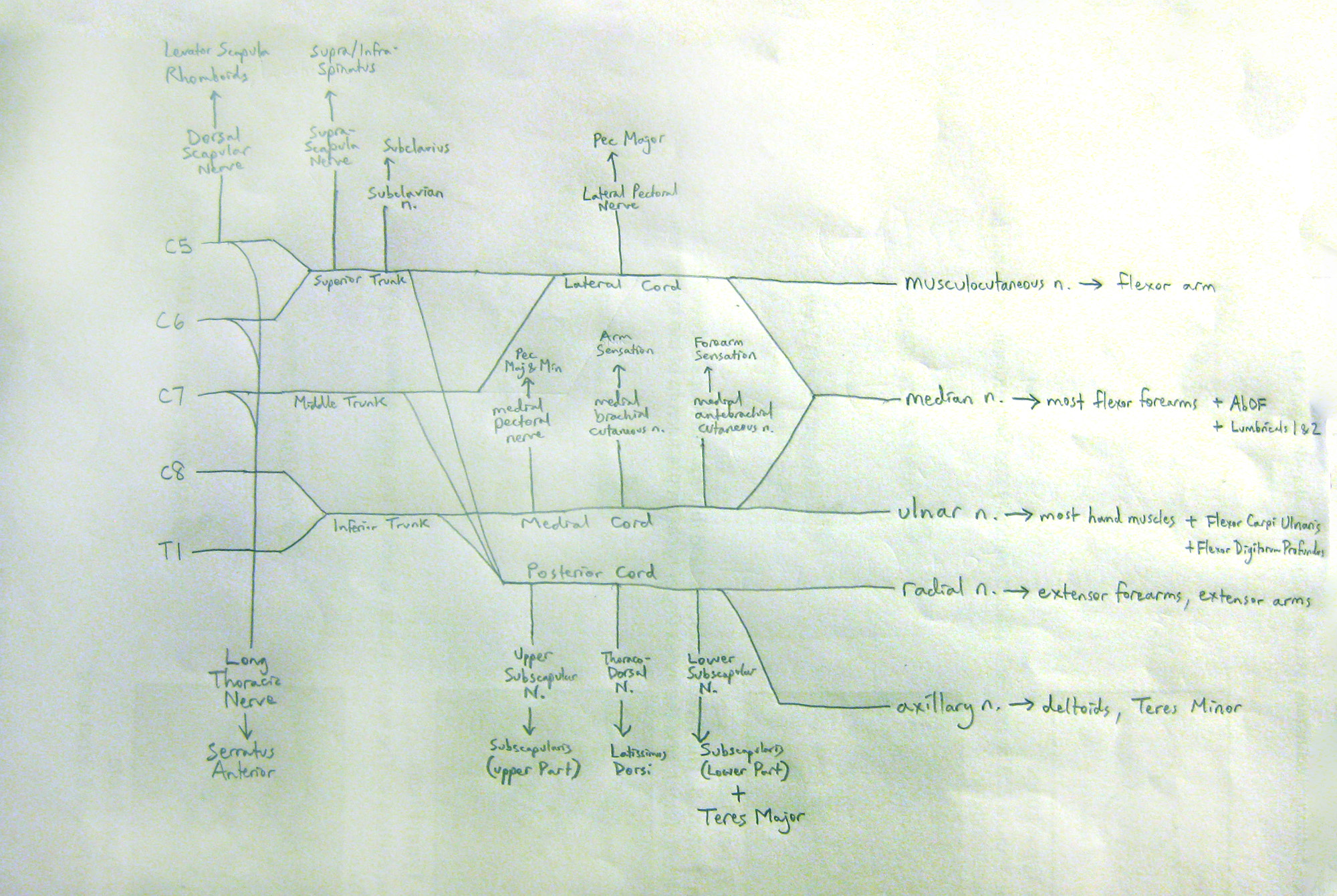
The median nerve innervates the majority of the muscles in the anterior forearm, and some intrinsic hand muscles. In the forearm, the median nerve directly innervates muscles in the superficial and intermediate layers: Superficial layer: Pronator teres, flexor carpi radialis and palmaris longus. Intermediate layer : Flexor digitorum superficialis.
What is the function of a median nerve?
The median nerve provides sensory and motor (movement) functions to your forearm, wrist and hands. The nerve starts at your armpit, but its functions all take place in your forearm or hand. The median nerve stimulates muscles in your forearm, allowing you to: Bend and straighten your wrists, thumbs and first three fingers.
What does the median nerve innervate?
What does the median nerve innervate? The median nerve innervates many muscles of the anterior forearm and hand, providing signals to and from the brain and spinal cord. The flexor digitorum superficialis and pronator quadratus are among the muscles of the anterior forearm that are solely innervated by the median nerve.
Are nerves needed for muscles to contract?
Your nervous system communicates with your muscles through structures called neuromuscular junctions, and the activation of a nerve triggers muscle contraction. Sodium and potassium help your nerve cells send electrical signals, called action potentials, that signal for your muscles to contract.
Which nerve stimulates muscles that flex the forearm?
- Attachments: Originates from the anterior surface of the ulna and attaches to the anterior surface of the radius.
- Actions: Pronates the forearm.
- Innervation: Median nerve (anterior interosseous branch).
Which of the following muscles are innervated by the median nerve quizlet?
Which muscle group is innervated primarily by the median nerve? The median nerve innervates all of the flexor muscles in the forearm except for flexor carpi ulnaris and the medial half of flexor digitorum profundus.
What intrinsic muscles of hand are innervated by median nerve?
Nerves of hand All of the remaining intrinsic muscles—that is, the two radial lumbricals, the APB, the opponens pollicis, and the superficial head of the FPB—are thus innervated by the median nerve.
How do you remember the median nerve Innervates?
All the intrinsic muscles of the hand are innervated by the ulnar nerve, except four muscles which are supplied by the median nerve and are easily recalled with the mnemonic: FOAL or LOAF.
Which nerve Innervates most muscles of the hand?
The muscles of the hand are innervated by the radial, median, and ulnar nerves. The radial nerve innervates the finger extensors and the thumb abductor; that is, the muscles that extend at the wrist and metacarpophalangeal joints (knuckles) and abduct and extend the thumb.
What are the intrinsic muscle of the hand?
Four muscle groups comprise the intrinsic hand. These are the thenar, hypothenar, interossei and the lumbrical muscles.
Which of these intrinsic hand muscles is not innervated by the ulnar nerve?
To summarize, the ulnar nerve supplies motor innervation to the flexor carpi ulnaris, the medial half of the flexor digitorum profundus and all the intrinsic hand muscles with the exception of the LOAF muscles (lateral two lumbricals, opponens pollicis, abductor pollicis brevis and flexor pollicis brevis).
How many intrinsic muscles of hand are supplied by ulnar nerve?
In the hand, the ulnar nerve provides motor innervation to the third and fourth lumbricals, dorsal interossei, palmar interossei, adductor pollicis, flexor pollicis brevis and palmaris brevis.
What are the extrinsic and intrinsic muscles of the hand?
The extrinsic muscle groups are the long flexors and extensors. They are called extrinsic because the muscle belly is located on the forearm. The intrinsic group is the smaller muscles located within the hand itself. The hand muscles are innervated by the radial, median, and ulnar nerves from the brachial plexus.
What is the median nerve?
The median nerve is a sensory and motor nerve of the arm (or upper limb). It arises from the lateral and medial cords of the brachial plexus, origi...
Where is the median nerve?
The median nerve spans the length of the upper limb. After arising from the lateral and medial cords of the brachial plexus, the median nerve enter...
What does the median nerve innervate?
The median nerve innervates many muscles of the anterior forearm and hand, providing signals to and from the brain and spinal cord. The flexor digi...
What happens if the median nerve is damaged?
The median nerve is usually damaged at either the elbow, due to a fracture of the humerus bone of the upper arm, or the wrist, due to either carpal...
How do you stretch the median nerve?
In order to exercise and improve the movement of the median nerve, it can be stretched. To stretch the median nerve, an individual can place their...
How do you diagnose and treat median nerve compression?
Clinical presentation of symptoms and physical examination are used to diagnose median nerve compression. For instance, a physical exam may confirm...
What are the most important facts to know about the median nerve?
The median nerve is a major nerve of the upper limb as it innervates the major muscles that enable an individual to flex their wrist and fingers, a...
What nerves are in the carpal tunnel?
Dissected carpal tunnel showing median nerve traversing the carpal tunnel with the nine flexor tendons; the flexor pollicis longus, the four flexor digitorum superficialis and the four flexor digitorum profundus.
What nerve is damaged at the elbow?
The median nerve is vulnerable to be damaged at the elbow, commonly from a supracondylar fracture. This results in the radial head of flexor digitorum profunda being denervated. The forearm is constantly supinated and the lateral two lumbricals have also been denervated, the flexion at the metacarpophalangeal and interphalangeal joints of 2 & 3 digits is lost. There is inability to make a fist as both of these fingers are extended and the hand is in a classic position known as the ‘ hand of benediction ’ (when the person tries to flex their fingers).
What is the million dollar nerve?
The recurrent branch to the muscles of the thenar eminence (flexor pollicis brevis, abductor pollicis brevis, opponens pollicis ). It is also known as the ‘million dollar nerve’ to signify its importance for basic hand function.
What is the brachial plexus?
Brachial plexus in cadaver: Median nerve seen arising from medial and lateral roots. The roots are recognized as they form an M-structure with musculocutaneous and ulnar nerves over the axillary artery.
What nerve is the origin of the hand?
Median nerve: Origin and course. The median nerv e is a branch of the brachial plexus that supplies most of the superficial and deep flexors in the forearm, thenar and lumbrical muscles. It also gives sensation to certain areas of the skin of the hand.
Which nerve supplies the motor supply to the flexor muscles in the forearm?
To summarize, the median nerve provides the motor supply to the flexor muscles in the forearm, except flexor carpi ulnaris and the ulnar head of flexor digitorum profundus (which is supplied by the ulnar nerve ). It also supplies the thenar muscles as well as the radial two lumbricals.
Which nerve passes through the carpal tunnel?
The median nerve then passes through the carpal tunnel beneath the flexor retinaculum, and terminates by dividing into two terminal branches, the common palmar digital nerves. Dissected carpal tunnel showing median nerve traversing the carpal tunnel with the nine flexor tendons; the flexor pollicis longus, the four flexor digitorum superficialis ...
What is the palmar digital branch?
Palmar digital cutaneous branch – arises in the hand. Innervates the palmar surface and fingertips of the lateral three and half digits.
What causes carpal tunnel syndrome?
Compression of the median nerve within the carpal tunnel can cause carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS). It is the most common mononeuropathy and is caused by an increased tissue pressure within the carpal tunnel.
Which nerve innervates the flexor and pronator muscles?
Motor functions: Innervates the flexor and pronator muscles in the anterior compartment of the forearm (except the flexor carpi ulnaris and part of the flexor digitorum profundus, innervated by the ulnar nerve ).
Which branch innervates the palmar surface and fingertips of the lateral three and half digits?
Palmar digital branch – innervates the palmar surface and fingertips of the lateral three and half digits. Also innervates the lateral two lumbrical muscles.
Which nerve innervates the skin of the lateral palm?
The median nerve gives off two major branches in the forearm: Anterior interosseous nerve – supplies the deep muscles in the anterior forearm. Palmar cutaneous nerve – innervates the skin of the lateral palm. (The functions of these nerves are explored in more detail later in the article).
Which branch of the palm innervates the lateral aspect of the palm?
Sensory functions: Gives rise to the palmar cutaneous branch, which innervates the lateral aspect of the palm, and the digital cutaneous branch, which innervates the lateral three and a half fingers on the anterior (palmar) surface of the hand. Anatomical Course.
Which part of the hand innervates the lateral three and a half fingers?
Sensory functions: Gives rise to the palmar cutaneous branch, which innervates the lateral aspect of the palm, and the digital cutaneous branch, which innervates the lateral three and a half fingers on the anterior (palmar) surface of the hand.
What nerve is involved in Riche Cannieu anastomosis?
Riche-Cannieu anastomosis can occur when a connection exists between recurrent branch of the median nerve and deep branch of the ulnar nerve of the hand.
What is the mechanism of carpal tunnel syndrome?
Common mechanism: Carpal tunnel syndrome, an injury by compression in the carpal tunnel, without transection of the median nerve, due to overuse by activities such as keyboard typing and cooking. Motor deficit: Weakness in flexion of radial half of digits and thumb, weakness in abduction and opposition of thumb.
Which nerve innervates the flexors of the forearm?
It innervates all of the flexors in the forearm, except flexor carpi ulnaris and that part of flexor digitorum profundus that supplies the fourth and fifth digits. The latter two muscles are supplied by the ulnar nerve (specifically the muscular branches of ulnar nerve ).
Which branch of the interosseous artery innervates the flexor pollicis longus?
The anterior interosseous branch is given off in the upper part of the forearm, courses with the anterior interosseous artery and innervates flexor pollicis longus and the lateral half of flexor digitorum profundus (the ulnar half is supplied by ulnar nerve, as is the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle). It ends with its innervation of pronator quadratus. In addition to its supply to muscles, this nerve also supplies the distal radioulnar joint and wrist joint.
Where is the median nerve located?
14385. Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy. The median nerve is a nerve in humans and other animals in the upper limb. It is one of the five main nerves originating from the brachial plexus . The median nerve originates from the lateral and medial cords of the brachial plexus, and has contributions from ventral roots of C5-C7 (lateral cord) ...
Where does the median nerve enter the arm?
After receiving inputs from both the lateral and medial cords of the brachial plexus, the median nerve enters the arm from the axilla at the inferior margin of the teres major muscle. It then passes vertically down and courses lateral to the brachial artery between biceps brachii (above) and brachialis (below).
What is the anomaly of the median nerve?
The naturally occurring anomalies of the median nerve are: Bifurcation of the median nerve typically occurs after the nerve exits the carpal tunnel; however, in a small percentage (5-10%) of individuals, the median nerve bifurcates more proximal in the carpal tunnel, wrist, or forearm. During gestation, a median artery that serves the hand retracts.
What is carpal tunnel syndrome?
Pathology/Injury. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is a condition which occurs due to pressure on the median nerve as it passes through the carpal tunnel. The median nerve is particularly vulnerable to damage at the elbow and wrist.
How to tell if you have median nerve lesion?
Signs of a median nerve lesion include weak pronation of the forearm, weak flexion and radial deviation of wrist, with thenar atrophy and inability to oppose or flex the thumb; - sensory distribution includes thumb, radial 2 1/2 fingers, and the corresponding portion of palm.
What is the most common injury to the retina?
Most common injury = Lacerations just proximal to the flexor retinaculum .
What are the functions of the median nerve?
The main two function of median nerve are Motor and Sensory, the muscles supplied by median nerve are mainly flexor aspect of forearm, hand, and thumb. Sensory innervation to the dorsal aspect of the distal first two digits of the hand is supplied by median nerve. The motor function is described in table above
What nerve is under tension during a tension test?
Extending the elbow and wrist, two key components of the upper limb tension test, puts the median nerve under tension. Rotating the head and neck to the opposite side puts the nerve under increasing stretch. If the entrapment is in the inter scalene triangle then raising the arm above the head usually increases the response. The purpose is to test for C5, C6, C7 nerve roots and median nerve as the source of the patient’s painful shoulder and arm.
Which nerve gives off no branches in the arm?
With the exception of the nerve to the Pronator teres, which sometimes arises above the elbow-joint, the median nerve gives off no branches in the arm. As it passes in front of the elbow, it supplies one or two twigs to the joint.
What is the posture of the thumb and fingers?
So on trying to flex the fingers and thumb to make a fist, the 1st 3 digits remain in extension, and the posture is known as the "hand of benediction". NB In lesions of the Ulnar Nerve the same posture occurs with the hand at rest, due to paralysis of the medial lumbricals.
How to memorize muscle innervations?
How to Memorize Muscles and Innervations. Associating muscles to a common nerve group is an excellent way to memorize muscle innervations. For example, when you realize that the radial nerve innervates the majority of the hand and wrist extensor muscles, you can form better associations and quickly reference this knowledge when you’re tested on it ...
What does the parenthesis next to the spinal nerve root mean?
The parenthesis () next to the spinal nerve root means this level contributes to the innervation but is not the primary nerve root. For example: the serratus anterior muscle is innervated by the long thoracic nerve with contributions from spinal nerve root C5, 6, 7 (8). The parenthesis around (8) means the nerve root at C8 may contribute to ...
Who is Tim Fraticelli?
Tim Fraticelli is a Physical Therapist, Certified Financial Planner™ and founder of PTProgress.com. He loves to teach PTs and OTs ways to save time and money in and out of the clinic, especially when it comes to documentation or continuing education. Follow him on YouTube for weekly videos on ways to improve your financial health.
