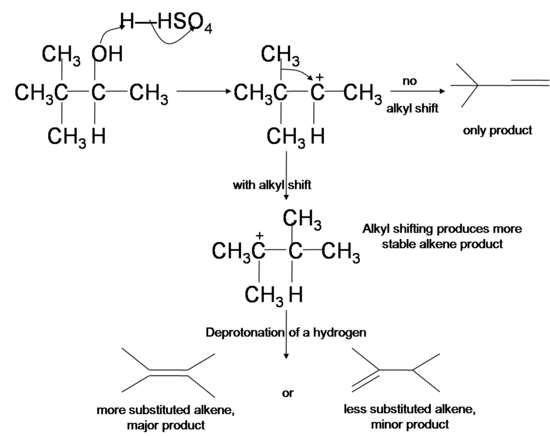What type of reaction is dehydration of primary alcohol?
The dehydration of either a tertiary or secondary alcohol is known as an E1 reaction (two-step mechanism), the dehydration of primary alcohol is an E2 (one step mechanism) reaction because of the difficulty encountered in forming primary carbocations. What is the main product of dehydration of ethanol?
How is an alkene produced from an alcohol?
An alkene is produced when dehydration of an alcohol is performed. Alcohol dehydration is an example of an elimination reaction which is quite the opposite of substitution reaction and addition reaction.
What is the Order of dehydration of alcohol?
Secondary Alcohol Dehydration Dehydration of alcohol requires a cleavage of a C-O bond with loss of a proton from the beta position. The result of dehydration is either an alkene or a mixture of the alkenes and the order of dehydration is first tertiary, then secondary, and finally primary.
What is the easiest form of alcohol to dehydrate?
Tertiary Alcohol Dehydration Tertiary forms of alcohol are easiest to dehydrate as the carbocations are more stable and thus easier to form compared to primary and secondary carbocations. For dehydration to take place, the alcohol must be heated to roughly 50⁰C in 5% H₂SO₄.

What is produced by the dehydration of alcohol?
Dehydration of Alcohols to Yield Alkenes The dehydration reaction of alcohols to generate alkene proceeds by heating the alcohols in the presence of a strong acid, such as sulfuric or phosphoric acid, at high temperatures.
What is the product of primary alcohol?
Primary alcohols can be oxidised to either aldehydes or carboxylic acids depending on the reaction conditions. In the case of the formation of carboxylic acids, the alcohol is first oxidised to an aldehyde which is then oxidised further to the acid.
How do you dehydrate a primary alcohol?
0:452:47Dehydration of Primary Alcohols - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo over here we have our primary alcohol and sulfuric acid. So as always the first step is always toMoreSo over here we have our primary alcohol and sulfuric acid. So as always the first step is always to activate that OAH group so that it can be kicked off later on in the reaction.
What is removed in dehydration of alcohol and what are the products formed?
The dehydration of ethanol to give ethene Ethanol is heated with an excess of concentrated sulphuric acid at a temperature of 170°C. The gases produced are passed through sodium hydroxide solution to remove the carbon dioxide and sulphur dioxide produced from side reactions. The ethene is collected over water.
What is the first product of primary alcohol?
Primary alcohols can be oxidized to either aldehydes or carboxylic acids, depending on the reaction conditions. In the case of the formation of carboxylic acids, the alcohol is first oxidized to an aldehyde, which is then oxidized further to the acid.
What are the products of the oxidation of primary alcohols?
Primary alcohols can be oxidized to form aldehydes and carboxylic acids; secondary alcohols can be oxidized to give ketones.
Which of the following Cannot be produced by dehydration of alcohol?
Product D cannot be obtained by the dehydration of the given alcohol as it will involve one tert carbocation into second tert carbocation. There is no significant difference in the stability of these carbocations. These two carbocations are shown below.
What will be major products of dehydration of ethanol?
For the dehydration of ethanol, the only likely product is ethene.
What is formed when primary alcohol undergoes catalytic dehydrogenation?
Main alcohols give aldehydes upon catalytic dehydrogenation, secondary alcohols give ketones, and tertiary alcohols give alkene.
What is the reactant in dehydration of alcohol?
Dehydration of alcohol is defined as a reaction in which alcohol reacts with protic acid to lose water molecules and form alkenes. This reaction is also known as dehydrogenation of alcohol.
What is the order of dehydration of primary secondary and tertiary alcohols?
Therefore the ease of dehydration of alcohols follows the order. Tertiary > secondary > primary alcohol.
When a primary alcohol is strongly oxidized The product is?
Carboxylic Acids“Strong” Oxidants Oxidize Primary Alcohols To Carboxylic Acids. A second class of oxidants are more vigorous. They will convert primary alcohols to carboxylic acids [two steps “up”] in one flask.
What is secondary alcohol dehydration?
Secondary Alcohol Dehydration. Dehydration of alcohol requires a cleavage of a C-O bond with loss of a proton from the beta position. The result of dehydration is either an alkene or a mixture of the alkenes and the order of dehydration is first tertiary, then secondary, and finally primary.
What is the reaction of dehydration of alcohol?
The dehydration of either a tertiary or secondary alcohol is known as an E1 reaction (two-step mechanism), the dehydration of primary alcohol is an E2 (one step mechanism) reaction because of the difficulty encountered in forming primary carbocations. Share this with your friends. Share.
What is the name of the chemical reaction where water is formed from the extraction of the components of water from a single
Dehydration reaction is a type of chemical reaction wherein water is formed from the extraction of the components of water from a single reactant. An alkene is produced when dehydration of an alcohol is performed.
What happens when alcohol reacts with protic acids?
When alcohol reacts with protic acids it tends to lose a molecule of water in order to form alkenes. These reactions are generally known as dehydration of alcohols. It is a basic example of an elimination reaction. The rates differ for the primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols. The carbonation is very much stable in the case ...
Which alcohol is the easiest to dehydrate?
Tertiary forms of alcohol are easiest to dehydrate as the carbocations are more stable and thus easier to form compared to primary and secondary carbocations. For dehydration to take place, the alcohol must be heated to roughly 50⁰C in 5% H₂SO₄.
Which is stronger, alcohol or ether?
Alcohol and ethers possess leaving groups which are stronger Lewis bases than halide ions (is a halogen atom which has a negative charge). This makes alcohols and ethers less reactive than the alkyl halides (compounds where one or more hydrogen atoms in an alkane get replaced by halogen atoms). They need to be protonated before undergoing an elimination or substitution reaction.
Is secondary alcohol oxidized?
Secondary alcohol gets oxidized to ketones and primary are oxidized to carboxylic acids by the chromic acid. They are categorized as SN₂ reactions in primary alcohols and SN₁ reactions in secondary as well as tertiary alcohols. Tertiary alcohols tend to be easier to dehydrate and primary alcohols to be the hardest.
Nomenclature of Alcohol
The most common way of naming alcohol depends on the alkyl group and adding alcohol to it. The last letter ‘e’ in the word alkene is replaced with ‘ol’. The one which contains the longest carbon chain is treated as the parent chain and determines the numerals and the position of the groups, and the other substituent are indicated.
Dehydration of Alcohol
This is a simple elimination reaction. This happens when alcohols react with protic acid to undergo dehydration and lose a molecule of water to form an alkene. Such reactions are categorized as dehydration reactions. The rate of word dehydration might vary depending on the type of alcohol, like primary, secondary, or tertiary.
Reaction Mechanism of Dehydration of Alcohol
The process of dehydration of alcohols generally tries to follow the E1 or E2 Mechanism. Therefore, primary alcohol mostly tries to follow the E2 mechanism, while tertiary and secondary alcohols follow the E1 mechanism.
Example of Alcohol Dehydration Mechanism
The dehydrogenation of alcohol followed the E2 mechanism shows a different selectivity known as anti and syn elimination. Anti eliminations are when the products have resulted from the groups removed from opposite sides, while syn elimination is when the products have been formed from the groups removed from the same side.
Reaction of Alcohol Dehydration
A dehydration reaction is a form of chemical reaction in which water is formed from the extraction of the components of water from a single reactant. When dehydration of alcohol is performed, an alkene is formed. The structural equation of alcohol dehydration is:
Protonated Primary Alcohol
Dehydration can take place easily when a neighboring double bond is formed. Alcohol that carries a carbonyl group, two carbons away readily undergoes through a dehydration process and finally yields α, β- unsaturated carbonyl compound.
Secondary Alcohol Dehydration
The process of alcohol dehydration requires cleavage of the C-O bond along with loss of a proton from the beta position, whose consequences will be either alkenes or a mixture of alkenes. And the order of dehydration will be first tertiary, then secondary, and at last primary.
What is the major product of dehydration?
Dehydration of an alcohol gives the more stable alkene (more highly substituted) as the major product. The major product is 1-methylcyclohexene and methylenecyclohexane is the minor product.
What happens to the 2° carbocation?
The initially formed 2° carbocation undergoes a methyl shift to form a more stable 3° carbocation, which loses a proton to form 1,2-dimethylcyclohexane as the major product. The 2° carbocation can rearrange by an alkyl shift to form another 3° cation that loses a proton to form isopropylidenecyclopentane as a minor product.
class 5
The Fish Tale Across the Wall Tenths and HundredthsParts and Whole Can you see the Pattern?
class 9
Circles Coordinate Geometry What is Democracy? Why Democracy?Nazism and the Rise of Hitler Socialism in Europe and the Russian Revolution