Why do you think albinism is a harmful mutation?
There is a cell called the melanocyte that is responsible for giving skin, hair, and eyes pigmentation. In albinism, the melanocytes are present, but genetic mutations interfere with their pigment production or their ability to distribute it to keratinocytes, the major cell type comprising the epidermis, or outer layer of the skin.
Is albinism associated with any health issues?
People with albinism have skin that is very sensitive to light and sun exposure. Sunburn is one of the most serious complications associated with albinism because it can increase the risk of developing skin cancer and sun damage-related thickening of the skin. Some people with albinism may experience discrimination.
Why is albinism a recessive allele?
This type of inheritance is called “autosomal recessive” inheritance. Ocular albinism (OA1) is caused by a change in the GPR143 gene that plays a signaling role that is especially important to pigmentation in the eye. OA1 follows a simpler pattern of inheritance because the gene for OA1 is on the X chromosome.
Is albinism a disability or not?
Yes, persons with Albinism are usually as healthy as everyone else; with growth and development occurring as normal, but can be classified as people with disability because of the health challenges associated with the condition. Very notable among such challenges is visual impairment. Most persons with albinism are shortsighted.

Is albino A deficiency?
Albinism is a rare genetic disorder where you aren't born with the usual amount of melanin pigment. Melanin is a chemical in your body that determines the color of your skin, hair and eyes. Most people with albinism have very pale skin, hair and eyes. They are prone to sunburn and skin cancer.
What protein is affected by albinism?
Classification of albinismOCA SubtypesGene PositionAffected ProteinOCA 1 OCA 1A (tyrosinase-negative OCA) OCA 1B (yellow-mutant/Amish/ xanthous, temperature-sensitive) OCA 1A/1B heterozygote11q14-21TyrosinaseOCA 2 (tyrosinase-positive OCA, brown OCA)15q11-13P proteinOCA 39p23Tyrosinase-related proteinSep 30, 2020
Which amino acid causes albinism?
Albinism is caused by a disorder of melanin metabolism, and the defect can lie with either melanin synthesis or distribution. Melanin is synthesized in melanocytes from the amino acid tyrosine. This process takes place in special organelles called melanosomes.
What enzyme do human Albinos lack in their skin that prevents melanin from being produced?
tyrosinaseOculocutaneous albinism Most TYR mutations eliminate the activity of tyrosinase, preventing melanocytes from producing any melanin throughout life. These mutations cause a form of oculocutaneous albinism called type 1A (OCA1A).
What causes albinism enzyme?
Mutations in the tyrosinase gene cause oculocutaneous albinism Type 1 (OCA1), an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by reduced melanin pigment in the hair, skin and eyes.
What genes are affected by albinism?
Oculocutaneous albinism can result from mutations in several genes, including TYR, OCA2, TYRP1, and SLC45A2. Changes in the TYR gene cause type 1; mutations in the OCA2 gene are responsible for type 2; TYRP1 mutations cause type 3; and changes in the SLC45A2 gene result in type 4.
What is PAH enzyme?
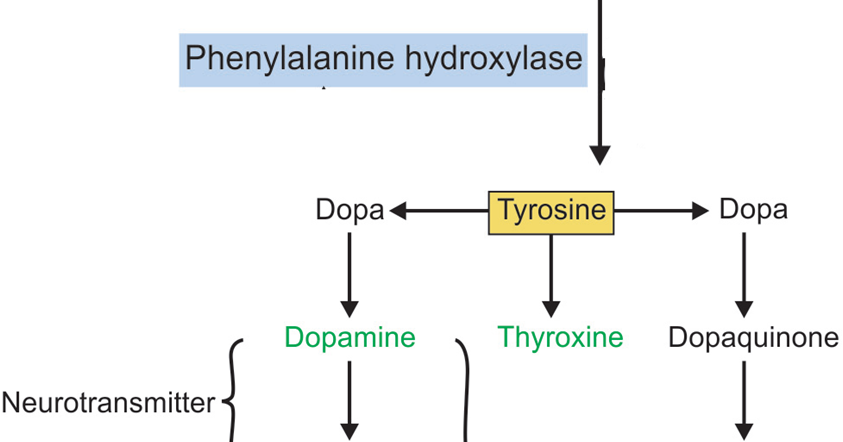
The PAH gene provides instructions for making an enzyme called phenylalanine hydroxylase. This enzyme is responsible for the first step in processing phenylalanine, which is a building block of proteins (an amino acid) obtained through the diet. Phenylalanine is found in all proteins and in some artificial sweeteners.
What chemicals cause albinism?
Albinism is caused by deficiency ofmelanin, the main pigment of the skin and eye (Table 103.1). Melanin is synthesized by melanocytes from tyrosine in a membrane-bound intracellular organelle, the melanosome.
What is a tyrosinase enzyme?
The tyrosinase enzyme (EC 1.14. 18.1) is an oxidoreductase inside the general enzyme classification and is involved in the oxidation and reduction process in the epidermis. These chemical reactions that the enzyme catalyzes are of principal importance in the melanogenesis process.
Why do Albinos lack melanin?
Albinism is caused by a mutation in one of these genes. Different types of albinism can occur, based mainly on which gene mutation caused the disorder. The mutation may result in no melanin at all or a significantly reduced amount of melanin.
What causes albinism tyrosinase?
Tyrosinase catalyzes the first two steps of melanin biosynthesis, i.e., the hydroxylation of tyrosine to 3, 4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (DOPA) and the subsequent oxidation of DOPA to dopaquinone [1]. Loss of tyrosinase (TYR) mRNA expression prevents melanin synthesis, thereby causing albinism [2].
What is a tyrosinase inhibitor?
Tyrosinases are responsible for melanin formation in all life domains. Tyrosinase inhibitors are used for the prevention of severe skin diseases, in skin-whitening creams and to avoid fruit browning, however continued use of many such inhibitors is considered unsafe.
What protein does the albinism gene encode?
OCA2 Melanosomal Transmembrane ProteinOCA2 (OCA2 Melanosomal Transmembrane Protein) is a Protein Coding gene. Diseases associated with OCA2 include Albinism, Oculocutaneous, Type Ii and Skin/Hair/Eye Pigmentation, Variation In, 1.
What is melanin protein?
Melanin is a complex polymer derived from the amino acid tyrosine. Melanin is responsible for determining skin and hair colour and is present in the skin to varying degrees, depending on how much a population has been exposed to the sun historically.
What is the function of the protein melanin?
Melanin is a pigment produced in the skin that helps protect cells from cancer-causing UV rays. Specialized cells called melanocytes produce the melanin, which is then transported to other epidermal cells (called keratinocytes) that make up the majority of the skin.
How does albinism affect the body?
Albinism affects the production of melanin, the pigment that colours skin, hair and eyes. It's a lifelong condition, but it does not get worse over time. People with albinism have a reduced amount of melanin, or no melanin at all. This can affect their colouring and their eyesight.
What is the gene that causes albinism?
Older sources often termed the gene that gives rise to albinism the albino gene, but this is misleading in two ways. First, the TYR gene does not code for the pigmentation defect we call albinism. It codes for the enzyme tyrosinase. Some mutant forms of TYR result in albinism; others do not. Second, several more genes have been found that can result in OCA. For example, OCA type 2 is related to a defect in a gene that codes for another protein that normally transports tyrosine from the blood into the cell (melanocyte) that manufactures melanin (Fig. 2.5 ). In cases where the defect is severe, tyrosine cannot get into the melanocyte from the blood, and melanin cannot be made, resulting in a physical appearance of the skin and eyes very similar to classical type 1 albinism that is related to a TYR mutation ( Table 2.2 ). The critical distinction between OCA types 1 and 2 is that there is normal tyrosinase activity in type 2, so that OCA2 is now termed tyrosinase-positive oculocutaneous albinism. It is a kind of albinism that is not caused by a mutation in the TYR gene. The exact nature of the chemical defect in OCA2 is only vaguely understood, and the gene itself has been named OCA2, which is also the name of the clinical disorder, not the protein involved. This can be confusing. Because melanin is manufactured via a long chain of chemical steps mediated by different proteins or enzymes, there are several kinds of genetic mutations that can stop the process short of its goal. When it stops, the result is called albinism. Why it stops needs to be investigated in greater depth.
What is albinism in the eye?
This chapter discusses albinism, refers to a group of inherited disorders of the pigment system in which there is a reduction or an absence of melanin formation. The abnormality in the formation in melanin can involve the melanocytes in the skin, in the hair follicles, and in the eyes, resulting in oculocutaneous albinism (OCA). The abnormality can be localized to the melanocyte in the eyes resulting in ocular albinism (OA). There are several types of OCA and OA, each presumed to represent a different mutation involving the melanin synthesis pathway. The clinical features and consequences of these mutations appear to be the result of the reduction or absence of melanin. Because of its visibility, the history of albinism is primarily that of OCA. Nystagmus has been considered a requirement for diagnosis of OCA and OA but rare individuals have been reported without nystagmus. The most constant and debilitating symptom of albinism is the reduction in visual acuity. The clinical history is often similar for many types of OCA and OA, and the diagnosis of a specific type is based on the physical examination and the laboratory studies.
How does TYR affect albinism?
Functions of a gene are best discerned in real people living ordinary lives, not just from a chemical path diagram. The TYR mutations that generate phenotypic albinism have a number of unexpected effects. For example, in people with normal pigmentation, fibers from the optic nerve of one eye divide into two bundles at the optic chiasm and travel to the left and right hemispheres, so that an image on the left half of the retina of the right eye projects to the visual cortex of the left hemisphere, while fibers from the right half of the retina of the right eye project to the right hemisphere. Roughly 50% of the optic nerve fibers from one eye cross to the opposite hemisphere. In albinism, however, the fraction of axons that project to the same side is greatly reduced and disorganized as well ( Creel, 2015; Creel, Summers, & King, 1990 ), which can change phenotypes such as stereoscopic depth perception and visual acuity. Thus, albinism reveals the important role of pigmentation in the retina for the organization of the visual system of the brain. Furthermore, myopia or nearsightedness is more common in albinism. Risk of skin cancers (melanoma) is also elevated. Those phenotypic changes effected by a TYR mutation reveal pleiotropic gene action; defects in a single kind of gene have multiple phenotypic effects. The phenotype in albinism even extends into the realm of social experience of the affected person, because in many countries, someone with albinism is subjected to not only impolite stares but also cruel discrimination and even murder ( "Tanzania's albino community: 'Killed like animals", 2014; Bever, 2015 ).
What is the vision of albinism?
A few patients with albinism who have vision 20/50 or better have some rudimentary foveal development, and some thinning of the retina in the foveal area has been demonstrated with optical coherence tomography ( Summers, 2009 ). Careful inspection can show granular melanin pigment in the macula in a few patients with albinism and occasionally finely granular pigment beyond the macula ( Summers, 2009 ). The presence of melanin pigment in the macula correlates with better visual acuity ( Summers, 2009 ). Recognition of visual acuity among persons with albinism varies from 20/20 to 20/400 but is commonly close to 20/80 ( Gronskov et al., 2007; Summers, 2009 ).
Why are melanocytes important?
The pigment that melanocytes contain and transfer to other cells is suspected to play important roles in the tissues in which they are found, mostly because of the consequences of their absence, such as occurs in albinism, and of the alteration of neuromelanin found in Parkinson's disease [3 ].
Is albinism a symptom of OCA?
The most constant and debilitating symptom of albinism is the reduction in visual acuity.
Is albinism a disorder?
Disorders in which albinism is part of a larger syndrome include Hermansky–Pudlak syndrome (HPS), Chediak–Higashi syndrome, Griscelli syndrome, and Waardenburg syndrome type 2 (WS2) ( Gronskov et al., 2007; Summers, 2009 ). All, except WS2, are inherited as autosomal recessive traits and can be distinguished on the basis of clinical and biochemical criteria ( Gronskov et al., 2007 ). Also, an association of hypopigmentation in Prader–Willi syndrome and Angelman disease with a deletion on 15q11 has been found ( Gronskov et al., 2007 ).
What is the main feature of albinism?
Vision impairment is a key feature of all types of albinism. Eye problems and issues may include:
How is albinism inherited?
The most common form is type 1, inherited by a gene mutation on the X chromosome. X-linked ocular albinism can be passed on by a mother who carries one mutated X gene to her son (X-linked recessive inheritance). Ocular albinism occurs almost exclusively in males and is much less common than OCA.
What are the symptoms of albinism?
Contact your doctor if your child with albinism experiences frequent nosebleeds, easy bruising or chronic infections. These signs and symptoms may indicate the presence of Hermansky-Pudlak syndrome or Chediak-Higashi syndrome, which are rare but serious disorders that include albinism.
How are albinisms classified?
Types of albinism are classified based on how they're inherited and on the gene that is affected.
What color is albinism?
The most recognizable form of albinism results in white hair and very light-colored skin compared with siblings. Skin coloring (pigmentation) and hair color can range from white to brown, and may be nearly the same as that of parents or siblings without albinism.
Why do people with albinism use the term "Albinism"?
Using the term "person with albinism" is preferred to avoid the stigma of other terms.
How do you know if you have albinism?
Signs of albinism are usually apparent in a person's skin, hair and eye color, but sometimes differences are slight. People with albinism are also sensitive to the effects of the sun, so they're at increased risk of developing skin cancer.
What are the symptoms of albinism?
Other symptoms can include light skin or changes in skin color; very white to brown hair; very light blue to brown eye color that may appear red in some light and may change with age; sensitivity to sun exposure; and increased risk of developing skin cancer. [1] [2] Albinism is caused by mutations in one of several genes, ...
What is the goal of treatment for albinism?
The goal of treatment is to address the symptoms present in each individual. People with albinism should protect their skin and eyes from the sun. This can be done by: [2] [3]
What is the name of the disorder that causes the color of the skin, hair and eyes?
Listen. Albinism is a group of inherited disorders that results in little or no production of the pigment melanin, which determines the color of the skin, hair and eyes. Melanin also plays a role in the development of certain optical nerves, so all forms of albinism cause problems with the development and function of the eyes.
Do albinism patients need corrective lenses?
Individuals with vision problems may need corrective lenses. They should also have regular follow-up exams with an ophthalmologist. In rare cases, surgery may be needed. Individuals with albinism should also have regular skin assessments to screen for skin cancer or lesions that can lead to cancer.
Is albinism curable?
Most people with albinism live a normal life span and have the same types of medical problems as the rest of the population. [2] [3] [5] Although the risk to develop skin cancer is increased, with careful surveillance and prompt treatment, this is usually curable. [5]
What is the name of the condition that causes albinism?
Chediak-Higashi syndrome. Chediak-Higashi syndrome is another rare form of albinism that’s the result of a defect in the LYST gene. It produces symptoms similar to OCA, but may not affect all areas of the skin. Hair is usually brown or blond with a silvery sheen. The skin is usually creamy white to grayish.
What is the cause of albinism?
The cause of albinism is a defect in one of several genes that produce or distribute melanin, the pigment that gives skin, eyes, and hair their coloring. The defect may result in the absence of melanin production or a reduced amount of melanin production.
What causes albinism in children?
A defect in one of several genes that produce or distribute melanin causes albinism . The defect may result in the absence of melanin production, or a reduced amount of melanin production. The defective gene passes down from both parents to the child and leads to albinism.
What is the name of the condition where the X chromosome is mutated?
Ocular albinism. Ocular albinism is the result of a gene mutation on the X chromosome and occurs almost exclusively in males. This type of albinism only affects the eyes. People with this type have normal hair, skin, and eye coloring, but have no coloring in the retina (the back of the eye).
What is the name of the disease that affects the eyes?
Other types of albinism, including one that only affects the eyes, mostly occur when a birthing parent passes the gene for albinism on to a child assigned male at birth.
What is it called when you have no color?
What is albinism ? Albinism is a rare group of genetic disorders that cause the skin, hair, or eyes to have little or no color. Albinism is also associated with vision problems.
Why do people with albinism have to limit their outdoor activities?
People with albinism may have to limit their outdoor activities because their skin and eyes are sensitive to the sun. UV rays from the sun can cause skin cancer and vision loss in some people with albinism. Last medically reviewed on March 29, 2018.
What was the first genetic disorder in humans shown to be caused by a specific enzyme deficiency?
Phenylketonuria - first genetic disorder in humans shown to be caused by a specific enzyme deficiency (1953)
What is the result of phenylalanine?
Results in buildup of phenylalanine, which is then converted to phenylpyruvic acid, which is then excreted in the urine
Why do people with PKU have blue eyes?
People with PKU tend to have blond hair and blue eyes b/c of this deficiency in melanin
What is albinism in biology?
Albinism is an autosomal recessive disorder. In most cases, it is seen that a major mutation in the human TRP-1 gene leads to malfunctioning of the Melanocyte Tyrosinase enzymes. This, in turn, impacts the process of melanin formation.
What is X-linked albinism?
X-linked ocular albinism: As the name implies, the disease is caused by genetic mutation on the X-chromosome and is more common in males. The patients may experience difficulties in vision. However, no visible changes are noticed in the skin and hair.
What are the symptoms of albinism?
Albinism is easily identifiable through a few symptoms. The most common ones are listed below-
What are the different types of Albinism?
According to the genes involved, Albinism is classified into the following categories-
Why is albinism irreversible?
Albinism occurs as a result of a particular genetic mutation , which is irreversible. The only thing can be done is to prevent sun damage to the skin and keep a check on the affected individual’s eyesight. Wearing a sunblock and protecting your skin and eyes from harsh sunlight is very important.
What is the name of the condition where the lyst gene is mutated?
Chediak-Higashi Syndrome: This is another category of rare Albinism that is caused by a mutation in the LYST gene. Here also, people have symptoms similar to Oculocutaneous albinism. Their hair is typically brownish and their skin is usually creamy white to greyish.
What is the rarest form of albinism?
Type 3: This category of albinism occurs due to the mutation of the genes located on chromosome 9. This is the rarest form of Albinism. The affected people have reddish brown hair and skin, and hazel or blue eyes. It is very common in Black South Africans. Type 4: It is caused by genetic mutation on chromosome 5.