Gross anatomy. Location. The kidneys are located on the posterior abdominal wall, with one on either side of the vertebral column, in the perirenal space. The long axis of the kidney is parallel to the lateral border of the psoas muscle and lies on the quadratus lumborum muscle.
What are the posterior surfaces of the kidneys?
The medial part of the inferior half and the inferior pole are contacted by the peritoneum of the jejunum The posterior surfaces of both kidneys are related to certain neurovascular structures and muscles: You can easily remember these with the mnemonic: “1-2-3-4 All Boys Need Muscle”.
What muscles are in the inferior half of the kidney?
The muscular relations of the inferior half are easy to remember by dividing the kidney surface into three vertical stripes, where the medial stripe represents the impression of the psoas major muscle, the central stripe the quadratus lumborum, and the lateral stripe the transversus abdominis muscle.
What is the difference between the anterior and posterior renal artery?
When the renal arteries enter the kidney through the hilum, they split into anterior and posterior branches. The posterior branch supplies the posterior part of the kidney, whereas the anterior branch arborizes into five segmental arteries, each supplying a different renal segment.
What is the anatomical position of the kidneys?
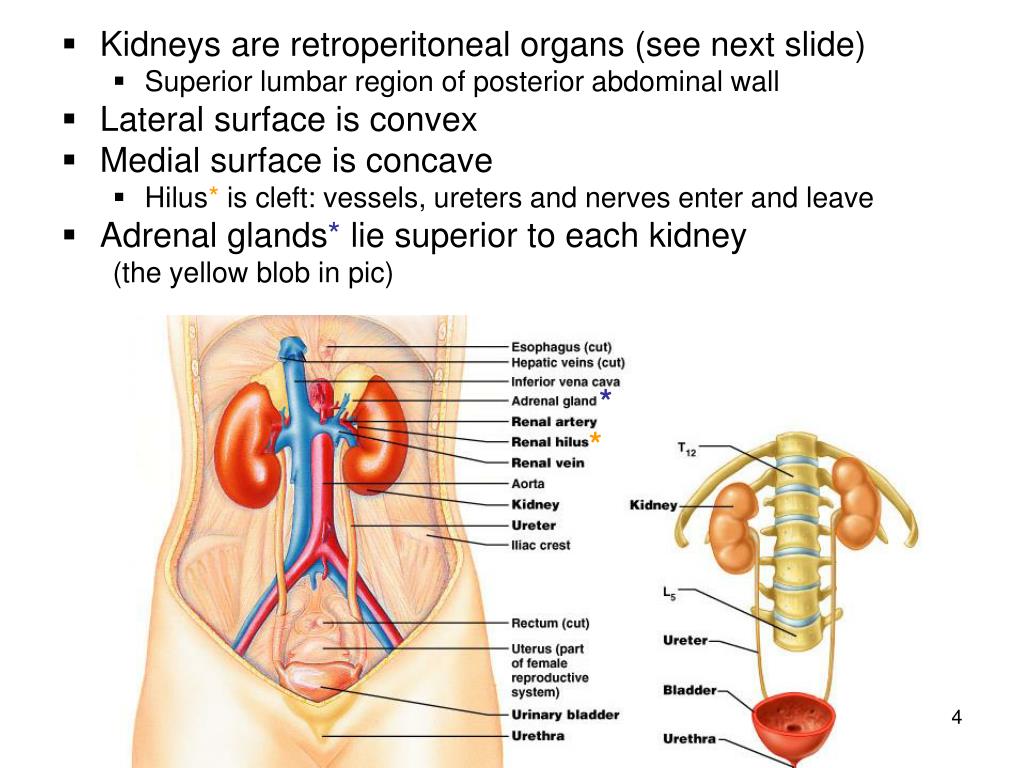
Anatomical Position. The kidneys lie retroperitoneally (behind the peritoneum) in the abdomen, either side of the vertebral column. They typically extend from T12 to L3, although the right kidney is often situated slightly lower due to the presence of the liver.
What are the kidneys posterior to?
The right kidney sits just below the diaphragm and posterior to the liver, the left below the diaphragm and posterior to the spleen.
What lies superior to the kidneys?
Adrenal gland is superior and anterior to the Kidneys. The kidney is surrounded by a distinct layer of fascia (Perirenal fascia) that separates the fat surrounding the kidney into the perinephric and paranephric fat.
Where are the kidneys posterior view?
1:206:45Location and Relations of the Kidney - 3D Anatomy Tutorial - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSit behind these organs so they sit quite far back in the abdomen so they sit on the posteriorMoreSit behind these organs so they sit quite far back in the abdomen so they sit on the posterior abdominal wall and the kidneys of retroperitoneal.
Is the heart superior to the kidneys?
Explanation: The heart sits in the mediastinum (central compartment of the thoracic cavity) while the kidneys are further down on the retroperitoneum (the space in the abdominal cavity behind the peritoneum/ membrane). They are below the heart - inferior.
Are the lungs superior to the kidneys?
It is correct to say that the kidneys are inferior to the lungs because the term "inferior" in anatomy means closer to the feet, below, or underneath. The lungs are above the kidneys in the thoracic cavity.
Are kidneys more anterior or posterior?
The kidneys are paired retroperitoneal structures that are normally located between the transverse processes of T12-L3 vertebrae, with the left kidney typically somewhat more superior in position than the right. The upper poles are normally oriented more medially and posteriorly than the lower poles.
Are kidneys posterior to pancreas?
The tail of the pancreas lies anterior to the left kidney, where it is closely related to the splenic hilum and the left colic flexure.
Is the kidney posterior to the liver?
Answer and Explanation: The right kidney is found posterior to the liver. In fact, there is an area in the liver that we call renal impression.
Are the kidneys superior to the diaphragm?
The kidneys are situated below the diaphragm, one on either side of the spine. They are just below the rib cage.
Is the spleen superior to the left kidney?
The spleen is the largest lymphoid organ in the body, located in the LUQ of the abdomen, superior to the left kidney and posterior to the stomach.
Which kidney is more superior in placement in the body and why?
left kidneyThe left kidney is located slightly more superior than the right kidney due to the larger size of the liver on the right side of the body. Unlike the other abdominal organs, the kidneys lie behind the peritoneum that lines the abdominal cavity and are thus considered to be retroperitoneal organs.
What part of the duodenum is retroperitoneal?
The descending part of the duodenum is retroperitoneal as well and it sits right up against the kidney. And if I just rotate the model around a bit further, you can see this thing on top of the kidney. This is the suprarenal gland or the adrenal gland.
What muscle is hidden in the psoas major?
It's this muscle here on either side. And you've got the diaphragm, so the posterior parts of the diaphragm sitting behind the kidney. You've got the quadratus lumborum, which is this muscle here. It's kind of obscured in this model by the huge psoas major muscle. If I just rotate it around to the front, you can see that the quadratus lumborum is hidden because the psoas major is so big in this model. And then you've also got the transversus abdominis muscle, which is not shown in this model.
What nerves are in front of the kidneys?
You've got the subcostal nerve, the iliohypogastric nerve, the ilioinguinal nerves. You can see these two here. You can see the iliohypogastric and the ilioinguinal nerve here. That’s what lies behind both the kidneys. But what lies in front of the kidneys is different for the right and the left kidney.
Why is the right kidney lower than the left?
There's a reason for this. It's because of this large organ, the liver, which sits on top of it.
What is the structure that comes out of the kidney called?
This is called the hilum. The structure that you can see here coming out of the kidney is called the ureter, but you also have the artery and vein, the renal artery and vein entering the kidney and you've also got nerves and lymphatics.
What can you see in the hilum?
I just brought in the cardiovascular system here and you can see the large inferior vena cava and the abdominal aorta here and coming off it, you can see the renal veins and arteries on either side entering the hilum together with the ureter.
What is the function of the kidneys?
The function of the kidneys is really to filter blood and excrete waste and excess water as urine. It also regulates blood pressure, blood pH, blood volume and it's important in salt balance and electrolyte balance. Let's just bring in some other structures in and take a look at the relative location of the kidneys.
How many renal pyramids are there in the kidney?
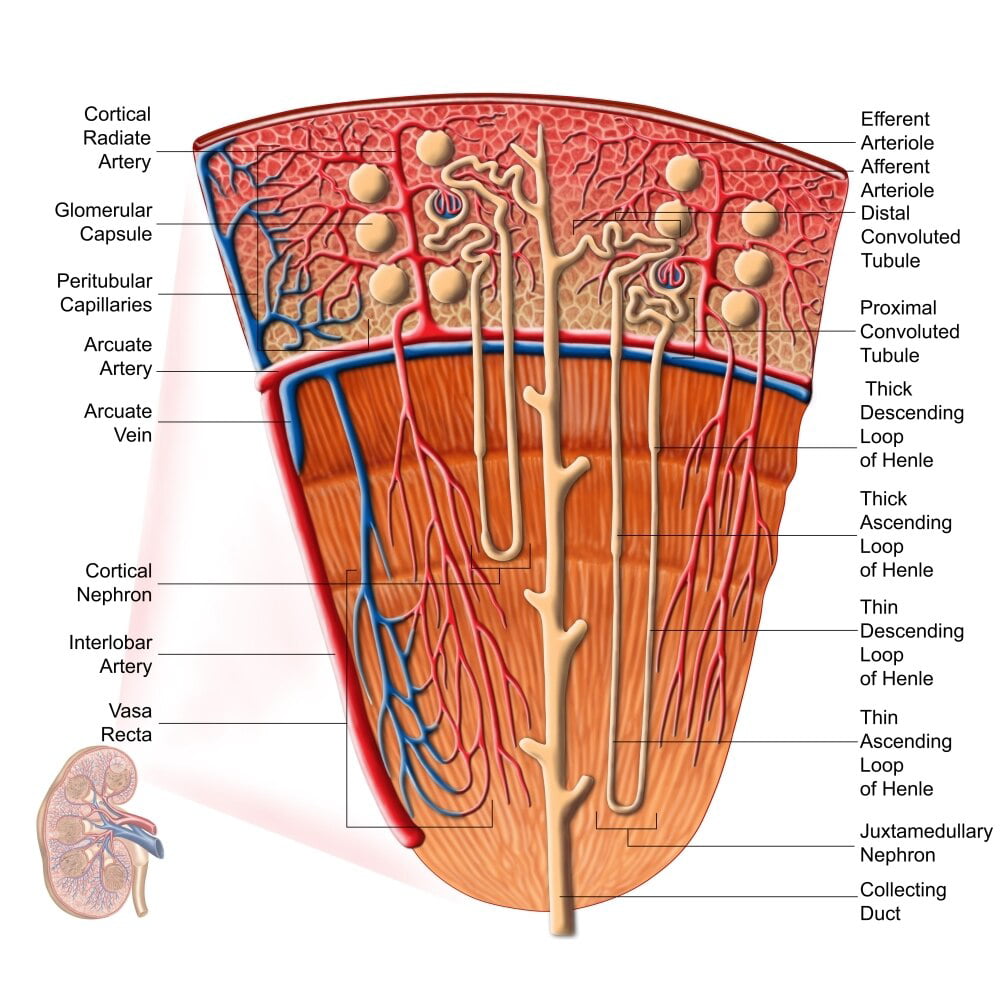
Internal anatomy of the kidney (overview) The main unit of the medulla is the renal pyramid. There are 8-18 renal pyramids in each kidney, that on the coronal section look like triangles lined next to each other with their bases directed toward the cortex and apex to the hilum.
How long does it take to read a kidney?
Reading time: 22 minutes. The kidneys are bilateral organs placed retroperitoneally in the upper left and right abdominal quadrants and are part of the urinary system. Their shape resembles a bean, where we can describe the superior and inferior poles, as well as the major convexity pointed laterally, and the minor concavity pointed medially.
Why does kidney failure cause a sudden fall in blood pressure?
It can be caused by a variety of factors, but most often arises because of the ischemia of the kidney and the toxic effect of some medications, resulting in the failure of all kidney functions. We’ve mentioned that the most important functions of the kidney are the regulation of the blood homeostasis and blood pressure, so acute kidney failure can lead to a quick fall of blood pressure which presents as a state of shock.
What is the function of the kidney?
The main function of the kidney is to eliminate excess bodily fluid, salts and byproducts of metabolism – this makes kidneys key in the regulation of acid-base balance, blood pressure, and many other homeostatic parameters. Key facts about the kidney. Functions.
What is the role of the kidney in homeostasis?
The kidney is a very important organ in regards to body homeostasis. It participates in vital processes such as regulation of blood osmolarity and pH, regulation of blood volume and blood pressure, production of hormones, and filtration of foreign substances.
Why does the left testicle have varicocele?
This can cause varicocele of the left testicle because gravity works against the column of the blood in the left testicular vein.
Where to find kidneys with ultrasound?
If we wanted to examine someone’s kidneys with ultrasound, we definitely must know where to find them. Since they are located deep retroperitoneally, the easiest way to examine them is from the patient’s back.
What is the apex of the renal pyramid?
The apex of a renal pyramid is called a renal papilla. Each renal papilla is associated with a structure known as the minor calyx, which collects urine from the pyramids. Several minor calices merge to form a major calyx . Urine passes through the major calices into the renal pelvis, a flattened and funnel-shaped structure. From the renal pelvis, urine drains into the ureter, which transports it to the bladder for storage.
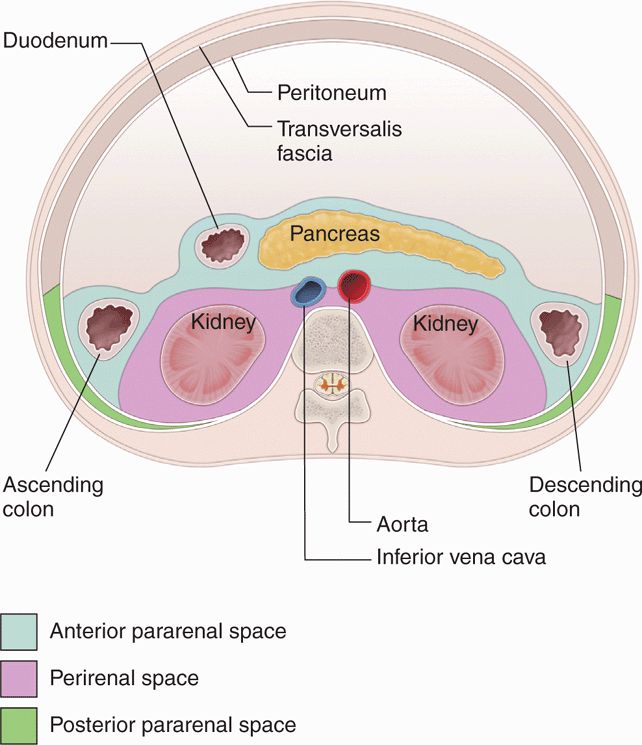
What is the difference between perirenal fat and pararenal fat?
Renal fascia (also known as Gerota’s fascia or perirenal fascia) - encloses the kidneys and the suprarenal glands. Pararen al fat - mainly located on the posterolateral aspect of the kidney. Internally, the kidneys have an intricate and unique structure.
What is the fascia of the kidney?
Renal fascia (also known as Gerota’s fascia or perirenal fascia) – encloses the kidneys and the suprarenal glands. Pararenal fat – mainly located on the posterolateral aspect of the kidney. Fig 2 – The external coverings of the kidney. Internally, the kidneys have an intricate and unique structure.
What are the two main areas of the renal parenchyma?
Internally, the kidneys have an intricate and unique structure. The renal parenchyma can be divided into two main areas – the outer cortex and inner medulla. The cortex extends into the medulla, dividing it into triangular shapes – these are known as renal pyramids.
What is the name of the capillary network that forms at 90 degrees to the arcuate arteries?
The afferent arterioles form a capillary network, the glomerulus, where filtration takes place.
How many vertebrae are in each kidney?
They typically extend from T12 to L3, although the right kidney is often situated slightly lower due to the presence of the liver. Each kidney is approximately three vertebrae in length. The adrenal glands sit immediately superior to the kidneys within a separate envelope of the renal fascia.
What is a horseshoe kidney?
A horseshoe kidney (also known as a cake kidney or fused kidney) is where the two developing kidneys fuse into a single horseshoe-shaped structure.