What are the most abundant gases in the atmosphere?
The most abundant gases in the atmosphere depend on temperature, altitude and water, but they are usually nitrogen, oxygen, argon, and carbon dioxide.
What is the percent volume of gases in the atmosphere?
Abundance of Gases in the Atmosphere Gas Formula Percent Volume Nitrogen N 2 78.08% Oxygen O 2 20.95% Water* H 2 O 0% to 4% Argon Ar 0.93% 7 more rows ...
Is water vapor the 4th most abundant gas in the atmosphere?
Usually, the 4 most abundant gases are: However, water vapor can also be one of the most abundant gases! The maximum amount of water vapor air can hold is 4%, so water vapor could be number 3 or 4 on this list. On average, the amount of water vapor is 0.25% of the atmosphere, by mass (4th most abundant gas).
Why is nitrogen more abundant in the atmosphere than oxygen?
Based on the relative volumes of the gases in Earth’s atmosphere, nitrogen is actually more than 3 times more than oxygen. Because the troposphere is the lowest atmosphere layer, it contains 75 percent of atmosphere’s mass.

Which gas is high in atmosphere?
NitrogenThe most abundant naturally occurring gas is Nitrogen (N2), which makes up about 78% of air. Oxygen (O2) is the second most abundant gas at about 21%. The inert gas Argon (Ar) is the third most abundant gas at . 93%.
Which gas is less in atmosphere?
By mole fraction (i.e., by number of molecules), dry air contains 78.08% nitrogen, 20.95% oxygen, 0.93% argon, 0.04% carbon dioxide, and small amounts of other gases. Air also contains a variable amount of water vapor, on average around 1% at sea level, and 0.4% over the entire atmosphere.
Why nitrogen is more than oxygen in atmosphere?
Oxygen is a major component of the solid earth, along with Si and elements such as Mg, Ca and Na. Nitrogen is not stable as a part of a crystal lattice, so it is not incorporated into the solid Earth. This is one reason why nitrogen is so enriched in the atmosphere relative to oxygen.
Why is the sky blue?
The sky is blue due to a phenomenon called Raleigh scattering. This scattering refers to the scattering of electromagnetic radiation (of which light is a form) by particles of a much smaller wavelength.
Which is the least component present in air?
air consist of various gases. the least component in the air is helium which is listed in other air components (1%) .
Which gas gases has have the highest amount present in the atmosphere which has the least?
By far, the most abundant gas in the Earth's atmosphere is nitrogen, which accounts for about 78% of the mass of dry air. Oxygen is the next most abundant gas, present at levels of 20 to 21%.
Which gas has maximum percentage by volume in dry atmosphere?
NitrogenNitrogen is far and away the most common gas in our atmosphere. It makes up 78.1 percent of clean (as IF), dry air by volume (since nitrogen is a fairly light molecule, it makes up about 75.5 percent of the mass of the atmosphere).
What are the gases in the atmosphere?
Key Takeaways: Gases in Earth's Atmosphere 1 The most abundant gas in the Earth's atmosphere is nitrogen. The second most abundant gas is oxygen. Both of these gases occur as diatomic molecules. 2 The amount of water vapor is highly variable. In hot, humid locations, it is the third most abundant gas. This makes it the most common greenhouse gas. 3 In dry air, the third most abundant gas is argon, a monatomic noble gas. 4 The abundance of carbon dioxide is variable. While it is an important greenhouse gas, it is only present an average of 0.04 percent, by mass.
What is the most abundant gas in the atmosphere?
By far, the most abundant gas in the Earth's atmosphere is nitrogen, which accounts for about 78% of the mass of dry air. Oxygen is the next most abundant gas, present at levels of 20 to 21%. Although humid air seems like it contains a lot of water, the maximum amount of water vapor that air can hold is only about 4%.
Which gas is less abundant than helium?
Some references include other gases on this list, such as krypton (less abundant than helium, but more than hydrogen), xenon (less abundant than hydrogen), nitrogen dioxide (less abundant than ozone), and iodine (less abundant than ozone). Gas. Formula. Percent Volume. Nitrogen.
Why is water vapor important to weather?
The amount of water vapor in the air is particularly relevant to weather forecasting. The gas composition helps us understand the effects of natural and man-made chemicals released into the atmosphere.
Which gas is the second most abundant?
The second most abundant gas is oxygen. Both of these gases occur as diatomic molecules. The amount of water vapor is highly variable. In hot, humid locations, it is the third most abundant gas. This makes it the most common greenhouse gas. In dry air, the third most abundant gas is argon, a monatomic noble gas.
Where is ozone found?
Ozone is concentrated around cities and in the Earth's stratosphere. In addition to the elements in the table and krypton, xenon, nitrogen dioxide, and iodine (all mentioned earlier), there are trace amounts of ammonia, carbon monoxide, and several other gases.
Is water vapor stable?
While the percentage of nitrogen and oxygen are fairly stable, the amount of greenhouse gases changes and depends on location. Water vapor is extremely variable. In arid or extremely cold regions, water vapor may be nearly absent. In warm, tropical regions, water vapor accounts for a significant portion of atmospheric gases.
What are the gases in the atmosphere?
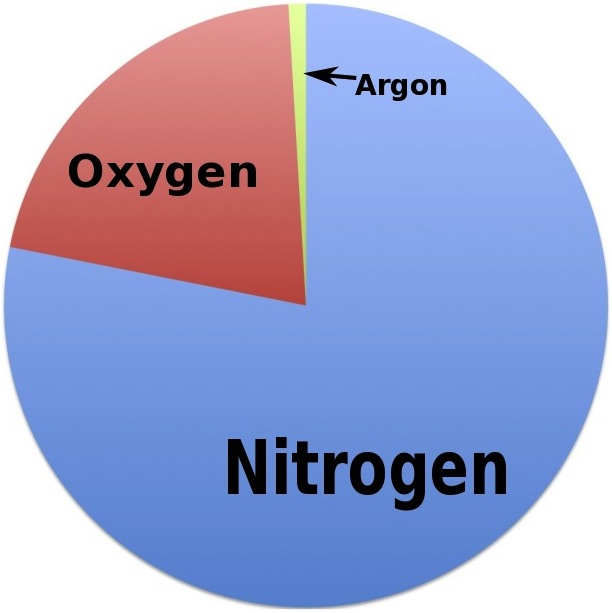
caption]There are different gases in the atmosphere. There’s nitrogen (the most abundant of them all), oxygen, and argon. There are of course a lot more but they’re no more than 1% of the entire atmosphere.
Where are heavier gases found?
Since the force of gravity pulls down on the masses of these gases, the heavier gases are typically found near the surface of the Earth while the lightest ones (e.g. hydrogen and helium) are found in higher altitudes. All these properties are just generalizations though.
Which layer of the atmosphere is where meteors ignite?
The Mesosphere is where meteors mostly ignite. The Thermosphere is where the International Space Station orbits. Since the Karman line (which serves as the boundary between the Earth’s immediate atmosphere and outer space) is found in the lower region of the Thermosphere, much of this layer of gases in the atmosphere is considered outer space.
Which layer of the atmosphere is the lightest?
Finally, the exosphere, being the outermost layer, is where you can find the lightest gases: hydrogen and helium. Many properties of the gases in the atmosphere are dependent on the altitude at which they are found. For instance, average density of these gases generally decrease as one rises to higher altitudes.
Is carbon dioxide harmful to the environment?
Among the minority are the greenhouse gases, carbon dioxide being the most prominent of them all. These gases are presently cast as harmful to the planet, being the primary cause of global warming. Of course, they’re only harmful because they’ve exceeded their ideal levels.
How much more than 3 times more than oxygen is in the atmosphere?
Based on the relative volumes of the gases in Earth’s atmosphere, nitrogen is actually more than 3 times more than oxygen. Because the troposphere is the lowest atmosphere layer, it contains 75 percent of the atmosphere’s mass. From largest to smallest, Earth’s atmosphere composition contains nitrogen , oxygen, argon, CO 2 and trace gases.
What is the most important gas in the Earth's life?
In this video, it displays a year in the life of Earth’s carbon dioxide. As you can see, carbon dioxide is the most important gas affected by human activity. In the northern hemisphere, we see the highest concentrations of carbon dioxide from major emission sources.
Why is there no argon cycle?
As an inert gas, argon doesn’t bond or do much in the atmosphere. This is why there’s no argon cycle. But we have nitrogen and carbon because of their ability to bond with other elements. When potassium radioactively decays, argon is one of the possible product. And the lithosphere has lots of potassium.
Why is oxygen important to life?
Oxygen is essential to human life as our lungs respire oxygen and uses it in metabolism. While nitrogen is an extremely stable gas, it’s difficult to break up and use for chemical processes. But oxygen will readily take part in chemical reactions because it’s an electron thief.
What is the composition of the atmosphere?
Earth’s Atmosphere Composition: Nitrogen, Oxygen, Argon and CO2. Atmosphere | Outside Earth. Updated on February 12, 2021 Atmosphere, Outside Earth. Some people are surprised to learn that oxygen isn’t the most abundant gas in Earth’s atmosphere composition. Based on the relative volumes of the gases in Earth’s atmosphere, ...
What are the trace gases in the atmosphere?
. The remaining portion of the atmosphere belongs to trace gases. For example, neon, helium, methane, methane, and krypton are some of the major trace gases that make up a small part of the atmosphere.
Why is water vapor removed from the 100% total?
Water vapor has been removed from the 100% total because of its region variability. But it can make up large portions of the atmosphere. For example, it can make up 5% by volume in hot regions but much less in colder regions.
What is the composition of the atmosphere?
Composition of Earth's atmosphere by volume, excluding water vapor. Lower pie represents trace gases that together compose about 0.043391% of the atmosphere (0.04402961% at April 2019 concentration ). Numbers are mainly from 2000, with CO. 2 and methane from 2019, and do not represent any single source.
What is the atmosphere of Earth?
The atmosphere of Earth, commonly known as air, is the layer of gases retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing for liquid water to exist on the Earth's surface, absorbing ultraviolet solar radiation, ...
How did plate tectonics influence the long-term evolution of the atmosphere?
The constant re-arrangement of continents by plate tectonics influences the long-term evolution of the atmosphere by transferring carbon dioxide to and from large continental carbonate stores. Free oxygen did not exist in the atmosphere until about 2.4 billion years ago during the Great Oxygenation Event and its appearance is indicated by the end of the banded iron formations .
What is the study of the atmosphere called?
The study of Earth's atmosphere and its processes is called atmospheric science (aerology), and includes multiple subfields, such as climatology and atmospheric physics. Early pioneers in the field include Léon Teisserenc de Bort and Richard Assmann. The study of historic atmosphere is called paleoclimatology .
How high is the equator?
It extends from Earth's surface to an average height of about 12 km (7.5 mi; 39,000 ft), although this altitude varies from about 9 km (5.6 mi; 30,000 ft) at the geographic poles to 17 km (11 mi; 56,000 ft) at the Equator, with some variation due to weather.
How much water vapor is in the atmosphere?
The concentration of water vapor (a greenhouse gas) varies significantly from around 10 ppm by volume in the coldest portions of the atmosphere to as much as 5% by volume in hot, humid air masses, and concentrations of other atmospheric gases are typically quoted in terms of dry air (without water vapor).
How much does the atmosphere weigh?
The atmosphere has a mass of about 5.15 × 10 18 kg, three quarters of which is within about 11 km (6.8 mi; 36,000 ft) of the surface. The atmosphere becomes thinner with increasing altitude, with no definite boundary between the atmosphere and outer space.
