The Tibial Nerve provides innervation to the muscles of the lower leg and foot. Specifically: Triceps Surae ( the two headed Gastocnemius and Soleus); Plantaris, Popliteus; Tibialis Posterior; Flexor Digitorum Longus; and Flexor Hallucis Longus muscles. It also has articular and cutaneous branches.
What is the function of a tibial nerve?
The tibial nerve sends signals from the brain to the muscles in the back of your leg to get them to move. It controls movement in the following muscles: These muscles rotate your leg inward and flex your knees, ankles, and toes.
Where is tibial nerve located?
They are lateral and superficial to the popliteal artery and vein in a separate sheath. The tibial nerve is the larger of the 2 divisions and runs in the middle of popliteal fossa passing inferiorly through the 2 heads of the gastrocnemius.
What is the spinal root of the tibial nerve?
The tibial nerve originates from the L4-S3 spinal nerve roots and provides motor and sensory innervation to most of the posterior leg and foot. In addition to its motor branches, the branches of the tibial nerve include the medial sural cutaneous nerve, medial calcaneal nerve, and the medial and lateral plantar nerves. The tibial nerve is one of the two terminal branches of the sciatic nerve, the largest nerve in the human body.
Which plexus does tibial nerve arise from?
The tibial nerve is a branch of the sciatic nerve, and arises at the apex of the popliteal fossa. It travels through the popliteal fossa, giving off branches to muscles in the superficial posterior compartment of the leg.

What muscle is innervated by the posterior tibial nerve?
Muscles innervated include the gastrocnemius, popliteus, soleus, tibialis posterior, flexor digitorum longus, flexor hallucis longus, abductor hallucis, flexor digitorum brevis, flexor hallucis brevis, foot lumbricals, quadratus plantae, flexor digiti minimi, adductor hallucis, foot interossei, abductor digiti minimi.
Which muscles are stimulated by tibial nerve?
The tibial nerve provides innervation to the muscles of the lower leg and foot. Specifically: triceps surae (the two headed gastocnemius and soleus), plantaris, Popliteus, tibialis posterior, flexor digitorum longus and flexor hallucis longus.
What muscle does the tibial nerve innervate quizlet?
The (femoral, fibular, tibial) nerve innervates the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles.
What is the tibial nerve responsible for?
The tibial nerve is one of the two terminal branches of the sciatic nerve, the largest nerve in the human body. The tibial nerve originates from the L4-S3 spinal nerve roots and provides motor and sensory innervation to most of the posterior leg and foot.
What nerve controls the calf muscle?
tibial nerveThe tibial nerve (S1, S2) innervates the majority of the muscles of the calf. The tibial nerve passes through the popliteal fossa and gives off branches to the gastrocnemius, popliteus, soleus, and plantaris muscles.
What is the tibial nerve called?
The tibial nerve is a branch of the sciatic nerve. The tibial nerve passes through the popliteal fossa to pass below the arch of soleus.
Which muscle is innervated by the tibial nerve Semimembranosus?
Semimembranosus muscleArteryProfunda femoris and gluteal arteriesNerveTibial part of sciatic nerve (L5, S1 and S2)ActionsExtension of hip and flexion of kneeAntagonistQuadriceps muscle and Tensor fasciae latae10 more rows
What nerve Innervates the ankle extensors quizlet?
The superficial peroneal nerve emerges between the peroneus longus and peroneus brevis muscles and descends superficial to the extensor retinaculum of the ankle on the anterolateral side of the leg and ankle, innervating the skin of the lower leg and foot.
What nerve innervates the diaphragm quizlet?
Terms in this set (5) phrenic nerve arises from this plexus and innervates the diaphragm.
What happens if the tibial nerve is damaged?
Tibial nerve dysfunction occurs when there is damage to the tibial nerve. Symptoms can include numbness, pain, tingling, and weakness of the knee or foot. The tibial nerve is commonly injured by fractures or other injury to the back of the knee or the lower leg.
What nerve Innervates the ankle extensors?
Deep fibular nerveDeep fibular nerve and superficial fibular nerve. In the leg, it supplies the four muscles of the anterior compartment: tibialis anterior, extensor digitorum longus, extensor hallucis longus, and fibularis tertius. It gives off an articular branch above the inferior extensor retinaculum to supply the ankle joint.
What nerve causes plantar flexion?
The muscles that are used in plantar flexion are innervated by the tibial nerve and often develop tightness in the presence of foot drop. The muscles that keep the ankle from supination (as from an ankle sprain) are also innervated by the peroneal nerve, and it is not uncommon to find weakness in this area as well.
What happens if the tibial nerve is damaged?
Tibial nerve dysfunction occurs when there is damage to the tibial nerve. Symptoms can include numbness, pain, tingling, and weakness of the knee or foot. The tibial nerve is commonly injured by fractures or other injury to the back of the knee or the lower leg.
What muscles are innervated by the peroneal nerve?
The deep peroneal nerve provides motor innervation to the four muscles of the anterior compartment: the tibialis anterior, extensor digitorum, extensor hallucis longus and peroneus tertius muscle.
What nerve causes plantar flexion?
The muscles that are used in plantar flexion are innervated by the tibial nerve and often develop tightness in the presence of foot drop. The muscles that keep the ankle from supination (as from an ankle sprain) are also innervated by the peroneal nerve, and it is not uncommon to find weakness in this area as well.
Which muscle is innervated by the femoral nerve?
The motor branches of the femoral nerve are the nerve to pectineus, nerve to sartorius and muscular branches to the quadriceps femoris. They innervate the flexors of the hip (pectineus, iliacus, sartorius) and the extensors of the knee (quadriceps femoris).
Overview
The tibial nerve is in the back of your leg. It has many branches that enable the lower leg to receive messages from the brain.
Function
Branches of the tibial nerve connect to (innervate) muscles in the back of the leg. Tibial nerve innervation enables you to move your leg, foot and toes.
Anatomy
The tibial nerve branches off from the sciatic nerve. This nerve starts in the lower spine and innervates the lower body.
Conditions and Disorders
Tibial nerve dysfunction is a group of conditions that often cause tibial nerve pain.
Care
Eating a healthy diet with foods containing vitamin D and vitamin B12, which support nerve health.
Frequently Asked Questions
You should contact your healthcare provider if you notice symptoms of tibial nerve dysfunction. These include:
Which nerve provides innervation to the muscles of the lower leg and foot?
The tibial nerve provides innervation to the muscles of the lower leg and foot. Specifically: triceps surae (the two headed gastocnemius and soleus ), plantaris, popliteus, tibialis posterior, flexor digitorum longus and flexor hallucis longus. It also has articular and cutaneous branches.
What nerve divides the tibial nerve into the medial plantar nerve and the lateral plantar nerve?
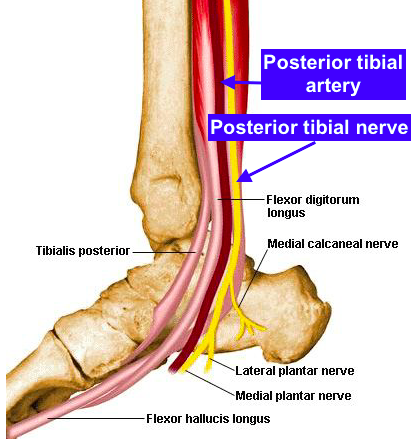
At the footlevel (just after the heel) the tibial nerve divides into the medial plantar nerve(MPN) and the lateral plantar nerve(LPN).[2] The MPN supplies muscular branches to the big toe and the two toes next to it, and the LPN the other two toes. The sural nerveis a cutaneous branch of the tibial nerve that supplies the skin of the legs and feet. [3]
What nerve is flossing?
The video below gives a good overview of the nerve and use of flossing techniques for the tibial nerve
What causes tendinous arch to compress popliteal artery?
Injury may occur due to e.g.: Entrapment in soleus arch: Soleus arch entrapment neuropathy can occur with sports that make special demands on the calf muscles. Swelling and hypertrophy of the soleus muscle may cause its tendinous arch to compress the popliteal artery and vein as well as the tibial nerve.
What nerve is affected by abnormal pressure in the ball of the foot?
Abnormal pressure at the ball of the footcan irritate the first plantar digital nerve causing Morton's neuroma/Metatarsalgia.
Which nerve is the terminal branch of the sciatic nerve?
The tibial nerve is the larger terminal branch of the two main muscular branches of the sciatic nerve. [1]
Which nerve supplies sensory innervation?
Branches of the tibial nerve supply sensory innervation to the following: Medial sural nerve supplies skin on lower half back of leg and skin of foot laterally to the little toe. Medial calcaneal nerve supplies skin on posterior and inferior surface calcaneus. Articular branches are to the knee (3 in total) and ankle joint.
What is the tibial nerve?
Tibial Nerve. The tibial nerve is a major peripheral nerve of the lower limb. It has several cutaneous and motor functions in the leg and foot. In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the tibial nerve – its anatomical course, functions and clinical correlations.
Which nerve innervates the i ntrinsic muscles of the foot?
The medial and lateral plantar branches of the tibial nerve provide innervation to all the i ntrinsic muscles of the foot (exept the extensor digitorum brevis, which is innervated by the deep fibular nerve). Sensory Functions. In the popliteal fossa, the tibial nerve gives off cutaneous branches.
What nerve is responsible for innervating the sole of the foot?
Within this tunnel, branches arise from the tibial nerve to supply cutaneous innervation to the heel. Immediately distal to the tarsal tunnel, the tibial nerve terminates by dividing into sensory branches, which innervate the sole of the foot.
What nerve innervates the posterior compartment of the leg?
The muscles of the posterior compartment of the leg are organised into a superficial and deep compartment. They are all innervated by the tibial nerve.
What is the posterior tibialis?
Tibialis posterior – inversion of the foot and plantarflexion of the ankle.
Which nerve innervates the digitorum brevis?
The medial and lateral plantar branches of the tibial nerve provide innervation to all the i ntrinsic muscles of the foot (exept the extensor digitorum brevis, which is innervated by the deep fibular nerve).
Which nerve innervates the skin of the posterolateral side of the leg and the lateral side of the foot?
In the popliteal fossa, the tibial nerve gives off cutaneous branches. These combine with branches from the common fibular nerve to form the sural nerve. This sensory nerve innervates the skin of the posterolateral side of the leg and the lateral side of the foot.
What nerve is the tibial nerve?
Tibial nerve. The tibial nerve branches off from the sciatic nerve. It provides innervation to the muscles of the lower leg and foot. The tibial nerve generally follows the course of the tibial artery through the body, which supplies blood to the same areas. There are two major branches of the tibial nerve in the foot: the medial plantar nerve ...
What nerve is responsible for the sensation of the big toe?
The former supplies instructions to the big toe and the two toes next to it, and the latter the other two toes. The split is seen just after the heel. The sural nerve also branches off the tibial nerve and provides sensation in the skin of the legs and feet.
Which nerve supplies blood to the same area?
The tibial nerve generally follows the course of the tibial artery through the body, which supplies blood to the same areas. There are two major branches of the tibial nerve in the foot: the medial plantar nerve and the lateral plantar nerve.
What is the name of the nerve that connects the tibial nerve to the hand?
The primary condition associated with the tibial nerve is tarsal tunnel syndrome, which is similar to carpal tunnel syndrome (in the hands), but far less frequent. It's also known as posterior tibial neuralgia.
What nerve is at the back of the knee?
At the back of your knee, it divides into two branches: The tibial nerve. The common peroneal (or fibular) nerve. A nerve isn't just a single line—it branches off to connect to skin, muscles, and connective tissues.
What nerve runs down the back of the leg?
The tibial nerve is a branch of the sciatic nerve that runs down the back of your leg and into the foot. It's involved in a condition called tarsal tunnel syndrome that's sometimes found in people with osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or ankle deformities due to injury.
Which nerve sends signals from the brain to the muscles in the back of your leg to get them to move?
Motor Function. The tibial nerve sends signals from the brain to the muscles in the back of your leg to get them to move. It controls movement in the following muscles: Popliteus. Flexor hallucis longus. Flexor digitorum longus. Tibialis posterior. Plantaris.
Which nerve is responsible for sensory nerves?
Sensory Function. The parts of the nerve that serve the skin are called cutaneous branches. The tibial nerve has cutaneous branches that supply sensation to the skin in an arc from the outside of your knee, down the back of the calf, to the outside portion of the foot and most of the sole of the foot.
What imaging can identify growths that may be compressing the nerve?
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): MRI can identify growths that may be compressing the nerve by creating a detailed image using magnets and radio waves.
Where does the sciatic nerve go?
It emerges from the spinal column in your lower back, then extends down through the buttock and into the leg.
Which branch of the ulnar nerve innervates?
Dorsal cutaneous branch of the ulnar nerve innervates
What nerves are scorebuilders?
Scorebuilders - nerves of brachial plexus and LE innervation
Which nerve innervates the tibialis anterior muscle?
Innervation. The deep fibular (peroneal) nerve (L4, L5), a branch of the common fibular nerve, innervates the tibialis anterior muscle.
What is the function of the tibialis anterior dorsiflex?
It plays an important role in the activities of walking, hiking and kicking the ball by stabilizing the ankle joint as the foot hits the floor and pull it clear of the ground as the leg continues moving.
How long does it take to read a tibialis?
Reading time: 4 minutes . Tibialis anterior muscle (Musculus tibialis anterior) Tibialis anterior is a fusiform muscle found in the anterior part of the leg. Lying superficially in the leg, this muscle is easily palpable lateral to the anterior border of tibia. Along with fibularis (peroneus) tertius, extensor digitorum longus ...
Which muscle tendon is located beneath the extensor retinaculum?
The tendon of tibialis anterior usually passes beneath the extensor retinaculum which holds it in place. However, in some cases, the superficial and deep layers of the extensor retinaculum form a separate tunnel for the muscle’s tendon.
Which muscle is the most medial?
Tibialis anterior muscle lies medial to extensor digitorum longus and extensor hallucis longus, which makes it the most medial muscle in the anterior compartment of the leg. It also covers the anterior tibial vessels and deep fibular nerve in the proximal part of the leg.
Which muscle is the main dorsiflexor of the foot?
Along with fibularis (peroneus) tertius, extensor digitorum longus and extensor hallucis longus, it comprises the anterior (or extensor) compartment of the leg . This muscle acts as the main foot dorsiflexor on the talocrural joint, but it also inverses the foot at the subtalar joint. Both actions play important roles in the gait cycle.
Where is the anterior intermuscular septum?
Anterior intermuscular septum. It courses inferiorly down the leg, giving off a cord-like tendon at the distal third of the tibia. The tendon travels across the ankle and dorsum of the foot to insert on the medial cuneiform bone and the adjoining of base of the first metatarsal.
How to memorize muscle innervations?
How to Memorize Muscles and Innervations. Associating muscles to a common nerve group is an excellent way to memorize muscle innervations. For example, when you realize that the radial nerve innervates the majority of the hand and wrist extensor muscles, you can form better associations and quickly reference this knowledge when you’re tested on it ...
What does the parenthesis next to the spinal nerve root mean?
The parenthesis () next to the spinal nerve root means this level contributes to the innervation but is not the primary nerve root. For example: the serratus anterior muscle is innervated by the long thoracic nerve with contributions from spinal nerve root C5, 6, 7 (8). The parenthesis around (8) means the nerve root at C8 may contribute to ...