
What is the lamina propria?
The lamina propria is one of three layers which make up the mucosa, or mucous membrane. The lamina propria is a large layer of connective tissue which separates the innermost layer of epithelial cells from a layer of smooth muscle tissue called the muscularis mucosa.
Where do lymphatics drain into the lamina propria?
Lymphatics penetrate the mucosa and lie below the basement membrane of the epithelium, from there they drain the lamina propria. The fast rate of cell death and regeneration of the epithelium leaves behind many apoptotic cell bodies. These have been found to go into the lamina propria, most of which are inside its macrophages.
Why is the lamina propria of the lungs arranged around vessels?
Therefore, the lamina propria of the lungs is arranged around and between these vessels, providing maximum surface area. In the intestines, there is less of a need gas exchange. Instead, the lamina propria is modified to allow the passage of a large number of ducts, which connect to the liver, pancreas and salivary glands.
What is the function of collagen in the lamina propria?
The collagen in the lamina propria of elastic organs has been shown to play a major role in mechanical function. In the bladder the collagen composition of its lamina propria allows for structure, tensile strength, and compliance, through complex coiling. It has been suggested that myofibroblasts also reside in the lamina propria of several organs.
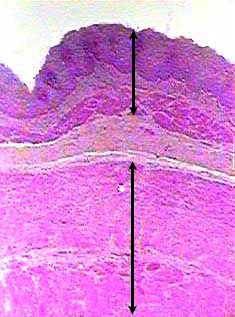
Where is lamina propria found?
mucous membraneA type of connective tissue found under the thin layer of tissues covering a mucous membrane.
What are the three layers of the lamina propria?
The vocal folds are made up of three major layers from deep to superficial:The Vocalis Muscle (labeled above as the muscularis)The Lamina Propria (really 3 layers: deep, intermediate, and superficial)The epithelium or epithelial tissue.
Which layer contains the lamina propria quizlet?
The mucosa contains a lamina propria (areolar connective tissue) and a muscularis mucosae (smooth muscle).
How many layers are in lamina propria?
three layersThe lamina propria is one of three layers which make up the mucosa, or mucous membrane. The lamina propria is a large layer of connective tissue which separates the innermost layer of epithelial cells from a layer of smooth muscle tissue called the muscularis mucosa.
What makes up the lamina propria?
The lamina propria is composed of noncellular connective tissue elements, i.e., collagen and elastin, blood and lymphatic vessels, and myofibroblasts supporting villi. However, the main characteristic of the lamina propria is to contain numerous immunologically competent cells as well as nerve endings.
Is the lamina propria part of the submucosa?
The mucosa consists of the epithelium itself and also the supporting loose connective tissue, called lamina propria, immediately beneath the epithelium. Deeper connective tissue which supports the mucosa is called the submucosa....Basic Tissues.Epithelial Tissue / GlandsConnective TissueNervous TissueMuscle TissueJun 14, 2022
What are the three layers of the muscularis externa of the stomach quizlet?
The muscluaris externa is a layer of smooth muscle in divided into three layers (the inner oblique, middle circular, and outer longitudinal). The serosa is simple squamous epithelium covering the outer surface where it protrudes into the peritoneal cavity is also referred to as the visceral peritoneum?
Which layer becomes the inner layer of the digestive tract quizlet?
mucosa = inner lining of digestive tract.
What are the layers of the intestine from inner to outer quizlet?
Mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa, and serosa.
What are the 3 layers of the digestive system?
General Structure of the Digestive SystemMucosa.Submucosa.Muscular layer.Serous layer or serosa.
What are the 4 layers of the small intestine?
Four-layered (mucosa, submucosa, muscularis mucosa, and serosa) organization of the digestive tract.
What are the 4 layers of GI tract?
The GI tract contains four layers: the innermost layer is the mucosa, underneath this is the submucosa, followed by the muscularis propria and finally, the outermost layer - the adventitia. The structure of these layers varies, in different regions of the digestive system, depending on their function.
What is lamina propria and what is its function?
Lamina propria is the thin layer of connective tissue beneath the epithelium of an organ. The lamina propria supports the epithelial cells and allows them to move with respect to deeper structures. Together, the epithelium and lamina propria form the mucous membrane.
What is the difference between lamina propria and basal lamina?
The lamina propria forms the connective tissue core of the villi and surrounds the crypt epithelium. The crypt and villus epithelial cells and the lamina propria are separated by a distinct basement membrane composed of an ultrastructurally apparent basal lamina and a deeper network of collagenous fibers.
What is the innermost layer of the GI tract?
The mucosa is the innermost layer of the GI tract. It consists of epithelium, lamina propria, and muscularis mucosa. The submucosa is connective tissue. Within it are lymphatic vessels and nerve plexuses. Meissner's plexus is located in the submucosa. The muscularis externa consists of thick layers of smooth muscle.
Which epithelium is lined with mucous surface cells?
The epithelium on the stomach is lined by mucous surface cells which are a simple columnar epithelium.
What are the features of the small intestine?
There are several features of the small intestine. The lymphatic capillary within a villus of the small intestine is a lacteal. Crypts of Lieberkuhn are the intestinal glands. The plica circulares is a projection with a core of submucosa. The plica circulares is also called the valve of Kerckring.
Which papillae do not contain taste buds?
Filiform papillae are the only papillae on the tongue which do not contain taste buds. Circumvallate papillae large papillae arranged in a "V" shape. Fungiform papillae are mushroom shaped. Foliate papillae are not well developed in man and are seen on the edges of the tongue.
Where are the papillae on the tongue located?
The papillae on the tongue are located anteriorly to the sulcus terminalis. The tongue contains primarily three types of papillae: filiform papillae, circumvallate papillae and fungiform papillae. The filiform papillae are the smallest and most abundant.
What is the submucosa?
The submucosa is connective tissue. Within it are lymphatic vessels and nerve plexuses. Meissner's plexus is located in the submucosa.
What is the lymphatic capillary in the small intestine?
The lymphatic capillary within a villus of the small intestine is a lacteal.
Why is the lamina propria important?
Because the epithelium is often under external stress and is somewhat delicate, the lamina propria hosts many immune cells. In the intestinal tract the immune system must have tolerance to the normal intestinal flora, yet respond to pathogenic microorganisms. Imbalance of this causes inflammation diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease. The lamina propria’s richness in macrophages and lymphoid cells makes it a key place for immune responses to occur. It forms part of the barrier that protects internal tissues from external pathogenic microorganisms, especially from the gastrointestinal tract.
What is the thin layer of connective tissue?
Thin connective layer forming part of the mucous membranes. Lamina propria. The lamina propria , a thin layer of connective tissue, is part of the mucosa. Here is an example of the mucosa of the mouth. Details.
What is the mucosa?
Thus, the term mucosa or mucous membrane refers to the combination of the epithelium and the lamina propria. The connective tissue of the lamina propria is loose and rich in cells. The cells of the lamina propria are variable and can include fibroblasts, lymphocytes, plasma cells, macrophages, eosinophilic leukocytes, and mast cells.
What is the name of the thin layer of connective tissue that forms part of the moist linings of the?
Mucosa. Identifiers. Latin. lamina propria mucosæ. FMA. 62517. Anatomical terminology. The lamina propria is a thin layer of connective tissue that forms part of the moist linings known as mucous membranes or mucosa, which line various tubes in the body, such as the respiratory tract, the gastrointestinal tract, and the urogenital tract.
Where do myofibroblasts live?
It has been suggested that myofibroblasts also reside in the lamina propria of several organs. These cells have characteristics of both smooth muscle and fibroblasts. The lamina propria may also be rich in vascular networks, lymphatic vessels, elastic fibers, and smooth muscle fascicles from the muscularis mucosae.
Where do lymphatics drain?
Lymphatics penetrate the mucosa and lie below the basement membran e of the epithelium, from there they drain the lamina propria. The fast rate of cell death and regeneration of the epithelium leaves behind many apoptotic cell bodies.
Which organs require expansion?
The connective tissue and architecture of the lamina propria is very compressible and elastic, this can be seen in organs that require expansion such as the bladder. The collagen in the lamina propria of elastic organs has been shown to play a major role in mechanical function.

Overview
- The lamina propria varies in chemical composition from animal to animal, and from organ to organ. In general, the lamina propria is a complex mesh of extracellular proteins and structural molecules. These molecules include collagen, a standard animal structural protein, as well as la…
Structure
Function
Clinical significance
The lamina propria is a thin layer of connective tissue that forms part of the moist linings known as mucous membranes or mucosa, which line various tubes in the body, such as the respiratory tract, the gastrointestinal tract, and the urogenital tract.
The lamina propria is a thin layer of loose (areolar) connective tissue, which lies beneath the epithelium, and together with the epithelium and basement membrane constitutes the mucosa. A…
See also
The lamina propria is a loose connective tissue, hence it is not as fibrous as the underlying connective tissue of the submucosa. The connective tissue and architecture of the lamina propria is very compressible and elastic, this can be seen in organs that require expansion such as the bladder. The collagen in the lamina propria of elastic organs has been shown to play a major role in mechanical function. In the bladder the collagen composition of its lamina propria allows for …
External links
Because the epithelium is often under external stress and is somewhat delicate, the lamina propria hosts many immune cells. In the intestinal tract the immune system must have tolerance to the normal intestinal flora, yet respond to pathogenic microorganisms. Imbalance of this causes inflammation diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease. The lamina propria’s richness in macrophages and lymphoid cells makes it a key place for immune responses to occ…