How to ease torticollis?
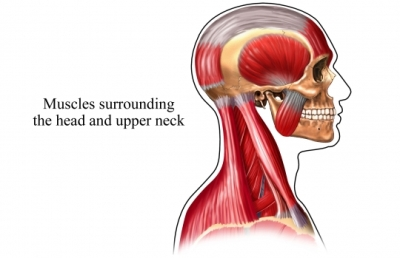
Other muscles of the region involved in torticollis include the splenius, the trapezius, the scapula, the scalenes, and the platysma. There are eight sets of cervical nerves, outlined C1 to C8, and each pair leaves the spinal cord at the corresponding vertebral level.
What is included in the physical exam for torticollis?
Mar 08, 2022 · Torticollis results in a fixed or dynamic posturing of the head and neck in tilt, rotation, and flexion. Spasms of the sternocleidomastoid, trapezius, and other neck muscles, usually more prominent on one side than the other, cause turning or tipping of the head. The cause of congenital muscular torticollis is unknown, however, it may be
How long does torticollis last in adults?
Jun 12, 2020 · Which muscles are involved in torticollis? Torticollis results in a fixed or dynamic posturing of the head and neck in tilt, rotation, and flexion. Spasms of the sternocleidomastoid, trapezius, and other neck muscles, usually more prominent on one side than the other, cause turning or tipping of the head. Click to see full answer.
Can drugs cause torticollis?
Sep 29, 2021 · Other muscles of the region involved in torticollis include the splenius, the trapezius, the scapula, the scalenes, and the platysma. There are eight sets of cervical nerves, outlined C1 to C8, and each pair leaves the spinal cord at the corresponding vertebral level.

Which muscle tightness is involved in torticollis?
Thickened or tight sternocleidomastoid muscle. Tenderness on the cervical spine.
Which muscle injury causes torticollis delivery?
Torticollis is a condition that occurs when an infant's neck becomes twisted, causing his or her head to tilt to one side. The twisting in the neck is caused by a shortened sternocleidomastoid (SCM) muscle.
What causes torticollis in the neck?
The cause is likely from the fetus's position in the uterus resulting in injury to the neck muscles. Acquired torticollis may be caused by irritation to the cervical ligaments from a viral infection, injury, or vigorous movement. Additional causes may include: Sleeping in an awkward position.
What causes weak neck muscles in babies?
In newborns, torticollis can happen due to the baby's position in the womb or after a difficult childbirth. This is called infant torticollis or congenital muscular torticollis. It can be upsetting to see that your baby has a tilted head or trouble turning his or her neck.
What is the origin of Sternocleidomastoid?
Sternocleidomastoid muscleSternocleidomastoidOriginManubrium and medial portion of the clavicleInsertionMastoid process of the temporal bone, superior nuchal lineArteryOccipital artery and the superior thyroid arteryNerveMotor: spinal accessory nerve sensory: cervical plexus Proprioceptive: ventral rami of C2-311 more rows
Can torticollis correct itself?
Torticollis will often self-correct when treated early — ideally, within the first month or two, says Dr. Burke. If parents wait until babies are 3 months of age or older, treatment can take longer.Nov 12, 2018
Is torticollis a neurological condition?
Cervical dystonia, also known as spasmodic torticollis, is a rare neurological disorder that originates in the brain. It is the most common form of focal dystonia in an office setting.
How do you get rid of torticollis in your neck?
Treatment for torticollis aims to relax the contracted neck muscles involved. Treatments include medication, physical devices, botulinum toxin, physical therapy, stretching exercises, and surgery. In most people, torticollis resolves in several days to a few weeks.
What is the cause of torticollis?
Trochlear torticollis. Torticollis may be unrelated to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, instead caused by damage to the trochlear nerve (fourth cranial nerve), which supplies the superior oblique muscle of the eye. The superior oblique muscle is involved in depression, abduction, and intorsion of the eye.
What causes noncongenital muscular torticollis?
Noncongenital muscular torticollis may result from scarring or disease of cervical vertebrae, adenitis, tonsillitis, rheumatism, enlarged cervical glands, retropharyngeal abscess, or cerebellar tumors. It may be spasmodic (clonic) or permanent (tonic). The latter type may be due to Pott's Disease (tuberculosis of the spine).
What is a wry neck?
Torticollis, also known as wry neck, is a dystonic condition defined by an abnormal, asymmetrical head or neck position, which may be due to a variety of causes. The term torticollis is derived from the Latin words tortus for twisted and collum for neck.
How to treat torticollis in children?
Physical therapy is an option for treating torticollis in a non-invasive and cost-effective manner. In the children above 1 year of age, surgical release of the tight sternocleidomastoid muscle is indicated along with aggressive therapy and appropriate splinting. Occupational therapy rehabilitation in Congenital muscular torticollis concentrates on observation, orthosis, gentle stretching, myofascial release techniques, parents’ counseling-training, and home exercise program. While outpatient infant physiotherapy is effective, home therapy performed by a parent or guardian is just as effective in reversing the effects of congenital torticollis. It is important for physical therapists to educate parents on the importance of their role in the treatment and to create a home treatment plan together with them for the best results for their child. Five components have been recognized as the "first choice intervention" in PT for treatment of torticollis and include neck passive range of motion, neck and trunk active range of motion, development of symmetrical movement, environmental adaptations, and caregiver education. In therapy, parents or guardians should expect their child to be provided with these important components, explained in detail below. Lateral neck flexion and overall range of motion can be regained quicker in newborns when parents conduct physical therapy exercises several times a day.
What is a fixed or dynamic tilt, rotation, with flexion or extension of the head and/or neck?
Torticollis is a fixed or dynamic tilt, rotation, with flexion or extension of the head and/or neck. The type of torticollis can be described depending on the positions of the head and neck. A combination of these movements may often be observed.
What is the term for a recurrent but transient contraction of the muscles of the neck?
Torticollis with recurrent, but transient contraction of the muscles of the neck and especially of the sternocleidomastoid, is called spasmodic torticollis. Synonyms are "intermittent torticollis", "cervical dystonia" or "idiopathic cervical dystonia", depending on cause.
What is the lateral bend of the head and neck called?
In veterinary literature usually only the lateral bend of head and neck is termed torticollis, whereas the analogon to the rotatory torticollis in humans is called a head tilt. The most frequently encountered form of torticollis in domestic pets is the head tilt , but occasionally a lateral bend of the head and neck to one side is encountered.
What is a torticollis?
Treatment. Torticollis is a condition in which the neck is involuntarily in a turned or twisted position. It can affect children and adults. There are two main types of torticollis—congenital (present at birth) and acquired (often caused by trauma, infection, or a reaction to a medication).
Why do babies get torticollis?
Vision problems are a common cause of torticollis. This type is called ocular torticollis. And gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) can cause torticollis in babies.
How to relieve neck pain?
To relieve neck pain and help relax the neck muscles, the following therapies may be recommended: 7 1 Medications like nonsteroidal anti-inflammatories (NSAIDs) and muscle relaxants 2 Physical therapy and home stretching exercises 3 Cervical collar
How to treat congenital torticollis?
The treatment of congenital torticollis usually involves physical therapy to help stretch and straighten out the neck. Less commonly, surgery to lengthen or release the muscle may be needed. 2
Why does my baby's head tilt?
Congenital torticollis is a painless condition that causes babies to have their head tilted to one side and rotated to the opposite side. If the baby's left ear is closer to their left shoulder, then their face will be turned more towards the right side. 2
What does it feel like to have a locked neck?
Acquired Torticollis. Children and adults with acquired torticollis usually experience neck pain with certain neck movements, as well as a "locked" sensation after quickly rotating their neck. 5 Headaches, head tremors, and stiff or swollen neck muscles can accompany these symptoms.
Why do children tilt their heads?
With ocular torticollis (also a type of acquired torticollis that's more common in children), a child may tilt their head to the side to avoid a visual disturbance, like double vision. Finally, torticollis that occurs as a reaction to a medication may be accompanied by tight jaw muscles and problems speaking.
What is spasmodic torticollis?
Spasmodic torticollis, features contractions or spasms of neck muscles that are not under ones control. These spasms forcefully alter head position and can greatly interfere with life activities as well as the quality of life. Spasmodic Torticollis, a type of cervical dystonia, causes the muscles of the neck contract uncontrollably, ...
What muscles are involved in neck pain?
The main neck muscles that are most prominently involved, are the sternocleidomastoid, trapezius, levator scapulae and splenius capitis. On occasion, when the muscles in the neck contract, they can cause tightness and contractions in the whole body. The pain may become worse and, in many cases, severe.
What is the best treatment for muscle paralysis?
Most commonly known as Botox for cosmetic rejuvenation, it can be injected into the involved muscles to cause a temporary paralysis of the muscles, lasting about 4 months. 2) Parkinson’s Medications. These help reduce tremors and can be combined with botulinum injections. 3) Muscle Relaxers.
What can help with postural pain?
Physical Therapy. Stretches and strength building exercises can have a positive effect on the resulting postural problems and may assist in the alleviation of pain, enhancing the effects of medications.
Can neck pain be worse?
The pain may become worse and, in many cases, severe. Symptoms will generally settle on one side of the neck; a shoulder may be higher; pain, numbness or tingling sensations may be felt in the arm or hand. At least two-thirds of the individuals additionally have neck pain which radiates into the shoulders.
What tests are used to diagnose torticollis?
Such diagnostic tests include X-rays, CT scan, and MRI. Lab studies may be useful if infection is suspected as the etiology for torticollis.
What is the term for a neck muscle that is locked into a sustained involuntary contraction?
Adult torticollis, also referred to as cervical dystonia or spasmodic torticollis, is a condition in which the muscles that control the neck are locked into a sustained involuntary contraction. These contractures can commonly cause twisting, repetitive movements, or abnormal posturing of the neck. Depending on the severity, it can be a very painful condition that may lead to a great deal of distress. Presentations of torticollis are defined using causal terms such as acute, congenital, chronic, acquired, idiopathic, or secondary.
Is there a randomized controlled trial for torticollis?
Little research has been done on physical therapy management of adult torticollis. No randomized controlled trials have been conducted , and the studies performed on specific interventions — such as vibration therapy and progressive muscular relaxation — consist of case studies or small sample sizes without control groups. Therefore, the adult patient with torticollis will follow an impairment based approach tailored to the individual.
What is the term for the rotation of the head or chin towards the shoulder?
Adult torticollis, also known as cervical dystonia, presents as the rotation of the head or chin towards the shoulder. Repetitive jerking of the head may be present with spasms that can be intermittent, clonic, or tremulous. The study by Qiyu Chen et al. suggests that the presence of Head Tremors (HT) and its type depend on a patient’s predominant posture (patients with retrocollis were more prone to have HT than patients with anterocollis), age (earlier age of onset compared to patients without HT), and duration (longer disease duration compared to patients without HT) .
Can physical therapy help with torticollis?
Given the absence of randomized controlled trials, and general paucity of research on physical therapy interventions for adult torticollis, and considering the fact that the physical therapist cannot address the cause of an idiopathic condition, there is no universally accepted intervention for the condition. An impairment-based approach focusing on the individual patient’s restrictions and limitations will produce the best outcomes. Primary components of treatment should include pain control, range of motion, and postural cueing. If the treating therapist has the suspicion of Wilson or Alzheimer disease that is not indicated in the patient history, proper referral protocols should be followed.
What is idiopathic cervical dystonia?
Idiopathic cervical dystonia (ICD) is the most common form of adult-onset focal dystonia. The prevalence of dystonia is difficult to ascertain. On the basis of the best available prevalence estimates, primary dystonia maybe 11.1 per 100,000 for early onset cases in Ashkenazi Jews from New York area, 60 per 100,000 for late onset cases in Northern England, and 300 per 100,000 for late onset cases in the Italian population over age 50. The chart in figure 1 displays that most of the cases were reported in the age group of 31 to 40 years of age, which indicates the prevalence of adult-onset idiopathic cervical dystonia.
Is botulinum toxin used for cervical dystonia?
The introduction of chemodenervation with botulinum toxin radically changed the prognosis of patients with idiopathic cervical dystonia. It is the most commonly used pharmacotherapy for overactive and dystonic cervical musculature. Botulinum toxin A provides graded, reversible denervation of the neuromuscular junction by preventing the release of acetylcholine from the presynaptic axon of the motor endplate. This treatment is now the first line therapy for cervical dystonia, but it's true efficacy is still unknown. However, botulinum toxin benefits the highest percentage of patients in the shortest amount of time. The most important aspect to consider when administering the botulinum toxin is identification of the sites of pain and the muscles responsible for the abnormal posture. The SCM, trapezius, splenius capitus, and levator scapulae are the most commonly injected sites. A benefit from botulinum toxin is generally seen within the first week, but may rarely be delayed for up to eight weeks. The benefit lasts for an average of twelve weeks and most physicians suggest repeating injections every 3-4 months. Medications are generally used as adjuncts to botulinum toxin, although no trial has sought to demonstrate a synergistic effect. Side effects of this treatment approach may include injection site pain, dysphagia, dry mouth, excessive weakness of the injected or adjacent muscles, and fatigue.
What is a torticollis?
Adult torticollis, also known as cervical dystonia or “wryneck,” is a condition where your neck muscles go into spasm and pull your head to one side. Torticollis is often painful and can provoke twitching, twisting, and other uncomfortable neck posture problems. There are several exercises that you can try to reduce ...
How to stretch torticollis?
Step 1: Stand next to a counter so that your torticollis causes you to lean your head towards it. Hold the counter with your nearest hand. Step 2: Place your other hand on top of your head. Step 3: Lean your head away from the counter, aiming your other ear towards your shoulder. You should feel a gentle stretch.
How to help dystonia?
Sensory Trick Training. The first exercise is a mental exercise to help relax stiff neck muscles. A unique aspect of any type of dystonia is how your muscles react to “sensory tricks.”. These tricks involve using your senses to signal your muscles to release.
What does a neck stretch do?
This stretch can help release the muscles running up the back and sides of your neck. It is helpful if your torticollis pulls your head back or to the side.
How to get rid of a swollen neck?
Step 3: When you feel a stretch in your neck, hold your position for thirty seconds, then release back to a neutral position. Repeat this three to five times a day. Once you feel comfortable doing this exercise on its own, you can add resistance to it.

Overview
Causes
Signs and symptoms
Anatomy
Diagnosis
Treatment
A multitude of conditions may lead to the development of torticollis including: muscular fibrosis, congenital spine abnormalities, or toxic or traumatic brain injury. A rough categorization discerns between congenital torticollis and acquired torticollis.
Other categories include:
• Osseous
Prognosis
Torticollis is a fixed or dynamic tilt, rotation, with flexion or extension of the head and/or neck. The type of torticollis can be described depending on the positions of the head and neck.
• laterocollis : the head is tipped toward the shoulder
• rotational torticollis : the head rotates along the longitudinal axis
Other animals
The underlying anatomical distortion causing torticollis is a shortened sternocleidomastoid muscle. This is the muscle of the neck that originates at the sternum and clavicle and inserts on the mastoid process of the temporal bone on the same side. There are two sternocleidomastoid muscles in the human body and when they both contract, the neck is flexed. The main blood supply for these muscles come from the occipital artery, superior thyroid artery, transverse scap…