What is the structure of serine amino acids?
The Structure of Serine. The side chain group is shown by R when diagramming amino acids, leading scientists to call the side change the R group. The specific structure of serine is indicative of its chemical formula, C3H7NO3. The R group structure, CH3O, attaches to the central carbon of the amino acid back bone.
What is serine?
- Functions and Structure of Serine with Examples Serine is a non-essential amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. They are derived from an amino acid glycine. They are obtained by the hydrolysis.
Is serine hydrophilic or hydrophobic?
The hydroxyl side chains and the amino groups in serine can form hydrogen bonds, which makes serine a hydrophilic molecule. The general structure of amino acids simply consists of an amino group, a carboxyl group, and a side chain attached to a central carbon atom.
Is serine polar or nonpolar in nature?
The R group structure, CH3O, attaches to the central carbon of the amino acid back bone. Remember, that's the carbon along with the amino and carboxyl groups. Serine is polar in nature. That means that the serine molecule is both positively and negatively charged.

What is the structure of amino acid serine?
Serine structure consists of the basic backbone of every amino acid: a carboxyl group −COOH − C O O H , an amino group −NH2 − N H 2 , a central carbon, and a hydroxymethyl CH2OH C H 2 O H as a side chain (R). The serine formula is C3H7NO3 C 3 H 7 N O 3 .
Is serine S or R?
D-serine is the R-enantiomer of serine. It has a role as a NMDA receptor agonist, a human metabolite and an Escherichia coli metabolite. It is a D-alpha-amino acid and a serine. It is a conjugate base of a D-serinium.
Is serine L or D?
Serine is an amino acid. An amino acid is a building block for protein. Serine comes in two forms: L-serine and D-serine. L-serine can be consumed in the diet.
What is serine and how it is formed?
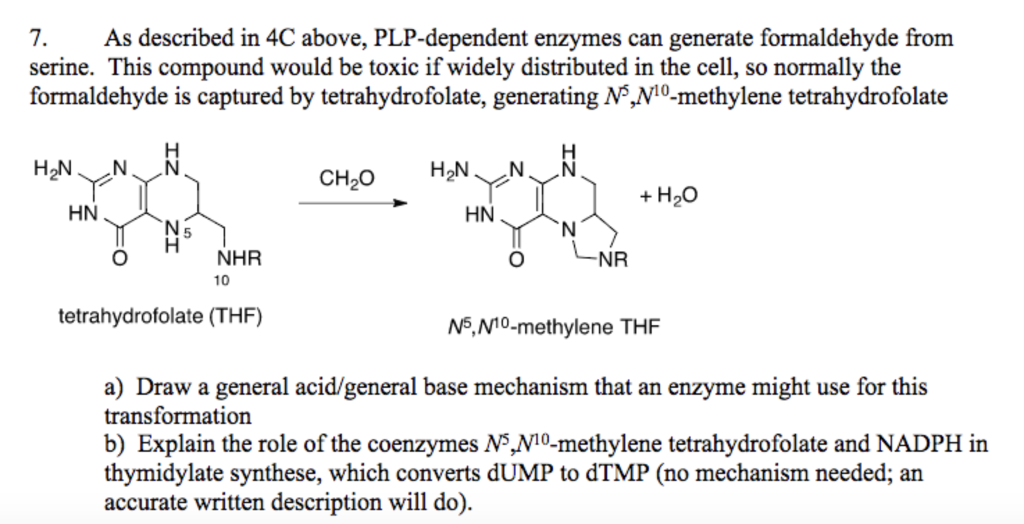
Serine is formed from the glycolytic intermediate 3-phosphoglycerate in a three-step pathway beginning with the conversion of 3-phosphorylglycerate hydroxyl group to a ketone yielding 3-phosphohydroxypyruvate. Transamination of 3-phosphohydroxypyruvate forms phosphoserine that, upon hydrolysis, yields serine.
What is R group of serine?
Serine is the amino acid's with its R group with a hydroxyl group attached to a CH2 group.
What is R group in amino acid?
An R-Group is a side chain attached to the α-carbon of all amino acids. It decides the chemical versatility of the amino acid. For example, some R-Groups carry a charge, creating a polar molecule. Some R-groups are hydrophobic or hydrophillic.
Does L-serine turn into D-serine?
Then, L-serine is exported to neurons where it is converted into D-serine by neuronal SR. Once released by neurons, D-serine binds to the co-agonist site of NMDARs.
Where is D-serine found?
As in other brain areas, D-serine has been localized within specific glia cells bodies of the cerebellum. In particular, high levels of D-serine are found in the radial processes and end feet of Bergmann glia surrounding Purkinje cell dendrites (Schell et al., 1997; Wolosker et al., 1999).
What functional group is serine?
hydroxyl amino acidsSerine is one of two hydroxyl amino acids. Both are commonly considered to by hydrophilic due to the hydrogen bonding capacity of the hydroxyl group.
What is special about serine?
Serine is generally classified as a nutritionally nonessential (dispensable) amino acid, but metabolically, serine is indispensible and plays an essential role in several cellular processes. Serine is the major source of one-carbon units for methylation reactions that occur via the generation of S-adenosylmethionine.
Is serine polar or nonpolar?
Six amino acids have side chains that are polar but not charged. These are serine (Ser), threonine (Thr), cysteine (Cys), asparagine (Asn), glutamine (Gln), and tyrosine (Tyr).
Is serine a neutral amino acid?
The digestion of cellular proteins is also an important source for amino acids....Amino acids.Amino acidserineSingle Letter CodeSThree Letter CodeSerCharge (+/-/ neutral)neutralPolaritypolar19 more columns•Dec 6, 2018
What functional group is serine?
hydroxyl amino acidsSerine is one of two hydroxyl amino acids. Both are commonly considered to by hydrophilic due to the hydrogen bonding capacity of the hydroxyl group.
What is the R group found in alanine?
methyl group CH3The R side chain in alanine is the methyl group CH3.
Is serine polar neutral?
Serine, threonine, glutamine, and asparagine are polar but neutral (uncharged) amino acids. These side chains can form multiple hydrogen bonds, so they prefer to project into the aqueous phase.
Does serine have an ionizable side chain?
P.S.: Actually, serine side chain is also ionizable, although it requires stronger bases most likely incompatible with any biological experiment.
What is serine used for?
Serine is used to improve cognitive abilities. D-serine specifically is used to activate NDMA receptors, which are neurotransmitters in the brain....
What type of amino acid is serine?
Serine is a non-essential amino acid; meaning that the body doesn't need to rely on food and external things to make it. The body can generate seri...
What food contains serine?
The food items that contain serine are: Meat products. Dairy products like milk, cheese, yogurt. Nuts like walnuts, peanuts, and almonds. Leafy...
What is the structure of a serine?
The structure of alpha amino acid is stated below. R = Side Chain that is specific to each amino acid.
Where is serine found?
They are found in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Serine’s side chain as a residue of proteins can undergo O-linked glycosylation. The residues of phosphorylated serine are referred as phosphoserine. L- serine tastes sour at a very high concentration.
What is the R side chain?
R = Side Chain that is specific to each amino acid. These two optical isomers of amino acids, and they are termed L and D. They represent the huge majority of amino acids that sunders in most of the amino acids. They actively participate in the protein synthesis. The synthesis of mammalian proteins involves only the L-Stereoisomers.
Where is serine protease found?
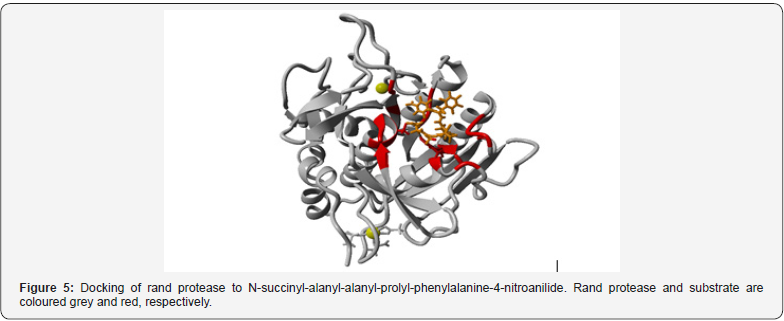
Serine protease that is found in the digestive system break down the proteins that are helping an enzyme catalyze in its reaction. A serine protease is an enzyme that sunders peptide bonds in proteins. They are found in prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
What is the function of serine?
Function of Serine. Serine plays an important role in the synthesis of many biological vital compounds namely glycine, cystine, purines, pyrimidines, phosphides, proteins and much more. It plays a crucial role in metabolism.
What is the amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins?
Serine is a non-essential amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. They are derived from an amino acid glycine. They are obtained by the hydrolysis. They do not require literary resources and can be synthesized from glucose. L-isomer is the only form of serine that is involved in the synthesis of proteins in humans.
What is the amino acid serine?
The amino acid serine is one of these non-essential amino acids and an important component in metabolism and the formation of nucleotides. You might see serine abbreviated as (ser) or (s) in articles and diagrams. Serine is also the starting molecule to other amino acids, such as glycine and cysteine in bacteria. It's also a building block to other nutrients such as folate, and it is vital for baby health and growth.
What is the role of serine in the body?
Serine's side-chain structure, the component of amino acid that makes is unique, is CH3O. Its structure is polar, giving it hydrophilic properties. There are many important roles that serine plays in biological processes. For example, it is vital in metabolism, playing an important role in the formation of enzymes. It is also a signaling chemical in the brain, specifically transmitting information related to memory. Supplemental serine has even shown potential in fighting schizophrenia or Lou Gehrig's disease. Serine is obtained from synthesis within the body and it can also be consumed through meat, soy products, dairy and plants, such as peanuts. Without serine many metabolites, including the building blocks of genetic code and chemicals vital to life would not be formed.
What makes serine so important?
What makes serine so important and versatile is its structure. In general, all amino acids have the same structure: an amino group attached to a hydrogen, a carboxyl group and a side chain group, all connected to a central carbon. The amino and carboxyl groups and central carbon are considered the amino acid backbone. That backbone is the same in all amino acids. It is the side chain that is specific to each amino acid. It is this side chain that distinguishes each amino acid from the others. The side chain group is shown by R when diagramming amino acids, leading scientists to call the side change the R group. The specific structure of serine is indicative of its chemical formula, C3H7NO3. The R group structure, CH3O, attaches to the central carbon of the amino acid back bone. Remember, that's the carbon along with the amino and carboxyl groups. Serine is polar in nature. That means that the serine molecule is both positively and negatively charged. This polar characteristic makes serine hydrophilic, or water-loving.
What is serine used for?
Serine is also used in the body as a signaling chemical in the brain to form memories. Research has shown that large doses of serine may be able to help patients with schizophrenia or Lou Gehrig's disease, also known as ALS.
What are the building blocks of chemicals?
Amino acids are the building blocks of chemicals that are vital to your very life. In this lesson, you will learn about one amino acid in particular - serine. You will discover its structure and learn how it is the building block of many chemicals.
What is the D-serine receptor?
D-serine is a selective full agonist at the glycine site of N-methyl-D-aspartate ( NMDA )-type glutamate receptor.
What is D-serine agonist?
D-serine is a selective full agonist at the glycine site of N-methyl-D-aspartate ( NMDA )-type glutamate receptor. Hypofunction of NMDA type of neurotransmission is believed to play a major role in pathophysiology of schizophrenia, therefore, administration of D-serine and subsequent activation of NMDA receptors may alleviate psychotic tendencies.
Is D-serine an enantiomer?
D-serine is the R-enantiomer of serine. It has a role as a NMDA receptor agonist, a human metabolite and an Escherichia coli metabolite. It is a D-alpha-amino acid and a serine. It is a conjugate base of a D-serinium. It is a conjugate acid of a D-serinate. It is an enantiomer of a L-serine. It is a tautomer of a D-serine zwitterion.
Does D-serine help with schizophrenia?
Hypofunction of NMDA type of neurotransmission is believed to play a major role in pathophysiology of schizophrenia, therefore, administration of D-serine and subsequent activation of NMDA receptors may alleviate psychotic tendencies.