
What is the primary function of the epidermis?
What does the epidermis do? The primary function of the epidermis is to protect your body by keeping things that might be harmful out and keeping the things your body needs to function properly in. Bacteria, viruses and other infectious agents are kept out, helping prevent infections on your skin. Asel Treffeisen Explainer
What are the 4 cells of the epidermis?
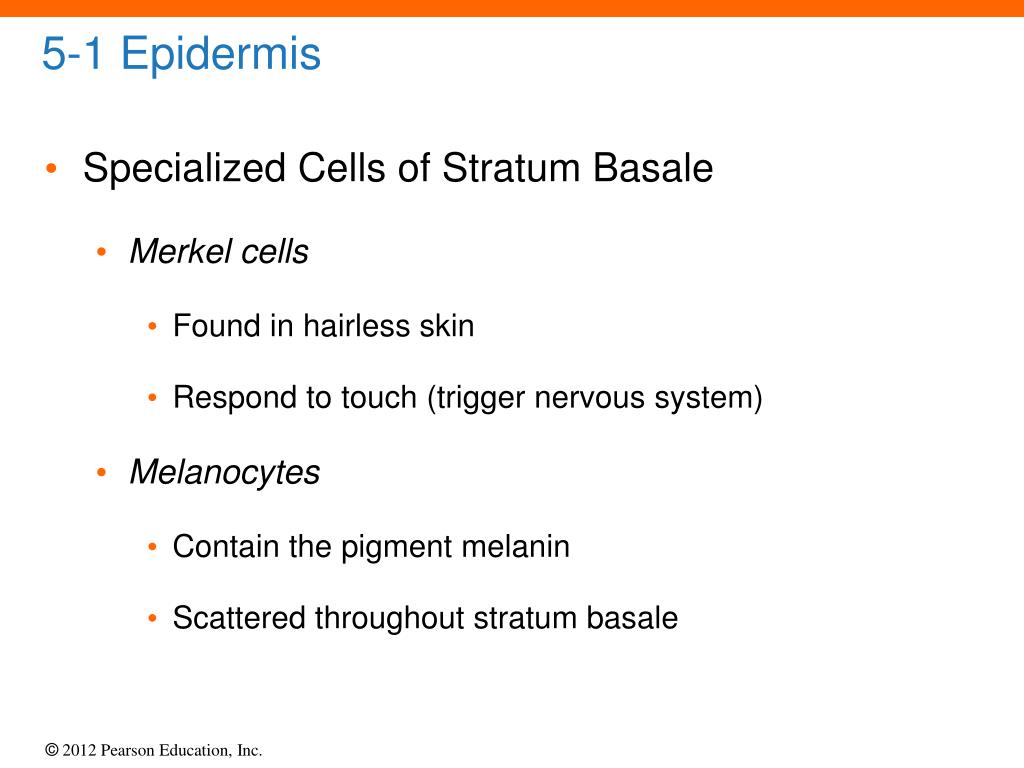
CELLS OF THE EPIDERMIS; The epidermis is made up of four cells. (1) Keratinocyte (2) Melanocyte (3) Langerhans cells (4) Merkel cell. KERATINOCYTE; These cells are arranged in layers within the epidermis. As the keratinocyte gets closer to the surface of the skin, produces keratin.
What are the five layers of the epidermis?
- (1) Keratinocyte
- (2) Melanocyte
- (3) Langerhans cells
- (4) Merkel cell
What are the two main layers of the dermis?
- The Basal Cell Layer.
- The Squamous Cell Layer.
- The Stratum Granulosum & the Stratum Lucidum.
- The Stratum Corneum.
- The Papillary Layer.
- The Reticular Layer.
What do the dermis and epidermis make up?
Three layers of tissue make up the skin: Epidermis, the top layer. Dermis, the middle layer. Hypodermis, the bottom or fatty layer.
What forms the epidermis of the skin?
stratified squamous epitheliumThe epidermis of the skin is a constantly renewing stratified squamous epithelium. It consists mostly of keratinocytes, but also of Langerhans cells, melanocytes, and Merkel cells resting on a supporting dermis that contains the nerve and vascular networks, which nourish the epidermis.
Which cells form the epidermis?
What are the 3 major cells that make up the epidermis?Keratinocytes: Keratinocytes produce the protein keratin, which is the main component of the epidermis.Melanocytes: Melanocytes make your skin pigment, known as melanin.Langerhans cells: Langerhans cells prevent things from getting into your skin.
What makes up most of the dermis?
[1] The composition of the dermis is mainly fibrous, consisting of both collagen and elastic fibers. Between the fibrous components lies an amorphous extracellular "ground substance" containing glycosaminoglycans, such as hyaluronic acid, proteoglycans, and glycoproteins.
What is epidermis layer of skin?
The epidermis is the thin outer layer of the skin. It consists of 3 types of cells: Squamous cells. The outermost layer is continuously shed is called the stratum corneum.
What is the main tissue of the epidermis?
The epidermis consists of stratified squamous epithelium. That means it consists of layers of flattened cells. Skin, hair and nails are keratinised, meaning they have a dead and hardened impermeable surface made of a protein called keratin.
What are the four types of cells that make up the epidermis?
Cell types in the epidermis include keratinocytes that produce keratin and make up 90 percent of epidermal cells, melanocytes that produce melanin, Langerhans cells that fight pathogens in the skin, and Merkel cells that respond to light touch. The epidermis in most parts of the body consists of four distinct layers.
How many layers make up the epidermis?
The epidermis is the topmost layer of skin – the one you can see and feel on the surface. It contains four to five layers (depending on body location), each with an important role. These 5 layers constantly renew themselves in a process called Exfoliation and desquamation of the skin.
What is the difference between dermis and epidermis?
Your epidermis is the top layer, and your dermis is the middle layer. Your dermis exists between your epidermis and hypodermis. Your epidermis is the thinnest layer of skin. It helps hydrate your body, produces new skin cells, protects your body from damage and makes melanin, which provides skin color.
What type of tissue makes up the dermis?
The dermis consists of dense, fibrous connective tissue whose predominant connective tissue component is collagen.
What makes up 80% of the dermis?
Underlying the papillary layer is the much thicker reticular layer, composed of dense irregular connective tissue which resists forces in many directions attributing to the flexibility of the skin. This layer makes up around 80% of the dermis and is well vascularized and has a rich sensory and sympathetic nerve supply.
What are the two main connective tissues in the dermis?
The three types of connective tissue include collagen, reticular fibers, and elastin. The dermis only houses collagen and elastin fibers.
What is plant epidermis made of?
The plant epidermis consists of three main cell types: pavement cells, guard cells and their subsidiary cells that surround the stomata and trichomes, otherwise known as leaf hairs.
What are the 5 layers of the epidermis in order?
The epidermis is subdivided into five layers or strata:stratum basale.stratum spinosum.stratum granulosum.stratum lucidum.stratum corneum.
What material makes the epidermis tough?
Almost 90% of the epidermis is made of cells known as keratinocytes. Keratinocytes develop from stem cells at the base of the epidermis and begin to produce and store the protein keratin. Keratin makes the keratinocytes very tough, scaly and water-resistant.
What is the stratum corneum?
The stratum corneum is the outermost layer of the epidermis and marks the final stage of keratinocyte maturation and development. Keratinocytes at the basal layer of the epidermis are proliferative, and as the cells mature up the epidermis, they slowly lose proliferative potential and undergo programmed destruction.
Function
Each layer of your skin works together to protect your body. Your dermis has many additional functions, including:
Anatomy
Your dermis is the middle layer of your skin, located between your epidermis (top layer) and hypodermis (bottom layer) in your skin.
Care
Your dermis is the middle layer of skin in your body. It has many important functions, including protecting your body from the outside world, supporting your epidermis, feeling different sensations and producing sweat. It’s important to take care of your dermis.
What is the difference between the dermis and epidermis?
The epidermis and dermis together form the basic body covering of the skin and both perform the function of protecting internal organs from dehydration , infectious diseases and other damages. Also Refer: Sense Organs.
What is Dermis?
The dermis is the layer of the skin present beneath the epidermis of the skin. This layer constitutes of fat, fibres, collagen and blood vessels which make the skin flexible and strong. The dermis is also involved in the synthesis of Vitamin D on exposure to sunlight. They are also involved in regulating body temperature.
What is the outermost layer of the human body?
Skin, the outermost layer of the human body serves as the body’s initial barrier against foreign particles. It is the largest organ of the human body and functions as a barrier between outside and inside environment. Skin is composed of different layers, cells, and tissues.
What are the three main areas of the human body?
Human skin plays an important role in overall health and well-being, which is divided into three main areas namely: dermis, epidermis and hypodermis. Here, in this article let us discuss the differences between dermis and epidermis. The main difference between epidermis and dermis lies in their structure. The various differences between the two are ...
Which layer of the dermis allows heat to radiate to the skin surface?
1) capillaries in the papillary layer in the dermis allow heat to radiate to the skin surface to cool off the body and will constrict blood flow temperarily 2) Sweat glands secrete perspiration that evaporates and takes amounts of body heat with it.
Which epidermal layer has the most mitoses?
major skin area where derivatives (nails and hair) reside. dermis. epidermal region exhibiting the most mitoses. stratum basale. most superficial epidermal layer. stratum corneum. has abundant elastic and collagenic fibers. dermis. region where melanocytes are most likely to be found.
Which protein in the skin toughens cells and pressure receptors causing the nervous system to be alerted by?
protein in the skin that toughens cells and pressure receptors causing the nervous system to be alerted by possible damage. keratin. immune cells that process antigen material and present it to the immune system for destruction. dendritic cells.
Which region of the body is most likely to have melanocytes?
region where melanocytes are most likely to be found. stratum basale. accounts for most of the epidermis. stratum corneum. what substance is manufactored in the skin (but is not a secretion) to play a role in calcium absorption elsewhere in the body? Skin is the site vitamin D synthesis for the body.
What happens if you get hit by a dermis injection?
Dermis is full of nerves, some respond to pain. If they get struck by the injection they send a message to the brain causing you to react to the "pain".
What are the layers of the dermis?
The dermis contains two layers : the outermost papillary layer and the deeper reticular layer. The thin papillary layer is composed of loose connective tissue and connects to the epidermis with papillae. Papillae may nourish the epidermis or act as touch receptors.
What are the two layers of skin?
Our skin has two principal layers : epidermis and dermis. The epidermis is composed of epithelial tissue, and the dermis is connective tissue. The dermis supports the epidermis and binds it to the subcutaneous tissue (hypodermis), the loose connective tissue directly under the skin. Diagram of different layers of skin :
Which layer of the skin contains sweat glands?
The reticular layer contains hair follicles, sweat glands, Pacinian corpuscles, which sense pressure, lymph vessels and smooth muscle. To read about the skin in more detail, check out this link. Answer link.
What is the thick reticular layer made of?
And the thick reticular layer is made of dense connective tissue with irregular bundles of collagen fibers ( dense irregular connective tissue ).
What are the structures of the dermis?
Structures found in the dermis include: 1 Connective tissues, specifically collagen and elastin 2 Blood capillaries (the smallest of blood vessels) and other small vessels 3 Lymph vessels 4 Sweat glands 5 Sebaceous glands (oil glands)—best known for its tendency of becoming clogged and causing the dreaded white heads of acne, it actually plays an important role in protecting the body 6 Nerve endings 7 Hair follicles —the body contains close to 2 million hair follicles
What is the role of the dermis?
It plays several key roles, including: Producing sweat and regulating the body's temperature: Within the dermis are sweat glands that produce sweat that comes out of the pores.
Why does the surface area of the epidermis decrease?
This results in less blood being made available from the dermis to the epidermis and fewer nutrients making it to this outer layer of skin. This flattening out of the connecting region also makes the skin more fragile.
What is the name of the skin cancer that starts in the dermis?
One type of tumor which begins in the dermis is called a dermatofibroma (or benign fibrous histiocytoma.) 8 These fairly common tumors often occur on the legs of middle-aged women. It's not known what exactly causes these tumors, but they frequently occur following some form of trauma.
How many sweat glands are there in the human body?
There are more than 2.5 million sweat glands in the body, and there are two different types: apocrine and eccrine. 2 Apocrine sweat glands are found in the more odorous parts of the body, including the armpits, scalp, and genital region.
What is the second layer of the skin?
The dermis is the second and thickest layer of the three major layers of skin, located between the epidermis and subcutaneous tissues, also known as the subcutis and the hypodermis . The skin was previously viewed as a body part that protects us from the elements. Today, new knowledge informs us that the layers of the skin are actually very complex ...
Why is it important to protect your epidermis from the sun?
Just as it's important to protect your epidermis from too much sun, it's important to protect your dermis as well. Sun exposure damages collagen (and causes changes in elastin), which can result in premature wrinkling. 6
