See more
Which nerves carry nerve impulses from the spinal cord?
The impulse travels out of the spinal cord along the length of the motor nerve. At the neuromuscular junction (where nerves connect to muscles), the impulse crosses from the motor nerve to receptors on the motor end plate of the muscle, where the impulse stimulates the muscle to move.
What carries nerve impulses to the body?
Neurons are cells that have been adapted to carry nerve impulses. A typical neuron has a cell body containing a nucleus, one or more branching filaments called dendrites which conduct nerve impulses towards the cell body and one long fibre, an axon, that carries the impulses away from it.
What carry impulses between the spinal cord and body parts?
The nervous system uses tiny cells called neurons (NEW-ronz) to send messages back and forth from the brain, through the spinal cord, to the nerves throughout the body. Billions of neurons work together to create a communication network.
Which type of neuron carries impulses toward the brain and spinal cord?
Sensory neuronsSensory neurons transmit nerve impulses from sense organs (eyes, ears, nose, tongue and touch) to the brain. They also carry nerve impulses to the brain and spinal cord. Motor neurons transmit nerve impulses from the brain and spinal cord to a specific area of the body.
What are the 3 types of nerves?
There are three types of nerves in the body:Autonomic nerves. These nerves control the involuntary or partially voluntary activities of your body, including heart rate, blood pressure, digestion, and temperature regulation.Motor nerves. ... Sensory nerves.
Which part of the nervous system carries impulses between the body and the central nervous system?
In the peripheral nervous system, bundles of nerve fibers or axons conduct information to and from the central nervous system. The autonomic nervous system is the part of the nervous system concerned with the innervation of involuntary structures, such as the heart, smooth muscle, and glands within the body.
Which structure carries nerve impulses away from the central nervous system?
Motor neuronesMotor neurones carry nerve impulses away from the central nervous system. The neurone ends in either a muscle or gland, which are effectors.
Which neuron carries nerve impulses between neurons?
The axon terminal connects the neuron to other neurons (or directly to organs), using a process called synaptic transmission. Information is passed down the axon of the neuron as an electrical impulse known as action potential.
Which part of the neuron receives nerve impulses?
DendritesDendrites extend from the cell body and receive nerve impulses from other neurons. The axon is a long extension of the cell body that transmits nerve impulses to other cells.
What is a nerve impulse called?
The nervous impulse is also called 'action potential'. It refers to the electric signal produced by a neuron when stimulated. This signal is then transmitted by synapses, or connections between the cells.
How a neuron transmits a nerve impulse?
Transmission of a signal within a neuron (in one direction only, from dendrite to axon terminal) is carried out by the opening and closing of voltage-gated ion channels, which cause a brief reversal of the resting membrane potential to create an action potential.
How do Schwann cells help injured neurons regenerate?
Help injured neurons regenerate. Undamaged Schwann cells near the injury divide to produce replacement Schwann cells- these new cells remove the damaged tissue and provide a mold to guide the extension of the new axon.
What is the process of allowing Na+ ions to flow into the cell?
A strong stimulus causes channels in the membrane to open and allow Na+ ions to flow into the cell. The inside of the membrane thus becomes positive. This initiates what is known as nerve impulse or action potential.
What is the next step of action potential?
The next step of the action potential, K+ ions flow out of the cell. Inside of the membrane is negative and the outside is positive
What is the cell that wraps around the axon?
In the PNS, myelin is actually entire cells. Wrap many times around the axon like a jelly roll.
Where does the neurotransmitter come from?
A neurotransmitter released in the parasympathetic nervous system- fibers that originate in the brain stem and sacral regions of the spinal cord.
Where do fibers originate?
Is also called the cholinergic system or the "rest and digest" system. Fibers originate in the thoracic and lumbar regions of the spinal cord.
Where are oligodendrocytes found?
Oligodendrocytes in the brain and spinal cord...
What is a neural impulse?
A neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon.
Where are the interneurons located?
Also called interneurons, located only in the brain or spinal cord, these neurons contact sensory neurons to motor neurons; the switch board of the nervous system.
What is the building block of the nervous system?
A nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system.
Which part of the brain is symmetrical?
Nearly symmetrical left and right halves of the cerebral cortex. (Left specializes in verbal and analytical functions; right in nonverbal abilities such as art and music).
Which system is not aware of reflexes?
Reflexes that are mediated through the autonomic nervous system, we are not usually aware of them. Activate smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, regulate body function, etc.
Which organ responds to integrated information?
Effector organs respond to the integrated information.
What is sensory information?
Information gathered by sensory receptors about internal and external changes.
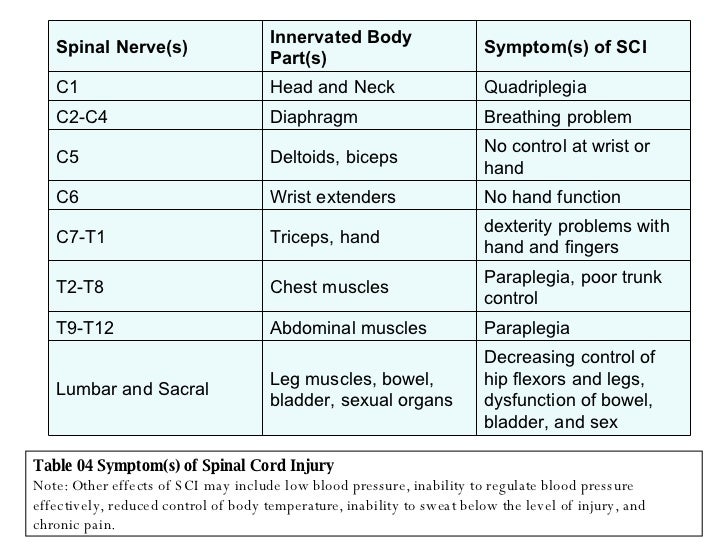
What nerves supply the shoulder, arm, forearm and hand?
A network of the last 4 cervical and first thoracic spinal nerves. These nerves supply the shoulder, arm, forearm and hand.
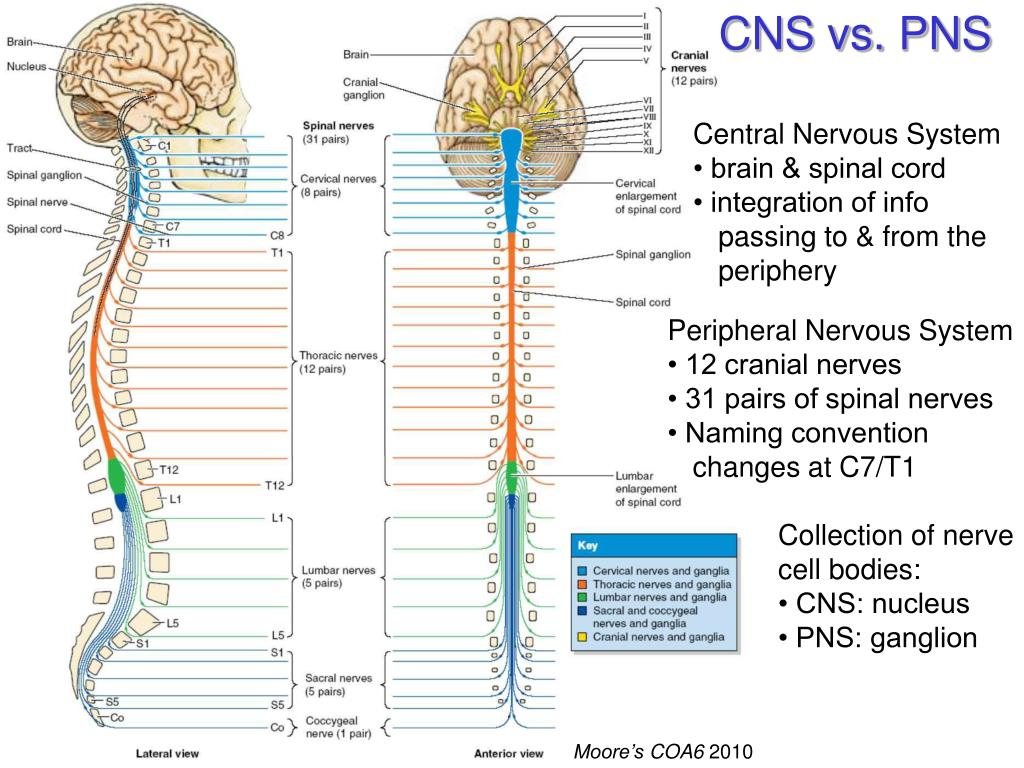
How many spinal nerves are there?
Spinal Nerves. There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves that arise from the spinal cord. Each spinal nerve corresponds to the level it emerges from: there are 8 cervical, 12 thoracic (chest), 5 lumbar (lower back), and 5 sacral, and one coccygeal (tailbone) nerves.
What is the sack around the spinal cord?
The meninges form a protective sack around the spinal cord. Within the spinal (or dural) sac, the spinal cord is surrounded by a nourishing fluid called cerebrospinal fluid. The dural sac is further protected by the bones of the spinal column. The internal anatomy of the spinal cord is quite complex. To keep things simple, the center of the cord ...
What nerves supply the skin on the rears of the legs, the feet and genital areas?
Sacral Region (yellow): Sacral nerves supply the skin on the rears of the legs, the feet and genital areas
What is the center of the spinal cord?
The internal anatomy of the spinal cord is quite complex. To keep things simple, the center of the cord consists of gray mater. White mater is arranged in tracts around the gray mater. It consists of axons that transmit impulses to and from the brain or between levels of gray mater within the spinal cord.
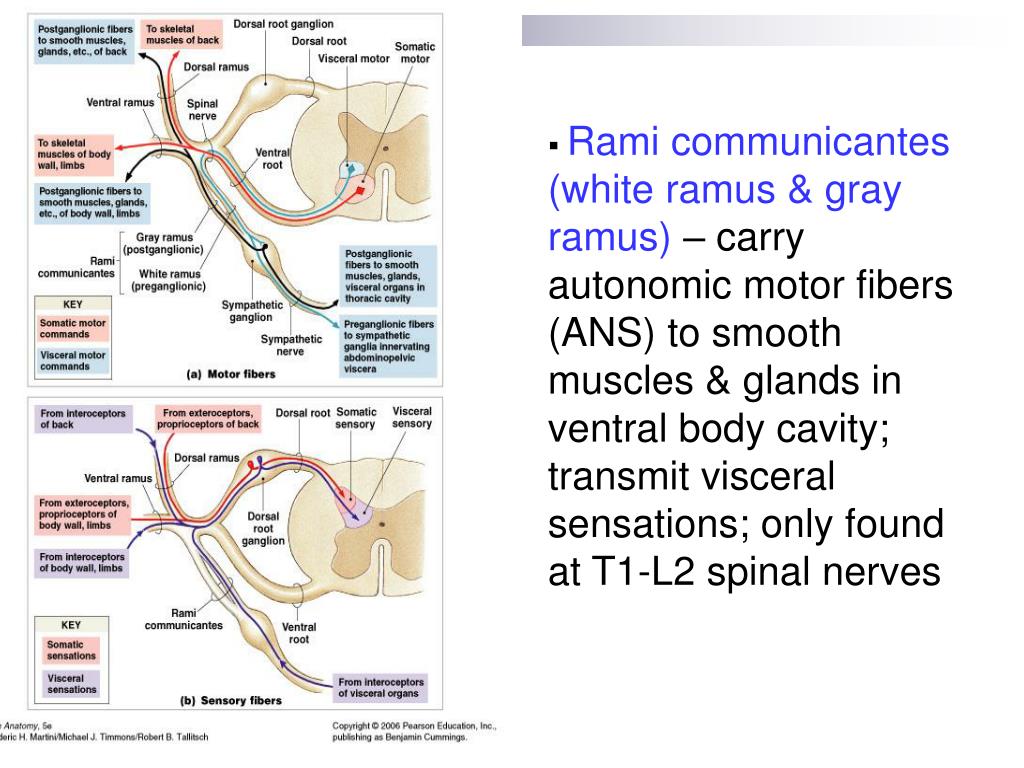
What is the white mater?
White mater consists of axons of neurons grouped in bundles that contain nerve fibers. These bundles travel between the spinal cord and the brain. Pathways to the brain are usually sensory, and pathways from the brain to the spinal cord are usually motor in nature.
Which nerves carry sensory impulses to the spinal cord?
Sensory nerves carry sensory impulses to the spinal cord. Sensory impulses include pain, temperature, touch and position sense (proprioception)—from tendons, joints and body surfaces. Every part of the body has a dermatome that is supplied by a spinal nerve. The exception to this rule is the face, which is supplied by the cranial nerves.