
Are organelles only found in eukaryotic cells?
Mitochondria and chloroplast are two organelles found in eukaryotic cells. Chloroplast is only found in plants while majority of eukaryotic cells have mitochondria. Even though both organelles are found in eukaryotic cells, both mitochondria and chloroplast have characteristics often found in prokaryotic cells.
What molecule is found in eukaryotic cells?
cell nucleus. In eukaryotic cells, most DNA is located in the cell nucleus (though some DNA is also contained in other organelles, such as in the mitochondria and the chloroplast in plants). Nuclear DNA is organized into linear molecules called chromosomes. See also where is new netherland.
Are plant cells prokaryotic or eukaryotic and why?
Plant cells are eukaryotic, because they have membrane bound organelles (small compartments tiny structures within the cell that are responsible for certain functions) and classified as multicellular organisms. Plant cells contain nucleus that is surrounded with double membrane lipids bilayer, and include it’s own DNA inside.
What are the two major parts of an eukaryotic cell?
Two major parts of a eukaryotic cell are the Nucleus and the Cytoplasm. 2.) Describe the steps in making, packaging and exporting a protein from a cell First, the ribosome makes a protein.
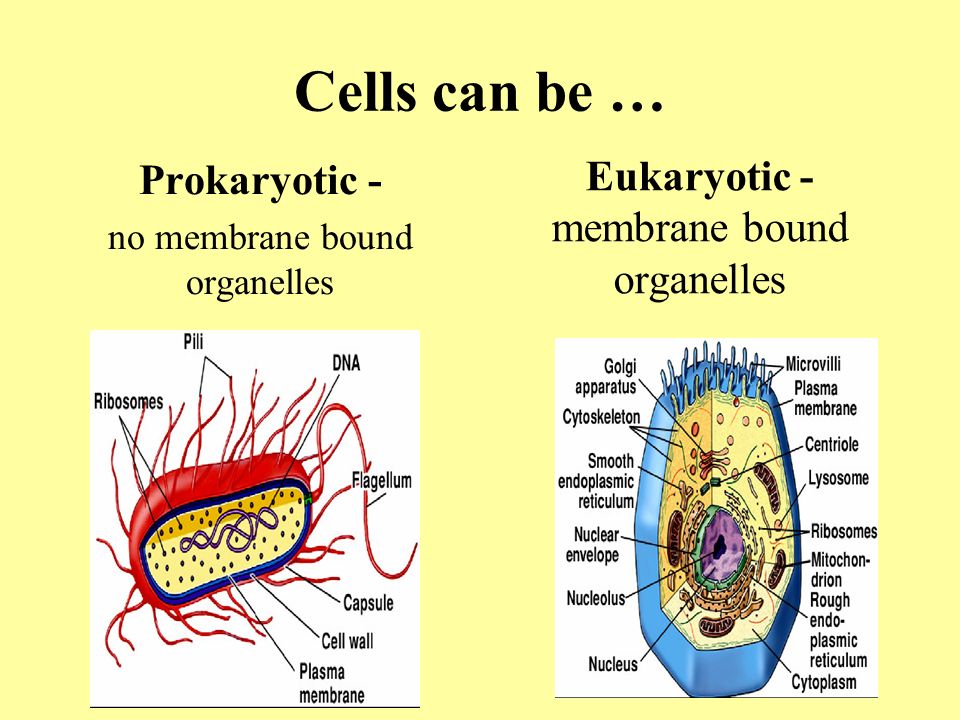
Which is present only in eukaryotic cells quizlet?
Structures or activities found only in eukaryotic cells include any of the organelles, a nucleus, or the activities of the endomembrane system.
Which organelles are present in only eukaryotes?
Eukaryotic cells contain a membrane-bound nucleus and numerous membrane-enclosed organelles (e.g., mitochondria, lysosomes, Golgi apparatus) not found in prokaryotes. Animals, plants, fungi, and protists are all eukaryotes.
What do eukaryotic cells contain?
Eukaryotes are organisms whose cells contain a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. There is a wide range of eukaryotic organisms, including all animals, plants, fungi, and protists, as well as most algae. Eukaryotes may be either single-celled or multicellular.
Do all eukaryotic cells have mitochondria?
Mitochondria are found in the cells of nearly every eukaryotic organism, including plants and animals. Cells that require a lot of energy, such as muscle cells, can contain hundreds or thousands of mitochondria. A few types of cells, such as red blood cells, lack mitochondria entirely.
Which organelles are found only in the prokaryotic cell?
Answer: (2) Ribosomes In both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, the ribosome is the only organelle that can be seen. They lack a nuclear membrane.
Is the nucleus only in eukaryotic cells?
Do eukaryotic cells have a nucleus? The answer is yes! Eukaryotic cells have membrane-bound organelles like the nucleus, while prokaryotic cells do not. In eukaryotic cells, the nucleus is the brain of the cell, responsible for protecting the DNA and telling other parts of the cell what to do.
What is not present in eukaryotic cells?
Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound organelles, such as the nucleus, while prokaryotic cells do not....Comparison chart.Eukaryotic CellProkaryotic CellLysosomes and peroxisomesPresentAbsentMicrotubulesPresentAbsent or rareEndoplasmic reticulumPresentAbsentMitochondriaPresentAbsent18 more rows
What organelles are unique to eukaryotic cells?
Eukaryotic cells have evolved an endomembrane system, containing membrane-bound organelles involved in transport. These include vesicles, the endoplasmic reticulum, and the Golgi apparatus.
What organelle is present in eukaryotes but not in prokaryotes?
Eukaryotic cells contain membrane-bound organelles, such as the nucleus, while prokaryotic cells do not. Differences in cellular structure of prokaryotes and eukaryotes include the presence of mitochondria and chloroplasts, the cell wall, and the structure of chromosomal DNA.
What is found in eukaryotes but not prokaryotes?
Prokaryotic cells differ from eukaryotic cells in that they lack any membrane-bound organelles, including a nucleus. Instead, prokaryotic cells simply have an outer plasma membrane, DNA nucleoid structure, and ribosomes.
Which cell organelles structure are present in prokaryotes but not in eukaryotes?
mitochondriaWhich structure is present in prokaryotic cells, but not eukaryotic cells? Explanation: In general, prokaryotic cells are smaller and less complex than eukaryotic cells. They lack membrane-bound organelles (such as mitochondria) and contain a nucleoid region instead of a membrane-bound nucleus.
Are eukaryotic cells unicellular or multicellular?
Eukaryotic cells may be unicellular or multicellular. Paramecium, Euglena, Trypanosoma, Dinoflagellates are unicellular eukaryotes. Plants and anim...
What is the most important characteristic of eukaryotic cells that distinguishes it from prokaryotic cells?
Eukaryotic cells have a membrane-bound nucleus. On the contrary, prokaryotic cells lack a true nucleus, i.e., they have no nuclear membrane. Unlike...
Are viruses eukaryotes?
Viruses are neither eukaryotes nor prokaryotes. Since viruses are a link between living and non-living they are not considered in either category.
What are the salient features of a eukaryotic cell?
A eukaryotic cell has the following important features: A eukaryotic cell has a nuclear membrane. It has mitochondria, Golgi bodies, cell wall. It...
How does a eukaryotic cell divide?
A eukaryotic cell divides by the process of mitosis. It undergoes the following stages during cell division: Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase...
When did the first eukaryotic cell evolve?
The first eukaryotic cells evolved about 2 billion years ago. This is explained by the endosymbiotic theory that explains the origin of eukaryotic...
What is the evidence for endosymbiotic theory?
The first evidence in support of the endosymbiotic theory is that mitochondria and chloroplast have their own DNA and this DNA is similar to the ba...
Where are eukaryotic cells found?
Eukaryotic cells are exclusively found in plants, animals, fungi, protozoa, and other complex organisms. The examples of eukaryotic cells are mentioned below:
What is an eukaryotic cell?
What is a Eukaryotic Cell? Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus enclosed within the nuclear membrane and form large and complex organisms. Protozoa, fungi, plants, and animals all have eukaryotic cells. They are classified under the kingdom Eukaryota.
Which reticulum lacks ribosomes?
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum that lacks ribosomes and is therefore smooth.
What is the process of dividing cells called?
The cells divide by a process called mitosis. The eukaryotic cells contain a cytoskeletal structure. The nucleus contains a single, linear DNA, which carries all the genetic information.
Which structure is found only in plant cells?
These are double-membraned structures and are found only in plant cells. These are of three types: Chloroplast that contains chlorophyll and is involved in photosynthesis. Chromoplast that contains a pigment called carotene that provides the plants yellow, red, or orange colours.
What is the membrane that separates cells from the outside environment?
Plasma Membrane. The plasma membrane separates the cell from the outside environment. It comprises specific embedded proteins, which help in the exchange of substances in and out of the cell.
Why are cells called powerhouses?
These are also known as “powerhouse of cells” because they produce energy.
What are some examples of eukaryotic cells?
Examples of eukaryotic cells are plants, animals, protists, fungi. Their genetic material is organized in chromosomes. Golgi apparatus, Mitochondria, Ribosomes, Nucleus are parts of Eukaryotic Cells. Let’s learn about the parts of eukaryotic cells in detail.
Where is the nucleus located?
The nucleus is found in all eukaryotic cells except human RBCs and sieve cells of plants. Structure: A nucleus has the following parts: Nuclear envelope – It is a double membrane structure that surrounds the nucleus. The outer membrane is continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum.
What is the cytoplasmic membrane?
The plasma membrane is a semi-permeable membrane that separates the inside of a cell from the outside. Structure and Composition: In eukaryotic cells, the plasma membrane consists of proteins, carbohydrates and two layers of phospholipids (i.e.
How many membranes does the mitochondria have?
Structure: It has two membranes – outer and inner. The outer membrane forms a continuous boundary around the mitochondria. The inner membrane is semi-permeable and divided into folds called ‘cristae’. The membranes divide the lumen of the mitochondria into an inner and outer compartment.
What is the ER in a cell?
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Description: It is a network of small, tubular structures. It divides the space inside of Eukaryotic cells into two parts – luminal (inside ER) and extra-luminal (cytoplasm). Structure: ER can be of two types –.
Which organelle carries out sorting, tagging, packaging, and distribution of lipids and proteins?
Golgi apparatus carries out sorting, tagging, packaging, and distribution of lipids and proteins. Peroxisomes carry out oxidation reactions that break down fatty acids and amino acids. Vesicles and vacuoles are storage organelles. Apart from these organelles, the animal cell contains lysosomes and centrosomes.
Where is the cell wall located?
Description: The cell wall is a non-living, rigid structure outside the plasma membrane in plant cells and fungi. It is absent in Eukaryotic cells of animals
Which metabolic mechanism is present only in the first cells?
d. It relies on chemiosmosis, which is a metabolic mechanism present only in the first cells' prokaryotic cells.
Why are bacteria attracted to red and blue light?
Bacteria are attracted to red and blue light and thus these wavelengths are more reactive than other wavelengths. e. Bacteria congregated in these areas due to an increase in the temperature caused by an increase in photosynthesis. C.
