What does vestibulocochlear nerve mean?
Vestibulocochlear nerve, also called Auditory Nerve, Acoustic Nerve, or Eighth Cranial Nerve, nerve in the human ear, serving the organs of equilibrium and of hearing.
Which sensation does the vestibulocochlear nerve carry?
Which sensation(s) does the vestibulocochlear nerve carry? hearing and balance hearing hearing, balance, and taste atmospheric pressure balance
What function does the trochlear nerve have?
What function does the trochlear nerve have?
- The Central Nervous System: It consists of the brain and the spinal cord. It is the central evaluating and commanding unit.
- The Peripheral Nervous System: It consists of the following subdivisions. A. ...
- 2K views
What is the function of the coccygeal nerves?
These pathways have both afferent and efferent fibers and, this way, they are responsible for conduction of sensory information from these pelvic organs to the central nervous system (CNS) and motor impulses from the CNS to the pelvis that control the movements of these pelvic organs. The coccygeal nerve is the 31st pair of spinal nerves.

What is the function of the vestibulocochlear nerve quizlet?
The branch of the vestibulocochlear nerve responsible for sending equilibrium information to the brain. The eighth cranial nerve. It is responsible for hearing and balance.
What are the two functions of the vestibulocochlear nerve?
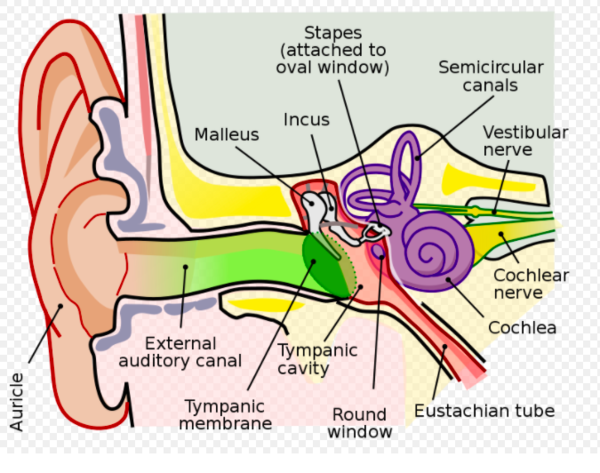
The vestibulocochlear is made up of two nerves—the cochlear nerve, which is responsible for hearing, and the vestibular nerve, which is responsible for balance.
What is the function of the auditory vestibulocochlear nerve?
vestibulocochlear nerve, also called Auditory Nerve, Acoustic Nerve, or Eighth Cranial Nerve, nerve in the human ear, serving the organs of equilibrium and of hearing.
Which of the following is the function of CN VIII?
This cranial nerve has a vestibular part, which functions in balance, equilibrium, and orientation in three-dimensional space, and a cochlear part, which functions in hearing.
Where does the 8th cranial nerve run?
The 8th cranial nerve runs between the base of the pons (the middle portion of the brainstem) and medulla oblongata (the lower portion of the brainstem). This junction between the pons, medulla, and cerebellum that contains the 8th nerve is called the cerebellopontine angle.
Which sensation does the vestibulocochlear nerve carry?
The vestibulocochlear nerve is the eighth cranial nerve. Its cochlear branch is responsible for the special sensation of hearing, and its vestibular portions are involved in balance, spatial sensation, and posture.
What is the main function of CN VIII quizlet?
What is the function of cranial nerve VIII? The vestibulocochlear nerve is responsible for hearing and equilibrium.
What do cranial nerves I II and VIII have in common?
What do cranial nerves I, II, and VIII have in common? a.) They all transmit general somatic motor impulses.
What is the eighth cranial nerve?
The vestibulocochlear nerve (8th cranial nerve) is a sensory nerve. It is made up of two nerves, the cochlear, which transmits sound and the vestibular which controls balance.
Which of the following are major functions of the nervous system?
The nervous system is the major controlling, regulatory, and communicating system in the body. It is the center of all mental activity including thought, learning, and memory. Together with the endocrine system, the nervous system is responsible for regulating and maintaining homeostasis.
Which of the following is a function of the efferent division of the nervous system?
The efferent or motor division transmits impulses from the CNS out to the peripheral organs to cause an effect or action.
How does the structure of the nervous system help with its function?
The nervous system helps all the parts of the body to communicate with each other. It also reacts to changes both outside and inside the body. The nervous system uses both electrical and chemical means to send and receive messages.
Is cochlea part of nervous system?
The cochlear nerve, also known as the acoustic nerve, is the sensory nerve that transfers auditory information from the cochlea (auditory area of the inner ear) to the brain. It is one of the many pieces that make up the auditory system, which enables effective hearing.
How to treat vestibulocochlear nerve?
Sometimes further intervention, like medication or surgery is required.
What is the vestibular nerve?
The vestibulocochlear is made up of two nerves—the cochlear nerve, which is responsible for hearing, and the vestibular nerve, which is responsible for balance. As one of the 12 cranial nerves, it runs between the pons (the middle of the brainstem) and the medulla oblongata (the lower part of the brainstem).
What is the name of the disorder that affects the inner ear?
Vestibular Neuritis and Labyrinthitis. Vestibular neuritis is a disorder of the inner ear that affects the vestibular part of the vestibulocochlear nerve, which is responsible for equilibrium. When this part of the nerve swells, it interferes with information it would normally send to the brain about balance.
What nerves affect balance?
Conditions of the vestibulocochlear nerve can affect balance and hearing. An otologist or neurotologist commonly work with disorders associated with the vestibulocochlear nerve.
What nerve is responsible for hearing?
The nerve is responsible for equilibrium and hearing. Conditions of the vestibulocochlear nerve include vestibular neuritis, labyrinthitis, and acoustic neuroma .
What is the difference between a keyhole craniotomy and a translabyrinthine?
In a keyhole craniotomy, a surgeon makes a small incision behind the ear in order to access the affected nerve. Translabyrinthine craniotomy is a more invasive surgery that may be chosen for larger tumors and if hearing is already compromised. A surgeon makes an incision in the scalp behind the ear and removes the mastoid bone and a portion ...
What is acoustic neuroma?
Acoustic neuroma is a noncancerous tumor that grows on the vestibulocochlear nerve. Tumors may grow on one or both nerves, with unilateral acoustic neuromas (those affecting one ear) being more common.
What is the function of the cochlear nerve?
The cochlear nerve is responsible for transmitting auditory signals from the inner ear to the cochlear nuclei, within the brainstem, and ultimately to the primary auditory cortex, within the temporal lobe.
What is the cochlear nerve?
Introduction. The vestibulocochlear nerve, also known as cranial nerve eight (CN VIII), consists of the vestibular and cochlear nerves. Each nerve has distinct nuclei within the brainstem. The vestibular nerve is primarily responsible for maintaining body balance and eye movements, while the cochlear nerve is responsible for hearing.
How to treat vestibular schwannomas?
Treatment options for vestibular schwannomas (acoustic neuromas) are microsurgical resection, radiation therapy, and observation. Post-operative mortality rates have decreased dramatically over the last century. Therefore, preserving facial nerve function has become the primary goal of surgery, while removing as much as of the tumor as possible. The three standard surgical approaches are middle fossa, retrosigmoidal, and translabyrinthine. Pre-operative hearing level, tumor size, and tumor location determine which approach is used. [17][18]
What nerves are in the brainstem?
Upon entering the brainstem, the cochlear nerve separates from the vestibular nerve and branches into anterior and posterior divisions. The anterior division innervates the AVCN, while the posterior division innervates the DCN and PVCN. Cochlear nerve fibers are characterized tonotopically. Afferent nerve fibers from hair cells at the base of the cochlea transmit high frequencies. The afferents from the apex of the cochlea transmit low frequencies. This organization is preserved within the cochlear nuclei. [5]
What nerve relays information related to motion and position?
The vestibular nerv e relays information related to motion and position. The vestibular system involves coordinated communication between the vestibular apparatus (semicircular canals, saccule, and utricle), ocular muscles, postural muscles, brainstem, and cerebral cortex. [3][8]
Which nerve is responsible for hearing and balance?
The vestibular nerve is primarily responsible for maintaining body balance and eye movements, while the cochlear nerve is responsible for hearing.
Where does CN VIII enter the brain?
CN VIII runs past the CPA and enters the brainstem at the pontomedullary junction. The vestibular nerve separates from the cochlear nerve before reaching the vestibular nuclear complex. The vestibular nuclear complex consists of four nuclei: medial, lateral, superior, and inferior.
Where does vestibulocochlear nerve come from?
Both sets of fibres combine in the pons to form the vestibulocochlear nerve. The nerve emerges from the brain at the cerebellopontine angle and exits the cranium via the internal acoustic meatus of the temporal bone.
Where does the vestibular nerve originate?
Anatomical Course. The vestibular and cochlear portions of the vestibulocochlear nerve are functionally discrete, and so originate from different nuclei in the brain: Vestibular component - arises from the vestibular nuclei complex in the pons and medulla. Cochlear component - arises from the ventral and dorsal cochlear nuclei, ...
What is the clinical significance of labyrinthitis?
Clinical Relevance: Labyrinthitis. Labyrinthitis refers to inflammation of the membranous labyrinth, resulting in damage to the vestibular and cochlear branches of the vestibulocochlear nerve. The symptoms are similar to vestibular neuritis, but also include indicators of cochlear nerve damage:
What is the clinical relevance of vestibular neuritis?
Clinical Relevance: Vestibular Neuritis. Vestibular neuritis refers to inflammation of the vestibular branch of the vestibulocochlear nerve. The aetiology of this condition is not fully understood, but some cases are thought to be due to reactivation of the herpes simplex virus.
What is vestibular neuritis?
Vestibular neuritis refers to inflammation of the vestibular branch of the vestibulocochlear nerve. The aetiology of this condition is not fully understood, but some cases are thought to be due to reactivation of the herpes simplex virus.
What is the eighth paired cranial nerve?
The vestibulocochlear nerve is the eighth paired cranial nerve. It is comprised of two parts – vestibular fibres and cochlear fibres. Both have a purely sensory function. In this article, we will consider the anatomical course, special sensory functions and clinical relevance of this nerve.
Where are vestibular hair cells located?
The vestibular hair cells are located in the otolith organs (the utricule and saccule ), where they detect linear movements of the head, as well as in the three semicircular canals, where they detect rotational movements of the head. The cell bodies of the vestibular nerve are located in the vestibular ganglion which is housed in the outer part of the internal acoustic meatus.
Where does vestibulocochlear nerve come from?
The vestibulocochlear nerve is derived from the embryonic otic placode .
Which artery is the vestibulocochlear nerve accompanied by?
The vestibulocochlear nerve is accompanied by the labyrinthine artery, which usually branches off from the anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA) at the cerebellopontine angle, and then goes with the 7th nerve through the internal acoustic meatus to the internal ear.
What is the name of the nerve that is located in the vestibular system?
Some older texts call the nerve the acoustic or auditory nerve, but these terms have fallen out of widespread use because they fail to recognize the nerve's role in the vestibular system. Vestibulocochlear nerve is therefore preferred by most.
What is the 8th cranial nerve?
Cranial nerve 8, the vestibulocochlear nerve, goes to the middle portion of the brainstem called the pons, (which then is largely composed of fibers going to the cerebellum). The 8th cranial nerve runs between the base of the pons (the middle portion of the brainstem) and medulla oblongata (the lower portion of the brainstem). This junction between the pons, medulla, and cerebellum that contains the 8th nerve is called the cerebellopontine angle . The vestibulocochlear nerve is accompanied by the labyrinthine artery, which usually branches off from the anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA) at the cerebellopontine angle, and then goes with the 7th nerve through the internal acoustic meatus to the internal ear.
Which sensory organs are supplied by vestibular neurons?
The other two sensory organs supplied by the vestibular neurons are the maculae of the saccule and utricle. Hair cells of the maculae in the utricle activate afferent receptors in response to linear acceleration while hair cells of the maculae in the saccule respond to vertically directed linear force.
Which cranial nerve transmits sound and balance information from the inner ear to the brain?
t. e. The vestibulocochlear nerve ( auditory vestibular nerve ), known as the eighth cranial nerve, transmits sound and equilibrium (balance) information from the inner ear to the brain. Through olivocochlear fibers, it also transmits motor and modulatory information from the superior olivary complex in the brainstem to the cochlea.
Which nerve is responsible for sound transmission?
The exact mechanism by which sound is transmitted by the neurons of the cochlear nerve is uncertain; the two competing theories are place theory and temporal theory . The vestibular nerve travels from the vestibular system of the inner ear. The vestibular ganglion houses the cell bodies of the bipolar neurons and extends processes ...

Overview
Structure
- The function of the vestibulocochlear nerve is purely sensory. It has no motor function. It communicate ssound and equilibrium information from the inner ear to the brain. The cochlea, the part of the inner ear where the cochlear part of the nerve originates, detects soundwaves. These then travel from the spiral ganglion to the brain. The vestibula...
Function
Clinical significance
History
The vestibulocochlear nerve or auditory vestibular nerve, also known as the eighth cranial nerve, cranial nerve VIII, or simply CN VIII, is a cranial nerve that transmits sound and equilibrium (balance) information from the inner ear to the brain. Through olivocochlear fibers, it also transmits motor and modulatory information from the superior olivary complex in the brainstem to the cochlea.
See also
The vestibulocochlear nerve consists mostly of bipolar neurons and splits into two large divisions: the cochlear nerve and the vestibular nerve.
Cranial nerve 8, the vestibulocochlear nerve, goes to the middle portion of the brainstem called the pons, (which then is largely composed of fibers going to the cerebellum). The 8th cranial nerve runs between the base of the pons (the middle portion of the brainstem) and medulla oblongata (t…
External links
This is the nerve along which the sensory cells (the hair cells) of the inner ear transmit information to the brain. It consists of the cochlear nerve, carrying details about hearing, and the vestibular nerve, carrying information about balance. It emerges from the pontomedullary junction and exits the inner skull via the internal acoustic meatus (or internal auditory meatus) in the temporal bone.
The vestibulocochlear nerve carries axons of type SSA (special somatic afferent).