See more

Which of the following muscle is supplied by the anterior division of mandibular nerve?
The Mandibular Nerve (V3) The buccal nerve pierces the skin on the face behind the ramus of the mandible, passes in front of the masseter, and innervates the skin anteriorly of the buccinator muscle.
Which muscle is supplied by mandibular nerve?
Efferently, the mandibular branch serves the muscles of mastication, the tensor veli palatini - muscle of the soft palate, and tensor veli tympani of the middle ear along with the mylohyoid and anterior digastric muscles.
Which muscles are innervated by the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve?
The only branch of the trigeminal nerve that has a motor component in the mandibular nerve (V3). This branch supplies motor innervation to the facial muscles involved in mastication which include the masseter, temporalis muscle, and the lateral and medial pterygoids.
What does mandibular branch of facial nerve supply?
[1] Of the five major branches of the facial nerve, the marginal mandibular branch of the facial nerve supplies muscles of the lower lip. The most frequent cause of paralysis of this nerve is iatrogenic injury during operations in the mandibular or parotid regions.
Is Buccinator supplied by mandibular nerve?
Innervation. Motor innervation is from the buccal branch of the facial nerve (cranial nerve VII). Sensory innervation is supplied by the buccal branch (one of the muscular branches) of the mandibular part of the trigeminal (cranial nerve V).
What is innervated by the mandibular nerve?
These nerve fibers innervate structures of the lower jaw and face, such as the tongue, lower lip, and chin. The mandibular nerve also innervates the muscles of mastication.
What does the posterior division of the mandibular nerve innervate?
The posterior division divides into three sensory branches: the auriculotemporal, lingual and inferior alveolar nerves. The latter gives off a motor branch which innervates the anterior belly of the digastric muscle and the mylohyoid muscle.
What is the masseter muscle innervated by?
the trigeminal nerveThe masseter is primarily responsible for the elevation of the mandible and some protraction of the mandible. It receives its motor innervation from the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve.
What are the 3 divisions of trigeminal nerve?
The nerve has three divisions: the ophthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular nerves (Figure 61.1). The innervation includes the cornea and conjunctiva of the eye; mucosa of the sinuses, nasal and oral cavities; and dura of the middle, anterior, and part of the posterior cranial fossae.
Which branch from the mandibular nerve supply the scalp?
The meningeal branch is the first collateral of the mandibular branch to emerge im-mediately beyond the foramen ovale. It enters the skull through the foramen spinosum with the middle meningeal artery to innervate the dura mater of the middle cranial fossa.
Which muscles are supplied by facial nerve?
Special visceral efferent (SVE) fibers (branchiomotor) are a major component of the facial nerve. Their function is to innervate the muscles of facial expression, the stapedius muscle, the stylohyoid muscle, and the posterior belly of the digastric muscle.
Which nerve supplies the muscles of facial expression?
cranial nerve VIIThe muscles of facial expression are innervated by the facial nerve (cranial nerve VII), and the muscles of mastication are innervated by the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve (cranial nerve V3).
What is the mandibular nerve responsible for?
Mandibular: The mandibular (lower jaw) branch aids sensation to the lower part of your face, such as the jaws, lower lip and gum. These nerves also have a motor function. They help you bite, chew and swallow.
What are the mandibular muscles?
The muscles of mastication are a group of muscles responsible for the chewing movement of the mandible at the temporomandibular (TMJ) joint, they enhance the process of eating, they assist in grinding food, and also function to approximate the teeth.
What does mandibular nerve control?
The mandibular nerve supplies both motor and sensory information, which means it's linked to movement and senses. One of its most essential functions is controlling the movements of the muscles that allow you to chew. These include the masseter, the lateral and medial pterygoids, and the temporalis muscle.
Which muscle is responsible for mandibular depression?
lateral pterygoidAmong all the four muscles of mastication (medial pterygoid, lateral pterygoid, masseter, and temporalis), the lateral pterygoid is the only muscle that participates in depressing the mandible.
How many branches does the anterior division of the mandibular nerve have?
Anterior division of the mandibular nerve. The anterior division of the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve has four branches, which are all motor branches except one. The four branches are:
What are the muscles of the head and neck?
muscles of the head and neck. muscles of the tongue (mnemonic) extrinsic muscles of the tongue. genioglossus muscle. hyoglossus muscle. styloglossus muscle. palatoglossus muscle. intrinsic muscles of the tongue. superior longitudinal muscle of the tongue.
Which nerve gives off the efferent nerves?
Branches. The mandibular nerve gives off the following branches: muscular branches, which are efferent nerves for the medial pterygoid, tensor tympani, and tensor veli palatini muscles (motor) mental nerve (sensory branch) and the nerve to mylohyoid (motor branch)
Which nerve passes between the medial pterygoid and the medial pterygoi?
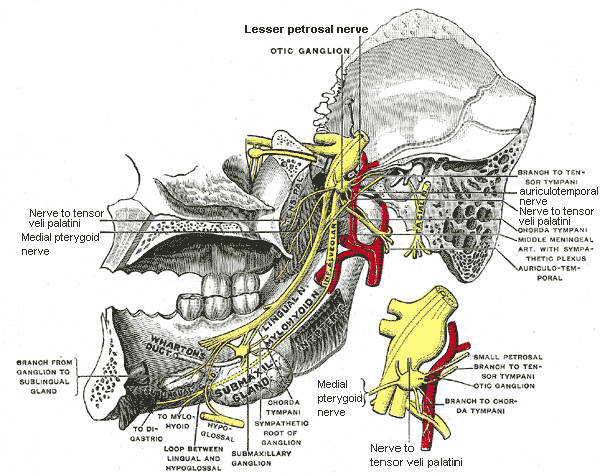
The mandibular nerve immediately passes between tensor veli palatini, which is medial, and lateral pterygoid, which is lateral, and gives off a meningeal branch (nervus spinosus) and the nerve to medial pterygoid from its medial side. The nerve then divides into a small anterior and large posterior trunk.
Which nerve is the largest of the three divisions of the trigeminal nerve?
The mandibular nerve ( V3) is the largest of the three divisions of the trigeminal nerve, the fifth cranial nerve (CN V).
What is the small figure of the otic ganglion?
The small figure is an enlarged view of the otic ganglion. The mandibular nerve ( V3) is the largest of the three divisions of the trigeminal nerve, the fifth cranial nerve (CN V).
Where does the sensory root exit the cranial cavity?
The large sensory root emerges from the lateral part of the trigeminal ganglion and exits the cranial cavity through the foramen ovale. Portio minor, the small motor root of the trigeminal nerve, passes under the trigeminal ganglion and through the foramen ovale to unite with the sensory root just outside the skull.
Which nerve is the sensory branch?
mental nerve (sensory branch) and the nerve to mylohyoid (motor branch)
Which division of the brain gives off the auriculotemporal, lingual, and inferior alveolar?
The anterior division gives off branches to three major muscles of mastication and a buccal branch which is sensory to the cheek. The posterior division gives off three main sensory branches, the auriculotemporal, lingual and inferior alveolar nerves and motor fibres to supply mylohyoid and the anterior belly of the digastric muscle .
What is the most common condition associated with the mandibular nerve?
The most common condition associated with the mandibular nerve is trigeminal neuralgia. Most cases of this extremely painful condition are due to nerve compression of the mandibular and/or maxillary branches of the trigeminal nerve. 4 .
What are the three branches of the trigeminal nerve?
It then splits into three branches: the ophthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular nerves. The mandibular nerve is made up of two roots. The larger of the two is sensory, and the smaller one is motor. The two roots join together to form ...
Why does the lingual nerve hurt during dental surgery?
These kinds of abnormalities can lead to nerve damage during surgery or dental procedures because the doctor doesn't expect the nerve to be where it is. 2
Why is it so hard to diagnose mandibular nerve pain?
Pain or other problems related to the mandibular nerve can be hard to diagnose due to the complexity of the anatomy in the head and neck. A lot of different structures are close to each other and even overlapping, making it hard for doctors to figure out exactly what's causing symptoms. 3 .
Which nerve is responsible for the motor function of the lower jaw and mouth?
Maxillary nerve (sensory): Upper jaw, the roof of your mouth, nostrils, sinuses, and middle of your face. Mandibular nerve (sensory and motor): Lower jaw and mouth, some areas of the scalp, and motor function to the lower jaw and mouth. Of the three branches of the trigeminal nerve, the mandibular nerve is the only one that serves both motor ...
Which nerve is responsible for moving your mouth?
The mandibular nerve, which plays an important role in moving your mouth, splits off from the trigeminal nerve to connect with the lower jaw. It plays both a motor and sensory role in your head as well as interacting with fibers of other cranial nerves. It's the largest of the three branches of the trigeminal nerve, which is the fifth cranial nerve. The trigeminal nerve is responsible for feeling in your face as well as biting and chewing motions.
Which nerve provides sensation or motor function to a different area of the head and face?
Each branch of the trigeminal nerve provides sensation or motor function to a different area of the head and face.
What is the mandibular division?
The Mandibular Division of the Trigeminal Nerve (CNV3) The mandibular nerve is a terminal branch of the trigeminal nerve ( along with the maxillary and ophthalmic nerves ). It has a sensory role in the head, and is associated with parasympathetic fibres of other cranial nerves.
What innervates the anterior two-thirds of the tongue?
General sensory fibers innervate the anterior two-thirds of the tongue, as well as the mucus membrane lining its undersides.
Which nerve contains sensory fibres?
The buccal branch of the mandibular nerve contains sensory fibres. As it emerges from the mandibular nerve, it passes between the two heads of the lateral pterygoid muscle before heading to its target sites.
Where do the remaining sensory axons enter?
The remaining sensory axons enter the mandibular canal, a narrow tunnel running through the mandible bone. Within this canal the nerve provides branches to the mandibular teeth.
Which nerve is the mandibular nerve?
The mandibular nerve is a terminal branch of the trigeminal nerve (along with the maxillary and ophthalmic nerves).
What is the purpose of a dental block?
The principle behind the block is to remove general sensation from the ipsilateral mandibular row of teeth. In doing so however, anesthesia can also spread over the buccal membranes, chin and jaw.
How many tributaries does the mandibular branch have?
Once the mandibular branch has emerged from the cranium, it courses through the infratemporal fossa, branching into four tributaries which are described below.

Overview
Structure
The large sensory root emerges from the lateral part of the trigeminal ganglion and exits the cranial cavity through the foramen ovale. Portio minor, the small motor root of the trigeminal nerve, passes under the trigeminal ganglion and through the foramen ovale to unite with the sensory root just outside the skull.
The mandibular nerve immediately passes between tensor veli palatini, which is medial, and later…
Supplies
The mandibular nerve innervates:
Anterior Division:
(Motor Innervation - Muscles of mastication)
• Masseteric nerve
• Medial pterygoid nerve
See also
• Ophthalmic nerve
• Maxillary nerve
• Marginal mandibular branch of facial nerve
Additional images
• Dermatome distribution of the trigeminal nerve
• The nerves of the scalp, face, and side of neck.
• Mandibular nerve
• Mandibular nerve
External links
• MedEd at Loyola GrossAnatomy/h_n/cn/cn1/cnb3.htm
• Anatomy figure: 27:03-02 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center
• cranialnerves at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (V)