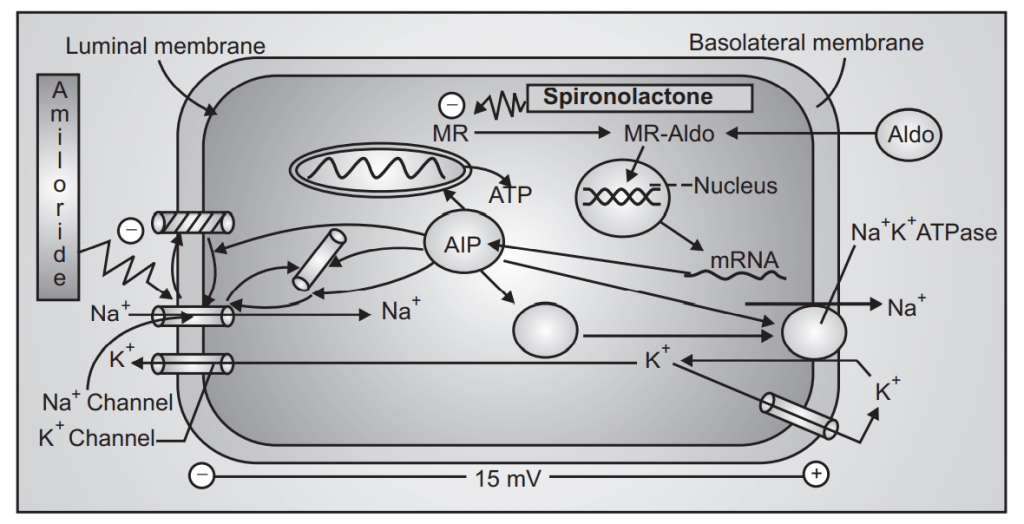
What is the name of the drug that blocks the action of aldosterone?
Eplerenone and spironolactone work in a slightly different way to amiloride and triamterene. These medicines block the action of a hormone called aldosterone and this causes the kidney to pass out more fluid and keep potassium. This is why they are sometimes referred to as aldosterone antagonists.
What are the different types of diuretics?
There are 5 main types of diuretics; carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, osmotic diuretics, thiazide and thiazide - like diuretics, loop diuretics ,, and last but not least, potassium sparing diuretics - which is the only class of diuretic that retains potassium, rather than wasting it.
How many types of diuretics are there?
There are 5 main types of diuretics; carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, osmotic diuretics, thiazide and thiazide-like diuretics, loop diuretics ,, and last but not least, potassium sparing diuretics - which is the only class of diuretic that retains potassium, rather than wasting it.
What pump pushes potassium into the tubule?
The principal cell has two pumps on the apical surface, an ATP-dependent potassium pump that pushes potassium into the tubule, and an epithelial sodium channel pump, called ENaC for short, that pulls sodium into the cell.
Which pump controls sodium and potassium levels in alpha intercalated cells?
Sodium and potassium levels in alpha intercalated cells are also controlled by Na/K ATPase pumps on the basolateral surface, which move two potassium ions into the cell and three sodium ions out of the cell.
What is the pump that pumps sodium into the cell?
The principal cell has two pumps on the apical surface, an ATP-dependent potassium pump that pushes potassium into the tubule, and an epithelial sodium channel pump, called ENaC for short, that pulls sodium into the cell.
Which hormone regulates the reabsorption of a molecule in the distal convoluted tubule?
Now the reabsorption and secretion of these molecules in the distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct are hormonally regulated by aldosterone, a mineralocorticoid hormone made in the adrenal cortex.
Does potassium sparing diuretic reduce potassium loss?
The addition of a potassium sparing diuretic increases the reabsorption of potas sium in the final stretches of the renal tubule, and therefore reduces potassium loss.
Which diuretics act on the distal parts of the nephron?
Amiloride, triamterene , and the spirolactones are potassium-sparing diuretics which act on the distal parts of the nephron, from the late distal tubule to the collecting duct.
Which hormone is a competitive inhibitor of aldosterone?
The spirolactones are competitive inhibitors of aldosterone, the mineralocorticoid hormone which promotes sodium reabsorption by increasing both the number of active sodium channels in the luminal membrane and the number of active Na-K pumps in the peritubular membrane.
Does amiloride block sodium?
Amiloride in micromolar concentrations reduces the sodium transport by blocking the luminal membrane sodium channel. Triamterene has a similar effect, although with a lower affinity; the available studies do not allow to determine if an inhibitory effect of triamterene on the Na-K-ATPase plays an additional role in its diuretic action. ...
What is potassium diuretic?
Potassium-sparing diuretics refers to drugs that cause diuresis without causing potassium loss in the urine and leading to hypokalemia. They are typically used as an adjunct in management of hypertension, cirrhosis, and congestive heart failure.
Where is sodium reabsorbed?
Mechanism of action. Normally, sodium is reabsorbed in the collecting tubules of a renal nephron. This occurs via epithelial sodium channels or ENaCs, located on the luminal surface of principal cells that line the collecting tubules.
Does aldosterone decrease potassium?
This results in a decrease in aldosterone release, which causes potassium-sparing-diuretic-like effects similar to those of the aldosterone antagonists, spironolactone, and eplerenone.
Does K+ cause hypokalemia?
This prevents excessive excretion of K+ in urine and decreased retention of water, preventing hypokalemia. Because these diuretics are weakly natriuretic, they do not cause clinically significant blood pressure changes and thus, are not used as primary therapy for hypertension.
Does sodium reabsorption increase water retention?
Increased sodium reabsorption also increases water retention . Potassium-sparing diuretics act to prevent sodium reabsorption in the collecting tubule by either binding ENaCs (amiloride, triamterene) or by inhibiting aldosterone receptors (spironolactone, eplerenone).
Types
- There are 5 main types of diuretics; carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, osmotic diuretics, thiazide and thiazide-like diuretics, loop diuretics,, and last but not least, potassium sparing diuretics - which is the only class of diuretic that retains potassium, rather than wasting it.
Function
- So the renal tubule plays a huge role in secretion and reabsorption of fluid and ions - such as sodium, potassium, and chloride - in order to maintain homeostasis - or the balance of fluid and ions in our body. The renal tubule has a few segments of its own: the proximal convoluted tubule, the U-shaped loop of Henle, with a thin descending, a thin ascending limb, and a thick ascendin…
Clinical significance
- Different kinds of diuretics act on different segments of the renal tubule. Aldosterone receptor antagonists like spironolactone and eplerenone are also useful in hyperaldosteronism. Hyperaldosteronism can be primary, meaning too much aldosterone is secreted by the adrenal cortex itself; like with Conn syndrome, or when a tumor secretes too much ACTH, which then tell…
Operation
- Now, the alpha intercalated cells mainly get rid of hydrogen ions from the blood, and they use two pumps on their apical surface for this. First, they have a H+/ATPase which uses ATP to pump hydrogen into the tubule. Second, they have a hydrogen potassium ATPase (H+K+ATPase) which uses ATP to push 1 hydrogen into the tubule in exchange for 1 potassium.
Pharmacology
- Now the reabsorption and secretion of these molecules in the distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct are hormonally regulated by aldosterone, a mineralocorticoid hormone made in the adrenal cortex.
Mechanism of action
- In the principal cells, aldosterone diffuses across the basolateral membrane and binds to a mineralocorticoid receptor in the cytoplasm. Then the aldosterone-receptor complex gets inside the nucleus of the cell where it triggers the increased synthesis of ENaCs, ATP-dependent potassium pumps, and the Na-K ATPase transporters. Together, they work to increase sodium r…
Mechanism
- This decreases the level of sodium inside the principle cells which decreases the action of the Na+/K+ ATPase on the basolateral membrane. However, at the end of the day, both categories have the same effect; first, they increase the excretion of sodium, and since water flows where the sodium goes, they also increase water loss through the urine. Next, they decrease the excretion …
Treatment
- Ok, so the major indication for diuretics is for the management of hypertension and edematous states. These medications increase sodium and water loss through the urine, which leads to decreased plasma volume and cardiac output, resulting in lower blood pressure.
Use
- This also treats edematous states like pulmonary edema or ascites where fluid builds up in the extracellular space. Potassium sparing diuretics are usually pretty weak, so they are used in combination with other diuretics, like loop or thiazides that would normally cause renal potassium wasting and hypokalemia. The addition of a potassium sparing diuretic increases the reabsorpti…
Causes
- Hyperaldosteronism can also be secondary, when high levels of aldosterone result from the activation of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. This is typically due to low plasma volume, because too much fluid escapes to the extracellular space, leading to edema.
Prevention
- Also, aldosterone receptor antagonists have been proven to reduce mortality after a myocardial infarction, presumably because they reduce the rate of remodelling in the heart.
Benefits
- Finally, spironolactone can also bind to androgen receptors and prevent testosterone from binding. This makes it useful for blunting the effects of testosterone in the body, like in polycystic ovarian syndrome, where there are many cysts on the ovaries that secrete excess testosterone. This can result in symptoms like infertility, hair loss, acne, and hirsutism, or unwanted facial hair …
Overview
Potassium-sparing diuretics refers to drugs that cause diuresis without causing potassium loss in the urine. They are typically used as an adjunct in management of hypertension, cirrhosis, and congestive heart failure. The steroidal aldosterone antagonists can also be used for treatment of primary hyperaldosteronism. Spironolactone, a steroidal aldosterone antagonist, is also used in managemen…
Types of Potassium-Sparing Diuretics
• Epithelial sodium channel blockers:
• Aldosterone antagonists, also known as mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists:
Mechanism of action
Normally, sodium is reabsorbed in the collecting tubules of a renal nephron. This occurs via epithelial sodium channels or ENaCs, located on the luminal surface of principal cells that line the collecting tubules. Positively-charged Na+ entering the cells during reabsorption leads to an electronegative luminal environment causing the secretion of potassium (K+) into the lumen/ urine in exchange. Sodium reabsorption also causes water retention.
Adverse effects
On their own this group of drugs may raise potassium levels beyond the normal range, termed hyperkalemia, which risks potentially fatal arrhythmias. Triamterene, specifically, is a potential nephrotoxin and up to half of the patients on it can have crystalluria or urinary casts. Spironolactone can cause gynecomastia, menstrual abnormalities, impotence, and decreased libido by binding non-selective estrogen and progesterone receptors.
Other diuretics
While not classically considered potassium-sparing diuretics, ACE inhibitors (ACEis) and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) are anti-hypertensive drugs with diuretic effects that decrease renal excretion of potassium. They work by inhibiting either the production (ACEis) or effects (ARBs) of angiotensin 2. This results in a decrease in aldosterone release, which causes potassium-sparing-diuretic-like effects similar to those of the aldosterone antagonists, spironola…
See also
• C03D Potassium-sparing agents
External links
• Potassium+Sparing+Diuretics at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)