
What bases are considered pyridamines?
Pyrimidines: Pyrimidine bases consist of a six-membered ring with two nitrogen atoms. The pyrimidine bases are – Cytosine (2-Oxy-4-amino pyrimidine): (C5H6O2N5), found in both RNA and DNA, is a white crystalline substance, with MW=111.12 daltons and a melting point 320 to 325 C.; Thymine (2, 4-dioxy-5-methyl pyrimidine): (C5H6O2N2), found in DNA molecules only, has MW=126.13 Daltons.
Which bases are purines, guanine or adenine and why?
What are the 4 types of mutation?
- Germline mutations occur in gametes. Somatic mutations occur in other body cells.
- Chromosomal alterations are mutations that change chromosome structure.
- Point mutations change a single nucleotide.
- Frameshift mutations are additions or deletions of nucleotides that cause a shift in the reading frame.
Which two bases are considered purines?
Purine and Pyrimidine Metabolism
- Overview. One of the important specialized pathways of a number of amino acids is the synthesis of purine and pyrimidine nucleotides.
- Nomenclature. ...
- Hydrolysis of Polynucleotides. ...
- Purine Catabolism. ...
- Pyrimidine Catabolism. ...
- De Novo Synthesis of Purine Nucleotides. ...
- De Novo Synthesis of Pyrimidine Nucleotides. ...
- Interconversion of Nucleotides. ...
- Salvage of Bases. ...
What kind of structure does a pyrimidine base have?
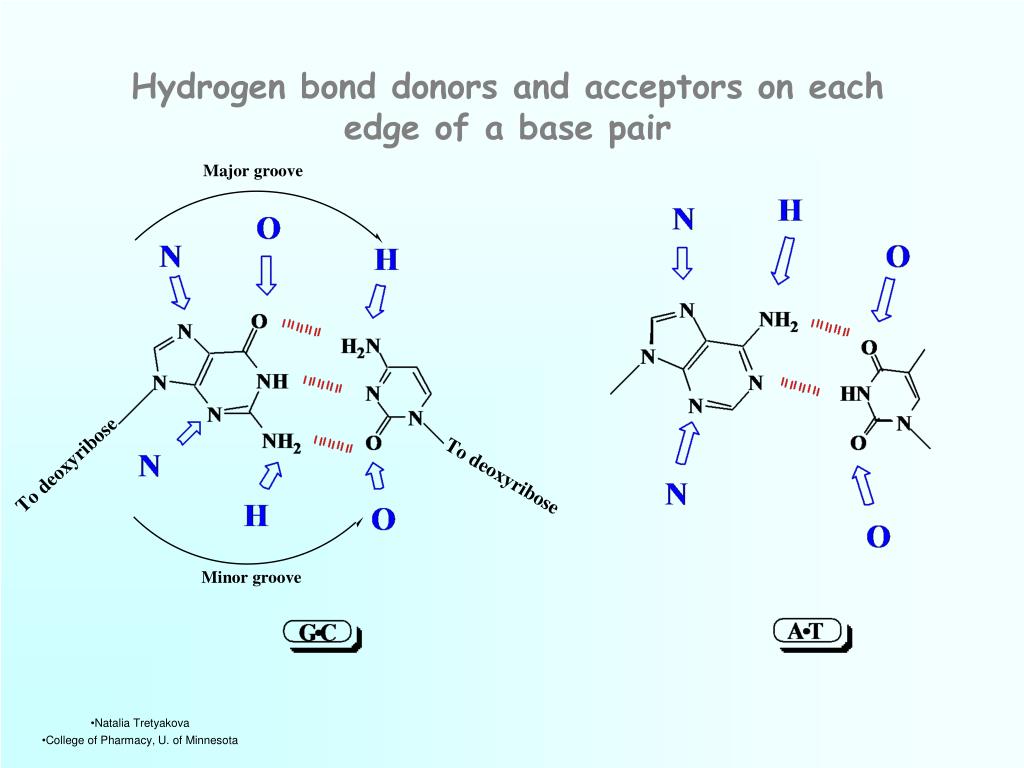
Pyrimidines are aromatic nitrogen heterocycles with a structure similar to benzene but containing two nitrogen atoms at the 1 and 3 positions of the ring. Cytosine and thymine are the two major pyrimidine bases in DNA and base pair (see Watson–Crick Pairing) with guanine and adenine (see Purine Bases), respectively.
What three bases are pyrimidines?
The pyrimidine bases are thymine (5-methyl-2,4-dioxipyrimidine), cytosine (2-oxo-4-aminopyrimidine), and uracil (2,4-dioxoypyrimidine) (Fig.
What are pyrimidine examples?
One of two chemical compounds that cells use to make the building blocks of DNA and RNA. Examples of pyrimidines are cytosine, thymine, and uracil. Cytosine and thymine are used to make DNA and cytosine and uracil are used to make RNA.
Which 2 DNA bases are pyrimidines?
The pyrimidines in DNA are cytosine and thymine; in RNA, they are cytosine and uracil. Purines are larger than pyrimidines because they have a two-ring structure while pyrimidines only have a single ring.
Which are the purine bases?
The most important biological substituted purines are adenine and guanine, which are the major purine bases found in RNA and DNA. In DNA, guanine and adenine base pair (see Watson-Crick pairing) with cytosine and thymine (see pyrimidines) respectively.
What is purine and pyrimidine bases?
Purines (adenine and guanine) are two-carbon nitrogen ring bases while pyrimidines (cytosine and thymine) are one-carbon nitrogen ring bases. Also Read: Amino Acids. Given below in a tabular column are the differences between Purines and Pyrimidines.
Is cytosine a pyrimidine?
cytosine, a nitrogenous base derived from pyrimidine that occurs in nucleic acids, the heredity-controlling components of all living cells, and in some coenzymes, substances that act in conjunction with enzymes in chemical reactions in the body.
Is guanine a purine or pyrimidine?
Purines and Pyrimidines are nitrogenous bases that make up the two different kinds of nucleotide bases in DNA and RNA. The two-carbon nitrogen ring bases (adenine and guanine) are purines, while the one-carbon nitrogen ring bases (thymine and cytosine) are pyrimidines.
Which nucleotides are pyrimidines?
Adenine and guanine are purine nucleotides, while cytosine, uracil, and thymine are pyrimidine nucleotides.
What are pyrimidines in DNA?
The pyrimidines found in DNA are Cytosine (C) and Thymine (T). They are capable of complimentary base pairing with the purines Guanine (G) and Aden...
What are the three pyrimidine bases?
Cytosine, thymine, and uracil are the three pyrimidine bases. Cytosine is found in both DNA and RNA, thymine is present only in DNA, and uracil is...
What are the pyrimidine bases and their structures?
The pyrimidine bases are modified pyrimidines which form the nucleotides of DNA and RNA. They are aromatic heterocyclic compounds composed of a six...
What are Pyrimidines?
A pyrimidine is an organic compound known as an aromatic heterocyclic compound and has the molecular formula of C 4 H 4 N 2. Heterocyclic compounds are stable, ring-shaped compounds in which not all atoms in the ring are carbon (Figure 1) .
Pyrimidine Bases
There are three pyrimidine bases found in nucleic acids: thymine (T), cytosine (C), and Uracil (U). These bases are substituted pyrimidines as they have molecular formulas which have been slightly altered from the generic C 4 H 4 N 2 formula (Figure 2).
Pyrimidines in DNA
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) contains the pyrimidines cytosine and thymine. Uracil is not present in DNA. In DNA, pyrimidines will form hydrogen bonds with another class of nucleotides, known as purines.
What is pyrimidine made of?
Pyrimidine Definition. Pyrimidines are simple aromatic compounds composed of carbon and nitrogen atoms in a six-membered ring. The term pyrimidine is also used to refer to pyrimidine derivatives, most notably the three nitrogenous bases that, along with the two purines, are the building blocks of both deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) ...
Where are pyrimidine nitrogenous bases found?
The pyrimidine nitrogenous bases are derived from the organic compound pyrimidine through the addition of various functional groups. The three pyrimidines are thymine which is only found in DNA, uracil which is only found in RNA, and cytosine which is found in both DNA and RNA.
What are the functions of pyrimidine nitrogenous bases?
Their function is two-fold: to pass information from parent to offspring through replication, mitosis, and meiosis, and between different organisms through horizontal gene transfer; and to encode genes and regulatory information.
What are the three nitrogenous bases?
Structure of Nitrogenous Bases. The three pyrimidine nitrogenous bases, thymine (T), cytosine (C), and uracil (U), are modified forms of the aromatic compound pyrimidine. They consist of a six-membered ring with two nitrogen atoms and four carbon atoms, but instead of being an aromatic ring with alternating double and single bonds they all have ...
What is the neurotoxin tetrodotoxin?
For example, the neurotoxin tetrodotoxin is a pyrimidine derivative. It is found in a number of species including the Japanese puffer fish, the blue-ringed octopus, and the orange-bellied newt. Tetrodotoxin prevents the transmission of nerve signals and can result in paralysis and death.
What are the effects of pyrimidines on DNA?
The nucleotides can be altered through oxidation, methylation, amination, or the addition of other functional groups such as aldehydes, thioketones, and alcohols These modifications often result in deleterious effects such as altering gene expression or disrupting replication. Modifications are more prevalent in RNA than DNA, particularly in small nuclear RNA (snRNA).
What are the functions of pyrimidine?
These derivatives play a variety of functions, from production of amino acids and proteins, contributing to an organisms’ health, providing vital nutrients, boosting the immune system, or antagonising and destroying cells. For example, the neurotoxin tetrodotoxin is a pyrimidine derivative. It is found in a number of species including the Japanese puffer fish, the blue-ringed octopus, and the orange-bellied newt. Tetrodotoxin prevents the transmission of nerve signals and can result in paralysis and death.
What are the two classes of pyrimidines?
Pyrimidine is one of two classes of heterocyclic nitrogenous bases found in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA: in DNA the pyrimidines are cytosine and thymine, in RNA uracil replaces thymine.
What is the name of the nitrogenous base in DNA?
2021-07-10. Create. 2004-09-16. Pyrimidine is one of two classes of heterocyclic nitrogenous bases found in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA: in DNA the pyrimidines are cytosine and thymine, in RNA uracil replaces thymine.
Is pyrimidine a diazine?
Pyrimidine is the parent compound of the pyrimidines; a diazine having the two nitrogens at the 1- and 3-positions. It has a role as a Daphnia magna metabolite. It is a member of pyrimidines and a diazine.
What is the name of the compound that is derived from pyrimidine?
2. (Elements & Compounds) Also called: pyrimidine baseany of a number of similar compounds having a basic structure that is derived from pyrimidine, including cytosine, thymine, and uracil, which are constituents of nucleic acids
What are the elements in pyrimidine?
Any of a group of organic compounds having a single ring with alternating carbon and nitrogen atoms. Pyrimidines include the bases cytosine, thymine, and uracil, which are components of nucleic acids.
What happens if radiation damage is sufficient to change or delete a purine or pyrimidine base?
If the radiation damage is sufficient to change or delete a purine or pyrimidine base, a point lesion may occur.
What are the building blocks of DNA and RNA?
The presence of pyrimidine basein thymine, cytosine, and uracil, which are the essential building blocks of nucleic acids DNA and RNA, is one possible reason for their widespread therapeutic applications.
What is pyrimidine derivative?
1. a heterocyclic compound, C 4 H 4 N 2, that is the basis of several important biochemical substances. 2. one of several pyrimidine derivatives, esp. the bases cytosine, thymine, and uracil, which are fundamental constituents of nucleic acids. [1880–85;b. pyridine and imide]
What is modified with polyaminophenols?
Electrodes modified with polyaminophenols: immobilization of purines and pyrimidines
What is the name of the compound that forms after UVA exposure?
After UVA exposure bind with py rimidine baseto form cyclobutane monoadducts
Where are thymine and uracil found?
Cytosine, thymine, and uracil are the pyrimidines found in nucleic acids. Cytosine can be found in DNA and RNA. Thymine is found in DNA, while uracil is found in RNA. Some kinds of RNA contain a few more modified pyrimidine bases, such as dihydrouracil and 5-methyl cytosine.
What are the two types of nitrogenous bases?
Two important types of nitrogenous bases; the purines and Pyrimidines are present in nucleic acids.
How is a nucleotide formed?
A nucleotide or nucleoside mono-phosphate is formed when a nucleoside is esterified to a phosphate group. A nucleoside diphosphate is formed when a second phosphate is esterified to the existing phosphate group. A nucleoside triphosphate is formed when a third phosphate group is attached to a nucleoside. Nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) are nucleoside monophosphate polymers.
Why are minor bases called minor bases?
These bases are called minor bases because they are found in modest concentrations in nucleic acids. Hypoxanthine (6-oxopurine) and xanthine are the two (2, 6-di-oxopurine).
What are the bases of nucleic acids?
Purine and Pyrimidine Bases of Nucleic Acids | Nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids, including deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). The storage and transmission of genetic information is dealt with by nucleic acids. A nucleotide derivative is the universal currency of energy, ATP. Important co-enzymes like NAD+ and FAD, as well as metabolic regulators like cAMP and cGMP, are made up of nucleotides.
