What are the hormones produced by the hypothalamus?
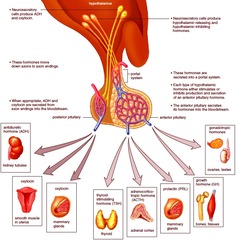
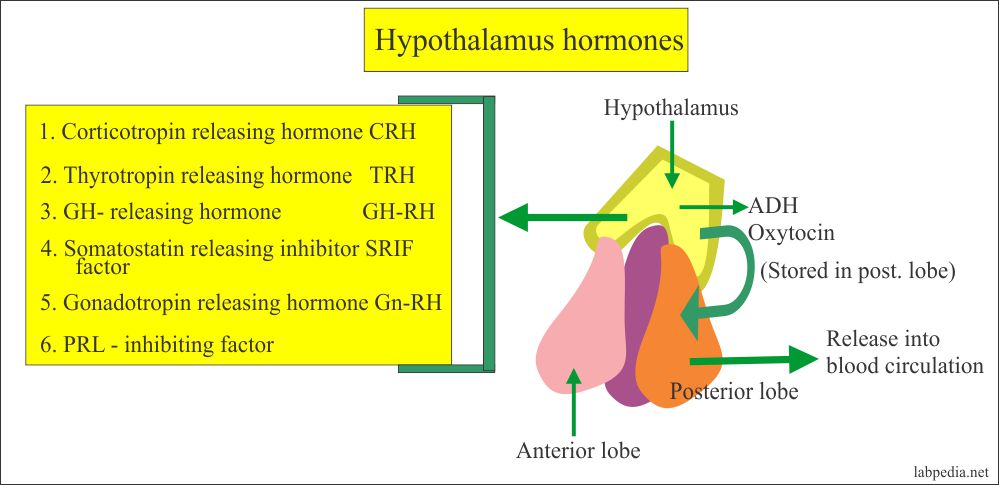
The hormones produced in the hypothalamus are corticotrophin-releasing hormone, dopamine, growth hormone-releasing hormone, somatostatin, gonadotrophin-releasing hormone and thyrotrophin-releasing hormone. Beside above, how does the hypothalamus control the anterior pituitary?
Where is the hypothalamus located in the endocrine system?
Location of the hypothalamus The hypothalamus is an area of the brain (about 3.5 cm long) that links the brain to the endocrine system. The hypothalamus sits at the base of the brain and is connected to the pituitary gland by a stalk made of both nerves and blood vessels.
Which hormone is secreted by the thyroid?
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) is secreted by the increase metabolic rate and body temperature by increasing protein synthesis in target cells. Thyroid hormone's effects are to Hypersecretion of thyroid hormone You are "shadowing" an endocrinologist who is examining a patient complaining of weakness, weight loss, and heat intolerance.
How does the hypothalamus affect growth hormone levels?
When levels are high, the hypothalamus releases somatostatin which signals the pituitary gland to make less growth hormone. These two hormones rise and fall in turn, which keeps growth hormone levels within a normal range. ^ Back To Top Common problems and conditions of the hypothalamus

Which hormones are not secreted by hypothalamus?
Correct answer: The correct answer is glucagon. Glucagon is secreted by the pancreas, not the pituitary gland. All the other answer choices are major hormones secreted by the pituitary that are essential to bodily functions.
Which hormones are produced by the hypothalamus?
The thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH), corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH), somatostatin, and dopamine are released from the hypothalamus into the blood and travel to the anterior pituitary.
Which hormone is produced in the hypothalamus quizlet?
The hypothalamus produces antidiuretic hormone and oxytocin.
Which of the following is not a hypothalamus?
Answer and Explanation: (C) Postural reflexes are NOT a function of the hypothalamus. It is a function of the cerebellum.
What are the 7 hormones of the hypothalamus?
The hormones produced in the hypothalamus are corticotrophin-releasing hormone, dopamine, growth hormone-releasing hormone, somatostatin, gonadotrophin-releasing hormone and thyrotrophin-releasing hormone.
Which of the following does not produce hormone?
The spleen does not have any endocrine function and does not secrete any hormones. So, the correct answer is option C.
Which of the following hormones is not produced by the pituitary gland quizlet?
Which of the following hormones is not secreted by the pituitary gland? Explanation: Melatonin is secreted by the pineal gland, which is also in the brain.
Does hypothalamus secrete FSH?
The hypothalamus produces GnRH, and it is released into the hypophyseal portal circulation to act on G-protein-coupled receptors at gonadotropic cells of the anterior pituitary. Those gonadotropic cells produce FSH and luteinizing hormone (LH) and release them into the peripheral circulation.
Does the hypothalamus produce ADH?
Anti-diuretic hormone is made by special nerve cells found in an area at the base of the brain known as the hypothalamus. The nerve cells transport the hormone down their nerve fibres (axons) to the posterior pituitary gland where the hormone is released into the bloodstream.
Which is not a function of hypothalamus quizlet?
Which of the following is NOT a function of the hypothalamus? Secretion of the hormone melatonin is a function of the pineal gland (not the hypothalamus). The hypothalamus is the main visceral control center of the body and is vitally important to overall body homeostasis.
What hormones are produced in the hypothalamus?
The hormones produced in the hypothalamus are corticotrophin-releasing hormone, dopamine, growth hormone-releasing hormone, somatostatin, gonado trophin-releasing hormone and thyrotrophin-releasing hormone. Also Know, how does the hypothalamus control the anterior pituitary?
What is the function of the hypothalamus?
One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus.
Which gland stores and secretes hormones?
These hormones are stored or released into the blood via the capillary plexus. The posterior pituitary gland does not produce hormones, but rather stores and secretes hormones produced by the hypothalamus. The paraventricular nuclei produce the hormone oxytocin, whereas the supraoptic nuclei produce ADH. Click to see full answer.
What is the function of the hypothalamus?
The function of each of the regulatory hormones of the hypothalamus is to trigger the release of a tropic hormone from the pituitary. corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH). The hypothalamic hormone that triggers the release of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) is. True.
Which glands are responsible for the production of hormones?
Each of the body's blood-borne hormones comes from one of the major glands, namely, the pineal, pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, or adrenal glands . The small, cone-shaped gland that is in the epithalamus of the brain is the _______ gland. posterior to the thyroid gland.
How does thyroid hormone affect metabolism?
increase metabolic rate and body temperature by increasing protein synthesis in target cells. Thyroid hormone's effects are to. Hypersecretion of thyroid hormone. You are "shadowing" an endocrinologist who is examining a patient complaining of weakness, weight loss, and heat intolerance.
Why do cells up regulate receptors?
up-regulate receptors in order to increase cell sensitivity. Reduced hormone concentration in the blood often causes target cells to: a cell decreases the number of receptors it has for a hormone. The term down-regulation refers to the process by which:
Does oxytocin increase smooth muscle contractions?
Oxytocin results in more forceful smooth muscle contractions in the uterus by causing target cells to increase production of: each step allows for amplification of the signal where one molecule can activate many. Intracellular signaling pathways within target cells are organized such that: There are a few different examples provided in section ...
Is hormone synthesis directly related to plasma hormone levels?
hormone synthesis is directly related to plasma hormone levels, and hormone elimination (by liver, kidneys, and target cell uptake) is inversely related to plasma hormone levels. Generally, there are two main factors that determine the levels of a hormone in the blood.
Which hormone is produced by the hypothalamus?
Your hypothalamus also produces somatostatin, which inhibits pituitary growth hormone production and TSH. Oxytocin is produced by your hypothalamus and stored and released by the pituitary gland. Oxytocin induces social bonding and acts on the breasts to release breast milk and the uterus to induce contraction.
Why is the hypothalamus not protected?
Because your hypothalamus is not protected by the blood-brain barrier, it’s exposed to toxins and viruses, and anything else floating around in your blood. This means making sure that you’re eating organic foods, being careful to not expose yourself to toxins in your occupation or environment, and supporting yourself with supplements like Genesis Gold® to help you detoxify.
What hormones are produced by GnRH?
GnRH also induces the pituitary gland to produce FSH and LH. ADH (antidiuretic hormone) controls your blood pressure. ADH, also known as vasopressin, conserves fluid volume in the blood by suppressing your kidneys’ production of urine and increases your blood pressure.
What hormones are produced by the adrenal glands?
CRH (corticotropin-releasing hormone) controls your adrenal glands’ production of the stress hormone, cortisol . TRH (thyrotropin-releasing hormone) induces pituitary TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone), which stimulates your thyroid to produce thyroid hormones T4 & T3, which control metabolism and energy production.
What is the best way to support hypothalamic function?
The best way to support hypothalamic function is to use supplementation. I created Genesis Gold® because full hypothalamic supplementation was not available when I was seeing so many patients with hypothalamus dysfunction in the late 90’s.
What is the main neurotransmitter in the hypothalamus?
Besides hormones, your hypothalamus produces many neurotransmitters. Dopamine is your main neurotransmitter. Dopamine wakes you up in the morning and suppresses prolactin production. It is also your memory and learning neurotransmitter, as well as your motivating neurotransmitter. Dopamine regulates your reward system.
What is the name of the hormone that is broken down into two different types of hormones?
ADH – Anti-diuretic hormone. Oxytocin. These nine hormones are broken into some big categories. The one I talk about the most is POMC (pro-opiomelanocortin) – a giant 241 amino acid pre-hormone that gets broken down into corticotropin-releasing hormone, melanocyte-stimulating hormone, and beta-endorphins.
What hormones are produced by the hypothalamus?
A number of important hormones are produced by the hypothalamus including: vasopressin (anti-diuretic hormone), corticotropin-releasing hormone, oxytocin, gonadotropin-releasing hormone, somatostatin, growth hormone-releasing hormone, and thyrotropin-releasing hormone. These hormones act on other organs or glands in the body.
What is the hypothalamus?
The hypothalamus is a complex area of the brain with a number of important functions. One of the most important is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland. Regina Bailey is a board-certified registered nurse, science writer and educator.
What are the connections between the hypothalamus and the limbic system?
In addition, the hypothalamus has connections with other limbic system structures including the amygdala, hippocampus, thalamus, and olfactory cortex.
What is the function of the hypothalamus?
The hypothalamus releases a number of hormones that control a variety of endocrine functions. As such, damage to the hypothalamus results in a lack of production of hypothalamic hormones needed to control important activities, such as maintaining water balance, temperature regulation, sleep cycle regulation, and weight control.
Which part of the brain controls the autonomic nervous system?
Located in the diencephalon region of the forebrain, the hypothalamus is the control center for many autonomic functions of the peripheral nervous system. Connections with structures of the endocrine and nervous systems enable the hypothalamus to play a vital role in maintaining homeostasis.
What are the three regions of the hypothalamus?
The hypothalamus consists of several nuclei ( neuron clusters) that may be divided into three regions. These regions include an anterior, middle or tuberal, and posterior component . Each region can be further divided into areas that contain nuclei responsible for a variety of functions.
Which hormone regulates blood volume and blood pressure?
Anti-Diuretic Hormone ( Vasopressin) - regulates water levels and influence blood volume and blood pressure. Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone - acts on the pituitary gland causing the release of hormones in response to stress. Oxytocin - influences sexual and social behavior.
Which hormone is produced by the hypothalamus?
CRH from the hypothalamus signals the pituitary gland to make adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH). ACTH then signals the adrenal glands to make glucocorticoid hormones. The major glucocorticoid hormone is cortisol. This system is called the hypothalamic pituitary adrenal axis (or HPA axis). Cortisol travels through the blood ...
What are the hormones that regulate the hypothalamus?
Together, the hormones made by the hypothalamus directly or indirectly regulate: 1 Body temperature 2 Sleep and alertness 3 Appetite and body weight 4 Thirst 5 Daily (circadian) rhythms
What happens when the hypothalamus releases somatostatin?
When levels are high, the hypothalamus releases somatostatin which signals the pituitary gland to make less growth hormone. These two hormones rise and fall in turn, which keeps growth hormone levels within a normal range. ^ Back To Top.
What is the TSH hormone?
TRH from the hypothalamus signals the pituitary gland to make thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH). TSH then signals the thyroid to make thyroid hormones. These hormones travel through the blood and are recognised by the hypothalamus and pituitary gland.
How does somatostatin work?
Growth Hormone Releasing Hormone (GHRH) and Somatostatin work together to control growth hormone (GH) levels. Growth hormone releasing hormone signals the pituitary gland to release growth hormone. Neurons (nerve cells) in the hypothalamus monitor growth hormone levels. When levels are high, the hypothalamus releases somatostatin which signals the pituitary gland to make less growth hormone. These two hormones rise and fall in turn, which keeps growth hormone levels within a normal range.
What is the main system that is activated in response to stress?
When a threshold is reached, cortisol signals to the hypothalamus and pituitary to make less CRH and ACTH. The HPA axis is the main system that is activated in response to stress.
How is oxytocin made?
Oxytocin is controlled through a positive feedback loop. Oxytocin starts to be made when nerves leading to the hypothalamus are activated. This occurs when a baby starts to suckle at the breast. As the baby feeds, the nerves in the breast signal to the hypothalamus to release oxytocin.
Which hormones are secreted in the anterior region of the hypothalamus?
Following are the hormones secreted by the anterior region of the hypothalamus: Corticotropin-releasing hormone. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone. Oxytocin. Vasopressin. Somatostatin.
What is the hypothalamus?
Hypothalamus is a minute region, almost the size of an almond, present at the centre of the human brain, near the pituitary gland. It consists of three main regions: The anterior region. The middle region. The posterior region. It plays a vital role in the production of hormones. Maintaining the hypothalamus health is very important.
How is ADH released into the bloodstream?
The release of ADH into the bloodstream is regulated by a number of factors: The decrease in the blood volume or blood pressure is detected by the large blood vessels and the receptors present in the heart, which stimulate the release of ADH.
What hormone is released during lactation?
Oxytocin . Oxytocin is a peptide hormone, released during childbirth and lactation. In females, it is mainly involved in stimulating the growth of prostaglandins, increasing the contractions of the muscles of the uterus, reduces the excess blood flow post-childbirth, promotes milk movement into the mammary glands.
Why is ADH high?
High levels of ADH may be caused due to the side-effects of drugs, lung diseases, etc. Increased ADH is associated with leukaemia, lymphoma, bladder cancer, brain cancer, etc. If the levels of ADH are lower, a lot of water is excreted by the kidneys. This increases urine volume and lowers blood pressure.
Where is ADH stored?
ADH- Anti-diuretic Hormone. ADH, also known as arginine vasopressin, is a hormone produced by the hypothalamus and stored in the posterior pituitary gland. It is made up of special nerve cells found at the base of the hypothalamus.
What is the function of the hypothalamus?
Hypothalamus stimulates or inhibits many of the body’s activities in order to maintain homeostasis, such as regulating body temperature, appetite and body weight, heart rate and blood pressure, etc. It is involved in many essential functions of the body, including: Childbirth. Emotions. Sleep cycles.