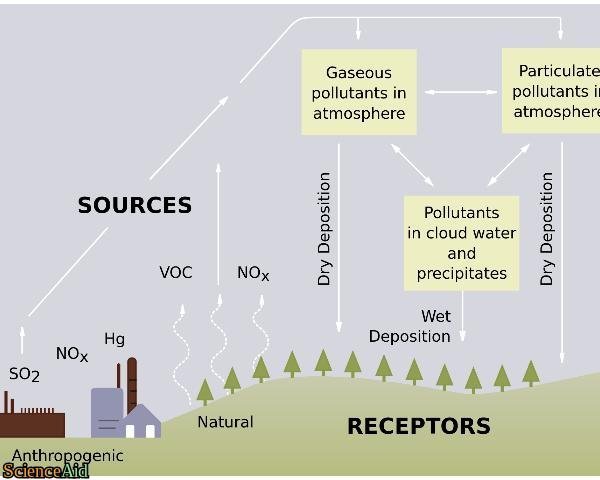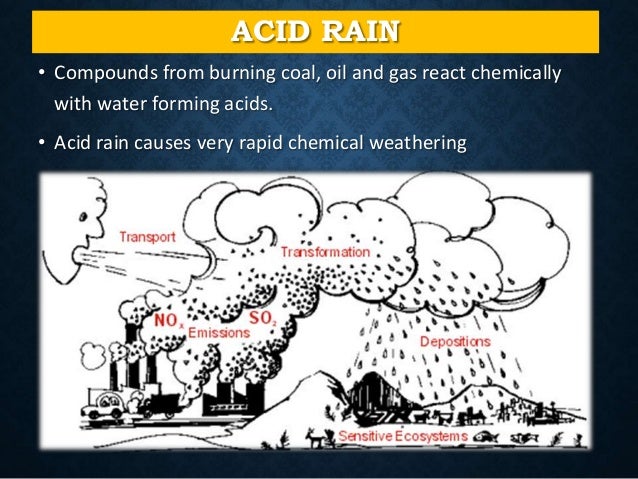
Man-made or Anthropogenic Causes of Acid Rain
- Combustion of coal and oil As stated earlier, the principal emissions accountable for acidic depositions in the atmosphere are oxides of nitrogen (NOx) and sulfur dioxide (SO2). ...
- Power plants and manufacturing industries Contemporary power plants use fuel to generate energy. ...
- Automobiles and other vehicles
Which gases are mainly responsible for acid rain?
What is Acid Rain?
- Chemicals in Acid Rain. Chemicals in acid rain are acids like nitric acid and even sulphuric acid present in the polluted air.
- Acid Rain Causes. ...
- The Atmospheric Reaction of Acid Rain. ...
- Gases Responsible for Acid Rain. ...
- Environmental Effects of Acid Rain. ...
Which gas is responsible for acid rain?
The gases responsible for acid rain are Sulphur dioxide (SO2) and Nitrogen (NOx). Acid rain usually forms high in the clouds where sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxides react with water, oxygen, and oxidants. This mixture forms a mild solution of sulphuric acid and nitric acid. Sulphur dioxide mainy comes from fossil fuel combustion at power plants and other industrial facilities.
What gases form that contribute to acid rain?
The electric discharge into the atmosphere as a result of lightning can facilitate the formation of nitric acid from oxides of nitrogen and water. Thus, the presence of gases like nitrogen dioxide and sulphur dioxide (in excess) in the atmosphere can contribute towards acid rain.
What are three gases that make rain water acidic?
- Causes of acid rain. Sources/Usage: Public Domain. ...
- Effects of acid rain. The environment can generally adapt to a certain amount of acid rain. ...
- Geographic distribution of acid rain. Acidity in rain is measured by collecting samples of rain and measuring its pH. ...
- Acid rain and stone. ...

What is the result of acid rain?
Acid rain results when sulfur dioxide (SO 2) and nitrogen oxides (NO X) are emitted into the atmosphere and transported by wind and air currents. The SO 2 and NO X react with water, oxygen and other chemicals to form sulfuric and nitric acids. These then mix with water and other materials before falling to the ground.
What is acid rain?
Acid rain, or acid deposition, is a broad term that includes any form of precipitation with acidic components, such as sulfuric or nitric acid that fall to the ground from the atmosphere in wet or dry forms. This can include rain, snow, fog, hail or even dust that is acidic.
How does acidic water affect the environment?
When the accumulated acids are washed off a surface by the next rain, this acidic water flows over and through the ground, and can harm plants and wildlife, such as insects and fish.
Where does acid rain come from?
While a small portion of the SO 2 and NO X that cause acid rain is from natural sources such as volcanoes, most of it comes from the burning of fossil fuels. The major sources of SO 2 and NO X in the atmosphere are: Burning of fossil fuels to generate electricity.
Is rain acidic or alkaline?
The lower a substance's pH (less than 7), the more acidic it is; the higher a substance's pH (greater than 7), the more alkaline it is. Normal rain has a pH of about 5.6; it is slightly acidic because carbon dioxide (CO 2) dissolves into it forming weak carbonic acid. Acid rain usually has a pH between 4.2 and 4.4.
What gases are responsible for acid rain?
The major gases responsible for acid rain are nitric oxide, nitrogen dioxide, sulphur dioxide, and sulphur trioxide. The gases responsible for acid rain when precipitates down causes the easing of nutrients from plants, and thus it damages the leaves of plants and trees.
What are the chemicals in acid rain?
Chemicals in acid rain are acids like nitric acid and even sulphuric acid present in the polluted air. These chemicals in acid rain are formed when oxides of nitrogen and sulphur come in contact with rainwater.
What is the reaction of nitric oxide and water?
In the air, nitric oxide (NO) is oxidized to nitrogen dioxide (NO2) , this, in turn, combines with water to give nitric acid (HNO3). This acid dissociates in water to yield hydrogen ions (H+) and nitrate ions (NO3-) in a reaction analogous to the dissociation of carbonic acid shown in the equation below, again lowering the pH of the solution. ...
Why does the pH of rainwater drop?
Answer: The pH of rainwater is less than 7 due to the presence of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. When water precipitates down in the form of rainwater, carbon dioxide reacts with the rainwater and forms carbonic acid. Therefore, it leads to a drop in the pH value.
What is the lowering of pH in rainwater?
In most of the water bodies, the lowering in pH is accounted for by the presence of sulphuric acid (H2SO4) in rainwater. Although there is a natural source of sulphuric acid production.
What is acid rain?
The term acid rain is used to describe all precipitations- rain, snow, fog, dew- which are more acidic than normal water. The normal rain is slightly acidic having a pH of about 5.6 as carbon dioxide gas reacts with it to form a weak carbonic acid. For example: Rainfall is declared as acid rain when its pH is less than 5.6 because natural ...
How is sulphuric acid produced?
Although there is a natural source of sulphuric acid production. Sulphuric acid is produced naturally in trace amounts from biological decay and volcanic activity , it is produced almost entirely by human activity, especially the combustion of sulphur-containing fossil fuels in power plants.
What causes acid rain?
Acid rain is caused by emissions of sulphur dioxide and nitrogen oxide, which react with the water molecules in the atmosphere to produce acids. Some governments have made efforts since the 1970s to reduce the release of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide into the atmosphere with positive results.
What is acid rain?
Definition. "Acid rain" is a popular term referring to the deposition of a mixture from wet (rain, snow, sleet, fog, cloudwater, and dew) and dry (acidifying particles and gases) acidic components. Distilled water, once carbon dioxide is removed, has a neutral pH of 7.
What are the two reactions that oxidize sulfur?
The most important oxidation reactions are with ozone, hydrogen peroxide and oxygen (reactions with oxygen are catalyzed by iron and manganese in the cloud droplets).
How much acid rain causes acidity in lakes?
The United States Environmental Protection Agency's (EPA) website states: "Of the lakes and streams surveyed, acid rain caused acidity in 75% of the acidic lakes and about 50% of the acidic streams".
How much acid deposition occurs in the absence of precipitation?
Acid deposition also occurs via dry deposition in the absence of precipitation. This can be responsible for as much as 20 to 60% of total acid deposition. This occurs when particles and gases stick to the ground, plants or other surfaces.
What is the pH of distilled water?
"Acid rain" is a popular term referring to the deposition of a mixture from wet (rain, snow, sleet, fog, cloudwater, and dew) and dry (acidifying particles and gases) acidic components. Distilled water, once carbon dioxide is removed, has a neutral pH of 7. Liquids with a pH less than 7 are acidic, and those with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline. "Clean" or unpolluted rain has an acidic pH, but usually no lower than 5.7, because carbon dioxide and water in the air react together to form carbonic acid, a weak acid according to the following reaction:
How does acid rain affect humans?
Acid rain has been shown to have adverse impacts on forests, freshwaters, and soils, killing insect and aquatic life-forms, causing paint to peel, corrosion of steel structures such as bridges, and weathering of stone buildings and statues as well as having impacts on human health.